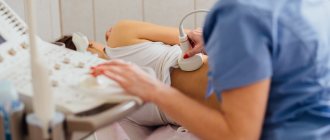
This study is widely used to diagnose pathologies of the urinary system. Unlike other techniques, such as X-rays with contrast, an ultrasound does not inject drugs into the patient or expose the body to radiation. Renal ultrasound is a painless, effective and bloodless method for diagnosing the kidneys.
THE COST OF AN ULTRASOUND OF A KIDNEY IN OUR CLINIC IS 1000 rubles. Kidney ultrasound + liver ultrasound - 1600 rubles.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT, TEST OR ULTRASOUND
An ultrasound of the kidneys can be done using new equipment at the Diana Clinic. The examination and interpretation of the kidney ultrasound will be performed by a highly qualified doctor. The results will be delivered to you.
Indications
Kidney ultrasound is prescribed by doctors:
- to examine for the presence of vascular damage from impacts;
- when the patient complains of discomfort in the lumbar region or severe pain in the kidney area;
- for preventive diagnosis of people with heart diseases;
- if vascular edema is suspected;
- for diagnosing pregnant women with too late toxicosis at 6-9 months of pregnancy;
- in case of endocrine system failures and problems with the thyroid gland;
- with chronic kidney disease, painful sensations when urinating;
- with high blood pressure and spinal bruises.
Ultrasound of the kidneys and blood vessels is mandatory for monitoring and examining organs after transplantation.
However, you should know that ultrasound cannot replace MRI of the kidneys and blood vessels.
It is prescribed as an additional additional examination if ultrasound diagnostics have given alarming results.
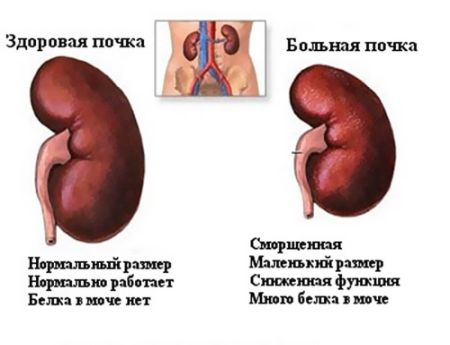
Possible reasons for size deviations
If the normal size of the kidneys is violated, this may indicate the development of a pathological process. It can affect both the genitourinary area and other body systems. Some diseases lead to abnormal enlargement of the organ, others to premature reduction.
Kidney reduction
There are a number of diseases that provoke the destruction of kidney tissue with subsequent atrophy of the organ. These include:
- nephrosclerosis;
- hypoplasia;
- low systolic pressure;
- glomerulonephritis;
- amyloidosis.
With nephrosclerosis, structural changes occur: the renal parenchyma is replaced by connective tissue. The disorder begins with vascular damage, which causes the organ to receive less blood and suffer from a lack of oxygen. Gradually, the tissues become denser and “shrink”. Such a kidney is not able to fully perform its functions, which will affect blood counts.
Hypoplasia is a congenital anomaly that forms at the stage of embryonic development. The structure of the smaller organ does not differ from the physiologically normal one, but there is a significant deviation from the accepted dimensions. In this case, the kidney can work, but will receive less load.
Low systolic blood pressure (less than 70 mmHg) provokes acute circulatory disorders, which negatively affects the condition of the human kidney. Cells become exhausted and die. Due to decreased blood filtration, the body experiences symptoms of intoxication, and the risk of developing kidney failure increases significantly. Additionally, arterial stenosis may occur: in an attempt to cope with an imaginary decrease in pressure, the organ produces renin, which narrows the blood vessels.
Glomerulonephritis is characterized by serious damage and necrosis of glomeruli - blood vessels woven into a ball. At the initial stage of the formation of renal failure, a temporary enlargement of the organ occurs, but gradually it begins to shrink and dry out.
Amyloidosis refers to systemic diseases that cause abnormal deposition of a complex protein-polysaccharide complex in tissues. The causes of the disorder are usually hypertension, renal tuberculosis or diabetes mellitus. The cells of the organ die, the size of the adult kidney becomes smaller.
