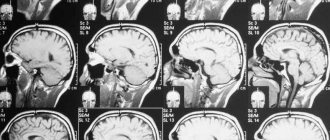
MRI is a safe diagnostic procedure that allows you to visualize the condition of organs and tissues. For pain in the cervical spine, MRI diagnostics are prescribed in order to finally confirm the diagnosis: to identify an intervertebral hernia or inflammation of the nerve endings.
MRI of the cervical vertebrae is the only way to visualize intervertebral discs that are not visible on CT or X-ray images.
Safety, effectiveness, speed and the ability to obtain detailed images of tissues, on the basis of which a detailed description is drawn up, make magnetic tomography the procedure of choice when it is necessary to diagnose diseases of the spine.
In this article we will tell you what an MRI of the cervical spine shows and when the study is prescribed.
Advantages of the diagnostic method
The main advantage of MRI of the cervical spine
is information content and safety. The equipment produces accurate images of the examined area, while soft tissues are examined simultaneously with the spinal column. The procedure is harmless and can be performed simultaneously for several departments. The tomograph takes pictures in different planes and creates a three-dimensional image. The advantage of MRI of the cervical spine is that the device shows the entire structure of the region being studied: vertebrae, neck vessels and muscles. This does not involve x-ray radiation; the method can be used several times to clarify the diagnosis and monitor the progress of the disease.
Diseases of the cervical vertebrae
Most often, pain in the neck can occur due to spasms or sprains. This can happen as a result of overexertion, sudden movements or hypothermia. These problems do not require long and complex treatment, and in some cases go away on their own, without drug intervention.
If the pain does not go away and interferes with a full life, the reason may lie deeper. The following diseases can be the cause of pain:
- osteochondrosis;
- herniation or protrusion of intervertebral discs;
- scoliosis;
- inflammatory process;
- soft tissue or spinal injuries;
- nervous disorders.
Osteochondrosis
According to statistics from the World Health Organization, 80% of people aged 30-40 years suffer from osteochondrosis.
The main symptoms of this disease include:
- pain, stiffness of movement, numbness and tingling of the limbs. These symptoms are caused by poor circulation, nerve compression, or bone deformation. The syndrome of narrowing of the spinal canal for various reasons is called stenosis;
- severe headaches, pulsating tinnitus, problems with smell and speech, facial deformities and breathing problems. These symptoms may be signs of radicular syndrome, in which the intervertebral disc begins to compress the nerve roots;
- throbbing pain localized in the temporal, parietal, superciliary and occipital lobes occurs due to compression of the vertebral artery;
- pain in the diaphragm, arrhythmia and high blood pressure are called cardiac syndrome.
The main reasons for the development of osteochondrosis are considered to be metabolic disorders, a sedentary lifestyle, lack of vitamins and fluids in the diet, excess weight, hypothermia, improper exercise technique, and heredity.
After the initial examination and clarification of complaints, the attending physician prescribes an additional examination, the most informative of which is magnetic resonance imaging, which will show pathological changes in the structure and functioning of the spine.
Spondylosis
Pathology of bone tissue growth, which occurs as a result of complications of osteochondrosis. It manifests itself in the form of headaches, loss of mobility and numbness in the neck.
At an early stage, the disease is amenable to drug and physiotherapeutic treatment. In later stages, surgical intervention may be required, after which rehabilitation actions in the form of exercise therapy are used.
The patient requires constant medical supervision, since spondylosis in an unfavorable course can lead to a stroke.
Protrusions
With curvatures, hernias and protrusions, attacks of dizziness and headaches may occur. This occurs because blood vessels and nerves are pinched. In addition, pain can radiate to almost any part of the body - head, shoulders, arms and chest.
Protrusions are a consequence of osteochondrosis and represent a protrusion of the intervertebral disc into the cavity of the spinal cord canal. However, the annulus fibrosus surrounding the disc does not rupture.
If the protrusion is not treated, it will rupture the disc lining and turn into a hernia.
Intervertebral disc herniation
When the fibrous ring is damaged, the inner part of the disc comes out, the nerve roots are compressed, which leads to intense pain.
A hernia or prolapse results in sudden severe pain in the shoulders and neck, numbness, muscle weakness and loss of sensation. The pain is localized in the place where the nerve is pinched.
In most cases, the hernia goes away with the use of painkillers, rest and wearing a special otropic collar.
Surgery is prescribed if the patient's symptoms do not go away, severe pain remains, muscle weakness and loss of sensation persists. During surgery, surgeons remove the pinched nerve or free the nerve root.
Scoliosis
Cervical scoliosis most often occurs in young people and affects the 3rd to 6th vertebrae.
The causes include injuries in early childhood, developmental disorders and diseases of the spine.
