Computed tomography of the throat is one of the new ways to examine bone structures and soft tissues in this area. Diagnostics provides an opportunity to identify existing pathological conditions and structural features of the tissues of the larynx. Through scanning, you can obtain highly accurate images of the part of the body being examined, and therefore making the correct diagnosis will not cause difficulties for a specialist.
What does a CT scan of the larynx reveal?
Using CT images, specialists have the opportunity to visualize a number of diseases and pathological conditions:
- neoplasms of soft and bone tissues of the larynx with the ability to assess their size and location;
- presence of esophageal diverticula;
- places of destruction of cartilage in the larynx;
- observe changes in the structure of the walls of the larynx, which may be a sign of a developing tumor;
- identify the presence of foreign bodies in the area being examined;
- determine the severity of injuries received;
- assess the condition of the lymph nodes;
- identify existing inflammatory processes in the cavity being examined;
- diagnose various developmental pathologies;
- examine the vascular network of the larynx.
Risk factors
It is important to understand that the presence of these factors does not mean that you will definitely encounter cancer, however, their absence does not guarantee that you do not have cancer.
The main factors that increase the risk of developing laryngeal cancer:
- Alcohol. Those who regularly drink strong alcoholic drinks are 6 times more likely to develop oral cancer. The combination of smoking and alcohol is very dangerous.
- Smoking. The more experience a smoker has and the more cigarettes he smokes, the higher the risk of getting sick. Passive smoking also increases the risk of cancer.
- Working conditions. Risk factors include: working in conditions of high dust (especially if the dust contains harmful chemicals, radioactive substances, metals), in contact with isotopes and at high temperatures.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV). Neoplasms with the HPV18 and HPV16 virus subtypes were considered HPV-positive.
- Wrong diet.
Confirmation that alcohol and smoking increase the risk of developing the disease was found in studies that examined how the p53 tumor suppressor gene behaves. According to these studies, among all patients with laryngeal cancer, a mutation of this gene was detected in 42%. In those who drink and smoke at the same time, the mutation was observed in 58% of cases. For those who smoke but do not drink – 33%. In non-drinkers and non-smokers, the mutation occurred in only 17% of cases. In addition, in non-smokers and non-drinkers, the p53 mutation was observed in a DNA region that is more typical for endogenous mutations.
CT scan of the throat and larynx using a contrast agent
A CT scan of the larynx, performed without contrast enhancement, allows one to obtain information about the condition of the bone tissue and the existing pathological process in the hyoid bone and in the cervical spine. Using this diagnostic method, the cartilage of the larynx and the soft tissues of the neck are practically not distinguished, which is a significant disadvantage of this scanning method.
Therefore, in order to improve the quality of images when performing a CT scan of the throat, the doctor may prescribe a CT scan of the throat and larynx using a contrast agent.
Contrast is most often injected into the patient's body intravenously, after which it immediately spreads along with the bloodstream to all tissues and organs. Through the use of a contrast agent, it is possible to examine anatomical formations and organs in great detail. They acquire detail and the clearest outlines.
Contrast can also be introduced into the patient gradually throughout the entire scan. Exactly how the contrast will be administered is always decided on an individual basis, based on the purposes of the examination and the intended disease.
Regardless of how the contrast enters the body, the following discomfort cannot be ruled out:
- the appearance of a metallic taste in the mouth;
- feeling of warmth in the body;
- feeling of rising heat.
Such symptoms are considered not dangerous. They represent a normal reaction of the body to the injected drug, so there is no need to stop the procedure.
Dangerous signs that may indicate the appearance of intolerance to contrast during a CT scan of the throat are:
- the appearance of severe swelling of the face;
- sore throat;
- dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- a skin rash and severe itching;
- decrease in blood pressure.
The presence of at least one such symptom becomes a compelling reason to stop administering the drug and provide first aid to the patient. Although such cases are extremely rare. Ideally, each patient should undergo a sensitivity test before using contrast. If, based on the test results, the doctor has no doubts about the safety of the contrast agent for the patient, then you can safely proceed to the next stage of the examination.
Treatment methods
For laryngeal cancer , radiation chemotherapy (rarely), targeted therapy , and surgery . A single method or an integrated approach can be used, depending on the stage of the tumor, its location, degree of aggressiveness, growth pattern, and extent of the process.
