Salmonella
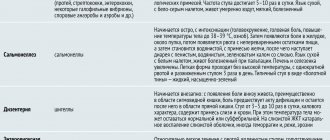
- a group of pathogens that cause intestinal infections such as typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever and, in fact, salmonellosis. The differences lie in the subspecies of bacteria that entered the patient’s body. This affects the clinical picture, diagnostic features, choice of treatment method and epidemiological actions. Let's consider the characteristics of pathogens and the diseases they cause.
S. paratyphi causes paratyphoid fever, they differ in the type of disease and are divided into A, B and C. Salmonellatyphi causes typhoid fever. These infectious diseases are accompanied by circulation of the pathogen in the blood, high body temperature, reaction of the lymph nodes and toxic manifestations. Salmonella causes salmonellosis, which is somewhat milder than typhoid and paratyphoid fever. These pathologies are difficult to distinguish based only on clinical phenomena; laboratory research methods are used for this. They are united by the fact that they are tropic to the digestive tract and most symptoms are observed precisely from these organs.
Epidemiological features of pathologies
An important point when making a diagnosis is the characteristics of the pathogen’s penetration into the body. Depending on this, several types of infections are distinguished. For example, bacteria that lead to the development of typhoid and paratyphoid fever are anthroponotic - transmission of infection is observed from people who are sick and are carriers. Salmonellosis and some paratyphoid fevers are zooanthroponoses - infections that are common to animals. and for people.
The structure of salmonella allows them to survive environmental conditions and continue their life cycle in water and soil. To destroy them, it is necessary to use disinfectants and other aggressive substances. Bacteria enter wastewater and soil mainly through feces, which is why the route of transmission is called fecal-oral. In addition to feces and urine, the patient’s saliva contains a significant amount of bacteria, from which conclusions can also be drawn about the transmission of the disease.
Salmonella, DNA Salmonella spp.
Salmonella, DNA Salmonella spp., quality
— determination of Salmonella species DNA in feces using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method with real-time detection.
The PCR method
allows you to identify the desired section of genetic material in a biological material and detect single molecules of microorganism DNA that are not detected by other methods. The principle of the method is based on a multiple increase in the number of copies of DNA sections specific to a given pathogen.
Using PCR analysis, it is possible to diagnose infection in the acute period and identify cases of carriage.
Salmonella species
- gram-negative, mobile, rod-shaped enterobacteria, capable of causing salmonellosis - an acute intestinal infection. Salmonella infection belongs to the group of zoonotic ones, that is, transmitted from animals to humans.
The main route of transmission is fecal-oral, that is, through contaminated food (drinking contaminated water, eggs or meat).
Salmonellosis occurs with primary damage to the gastrointestinal tract (small intestine), similar to diseases such as enteritis, gastroenteritis, gastritis (without diarrhea), in a typhus-like form and a septic form.
The incubation period of the disease is 6–8 hours.
Clinical signs of salmonellosis
Salmonellosis manifests itself acutely - with nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, fever, and headaches. In chronic cases, symptoms of arthritis may occur. When the intestines and abdominal lymph nodes are affected, salmonellosis gastroenteritis develops, which is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, cramping abdominal pain and fever.
If the infection is generalized, in 5–10% of cases thromboembolic complications, salmonella sepsis and meningitis, pneumonia, endarteritis, endocarditis, and pyelonephritis are possible.
When the cells of the reticuloendothelial system are damaged, a systemic infection develops - typhoid fever with fever, stool disturbances, rash in the abdomen and chest and symptoms of damage to the central nervous system (lethargy, impaired consciousness and delirium).
After an illness, in 20% of cases, bacterial carriage occurs, which can last for life.
Laboratory diagnosis of infection caused by bacteria of the genus Salmonella
Laboratory diagnosis of salmonellosis is based on the isolation of the pathogen by inoculating various types of biomaterial from the patient (feces, vomit, bile, blood in septic forms) during microbiological examination.
Indications:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract accompanied by diarrhea (the main purpose of the study is to identify dysentery and salmonellosis in children and adults);
- preventive examination of persons before hospitalization.
Preparation
To obtain a reliable result, the analysis should be carried out 14–21 days after the last dose of antibacterial drugs.
It is preferable to take a sample in the first 72 hours from the onset of the disease.
Feces are collected in a disposable container with a screw cap in a volume of no more than 1/3 of the container's volume. The feces must be freshly collected. The material is delivered to the medical office within 4–6 hours from the moment the analysis is collected.
The referral form must indicate the diagnosis and date of onset of the disease, information about taking antibiotics. When taking material, sterility must be observed.