Kidney enlargement
An enlargement of one of the kidneys may be compensatory in nature if the paired organ has ceased to function. This refers to the physiological norm in adults and children. The reasons that cause abnormal kidney growth include:
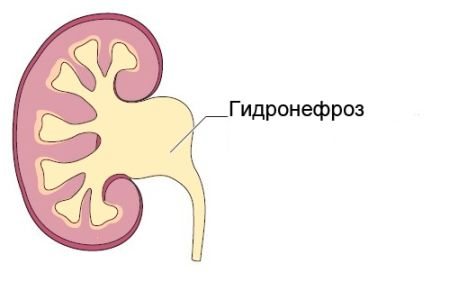
- hydronephrosis;
- polycystic disease;
- infections;
- Urolithiasis
Hydronephrosis is characterized by excessive accumulation of urine in the calyces and renal pelvis. Stagnation leads to impaired blood supply and pyelectasis - pathological expansion of the renal pelvis. Usually one organ suffers: it gradually becomes thinner and loses functionality.
During polycystic disease, cysts appear in the kidney, inside of which there is fluid. They gradually increase in size and are capable of causing destructive changes, gradually replacing healthy tissue. Acute insufficiency develops, accompanied by increased blood pressure, an enlarged abdomen and frequent cystitis.
Various infectious lesions affecting the urinary tract can also provoke size disturbances. If left untreated, they spread to the kidneys and cause pyelonephritis. At particular risk are young children and women, as well as people who have a catheter inserted into their urinary tract.
Urolithiasis is a urolithiasis in which stones form in the calyces and renal pelvis. They can move to the ureters or into the urinary tract, provoking acute colic and causing inflammatory diseases. Large stones gradually stretch the organ, while small ones interfere with the passage of urine. It stagnates and leads to kidney expansion.
The main danger of pathological changes in the size of the kidneys is the likelihood of developing acute failure and failure of one or both organs. At the first symptoms of a disorder, you should consult a doctor in order to begin treatment in a timely manner and reduce the likelihood of complications.
Preparation
To conduct ultrasound diagnostics of renal vessels in order to improve visualization of the organ, simple preparation will be required, which consists of limiting nutrition and cleansing the intestines. Diet . Three days before the start of the study, foods that cause flatulence should be excluded. The list of such products includes all baked goods, lactic acid products, raw vegetables and fruits, carbonated drinks and lively fermented drinks, sauerkraut, and alcohol. It will also be useful these days to take medications that improve digestion, this could be “Espumizan”, “Mezim-Forte”. Colon cleansing . The second stage of preparation for an ultrasound of the kidneys with Dopplerography of blood vessels will be cleansing the intestines. To do this, the day before—the evening before the day of the scheduled ultrasound procedure—you will need to perform a cleansing enema. Fasting . Since the procedure is carried out on an empty stomach, it is of course better to carry out the diagnosis in the first half of the day, this will help to avoid prolonged fasting. If, however, the procedure is scheduled for the afternoon, then you are allowed to eat a light breakfast, but no later than 6 hours before the study. It is not recommended to carry out diagnostics after fibrogastroscopy and colonoscopy, since during these procedures air will accumulate in the stomach and intestines, which will subsequently prevent a high-quality ultrasound of the kidney vessels.
Characteristics of pathologies
But before analyzing the data obtained, you need to know what a kidney ultrasound shows, since not all types of pathologies are visualized using this diagnostic method. Ultrasonography “sees” the following pathology:
- Anomalies of development and location.
- Echopositive stones.
- Neoplasms of various nature.
- Acute obstructive or chronic pyelonephritis.
- Chronic forms of glomerulonephritis.
- Hydronephrosis and abscesses.
- Amyloidosis.
- Nephroptosis, etc.
Developmental anomalies
Quantitative and qualitative changes in the urinary system, namely: hypo- or aplasia of the kidney, its complete or incomplete doubling. Such anomalies of location as lumbar or pelvic dystopia, horseshoe-shaped, L and S-shaped kidneys.
Urolithiasis disease
It is possible to detect various kidney stones using ultrasound, which are visualized as hyperechoic (that is, brighter than the kidney tissue itself) round or oval formations with an anechoic track. Being in the pyelocaliceal system, they can move relative to each other. In addition, the diagnostician must determine their number, size and location.
Unfortunately, not all stones are visualized using ultrasound, but obstruction of the lumen of the pelvis or ureter by a stone can be suspected by the pronounced hydronephrotic transformation of the kidney above the obstacle.
Cysts and tumors
Volumetric neoplasms. Cysts of various etiologies are defined as round volumetric formations with smooth and clear contours, having an anechoic internal structure and distal ultrasound enhancement. Benign tumors have a homogeneous hyperechoic echostructure, an even contour and a rounded shape. Malignant ones are distinguished by uneven contours, even blurring, and heterogeneity of structure. The appearance of echo-negative areas in the tumor indicates the presence of hemorrhages or foci of necrosis.