Conservative therapy
Almost always, the first stage of treatment is radiation therapy . It is used to treat cancer of the middle section of the larynx, which is highly radiosensitive, as well as for tumors of the upper and lower regions of the larynx of stages I-II. Radiation is sometimes combined with hyperbaric oxygenation - saturating the blood with oxygen in a special chamber. This procedure enhances the effect of rays on degenerated cells and reduces damage to healthy tissue.
Treatment of stage III-IV laryngeal cancer, localized in the upper region of the organ, begins with chemotherapy . Chemotherapy is ineffective for the lower and middle parts of the larynx.
Radiation and chemotherapy can be used in combination.
Targeted therapy is the directed effect of a drug on the epidermal growth factor receptor. In laryngeal cancer, a large amount of the EGFR receptor protein is often found on the surface of tumor cells, which stimulates cell division. The drug Cetuximab, used for targeted therapy of the disease, suppresses the activity of this receptor. The drug is administered intravenously, usually used in combination with radiation, and in later stages - together with chemotherapy.
Surgical treatment
Sometimes, for stages I-II of laryngeal cancer, conservative therapy is sufficient. If it turns out to be ineffective, as well as for tumors detected at stages III-IV, surgical intervention is recommended. Before surgery, radiation therapy is always indicated to reduce the size of the tumor.
For stage I-II tumors, doctors try to perform organ-preserving resection: hemilaryngectomy - removal of one vocal cord, supraglottic laryngectomy - removal of part of the larynx above the ligamentous apparatus.
In the early stages, laser removal of the tumor using an endoscope can be used. The advantage of this method is that it is less traumatic; the disadvantage is that it is not possible to take a tissue sample for histological examination.
In later stages of the disease, it is necessary to resort to radical operations: chordectomy - complete removal of the vocal cords, total laryngectomy. In this case, the patient completely loses his voice.
Auxiliary Operations
In addition to direct removal of the malignant tumor, other surgical operations are performed. When laryngeal cancer metastasizes to regional lymph nodes or there is a high risk of metastases, these nodes are excised along with the surrounding tissue. The operation is called a cervical dissection .
When the larynx is completely removed, the patient needs a tracheostomy , a surgically created hole in the trachea. When creating a tracheostomy, the upper end of the trachea is sutured to the skin of the neck.
If laryngeal cancer makes it difficult to eat, the patient will have gastrostomy tube placed directly into the stomach.
If necessary, after extensive surgery, reconstructive plastic - operations that allow at least partially restoring the functions of the removed organs.
Indications for CT scanning
Each patient can receive a referral for a CT scan of the throat and larynx from a doctor in the following cases:
- in case of previous neck injuries, as a result of which there is a high probability of injury to internal organs;
- when foreign bodies get into the throat;
- with existing pathologies of the development of the throat and larynx;
- with progressive inflammatory diseases;
- for pathologies of the vascular network of the neck;
- for the purpose of precise location of the pathological process before surgery;
- to assess the effectiveness of treatment after surgery.
Doctors prescribe a CT scan of the larynx only in cases where another diagnostic method carried out in the future will not provide sufficient information and will complicate diagnostic measures.
As a rule, the patient is initially referred to undergo ultrasound diagnostics or x-rays, and only if these examination methods do not lead to results, the patient will be sent to a CT scan of the throat and larynx.
Rehabilitation
Recovery after surgery to remove the larynx or part of it is a difficult and lengthy process. The patient cannot eat normally and is forced to take food through a tube, and cannot speak. After a certain time, when it becomes clear that the operation was successful, the patient’s larynx is restored and plastic surgery of the vocal cords is performed. To restore voice function, it is necessary to undergo a rehabilitation course, which includes special physical procedures, exercise therapy exercises, sessions with a psychotherapist, and training in new speech skills.
Contraindications for diagnostics
CT scan of the throat and larynx has some contraindications for the following patients:
- women expecting the birth of a baby;
- patients with excess body weight;
- patients with mental illness.
CT scans are performed with extreme caution:
- children under 12 years of age;
- women breastfeeding babies;
- patients with kidney problems;
- patients with multiple myeloma.
Carrying out computed tomography using contrast is unacceptable:
- during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- patients with disorders of the liver and kidneys;
- diabetics;
- patients with an allergic reaction to contrast.