Scoliosis occurs due to the fact that the muscles on one side are more tense than the other. This asymmetry leads to blocks and spasms, and as a result, pain and pinched nerves.
In childhood, scoliosis responds well to treatment; in adulthood, pain can be reduced.
To make a diagnosis, magnetic tomography of the cervical spine is used to obtain accurate images and tissue sections.
Radiculitis
Radiculopathy is a pain syndrome that occurs when the nerve roots are inflamed. It can affect the 4th to 6th vertebrae, although it most often appears in the lumbar region.
This syndrome occurs against the background of spinal diseases, for example:
- osteochondrosis;
- intervertebral hernia;
- inflammation of ligaments and muscles from hypothermia or overexertion;
- general hypothermia of the body from prolonged exposure to damp and cold conditions;
- Cervical radiculitis can also occur as a complication after an infectious disease.
In order to prevent the nerve roots from being irritated, it is necessary to reduce the load on the neck; for this you will need a collar that holds the neck in a fixed position. In case of severe pain, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, and after the pain has reduced, a course of manual therapy or massage is prescribed.
Who is indicated for MRI?
The study is prescribed for dizziness, numbness of the hands, and headaches of unknown origin. Indications:
- neck injuries;
- stiffness and discomfort in the cervical spine;
- blurred vision, loss of consciousness;
- diseases of the vertebrae, nerve roots, discs, muscles;
- osteochondrosis;
- suspicion of degenerative-dystrophic changes;
- short neck syndrome.
The procedure is prescribed before neurosurgical intervention to make orthopedic diagnoses.
Algorithm for the procedure
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
The principle of testing with and without contrast is not very different. In any case, the person will be placed on a medical couch, which, when the equipment is activated, will move under the scanner, where there is a magnet.
Since modern devices usually have a wide design, most of the body will not be under the arch, which will help those suffering from claustrophobia to survive the panic. For convenience, the subject’s head is fixed so that during subsequent manipulations it will be easier for him to maintain immobility. Some lab technicians even suggest using a head roller.
Since during operation of the tomograph it constantly emits sound signals. Patients, especially children, are recommended to wear special vacuum headphones. And if an unforeseen situation occurs during testing, you can always contact the x-ray technician via internal two-way communication.
Contraindications
The tomograph creates a magnetic field, so patients who have an insulin pump, pacemaker, hearing aid, or cardioverter-defibrillator in their body do not undergo the procedure. Scanning is not performed for people who have metal objects in their bodies (Ilizarov apparatus, staples and wires, stents on blood vessels). The procedure with contrast is contraindicated for pregnant women and nursing mothers. Contraindications include renal failure. For technical reasons, the study is not possible if the patient weighs more than 120 kg.
How is the procedure done?
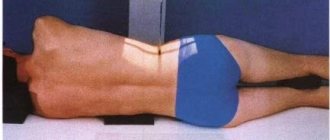
During the entire examination, the patient lies horizontally on his back.
Muscle tension can distort the picture, so special headrests are placed under the neck to help you take the most relaxed position. During the study, the patient sits on a movable table that slides directly into the tomograph. During operation of the tomograph, the ring part containing heavy-duty magnets rotates around the table. The operation of the device does not cause any discomfort, however, if necessary, the patient can always stop the procedure thanks to the signal button. The staff remains at the control panel the entire time the diagnostics are being carried out. It is important that there are no metal objects on the human body while the tomograph is operating, and that there are no phones or other devices with you, since metal objects significantly degrade the quality of the image. The presence of tattoos does not affect the final result in any way.
The whole procedure will not take more than 25 minutes. In cases where it is necessary to increase the information content of the image, the patient can be administered special contrast agents, which will increase the duration of the session.
Within an hour, all the examination results are available to the patient or the attending physician, and a diagnosis can be made.
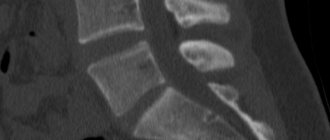
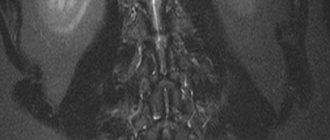
What does the cervical spine look like on a scan?
In the absence of diseases, the cervical vertebrae are smooth and intact, the discs are the same size with a flat and smooth surface. In this case, the joints are without roughness, the structures are located symmetrically. A healthy spine has no obstacles to the exit of the spinal nerves; there are no neoplasms, inflammations or infectious foci on it. If there is a fracture, the fracture line, deformation and displacement are visualized on the image. Using MRI, the causes of pathological fractures are determined: chronic diseases of the spinal column. It is possible to determine whether the spinal cord is affected by injury. If the image shows a decrease in the height of the disc, this indicates a herniation. When the marginal areas with the surface of the nerves grow, osteochondrosis is diagnosed.
