JSC "Medicine" (academician Roitberg's clinic) carries out a wide range of diagnostic measures, including to determine pathological conditions that are extremely difficult to identify. Such methods include MRI of the whole body - a highly accurate diagnostic method that can be used for patients of different ages in order to evaluate and identify abnormalities in the structural features of tissues of the entire body. The diagnostic value of the procedure is very high, therefore in our clinic it is performed by the most highly qualified personnel, and for the examination itself we use modern tomographs with a strong magnetic field (3 Tesla - 2 times more powerful than most devices).
Indications for whole body MRI
Magnetic resonance examination of the whole body in most cases is the last among other diagnostic measures. The procedure is prescribed when other available tests have been performed, but have not given accurate results and have not helped make a diagnosis. Therefore, indications for whole body MRI are quite limited. Their list includes:
- diagnostically complex cases of diseases in which the symptoms do not fit into the standard clinical picture of a particular pathological process;
- oncological disease of any localization, stage 2-3 and suspicion of the spread of metastases;
- the presence of a family history of cancer;
- febrility (temperature more than 38°C) for a long time of unknown origin.
Thus, whole-body MRI is of particular value in cancer screening. This diagnostic method is also known as preventive cancer screening. Only with the help of a full body scan is it possible to identify tumors of different locations in the early stages.
Features of complex MR diagnostics
One of the main advantages of MRI studies is the small number of contraindications, however, MRI diagnostics has a number of limitations associated with the peculiarities of the scanning process. General MRI of the body is carried out using high-field closed-type tomographs, the technical parameters of which require matching the size of the body and the scanner and maintaining complete immobility during the study.
Conditions under which it is impossible to conduct MRI of the whole body:
- the patient's waist diameter is more than 60 cm;
- body weight 150 kg and above;
- inability to remain still;
- age up to 5 years;
- severe claustrophobia.
The above limitations are typical only for closed tomographs with a tunnel magnet, which are traditionally used to scan the entire body. The use of open tomographs makes it possible to diagnose patients with such parameters, avoid attacks of claustrophobia and record individual areas of the body if necessary. However, open tomographs do not have high enough power to obtain high-quality images, and high-field open-type devices are still under development.
Contraindications
A complete examination of the body using MRI has the same contraindications as in the case of analyzing a single part of the body or organ using a similar method. Thus, there are the following restrictions on magnetic resonance imaging:
- the presence of a pacemaker, insulin pump, neurostimulators or other built-in magnetic devices in the body;
- metal fragments in the body, for example, after being wounded by shells;
- metal fixed dentures.
Relative contraindications include claustrophobia – fear of being in confined spaces. But the large clearance of the MAGNETOM Skyra tomograph installed at Meditsina JSC allows examinations to be carried out even for patients suffering from claustrophobia.
Physical basis and essence of MRI
In the course of studies of atomic nuclei and their properties, it was discovered that, when placed in a uniform magnetic field, the nuclei of some atoms are capable of absorbing energy in a certain radio frequency range and inducing it after the radio frequency pulse is stopped. The object under study is placed in a powerful constant field and exposed to a radio frequency field, the intensity and frequency of which strictly correspond to each other. Registration of a radio frequency signal occurs from nuclei that have their own magnetic potential. Small changes in the frequency of the outgoing signal make it possible to identify atomic nuclei and study the molecular structure of matter.
In 1971, American scientists first recorded a signal emanating from a living organism, which marked the beginning of the use of NMR for medical purposes. In tomography, the greatest interest is in hydrogen atoms, the concentration of which is maximum in the human body, and the nucleus consists of one proton, so its signal is easier to register and identify. It was experimentally found that a stronger signal comes from malignant formations than from healthy tissues.
A device that allows you to quickly capture the radio frequency signal of the human body and convert it into a two-dimensional image was invented in 2003 and called an MRI scanner.
MR tomograph design:
- superconducting magnet generating a powerful magnetic field;
- magnet cooling system;
- a patient table placed in the magnet tunnel;
- coils for transmitting, receiving and visualizing radio frequency signals;
- computer system and control consoles;
- video surveillance and patient communication system.