How to properly prepare for a CT scan of the larynx
For those patients for whom CT of the throat and larynx is planned to be performed in the native mode, there is no need to observe any strict restrictions in their usual lifestyle or follow a special diet.
However, those patients who are indicated to undergo a scan using a contrast agent will have to comply with some restrictions. So, before undergoing a CT scan of the throat, it is prohibited to eat any food 6 hours before the start of the scan. However, drinking water in small volumes is allowed.
All patients, regardless of how the examination will be carried out: with or without contrast, must remove absolutely all jewelry and objects with metal parts before entering the office. You will also have to leave your mobile phone, watch, bank cards outside the office - all these items can cause poor-quality photographs.
Survival prognosis
The prognosis for laryngeal cancer is influenced by various factors, but the stage of the tumor and its location are most important. The table below shows the average 5-year survival rates (the percentage of patients who remain alive 5 years after their cancer diagnosis):
Tumors in the upper larynx:
- Stage I: 59%
- Stage II: 59%
- Stage III: 53%
- Stage IV: 34%
Tumors in the vocal cords:
- Stage I: 90%
- Stage II: 74%
- Stage III: 56%
- Stage IV: 44%
Tumors in the lower part of the larynx:
- Stage I: 53–65%
- Stage II: 39–56%
- Stage III: 36–47%
- Stage IV: 24–32%
Progress of CT scan of the larynx
To conduct a CT scan of the throat and larynx, the patient is asked to take a horizontal position on a sliding table, where he will remain for the duration of the study.
His body is fastened with belts for secure fixation, after which the table slides inside the device. All that is required of the patient during a CT scan of the throat is to remain completely calm and not make any movements. The tomograph scans, resulting in a series of images. As a rule, the entire examination process takes no more than 15-20 minutes.
During the scan, the patient is alone in the room. Medical staff monitors the examination progress through a special window from an adjacent office. The patient is not left for a minute without the supervision of doctors. Both the patient and the doctors have the opportunity to communicate through the use of a microphone, so if there are any changes in well-being, the patient will always be able to inform the staff and not be afraid that he is isolated from the outside world.
The latest generation of tomographs meets all safety requirements, so they do not pose any significant harm to the health of patients. Although CT is based on X-ray radiation, it has a very low intensity and, when compared with a classic X-ray examination, it is quite insignificant.
However, due to the fact that X-rays are used during a CT scan of the larynx, this procedure cannot be called absolutely harmless, and it has certain time restrictions for repeated scanning.
Thus, it is unacceptable for women who are expecting the birth of a baby to undergo a CT scan, regardless of the stage of pregnancy, as well as for patients who have already undergone this type of examination in the recent past.
A CT scan of the throat cannot be performed an unlimited number of times, since the radiation dose cannot be exceeded. And only in exceptional cases, if there is strong evidence for this, specialists can prescribe an additional CT examination.
Stages of the disease
Let's consider the TNM clinical classification. In accordance with it, the symbol N indicates whether there are metastases in the regional lymph nodes (L/N):
- NX – there is not enough data to evaluate regional hospitals;
- N0 – there are no signs of metastasis in regional lymph nodes;
- N1 – metastases are noted in one lymph node located on the affected side, measuring up to 3 cm in the greatest dimension;
- N2 – on the affected side there are metastases in one lymph node up to 6 cm in the greatest dimension, or metastases up to 6 cm in the greatest dimension are present in several lymph nodes on the side of the tumor, or metastases up to 6 cm in the greatest dimension are located in the lymph node at both sides;
- N2a – on the affected side in one lymph node there are metastases up to 6 cm in greatest dimension;
- N2b – on the affected side in several lymph nodes there are metastases up to 6 cm in greatest dimension;
- N2c – metastases up to 6 cm in greatest dimension are located on both sides or opposite the tumor in the lymph node;
- N3 – metastases more than 6 cm in greatest dimension are detected in the lymph node. The left midline is referred to as the nodes on the affected side.
The M symbol indicates whether there are distant metastases:
- MC – there is no data to evaluate distant metastases;
- M0 – no signs of distant metastases were found;
- M1 – distant metastasis is noted.