Conditions that must be observed:
- freezing is not allowed;
- Long-term storage is not allowed (more than 5–6 hours);
- no transport media other than those specified are suitable;
- A container that is not tightly closed is not allowed;
- Biomaterial collected the day before cannot be examined.
Interpretation of results
The answer is given in a qualitative format: “detected” or “not detected”.
Reference values: not found.
If the answer is positive, the presence or absence of obligate intestinal pathogenic bacteria (Salmonella) is indicated.
Interpretation of the result: normally the result is negative.
When is it necessary to undergo diagnostics?
Tests must be taken by those who work in food production, visit or work in a children's group. This is necessary in order to exclude the fact of carriage of the bacteria. The food industry is dangerous in epidemiological terms, since the pathogen thrives on nutrient media that are used in the production of ready-made meals or products. Children's groups also have their own peculiarity - in childhood, hygiene measures are not observed so seriously; poor hand washing and contact of dirty surfaces with the oral mucosa are more common. Diagnostics is especially important for pregnant women. In other cases, tests are performed if the following symptoms are present:
- acute increase in temperature;
- increasing intoxication, which manifests itself as weakness, headache, aching bones and joints;
- abdominal pain, which is spastic in nature, is localized around the umbilical ring and in the place where the costal arches meet;
- nausea followed by repeated vomiting;
- diarrhea, in which there may be a greenish tint to the stool and an unpleasant odor;
- pale skin;
- dry mucous membranes;
- a finely spotted red rash that gradually becomes paler.
There are various forms and characteristics of the course of the disease, so the symptoms may differ slightly. As a rule, with a suspicious clinical picture, patients go to the doctor, and he refers them for tests. Laboratory diagnostics are also used retrospectively - after recovery, to determine the immunological picture, as well as to identify stable forms of pathology.
go to analyzes
Stool analysis
1. Coprogram
— No special training is required to perform the coprogram.
- Collect feces in a clean glass or plastic container from several sections in an amount of 10-15 g using a spoon from a plastic container or spatula.
— Avoid mixing urine, genital secretions and other substances, including medications, into stool.
— If delivery of stool to the laboratory is not immediately possible, store stool in a sealed container on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator for no more than 24 hours.
2. Fecal occult blood test
— From the diet 3-4 days before the test, exclude meat, fish, spring eggs, all types of green vegetables, tomatoes, medications containing iron, copper and other heavy metals.
- Collect feces in a clean glass or plastic container from several sections in an amount of 3-5 g using a spoon from a plastic container or spatula.
— If delivery of stool to the laboratory is not immediately possible, store stool in a sealed container on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator for no more than 24 hours.
3. Testing for the presence of helminths and their eggs
- Take feces from different parts of a freshly isolated single portion (in a total amount of about 10-15 grams) using a spoon from a plastic container or spatula. In addition, parasites that spontaneously came out or were isolated during treatment are delivered to the laboratory.
— Helminth eggs may not appear in the stool every day, so the analysis must be repeated several times.
— If delivery of stool to the laboratory is not immediately possible, store stool in a sealed container on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator for no more than 24 hours.
4. Research on protozoa
— The feces are delivered freshly excreted and warm. To detect vegetative forms, the study is carried out no later than 15-20 minutes after defecation.
— You can’t keep feces in a thermostat or warm water, because this causes death and degenerative changes in the protozoa.
5. Dysbacteriosis
— To perform stool sampling for dysbacteriosis, special preparation of the patient is required.
— 3 days before the test, avoid spicy foods, alcohol, antibiotics and chemotherapy drugs.
— For analysis, take freshly excreted stool obtained naturally. Take 1-3 grams with a spoon or sterile spatula and place in a sterile container. Take material from areas containing mucus, pus, flakes, but free of blood. No urine allowed.
— If it is not possible to deliver stool to the laboratory immediately, store the stool in a sealed container on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator for no more than 24 hours.
6. Stool analysis for salmonellosis and dysentery
— To collect stool for testing for salmonellosis and dysentery, special preparation of the patient is required.
— 3 days before the test, avoid spicy foods, alcohol, antibiotics and chemotherapy drugs.
— For analysis, freshly excreted feces obtained naturally are taken. Using a spoon or sterile spatula, take 1-3 grams and place in a sterile container. Take material from areas containing mucus, pus, flakes, but free from blood. No urine allowed.
— If the patient does not have stool, it is possible to collect stool with an aluminum loop mounted in a sterile glass tube with saline solution. Insert the loop into the rectum at a distance of 2-3 cm.
