Clinical manifestations and symptoms
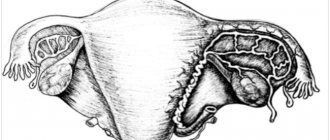
In most cases, there is a tubal pregnancy, which often forms in the right fallopian tube. The clinical picture depends on the location of the ovum, the duration of pregnancy, whether the pregnancy progresses or is terminated. In the latter case, the clinical manifestations depend on the nature of the termination of pregnancy - such as tubal abortion or tubal rupture.
Classic clinical signs of a failed ectopic pregnancy are: pain, delayed menstruation and vaginal bleeding. However, these typical manifestations do not occur in all cases. Patients with an ectopic pregnancy also experience some other symptoms that can occur in the early stages and during intrauterine pregnancy: nausea, enlarged mammary glands, weakness, cramping pain in the lower abdomen, pain in the shoulder area.
There are no symptoms characteristic only of progressive tubal pregnancy. The patient experiences exactly the same sensations as during a normal progressive intrauterine pregnancy.
However, during a gynecological examination with a progressive tubal pregnancy, the following signs are noted:
- insufficient softening of the uterus and its isthmus;
- mild cyanosis of the mucous membranes of the vagina and cervix;
- preservation of the pear-shaped uterus; absence of early signs of intrauterine pregnancy;
- in the area of the appendages, a tumor-like formation is determined, oval or sausage-shaped, soft or elastic in consistency;
- limited mobility and pain of this formation.
Tubal pregnancy is usually terminated at 4-6 weeks (it develops much less frequently before 8 weeks). More often, a tubal pregnancy is terminated as a tubal abortion, which is accompanied by cramping pain, indicating damage to the integrity of the ovum. Characterized by a sudden onset of pain, which may be accompanied by complaints of severe weakness, dizziness, nausea, and sweating. Loss of consciousness is also possible. The pain can radiate to the anus, lower back, legs.
Usually, after some time (several hours) after a painful attack, 50-80% of patients experience bleeding or scanty dark, sometimes brown spotting from the genital tract. In the early stages, the embryo dies, bleeding stops, and the fertilized egg is reabsorbed. At a later date, the fertilized egg is completely rejected and, entering the abdominal cavity, can be implanted on various organs, which can result in abdominal pregnancy. However, most often, after rejection of the fertilized egg, bleeding does not stop, and the clinical picture depends on the severity of blood loss. In most cases, tubal abortion is not characterized by massive intra-abdominal bleeding and acute anemia. The symptoms are erased, the course of the disease is usually slow, from several days to several weeks.
In every third patient, an ectopic pregnancy disorder occurs as a ruptured tube, which is accompanied by heavy bleeding. Patients, as a rule, experience sharp, severe pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the rectum, collarbone, and hypochondrium. There is a sharp deterioration in condition, weakness, cold sweat, loss of consciousness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting. On external examination, lethargy and apathy are noted; pallor of the skin and mucous membranes; pale or cyanotic lips; cold sweat; dyspnea. Due to significant blood loss during intra-abdominal bleeding, there is noise in the ears, flashing “spots” before the eyes, and a drop in systolic blood pressure below 80 mm Hg. Art. The abdomen is soft, moderately swollen, and there is severe pain in the lower parts. Vaginal examination reveals cyanosis or pallor of the mucous membranes of the vagina and cervix; no external bleeding; increased and soft consistency of the uterus; sharp pain when the cervix moves towards the pubis; smoothness is observed more often than one lateral arch; tumor-like formation of doughy consistency, detected in the area of the appendages.
Are errors possible when making a diagnosis?
Errors in making a diagnosis are extremely rare, but they are not excluded. Therefore, in order to avoid any inaccuracies, it is advisable to undergo an ultrasound scan if you suspect pregnancy in a specialized clinic equipped with high-precision, new diagnostic equipment.
The reasons why pathological pregnancy cannot always be determined in a timely manner:
- false embryo;
- fluid in the uterine cavity, mistaken for a fetus;
- outdated equipment;
- too short a period.
To exclude any errors and suspicions, the doctor is obliged to give a referral for additional diagnostic examination. In this case, a blood test for hCG levels is informative. With this pathology, the titer of human chorionic gonadotropin grows slowly and does not correspond to the duration of pregnancy.
FAQ
Is it possible to independently resolve an ectopic pregnancy?
No, the situation requires medical intervention. There are no proven methods of home treatment; mortality due to too late seeking medical help reaches 3.6%
Will I be able to have a child in the future?
If pathologies in the development of the reproductive organs are excluded and at least one fallopian tube is preserved, a normal pregnancy is possible in 50% of cases. If there are no fallopian tubes, an IVF procedure is available.
Is this gap hereditary?
No. Ectopic pregnancy is not hereditary.
When can I plan to have a baby again?