Classification of tumors according to the T symbol, taking into account localization in the larynx
| Supraglottic region | T1 | The tumor is located only in the supraglottic part, the vocal cords are mobile |
| T2 | The mucosa of several anatomical areas of the ligamentous or supraglottic part or the area outside the supraglottic part (medial wall of the pyriform sinus, mucous membrane of the tongue root, etc.) is affected without fixation of the larynx | |
| T3 | The neoplasm is limited to the larynx with fixation of the vocal cords and/or extended to the posterior part of the laryngeal cartilage, tissue in the preepiglottic region; erosion of the thyroid cartilage is minimal | |
| T4a | The tumor affects the thyroid cartilage and/or has spread to the soft tissues around the larynx: esophagus, neck (external and deep muscles), thyroid gland, ribbon muscles, tongue | |
| Т4b | The neoplasm affects the mediastinum or the lining of the carotid artery, as well as the prevertebral region | |
| Ligamentous department | T1 | The neoplasm is limited to the vocal cords and does not impair their mobility; the posterior and anterior commissures may be involved in the process |
| T1a | The tumor is limited to one vocal cord | |
| Т1b | Both vocal cords are affected | |
| T2 | The pathology affects the sub- and/or supraglottic zones, impairs the mobility of the vocal cords | |
| T3 | Only the larynx is affected with fixation of the vocal cords and/or the tumor grows into the supraglottic region and/or provokes erosion of the thyroid cartilage | |
| T4a | The tumor involves the tissues around the larynx (ribbon muscles, trachea, deep/external muscles of the tongue, neck, esophagus, ribbon muscles) or thyroid cartilage | |
| Т4b | The neoplasm has grown into the mediastinum, prevertebral space or carotid artery sheath | |
| Subglottic region | T1 | The tumor is limited to the subglottic region |
| T2 | The tumor affects one or two vocal cords, mobility is free or limited | |
| T3 | The tumor does not extend beyond the larynx with fixation of the vocal cords | |
| T4a | The neoplasm grows into the thyroid or cricoid cartilage and/or affects the tissues located around the larynx (thyroid gland, neck, including the external/deep muscles of the tongue, trachea, ribbon muscles) | |
| Т4b | The tumor spreads to the prevertebral space, the carotid artery sheath, or the mediastinum |
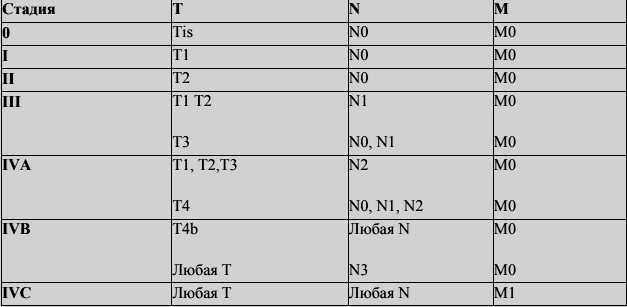
Table of general grouping of the disease by stages
Alternative diagnostic methods
Alternative diagnostic methods include ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. However, CT of the throat has a clear advantage - this method is the most informative and fastest. In addition, it allows you to identify even minor pathological processes and evaluate the structures of internal organs.
If we talk about which type of diagnosis is better: MRI or CT, then it will be quite difficult to answer this question unambiguously. Both research methods serve completely different purposes, although many of the data obtained may be duplicated.
A CT scan of the throat is performed using X-rays, so it allows you to examine dense formations and hollow organs. Magnetic resonance imaging is the best way to identify soft tissue conditions and is widely used to evaluate injuries to the neck and ligaments.
If there is a need to scan patients in an emergency situation, the choice of one or more examination methods is at the discretion of the doctors, based on the nature of the pathological condition.
Where to get a CT scan of the throat and larynx
Regardless of the exact reasons for which the patient was prescribed a CT scan of the throat, a fundamentally important point is to find a suitable clinic. She must not only satisfy the patient with her pricing policy, but also perform the examination at the highest level.
Unfortunately, sometimes it is not so easy to make the right choice: some medical centers do not have modern equipment, and tomography performed on old scanners does not provide a complete picture of the existing pathological process. In other clinics, the medical staff does not have sufficient experience, so there is a high probability of making an incorrect diagnosis.
We are pleased to offer our services to patients: on our website, every visitor can see for free a large list of medical clinics, as well as detailed information on each of them.
After selecting the required medical center, you can call the phone number listed on the website to make a preliminary appointment. We provide a discount on CT scanning to everyone who turns to us for help.
By contacting us for help, you can easily decide on the choice of the necessary medical center from a huge list, and also receive a guarantee of the lowest price.