Tomographs differ in the type of magnet and the power of the generated field. In modern medicine, open-type low-field tomographs are used for local diagnostics, and closed high-field tomographs are used for complex MRI of the whole body. The induction power of closed-type tomographs varies from 1 to 3 T, and their magnet is a hollow cylinder with a diameter of 60 cm and a length of up to 2 m. The patient is completely placed inside the magnet-scanner in a supine position, which makes it possible to obtain a complete magnetic resonance image of the entire body .
Preparing for a whole body MRI
To perform a full body MRI, no fundamental preparation is required. But in connection with the examination of the whole body, including the abdominal cavity and pelvis, the patient is required to follow some recommendations:
- 2-3 days before the MRI, switch to a special diet that eliminates constipation;
- take your last meal 4 hours before the examination;
- empty your bladder no later than 1 hour before the examination;
- If you have claustrophobia, take a sedative 1 hour before the examination (prescribed by the personal physician at our clinic).
Where to start a complete examination of the body
In order to undergo a full medical examination, you first need to choose a clinic and sign up for an initial consultation.
The websites of many medical centers offer the ability to register online. The initial appointment is conducted by a general practitioner. He conducts a conversation with the patient, during which he finds out the purpose of the examination, general health, the nature of the complaints (if any), the individual characteristics of the body, lifestyle and eating habits, hereditary factors and much more.
It is recommended to bring the results of previous studies with you to the initial consultation. This will help the doctor obtain the most complete information about the patient’s health status.
If the patient is taking any medications, this must also be reported to the doctor.
Advantages of CHECK-UP programs The main advantages of comprehensive diagnostic programs are short deadlines and lower cost compared to individual tests. Learn more THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS. YOU MUST CONSULT A SPECIALIST
Important!
Many instrumental studies and especially laboratory tests are performed on an empty stomach. The diagnostic results may also be affected by taking certain medications (the doctor will tell you more about this during the consultation). It is also recommended to stop drinking alcohol a few days before the examination.
Based on the results of the conversation, the doctor selects an individual diagnostic program and prescribes tests. Changes and additions may be made to the standard list of procedures.
A basic checkup allows you to assess the condition of the most important systems of the body and identify underlying diseases. This examination is suitable for patients without visible health problems who undergo check-ups for preventive purposes, as well as for those who have unpleasant symptoms of unknown origin. However, in some cases, specialized programs aimed at solving specific problems are necessary.
For example, a woman with a family history is strongly recommended to undergo regular mammological or oncological check-ups. There are specialized check-ups for children, for athletes, and even for those who are susceptible to such addictions as smoking.
Another study is gradually gaining popularity - genotest, that is, deciphering a person’s genotype[3]. The information obtained during the study does not change throughout life, so the genotest is performed once.
How long will the research last?

The duration of a checkup depends on its type, that is, on the number of consultations, diagnostic procedures and tests to examine the body. The basic program for men and women aged 30–40 lasts on average one day. In five to six hours, the patient manages to visit a therapist, four to five specialists, take tests, undergo an ultrasound and other types of instrumental studies.
Check-up for older people usually lasts a little longer because it includes more types of research.
Some in-depth diagnostic programs can take three to five days.
In most cases, examination results may not be ready immediately, which is due to the specifics of certain tests. But usually within a week the patient already receives a conclusion about the state of his health.
Tests at home You can take the necessary tests without leaving your home. Call a specialist at home THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS. YOU MUST CONSULT A SPECIALIST
What does the patient receive after completing the study?
The results of all studies and the conclusions of highly specialized specialists are transferred to the therapist-supervisor. After completion of the diagnostic program, a final consultation with the patient is carried out.
The doctor-supervisor tells the patient about the results of the examination, answers questions, gives recommendations regarding lifestyle, nutrition, elimination of risk factors, prevention of diseases to which a predisposition has been identified. If any pathology is detected during diagnostic tests, the therapist issues a referral for further specialized examination or treatment.
After the final consultation, the patient is given a written report on his state of health. He also receives the results of all tests and diagnostic procedures. All documents are filed and given to the patient in the form of a book, which is convenient to take with you the next time you visit the doctor.

How does the procedure work?
When the entire body is examined during MRI, the procedure is practically no different from MRI of one department or organ. The patient also lies down on the machine table and puts on headphones to block out the noise. The table is rolled into the tomograph ring and the examination begins. The main difference between the procedure is the duration. A full body examination may take about 60 minutes, and in some cases more. All this time it is difficult to maintain a motionless body position, so the procedure is often carried out with a break.