Pyelonephritis
Ultrasound of the kidneys for pyelonephritis has the following indicators:
- Due to tissue infiltration, an uneven contour of the kidneys appears.
- In the acute form of the disease, the uniformity of the renal tissue and its density may be unevenly reduced due to diffuse or focal inflammation. In the chronic form, on the contrary, echogenicity is increased.
- With unilateral pyelonephritis, due to swelling of inflammatory origin, asymmetry in size is observed (that is, the affected kidney is larger than the healthy one). If the process is bilateral, then both kidneys exceed normal sizes.
- Also, ultrasound with pyelonephritis notes a decrease in the mobility of the organ with its simultaneous increase.
- The diagnostic criterion for acute obstructive pyelonephritis is expansion or deformation of the collecting system.
- However, primary pyelonephritis (non-obstructive) on ultrasound may give an ultrasonographic picture that is normal. Only as inflammation and edema increase does the echogenicity of the kidney tissue increase.
Glomerulonephritis
In acute glomerulonephritis, ultrasound diagnosis is practically uninformative; the diagnosis is made on the basis of complaints, clinical manifestations and results of laboratory examination methods. Only occasionally can an experienced diagnostician detect protruding pyramids of the medulla and tissue hyperinfiltration.
Chronic glomerulonephritis is characterized by hyperechogenicity of the tissue, reduction of the kidneys in size, blurring of the boundaries between the medulla and cortex, the appearance of scars, abscesses and areas of necrosis.
Hydronephrosis and abscesses
With hydronephrotic transformation, the ultrasound conclusion of the organ structure looks like this (depending on the stage):
- I degree – slight flattening of the arches of the cups.
- II degree – flattening is accompanied by expansion of the arches of the calyxes, while the papillae are clearly visualized.
- Ⅲ degree - the calyxes become rounded and the papillae become obliterated.
- Ⅳ degree - the cups are sharply expanded.
Abscesses (enclosed collections of pus) look like this - round, hypoechoic formations with smooth but uneven contours.
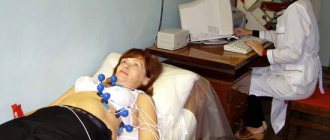
How is a kidney ultrasound done?
Ultrasound of the kidneys is performed in a lying position: on the stomach, on the side, on the back. During the procedure, the doctor periodically asks the patient to inhale or exhale deeply and hold his breath. In order to exclude nephroptosis, diagnostics are also performed in a standing position. Before the examination, a conductive gel is applied to the patient’s skin, which allows the device’s sensor to glide more easily over the skin. The sound waves sent penetrate to the kidneys, adrenal glands and other internal organs. The ultrasound signal is reflected and visualized on the monitor screen. An ultrasound diagnostic specialist takes the necessary measurements, evaluates the contours and structure of the kidneys, notes the presence/absence of tumors and prints out the results.
Make an appointment with a urologist
If you have discovered one or more signs of hydronephrosis, contact our State Urology Center.
We invite you to make an appointment with a urologist at a convenient time. In our clinic you can undergo diagnosis and treatment of hydronephrosis free of charge as part of the compulsory medical insurance program. The sooner the disease is confirmed, the more effective the therapy will be. It is equally important to consult a doctor on time, as this reduces the risk of complications and generally improves the prognosis for recovery. October 19, 2020
Hakobyan Gagik Nersesovich - urologist, oncologist, MD, doctor of the highest category, professor
All the symptoms of the disease...
Is it dangerous to do an ultrasound of the kidneys?
The procedure for ultrasound examination of the kidneys is completely painless, quick and not accompanied by any unpleasant sensations. The safety of ultrasound examination was officially confirmed by the American Ultrasound Institute in 1979. Scientists have found that ultrasound has no adverse effects on the human body. Therefore, kidney ultrasound can be performed on patients of any age, pregnant women and children, including infants. In order to track the dynamics of changes, it is possible to do ultrasound diagnostics over several days or at certain intervals of several hours.
Diagnosis and methods
Kidney diseases have a different nature and causes of manifestation. Since the kidneys are responsible not only for purifying the blood.
The manifestations of disturbances and deviations in work may result in renal failure.
What are the symptoms of progression of kidney disease:
- pain in the lower back, at the location of the kidneys;
- severe swelling and redness of the skin in the area where the kidneys are located;
- dark skin appearance;
- frequent urination, sometimes accompanied by painful symptoms;
- strong and unpleasant odor of urine at the time of bowel movement;
- swelling of the facial part in the morning and of the limbs in the evening.