Which doctor performs the magnetic resonance imaging procedure?
According to the regulatory documents of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, a diagnostician working with MRI equipment must have:
- a document confirming receipt of higher professional education (medical diploma in the specialty “General Medicine”, “Pediatrics”, “Medical Cybernetics”, “Medical Biophysics”);
- a document confirming completion of residency training (internship) in the specialty “Radiology” or a document confirming professional retraining in the specialty “Radiology”;
- a valid radiologist certificate.
All diagnostic doctors working at the Rostov MC “DiMagnit” not only have a full package of documents for carrying out medical activities, but also systematically undergo advanced training courses to improve their professional level. Specialists have at least 7 years of experience in diagnostics.
All services comply with accepted international standards.
How to prepare for scanning?
Special preparation for MRI of the cervical spine
not required, there is no need for dietary restrictions (if the MRI will be performed without a contrast agent), no need to stop taking medications. If contrast will be used, the doctor should be informed of any allergic reactions. It also needs to be said about pregnancy and the presence of claustrophobia. Before the procedure, metal objects, including piercings, removable dentures and hearing aids, must be removed. If you are using a contrast agent, you should not eat anything five hours before the procedure.
What does a patient get after an MRI, where to go with the results
After completing the MRI procedure, you will receive images and their description.
If you underwent research on the direction of your doctor, you need to show the conclusion to him. He will prescribe the necessary treatment or give a referral to another doctor who will take care of your problem.
If you underwent an MRI on your own initiative, the choice of doctor will need to be made depending on the identified disorder.
If you don’t know where to turn, you can clarify this issue with a specialist who will describe your results.
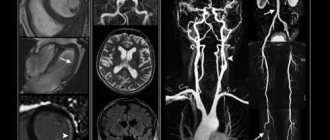
What does an MRI of the soft tissues of the neck show?
Magnetic resonance imaging is a safe technique for scanning the body using magnetic waves, which, unlike X-rays, are safe for humans.
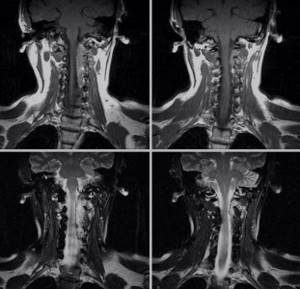
MRI images of the neck in coronal projection
An MRI of the neck area may be prescribed if the following symptoms occur:
- pain in the neck that does not go away for a long period of time;
- feeling of a lump in the throat, feeling of fullness or difficulty swallowing;
- the appearance of swellings of various sizes and shapes;
- headaches of unknown origin;
- violation of voice functions.
The appearance of the above symptoms requires an early examination by a doctor, based on the results of which magnetic resonance imaging of the soft tissues of the neck may be prescribed.
MRI diagnostics of the neck area can be carried out either as an independent study or in conjunction with scanning of other areas to identify oncological and hematological diseases.
CT, MRI or ultrasound of the neck, which is better to do?
To study the soft tissues of the neck, MRI is most often used as a more progressive, informative and accurate type of diagnosis. However, different methods can be used for different tasks:
- Ultrasound provides a two-dimensional picture of the area being examined and does not always clearly show small structures such as lymph nodes or small lesions. The quality of diagnostics depends to a very large extent on the qualifications of the specialist. But this method is very affordable; ultrasound machines are available in almost all medical institutions, so some ultrasound is used as the first stage of diagnosis.
- X-rays do not provide images of soft tissues and are used to diagnose bone and joint pathologies. Due to its low cost, it can be used as the first stage, but it is very much inferior to tomography in terms of information content.
- CT (computed tomography) is a more progressive technique than ultrasound and radiography, which in terms of image detail can be compared with MRI, but like radiography, it more clearly visualizes solid structures, and is also used when MRI cannot be performed based on objective reasons.
- MRI is more suitable than CT for imaging soft tissue. The level of detail in the images obtained using MRI diagnostics makes it possible to identify foci of inflammation and neoplasms ranging in size from several millimeters. This method can be used both as a primary diagnosis and to clarify the nature of pathological changes identified by other methods.
Use of contrast in MRI of the neck
Contrast enhancement in magnetic resonance imaging of the soft tissues of the neck is mainly used in cases of suspected benign or malignant neoplasm, metastases to the organs of the neck, as well as after medical and surgical treatment of tumors.
Contrast is carried out using intravenous administration of gadolinium-based drugs (most often gadodiamide), which, accumulating in the affected area, increase the contrast of pathologically altered tissues in the images, which makes it possible to clearly determine their boundaries and localization in relation to healthy tissues.
The use of contrast agent is harmless. However, contraindications to its use may include pregnancy, breastfeeding and severe renal failure.