The essence of the method
The computed tomography method is based on the measurement and complex computer processing of the difference in the attenuation of X-ray radiation by tissues of different densities. During a CT scan, images are taken layer by layer, at different depths, and then processed using a computer. Computed tomography of the whole body is performed at a reasonable cost at the Yusupov Hospital.
A stream of X-rays emerges from the radiation source, passes through slits whose size corresponds to the thickness of the planned tissue section, and describes a complete circle around the patient. Sensitive detectors located opposite the source record the radiation that passes through the body during the CT scan.
The distribution of X-ray absorption coefficients is reconstructed into an image using a computer. Areas with higher absorption coefficients or higher density appear light, and vice versa. Resolution depends on the following factors:
- Radiation doses;
- Thickness of the scanned layer;
- Fields of View;
- Display resolutions.
A conventional modern tomograph allows you to obtain slices 1-2, 5 and 10 mm thick with a layer scanning speed of 1-3 seconds, a complete examination of the brain takes 2-3 minutes. Computed tomography has the main advantage over conventional x-ray examinations - the clarity of the objects being examined. In X-ray computed tomography, a single scan creates an image of one layer. The scanning cycle is repeated after the next movement of the table as many times as layer-by-layer images need to be obtained.
Spiral computed tomography provides continuous three-dimensional imaging. In a spiral tomograph, the table with the patient constantly moves through a rotating source of X-rays. In this case, the entire body is scanned in a spiral. Reconstruction of slices of various thicknesses then occurs. Spiral computed tomography of the whole body has the following advantages: it allows you to reduce the duration of the study, eliminate distortions from changes in body position, respiratory movements of the patient and movements of internal organs.
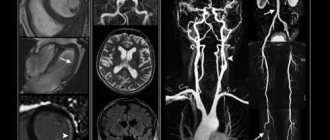
The spiral scanning technique can significantly reduce the time spent on CT examinations and significantly reduce the radiation dose to the entire patient’s body. Multislice CT of vessels is used for a quick, complete and accurate study of the state of the vascular system of the entire human body. At the Yusupov Hospital, the study is carried out using the latest generation multislice computed tomograph. Vascular examination is carried out with an intravenous bolus injection of a contrast agent. The Yusupov Hospital uses contrast agents that have undergone clinical trials and are registered in the Russian Federation.
Multislice computed tomography makes it possible to obtain accurate, visual images due to the fact that scanning occurs directly at the moment the radiopaque substance passes through the vessels. Using the study, doctors assess the condition of the walls of blood vessels, determine the composition of atherosclerotic plaques, the presence of blood clots in the lumen, clarify the degree of narrowing or blockage, identify features of vascular development, and evaluate the results of surgical intervention. At the Yusupov Hospital they do CT scans of any part of the body with contrast at an affordable price.
Advantages of the “Medicine” clinic
We consider our main advantage to be the very high information content of the study, which is due to the use of a high-field magnetic resonance imaging scanner with a magnetic field strength of 3 Tesla. Such high power also ensures very high image quality, which is an important indicator in identifying difficult-to-diagnose diseases.
In addition, the device is equipped with a noise suppression system, making the examination process comfortable for the patient. Other advantages of examination in our clinic include:
- efficiency (even MRI of the whole body is performed as quickly as possible);
- reliability (conducting research in accordance with international standards);
- effectiveness (if necessary, MRI with contrast is performed);
- quality (in difficult cases, professors from leading medical universities are involved in decoding);
- convenience (documents are provided both in the form of photographs and in electronic version).
Prices, discounts, benefits
Whole body MRI can be done at Meditsinsky in St. Petersburg. The procedure helps in identifying pathologies and prevents the development of serious diseases. The diagnostic cost includes:
- Examination using a Vantage Elan 1.5T tomograph (Canon, Japan)
- Detailed and comprehensive conclusions made based on the images by a highly qualified radiologist. The description of the study is checked by the chief physician.
- Internal quality control of research.
Detailed information about prices can be found in the “Prices” section. You can find out about the benefits and ongoing promotions in the “Promotions” section.