These symptoms of the disease, based on general signs, cannot always confirm kidney pathology, so it is necessary to contact a medical institution for diagnostic measures and laboratory tests.
How often should a kidney ultrasound be done?
For the purpose of preventive health monitoring, healthy people are recommended to undergo an ultrasound examination of the kidneys and abdominal cavity once a year. Persons suffering from chronic kidney disease need to monitor the disease process and have an ultrasound scan at least once every 3 months.
| Ultrasound service | Price according to Price, rub | Promotion price, rub |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, stomach) | 1500 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of one organ (liver, gall bladder, spleen, pancreas, bladder, adrenal glands) | 800 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys | 1700 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the bladder | 2000 rub. | |
| Kidney ultrasound | 800 rub. | |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland) | 2400 rub. | 1999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidney + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + pelvic ultrasound with an abdominal probe + ultrasound of the mammary glands) | 4200 rub. | 2999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the prostate gland with an abdominal probe) | 3300 rub. | 2499 rub. |
| Comprehensive body diagnostics (MRI of the thoracic spine, MRI of the lumbar spine, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, ultrasound of the kidneys, ultrasound of the bladder, consultation with a neurologist, consultation with a therapist) | 11700 rub. | 7000 rub. |
Functional features of the organ
During the biological life of this organ, it passes through itself up to 250 liters of blood per day.
At the same time, the bloodstream is cleansed of pathogenic bacteria and microbes, cleanses the blood of toxins and harmful substances.
The main functions and responsibilities of this body:
- excretory function;
- homeostatic function;
- carry out metabolism;
- support the endocrine system;
- participate in the secretory activity of the body;
- carry out hematopoiesis, which significantly renews the contents of the blood.
Excretory function of the kidneys
The production of urine and its further removal from the body is the main task of the kidney organ.
This function involves the removal of toxins or harmful substances, regulates the presence of salts in the body, and is heavily involved in maintaining blood pressure.
Big problems are caused by the lack of necessary treatment for pathology, and a violation in the excretory systems causes a complete lack of control over the state of the body.
The excretory function itself passes through the nephrons, which control the proper functioning of the organ and the small internal mechanisms of the kidneys.
This function has its own individual stages, which include:
- secretion function;
- filtering human urine and bloodstream;
- reabsorption.
When this system malfunctions, the body begins to choke from toxic poisoning.
Homeostatic function of the body
This function controls the salt and acid-base balances of the human body.
- Water-salt functions – constant maintenance of a liquid substance in the body.
- Acid-base balance – maintaining blood in normal working condition. If there is a malfunction, an irreparable blow to health is caused.
Decoding
The diagnostic doctor will give the results recorded in the protocol to the patient upon completion of the diagnosis. The conclusion reflects all important parameters indicating deviations from the norm. In normal condition, the buds should be bean-shaped with smooth, clearly defined edges. The diagnostician must indicate the size of the organ and the thickness of the capsule. The pelvis system, as well as the calyces, should not be visualized. The most difficult thing to visualize with this examination method is small vessels.
Renal ultrasound protocol
Right kidney
10.39 x 4.88 cm, position and shape are typical, the contours are smooth, clear, the parenchyma is 1.32 cm thick, homogeneous, uniformly hypoechoic, the jaw is not expanded.
The vascular pedicle is not changed.
Pathological formations in the area of the adrenal gland are not visualized.
Left kidney
10.9 x 5.6 cm, position and shape are typical, the contours are smooth, clear, the parenchyma is 1.3 cm thick, homogeneous, uniformly hypoechoic, the jaw is not expanded.
The vascular pedicle is not changed.
Pathological formations in the area of the adrenal gland are not visualized.
Conclusion:
Ultrasound signs of mineral metabolism disorders.
Renal ultrasound protocol
Right kidney
10.17 x 3.99 cm, position and shape are typical, the contours are smooth, clear, the parenchyma is 1.2 cm thick, homogeneous, uniformly hypoechoic, the jaw is not expanded. Weak hyperechoic signals (crystals) are detected in the abdominal system. Concrete 0.4 cm
The vascular pedicle is not changed.
Pathological formations in the area of the adrenal gland are not visualized.
Left kidney
10.07 x 4.53 cm, position and shape are typical, the contours are smooth, clear, the parenchyma is 1.2 cm thick, homogeneous, uniformly hypoechoic, the jaw is not expanded. Weak hyperechoic signals (crystals) are detected in the abdominal system.
