What is the sugar curve
A glucose tolerance test (abbreviated GTT) is a laboratory test used by endocrinologists to determine the state of glucose tolerance, which is necessary to diagnose diseases such as prediabetes and diabetes. The study determines the patient's blood sugar levels on an empty stomach and after meals and physical activity. The glucose tolerance test is distinguished by the route of administration: oral and intravenous.
When carbohydrates enter the body, the amount of sugar in the blood rises after 10-15 minutes, increasing to 10 mmol/l. With normal pancreatic function, after 2-3 hours, sugar returns to normal - 4.2-5.5 mmol/l. An increase in glucose concentration after 50 years is not considered a normal manifestation of age. At any age, the appearance of such a sign indicates the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus. GTT is used to determine the disease.
How to evaluate the results of the sugar curve?
In a healthy person, blood sugar from a vein on an empty stomach is no higher than 6.1 mmol/l, and 2 hours after a meal or glucose load is 7.8 mmol/l.
If fasting sugar is 7.0 mmol/l and higher, or after 2 hours is higher than 11.0 mmol/l, then diabetes mellitus is diagnosed. If the sugar levels are between normal and diabetic, then this is prediabetes (the diagnosis will sound like impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glycemia).
For pregnant women, the norms are different - on an empty stomach less than 5.1 mmol/l, after 1 hour no higher than 10.0 mmol/l, after 2 hours no higher than 8.5 mmol/l. If blood sugar is higher than normal in at least one measurement, diabetes is diagnosed.
Indications for analysis
A diagnostic research method such as a glycemic curve is necessary to find out the concentration of sugar in the blood at different times and to know the body’s reaction to an additional load of glucose administration. In addition to people who have already been diagnosed with diabetes, GTT is prescribed in the following cases:
- if the patient's weight increases rapidly;
- sugar was detected in the urine;
- high blood pressure is constantly maintained;
- diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome;
- during pregnancy (if urine values, weight gain, and blood pressure are abnormal);
- with genetic predisposition (presence of relatives with diabetes).
Indications for analysis and contraindications for testing
The study of the sugar curve is indicated in the following cases:
- upon initial detection of sugar in the urine;
- people whose close relatives suffer from diabetes;
- if you are overweight;
- patients with hypertension;
- when there are diseases of the endocrine organs - ovaries, thyroid gland, adrenal glands;
- pregnant women with high blood pressure , excessive weight gain, pathology in urine analysis;
- diabetic patients.
GTT is contraindicated in children under 14 years of age, diabetic patients with high fasting sugar levels , pregnant women with already identified gestational diabetes, and any patients during acute illnesses and exacerbations of chronic ones.
Preparing for analysis
The study does not require preliminary special preparation or changes in habitual lifestyle, since exclusion or restriction of high-carbohydrate foods in food can lead to incorrect results. During the three days preceding the test, you should not change your diet; the use of medications must be agreed with your doctor. To ensure the reliability of the research results, it is assumed that you are in a calm state, smoking and physical exertion are prohibited. During menstruation, it is better to reschedule the tests.
Indications for analysis
During pregnancy, it is important for women to undergo all examinations prescribed by a doctor, since not only their own health, but also that of the unborn baby depends on the processes occurring in the body.
The sugar curve is considered one of the mandatory tests. It is important for patients to know why they should take it and in what cases testing is prescribed. There are several indications for analysis:
- abnormalities in urine test results;
- high blood pressure values;
- weight gain;
- suspicion of developing diabetes;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- predisposition to diabetes, inherited;
- development of the gestational form of the disease in a previous pregnancy;
- birth of overweight children;
- maintaining a sedentary lifestyle (as prescribed by a doctor).
The number of such tests prescribed during pregnancy is determined by the doctor. In some cases, it is necessary to donate blood again if the results of a previous test are questionable.
A stress blood test can not be performed on all women, but only on those for whom it is not contraindicated.
List of restrictions:
- cases when the concentration of glucose tested on an empty stomach exceeds 7 mmol/l;
- the patient's age is less than 14 years;
- third trimester of pregnancy;
- inflammatory processes occurring in the body;
- infections;
- pancreatitis (during exacerbation);
- taking certain pharmacological drugs that increase glycemia;
- malignant tumors;
- toxicosis (the test increases attacks of nausea).