— If delivery of stool to the laboratory is not immediately possible, store the stool in a sealed container on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator for no more than 24 hours.
IT IS FORBIDDEN!
- deliver feces for research after enemas, administration of suppositories, ingestion of dyes (iron, barium, bismuth), medications that alter intestinal motility (belladonna, pilocarpine), castor and petroleum jelly, blueberries, beets, chokeberries, hematogen.
— Feces should not contain foreign impurities, for example: urine, water, disinfectants.
Salmonellosis
Salmonella can cause both typhoid fever and salmonellosis. True, these two diseases are caused by different serotypes of bacteria. The symptoms of salmonellosis differ little from those of other intestinal infections:
- diarrhea,
- nausea,
- vomit,
- heat,
- abdominal cramps.
The fever usually resolves within 48 to 72 hours, and the diarrhea within 4 to 10 days.
You can become infected by eating chicken, eggs and milk and by contact with reptiles, such as turtles. There is no treatment for the infection as such, other than constant fluid replacement. If patients under 50 years of age take antibiotics, then, firstly, this does not speed up recovery, and secondly, it may increase the risk of asymptomatic carriage of salmonella. But more often, after the acute period, older people and those who have problems with the biliary tract or, for example, gallstones, remain contagious.
Usually the bacteria stay in the body for no more than 4-5 weeks after recovery, but in some people salmonella can live for years. In this case, it is enough to wash your hands poorly after using the toilet and start preparing some dish for the food to become dangerous.
Tests for salmonellosis in children
Since the younger generation is at risk, preventive measures must be systematic. At the first suspicion of a progressive disease, a comprehensive diagnosis of salmonellosis in children is necessary, which speeds up the process of making a diagnosis and determining an intensive care regimen. These are definitely the following methods:
- Serological method. It is used 7 days from the moment of illness, and then repeated after another week of effective treatment.
- A bacteriological method that provides a reliable conclusion to the patient in 3-4 days.
- Express diagnostics of salmonellosis, represented in medical practice by the implementation of the immunofluorescent method.
2.What is the cause of the disease?
You can get salmonellosis by eating foods contaminated with salmonella.
. Salmonella enters food in one of the following ways:
- Food can become contaminated with bacteria during preparation or transportation.
- Salmonella can get onto food from dirty hands. A common cause of salmonellosis is unwashed hands after using the toilet.
- Salmonella is also present in the feces of many pets, especially if they themselves suffer from diarrhea. If you don't wash your hands after handling pets, you can also become infected.
- Reptiles, chickens, ducklings and small rodents such as hamsters are also common carriers of salmonella.
- Beef, poultry, eggs and milk also often contain salmonella. However, this does not mean that it is not found in vegetables.
Be careful, as products contaminated with salmonella taste and smell no different from safe ones.
Visit our Gastroenterology page
Salmonellosis test results
If there are prerequisites for salmonellosis, it is necessary to get tested. The doctor tells you how long you have to wait for the results, and on the specified day he will explain the transcript he received. If tests for salmonellosis show the absence of antibodies, this means that the health problem is completely absent. To be more sure, it wouldn’t hurt to perform a second smear, for example, in another week. This is the only way to be sure that salmonellosis is absent.
If the answer is yes, the adult patient and child will receive immediate treatment. An acute attack of poisoning is accompanied by intoxication of the body, so it is necessary to eliminate unpleasant symptoms and get rid of the remains of infected food, as the main provoking factor. The performed blood test provides the following changes in the composition of the biological fluid:
- leukocyte count increased
- there is a shift in the formula to the left;
- increase in ESR;
- erythrocytosis;
- diagnostic titer for RPHA – 1:200;
- increase in antibody titer in paired sera;
- the presence of Salmonella O and H - monodiagnosticums.
The child must undergo analysis strictly according to indications, but it is also possible that a laboratory test will be necessary upon admission to kindergarten or another educational institution. To get a ticket to a camp or for inpatient treatment, it is important to perform a smear for salmonellosis. This survey method can be used in other instances. For example, adults are required to take a test for typhoid fever for their health certificate when applying for a new job. More often, this research is carried out on a paid basis.
How to take a smear for salmonellosis during pregnancy
To ensure that the intrauterine development of the fetus is not involved in the pathological process, it is necessary to conduct an analysis for salmonellosis during pregnancy. Some patients are unaware of the infection, so they do not think about treatment. Such delay by pregnant women only harms the child, and a disabled person may be born. To prevent this from happening, enterobacteria are detected by laboratory methods. It is better to carry out this smear when planning pregnancy, so that, if necessary, timely treatment. Only after this can you safely plan conception.