In the absence of pathological processes, the intestinal lumen of a healthy person contains a large number of bacteria. They provide normal microflora involved in the process of food digestion, and also provide the body with important microelements and vitamins. Some bacteria are considered completely harmless, while others are considered opportunistic.
In other words, when the immune system decreases, these bacteria degenerate into pathogenic ones and act as a provoking factor in the development of certain gastrointestinal pathologies. However, there are microorganisms that are initially pathogenic.
They should not exist in the body of a healthy person. To identify such bacteria, a stool test is performed for the intestinal group.
What is included in the intestinal group
At the same time, their successful interaction with macroorganisms is noted. In addition, they are involved in the process of performing a number of important functions. Nutrition comes from the contents of the intestines .
Depending on the danger, all microflora is divided into three types:
- useful;
- conditionally pathogenic;
- pathogenic microorganisms.
The first group includes bacteria that support the normal functioning of digestion under any conditions. At the same time, they are also capable of producing vitamins that provide the human immune system.
These include:
- Escherichia;
- mushrooms;
- bifidobacteria;
- lactobacilli;
- bacteroides.
There are no more than fifteen such microorganisms in total.
Conditionally pathogenic bacteria are not dangerous to health if a person does not have any disease. However, when the protective functions are weakened, they act as a causative agent of the pathological process.
This group includes:
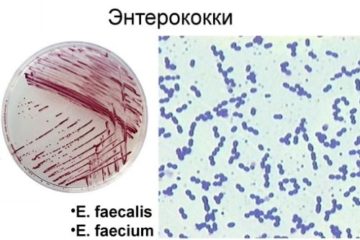
- enterococci;
- clostridia;
- staphylococci;
- coli;
- Candida mushrooms.
Against the background of the presence of pathogenic microorganisms, an infectious disease may develop. Normally, such bacteria should not exist.
Their peculiarity is that they take a protected form, which allows them to be present in the intestines for a long time.
Among these pathogens are:
- shigella;
- salmonella;
- balantidium;
- dysenteric amoeba;
- cholera vibrio and others.
If a specialist refers a patient to undergo a bacteriological analysis of stool, then he first of all wants to know about the presence of probable provocateurs of the disease.
Taking stool for analysis in a laboratory or hospital
In some cases, material for research is collected by a medical professional, regardless of the patient’s natural bowel movement. Tampons or special loops can be used for this. This stool sampling algorithm is also suitable for small children.
The technique for collecting stool looks like this: the examinee lies down on the couch in the “sideways” position, bending his knees and pulling his hips towards his stomach. He needs to spread his buttocks with his palms. A loop or tampon is inserted into the anus to a depth of up to 10 centimeters, with which the nurse carefully removes the intestinal contents from the wall of the rectum.
The collected material is placed in a sterile tube, container or container with a preservative. Without a preservative, the material must be processed no later than 2 hours after its removal.
When is it appointed?
Stool culture is prescribed if a person begins to show characteristic signs indicating the development of an intestinal disease:

- increased body temperature;
- nausea accompanied by vomiting;
- feeling of pain in the abdominal region;
- diarrhea.
Based only on clinical symptoms, it is not possible to make an accurate diagnosis . In this case, one can only make certain assumptions about the presence of some intestinal pathological process.
To make a final diagnosis, the patient undergoes a comprehensive examination, on the basis of which a conclusion is made about the disease and the type of its causative agent.
It is also necessary to remember that in certain professions it is necessary to take a stool culture tank every year.
What helps to identify
Stool examination shows the presence of microorganisms from one of the three groups mentioned above.
To determine the number of bacteria, feces are inoculated on a special nutrient medium.
In other words, in laboratory conditions a favorable environment is created that allows microorganisms to exist normally. Each type of bacteria has its own specific conditions.
First of all, the bacteria need to grow a little in a liquid medium. After this, they are placed in a solid nutrient medium in order to be able to differentiate them into species.
To accurately determine the genus and type of bacteria, additional hemotest and microscopy are performed.
How to take it
To obtain the most accurate research results, it is necessary to follow certain recommendations of specialists.
Preparatory stage
At least seven days before the procedure, treatment with antibacterial drugs and laxatives should be avoided. These medications contribute to disruption of the intestinal microflora, which can result in distortion of the data obtained.
For three days, exclude from the diet foods that can trigger the fermentation process. It is also not recommended to drink alcohol .
You should not use rectal suppositories either.
For hospitalization, when a patient is admitted to a hospital, he must also undergo additional examination.
In this case, the study includes:
- urine analysis;
- biochemical analysis of blood fluid;
- a swab taken from the nose and throat;
- analysis of stool.
Such measures make it possible to eliminate the threat to other patients.
Stool collection
For the study to be effective, feces must be collected correctly. The biomaterial should be taken after natural defecation from a clean surface. This will avoid contamination with foreign bacteria.
The volume of stool should contain at least three measuring spoons. Stool should be collected from the middle part.
If the biomaterial contains blood, purulent impurities or mucus, then for research it is necessary to collect material from this particular area.
The test must be taken in the morning.
Preparing containers
Stool is collected into a special container.
A container designed for these purposes is sold at any pharmacy. If it is not possible to buy such a container, then you can use a dry glass jar. It must be well washed and sterilized.
Material storage
For the result to be as accurate as possible, the biomaterial must be delivered to the laboratory within two hours after collection. If this is not possible, then the feces are stored in the refrigerator in a tightly closed jar. The shelf life of the material is no more than four hours.
How it is researched
There is a special algorithm for examining stool that every laboratory technician must adhere to.