A favorable period for performing the analysis is considered to be between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. If the expectant mother has already encountered a similar pathology in previous periods of pregnancy, then testing is recommended earlier (16-18 weeks). The analysis is performed from 28 to 32 weeks in exceptional situations; in a later period, the study is not indicated.
How to take it
The patient donates blood for a sugar curve from a vein or from a finger, depending on the type of sampling, its own standards have been approved. The diagnosis requires repeated blood donation: the first time the blood is taken on an empty stomach, after a 12-hour fast (only water is allowed). After which you need to take glucose dissolved in a glass of water. It is advisable to carry out a glycemic curve test every half hour for two hours after taking a carbohydrate load. However, in practice, one analysis is more often carried out 0.5-2 hours after consuming the glucose solution.
How the analysis is performed
Of course, this study is not a simple one; it requires special preparation and is carried out in several stages. Only in this way can the reliability of the sugar curve be achieved.
Test results should only be interpreted by a doctor or medical consultant. A blood sugar test is studied by taking into account:
- current state of the body
- person's weight
- lifestyle
- age
- presence of concomitant diseases
Diagnosis involves donating blood several times. In some laboratories, blood is taken from a vein, in others - from a finger. Depending on whose blood is being studied, standards will be approved.
The first analysis is carried out on an empty stomach. Before it you need to fast for 12 hours, drinking only clean water. In this case, the fasting period should not exceed 16 hours.
After donating blood, a person takes 75 grams of glucose, which is dissolved in a glass of tea or warm water. It is best if after this the analysis is carried out every half hour for 2 hours. But, usually, laboratories simply do another test 30-120 minutes after consuming glucose.
How to dilute glucose for sugar analysis
The test will require glucose, which you must take with you, since the solution must be prepared immediately before use. To dissolve, you need clean still water. When referring for research, the doctor determines the required concentration of the solution for the procedure. So, for a one-hour test, 50 grams of glucose are taken, for a 2-hour test - 75 grams, for a three-hour test - 100 g. Glucose is diluted in a glass of boiled or still mineral water. It is allowed to add a little lemon juice (citric acid crystals), since not everyone can drink very sweet water on an empty stomach.
- Children's blanket knitted
- Psilocybin mushroom - consequences of use and hallucinogenic properties. How to identify a psilocybin mushroom
- How to draw a family tree: templates and programs
Preparing for the study
It is not recommended to go through the sugar curve without prior preparation. The influence of any factor affecting glycemia leads to an unreliable result.
To avoid such an error, you should go through several stages of preparation:
- For 3 days before testing, do not change your food preferences, continuing to maintain your usual lifestyle.
- Do not use any medications (only after prior agreement with your doctor) so as not to artificially distort the data.
- During the examination, you should be in a calm state and not tense.
- The last meal should be taken 10 or 14 hours before donating blood.
Rules for diluting glucose:
- the solution should be prepared only before the study;
- To dilute glucose, you need to use clean still water;
- the concentration of the solution should be determined by a doctor;
- At the request of the pregnant woman, a small amount of lemon juice is added to the liquid.
The amount of glucose required for analysis depends on the time it is carried out:
- 1 hour – 50 g;
- 2 hours – 75 g;
- 3 hours – 100 g.
Reasons for the increase:
- eating on the eve of testing;
- emotional stress;
- physical fatigue;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- taking medications (diuretics, adrenaline and others).
Reasons for lower results:
- long-term fasting (over 14 hours);
- diseases of the liver and other digestive organs;
- tumors;
- obesity;
- poisoning
For the expectant mother, obtaining the correct results of any analysis is a paramount task, since the successful course of pregnancy and the health of the baby depend on them. Timely detection of the disease allows for faster determination of therapeutic methods and observations.
Interpretation of results
When assessing indicators, factors influencing the result are taken into account, and a diagnosis of diabetes cannot be made based on one test alone. The outcome of the glycemic curve is influenced by the patient’s bed rest, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, the presence of tumors, and infectious diseases that impair the absorption of sugar. The result of the glucose tolerance test significantly depends on the use of psychotropic, diuretic drugs, antidepressants, morphine, also caffeine and adrenaline. Distortion is also possible if strict blood collection instructions are not followed in the laboratory.
Procedure algorithm
The test involves repeated blood sampling, one of which is performed on an empty stomach, and the next - 3 times every hour after taking glucose diluted with water. Some laboratories use the venous method of examination, while others use the capillary method.