The vascular pedicle is not changed.
Pathological formations in the area of the adrenal gland are not visualized.
Conclusion:
Ultrasound signs of mineral metabolism disorders. Right kidney stone.
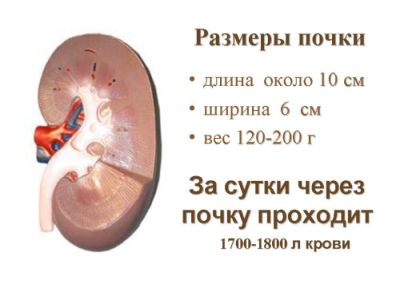
Size is ok
The standard kidney sizes for an adult are as follows:
- thickness: 40-50 mm;
- width: 45-70 mm;
- length: 100-120 mm.
The ratio of length and width should be 2:1. Normally, the size of the kidney does not exceed the dimensions of the fist.
At a young age, the thickness of the renal parenchyma ranges from 15 to 25 mm. With age, atherosclerotic processes appear, leading to tissue thinning. In a person over 60 years of age, the levels drop to 11 mm.
During pregnancy, the size of a woman's kidneys changes temporarily. The body of the expectant mother has to work for two, and the load is constantly increasing. Normally, the organ lengthens by 1.5-2 centimeters; expansion is possible with the ureters and pelvis.
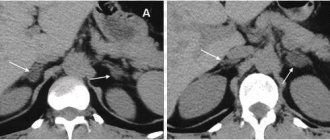
Traumatic injuries
Kidney damage implies a violation of the integrity of the organ due to physical impact. It varies in severity: from minor injuries to those that pose a threat to human life.
In medicine, two types of injuries are distinguished: closed and open kidney injuries.
Closed damage
These include:
- bruise (there may be hemorrhages in the parenchyma, but there is no rupture of the hematoma);
- contusion;
- subcapsular rupture, with a hematoma present;
- crushing;
- separation of the ureter, complete or partial damage to the vascular pedicle (rupture of tissue and fibrous capsule of the kidney).
Open damage
The causes of open damage can be:
- gunshot wounds;
- knife wounds;
- possible damage to the abdominal cavity with subsequent development of peritonitis.
Photo gallery
Bruise (hematoma) of the kidney
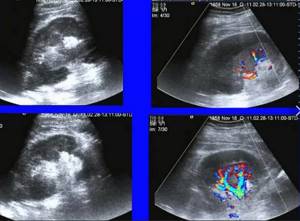
Kidney crush
Kidney injury
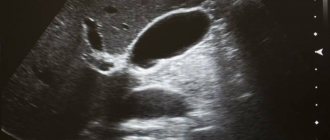
Photo gallery
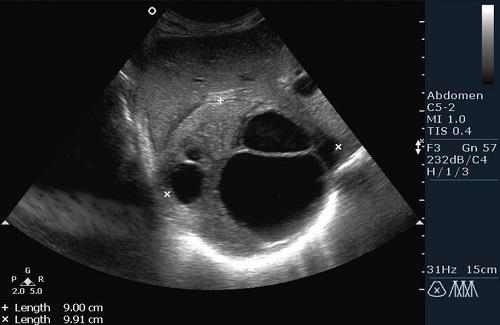
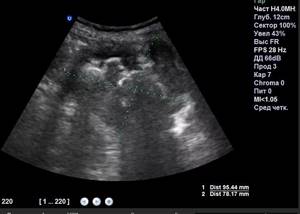
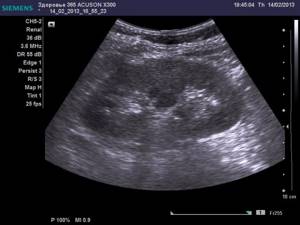
The photo clearly shows kidney pathologies on ultrasound images.
Coral kidney stones on ultrasound
Angiomyolipoma of the kidneys on ultrasound
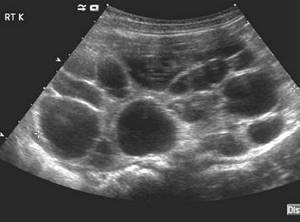
Multicystic kidneys on ultrasound
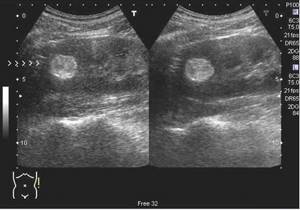
Kidney tumor on ultrasound