After this, the biological material is examined under a microscope.
Thanks to special modern equipment that allows bacteria to be increased, specialists are given the opportunity to establish the type and mobility of existing bacteria. Within 24 hours, an experienced laboratory technician can sum up the results.
However, to avoid any doubt, the causative agent of intestinal infection is examined as thoroughly as possible.
Indications and contraindications for stool culture
Stool examination is prescribed in certain cases when the doctor needs specific information about the patient’s health status. Indications for prescribing bacteriological examination of stool are:
- the need to prescribe antibiotics;
- preparation for conceiving a child;
- presence of digestive problems: constipation, diarrhea, heartburn, nausea and vomiting, heaviness in the stomach:
- stomach ache;
- increased gas formation;
- completed course of antibiotic treatment;
- manifestations of allergic reactions;
- frequent infectious diseases, suspicion of helminths;
- diagnosed cancer;
- immunodeficiency.
As for possible contraindications, this procedure does not have any - bacteriological examination of stool can be carried out at any age and in any condition of the patient.
How to decrypt
The interpretation of the results is carried out exclusively by a specialist. The test makes it possible to identify many groups of pathogens.
These can be microorganisms such as:

- Lactobacilli. They make up approximately 5% of the normal intestinal microflora. They are involved in the process of maintaining normal pH levels. They are also a definite obstacle to the development of bacteria belonging to the pathogenic group. If their concentration in the body decreases, this indicates the presence of some pathological process, for example, helminthic infestation or dysbacteriosis in the human body.
- Bifidobacteria. They belong to the normal microflora and make up 95%. They participate in the production of vitamin K, group B. In addition, they contribute to the normal absorption of vitamin D. When their amount decreases in the body, intestinal dysbiosis may develop.
- Staphylococcus aureus. This is a pathogenic microorganism. In normal condition it should be absent. An increase in its number contributes to a decrease in the immune system, which in most cases leads to allergies.
- Escherichia coli. It has been in the intestines since birth. It also participates in the synthesis of vitamin K, helps destroy pathogenic bacteria and strengthen the body's defenses.
Pathogenic microorganisms include Shigella and Salmonella, which are also absent in a healthy person.
Analysis of stool for the intestinal group is necessary so that the provoking factor contributing to the development of intestinal infection can be accurately identified. This will allow you to prescribe the most effective therapeutic tactics.
The technique of taking biomaterial is not a complicated process . The main thing is that all necessary recommendations by a specialist are followed, which will allow you to obtain more accurate results.
It is necessary to conduct an examination of the intestines for microflora regularly - at least once a year. This will ensure the patient’s normal functioning of the digestive system.
Decoding the analysis, evaluating the results
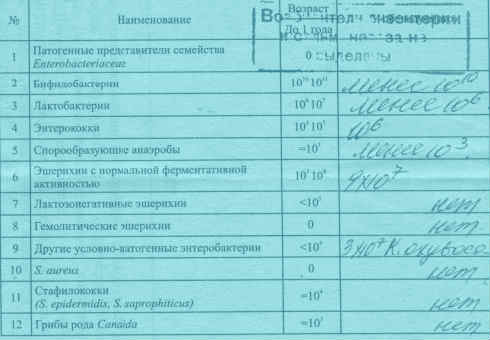
The attending physician interprets the tests. But you can also figure out for yourself whether everything is okay. Normal indicators are as follows (accounting in CFU):
- number of bifidobacteria: from 1*108;
- lactobacilli – from 1*106;
- Escherichia coli – up to 4*108;
- spore-forming anaerobes – no more than 1*103;
- enterobacter – up to 5%;
- cocci – no more than 25% of the total;
- no pathogenic flora should be detected.
In children of the first year of life, these indicators may differ, more often - to a greater extent.
The results are issued on a special form; if pathogens are present, this is marked with a plus sign in the appropriate column or recorded with a stamp.