The main thing is that the methods do not alternate during the same testing. The intervals between blood draws are also determined by the medical institution (they can be half an hour or 60 minutes).
Based on the data obtained after measuring the sugar concentration, a sugar curve is drawn up. It reflects the presence or absence of impaired glucose tolerance that occurred during gestation.
The disadvantages of this study, according to many patients, are the need to repeatedly puncture the fingers or veins, as well as taking a sweet solution. While the blood sampling procedure is a familiar procedure for many people, not every person can tolerate oral consumption of glucose; this is especially difficult for pregnant women.
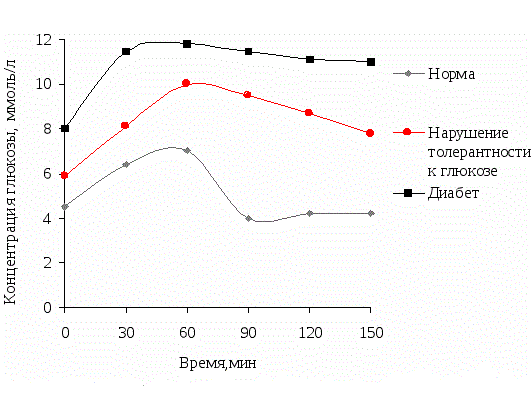
Normal sugar curve
A sugar load is necessary to identify hidden, possible metabolic disorders in the body. The results standards are established depending on the method of sampling - from a vein or from a finger:
| Body condition | Blood concentration, mmol/l | |
| deoxygenated blood | capillary | |
| Normal | up to 6.10 | up to 5.50 |
| Prediabetes | 6,10-7,0 | 5,50-6,0 |
| Impaired glucose tolerance behavior | 7,0-11,1 | 6,0-7,8 |
| Diabetes | > 11,1 | > 7,8 |
| The analysis is not performed if the first sample is taken on an empty stomach (probability of hyperglycemic coma) | 11,1 | 7,8 |
Sugar curve during pregnancy
The body bears a greater burden in pregnant women. At this time, exacerbations of chronic diseases or the emergence of new ones are possible. During the normal course of the process, the female body must produce insulin in quantities greater than in the normal state. Analysis of the sugar curve during pregnancy is carried out several times for greater accuracy. The research norm in this situation is slightly changed.
A glucose tolerance test will help the doctor determine the absence or presence of a problem, taking into account the characteristics of the woman’s body. If, after a sweet solution, the test transcript shows an increased sugar level, a repeat test is required to confirm the diagnosis of gestational diabetes. The disease is confirmed by the following indicators:
- fasting blood >5.3 mmol/l;
- one hour after exercise >10 mmol/l;
- after two hours >8.6 mmol/l.

Indications for analysis
Basically, an analysis of the sugar curve is prescribed during pregnancy. The test should be carried out in healthy people who are prone to developing diabetes or suffering from it. A glucose tolerance test is prescribed for women diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome.
The analysis is carried out during a routine examination of persons at risk. Signs of predisposition to developing diabetes: excess weight, sedentary lifestyle, diagnosed disease in family history, smoking or alcohol abuse.
A referral for analysis is issued by a therapist, gynecologist or endocrinologist.
A sugar curve study is carried out if diabetes is suspected. Symptoms of a developing disease: constant feeling of hunger, thirst, drying out of the oral mucosa, sudden jumps in blood pressure, causeless increase or decrease in body weight.
A referral for a glucose tolerance test is prescribed by a gynecologist, endocrinologist or therapist. You can undergo a self-examination every six months.
Possible deviations
If the test results show problems, it is recommended to donate blood again, observing the conditions very carefully: the day before and on the day of taking the test, avoid stress, physical activity, avoid alcohol, and medications. Treatment is prescribed if a deviation from the norm is noted in both cases. An analysis of pregnant women can be better interpreted by a gynecologist-endocrinologist who knows the characteristics of a pregnant woman’s body. The glucose tolerance test also reveals other diseases; for example, a decrease in the indicator after exercise indicates hypoglycemia.
The results of GTT also indicate the following possible states of the body:
- hyperfunction of the pituitary gland;
- the intensity of the thyroid gland;
- damage to the nervous tissue of the brain;
- disorders of the functioning of the autonomic nervous system;
- infectious and inflammatory processes;
- inflammation (acute, chronic) of the pancreas.