Doctors recommend postponing conception for at least a year to fully restore the body. During this period, it is recommended to take oral contraceptives and undergo mandatory examination before planning pregnancy.
Womenfirst
- Ed. V.E. Radzinsky, A.A. Orazmuradova. Early pregnancy. From preconception preparation to healthy gestation. 800 s, 2021
- Dzigua Manana Vladimirovna. Medical care for women with gynecological diseases at different periods of life. Textbook., 400 pp., 2021.
- Sidorova I.S. Ishchenko A.I. Unanyan A.L. Nikitina N.A. Chushkov Yu.V. OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY. 1304 pp., 2021
- Pryakhin V.F., Groshilin V.S. Surgical diseases, injuries and pregnancy. Textbook. 496 pp., 2021
RUS2193270 (v1.0)
Associated symptoms
In the early stages (up to 2–3 weeks), the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy coincide with the signs of a normal pregnancy. During this period, a woman experiences:
- delayed menstrual bleeding. The process of fertilization of an egg triggers hormonal changes in the body. The production of progesterone increases, so menstruation does not occur during ectopic pregnancy;
- enlargement of the mammary glands;
- nausea;
- change in taste, intolerance to certain smells;
- unstable emotional state.
Signs of an ectopic pregnancy at 3–5 weeks are spotting brown vaginal discharge, nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, painful urination.
A ruptured fallopian tube is a dangerous condition that leads to internal bleeding.
As a rule, rupture occurs at 4–6 weeks and is accompanied by excruciating pain in the lower abdomen. With excessive internal bleeding, the phrenic nerve is irritated. Pain syndrome occurs in the anus, neck, and shoulders.
A sharp decrease in progesterone levels often causes uterine bleeding. Low blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, dizziness, urge to defecate, and loss of consciousness may occur.
If such symptoms do not seek medical help in time, the woman may die.
How to recognize an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages
The woman’s feelings and general health are not much different from pregnancy, which proceeds normally. For example, a woman may notice delayed menstruation and other symptoms that indicate pregnancy. From about 4 weeks, alarming symptoms may occur, such as pain in the lower abdomen, abdominal or uterine bleeding, and with large blood loss, symptoms of shock may even occur, for example, a drop in blood pressure, weakness and pallor. Symptoms are completely individual and may completely depend on the type of pathology and the outcome of such a pregnancy. Among them are detachment of the embryo from the fallopian tube, rupture of the fallopian tube, etc.
But, one way or another, a woman should not hesitate and consult a doctor as quickly as possible. You should go to a gynecologist if you suspect pregnancy or if your period is delayed, even if the test does not confirm pregnancy.
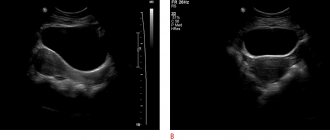
Diagnostics of tubal pregnancy
If menstruation is delayed, it is recommended to consult a gynecologist to clarify the diagnosis and conduct an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, where it is possible to clearly identify all possible signs of pregnancy.
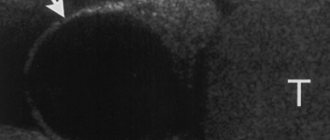
At the moment, transvaginal ultrasound, namely when the sensor is inserted through the vagina, for ectopic pregnancy serves as the first and most important step in the overall set of diagnostic measures that should be carried out. In this case, an ultrasound can confirm the fact that the fertilized egg is not in the uterus and is located in the fallopian tube. Sometimes, in order to clarify the diagnosis, in addition to ultrasound, diagnostic laparoscopy can be performed. In this case, an optical system is inserted into the abdomen through miniature punctures, thanks to which the doctor can see thickening of the fallopian tubes with increased vascular patterns, as well as blood in the abdominal cavity. In addition, the condition of the uterus, fallopian tube and ovaries is assessed.
Provoking factors
The main causes of ectopic pregnancy are obstruction of the fallopian tubes and a decrease in their transport function. The following factors can provoke such violations:
- inflammatory processes.
For example, chronic adnexitis. The disease begins when an infection enters the fallopian tubes. If inflammation is not treated in a timely manner, the acute stage of the disease becomes chronic. Often the result of chronic adnexitis is a disruption of the secretory activity of the tubes, the formation of adhesions in them; - imbalance in the body of female sex hormones.
The level of estrogen affects the functioning of the cilia of the fallopian tube epithelium. With estrogen deficiency, the transport function of the cilia is disrupted, and the fertilized egg cannot reach the uterine cavity; - disruption of innervation.
Innervation - supply of tissues with nerve endings. With frequent inflammatory processes in the fallopian tubes, a deficiency of nerve fibers is formed, which negatively affects their transport function; - surgical interventions.
At the site of the cut and seam, connective tissue is formed, which reduces the contractility of the pipe and its diameter. Often, surgical operations cause adhesions.
Other provoking factors are abnormal development of the genital organs, tumors of the uterus and ovaries, and long-term use of intrauterine contraceptives.