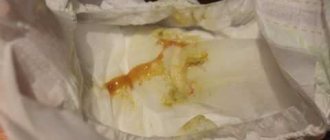
The most important thing that parents should understand about acetone in a child is that it is not a disease, but a natural physiological process associated with metabolism. The body resorts to this option as an alternative way to obtain energy. Acetone in children has nothing to do with bacteria and viruses. An increase in acetone in the urine signals a deficiency of glucose in the body, and therefore the concentration of ketones (products of partial breakdown of fats) in the blood increases.
With the information support of pediatricians at the Amel Dental clinic, we have prepared an article in which we talk about the mechanism of acetone formation in children, its causes and symptoms, and most importantly, how to react correctly, what measures to take to cope with the problem.
What is this substance and why does it increase?
Every day a person eats carbohydrates. After entering the stomach, they are digested and glucose enters the blood. Part of it is needed for energy, and the remaining amount is stored as glycogen in the liver. Here, glucose is stored until the body needs additional energy. This can happen during intense physical activity, during illness, or under severe stress. In this case, glycogen enters the blood and is converted into energy.
Most children have sufficient glycogen reserves, so in stressful situations for the body they are not in danger. Sometimes the liver is able to store only a small portion of glycogen. When glucose stores run out, the liver releases fats into the blood. After their breakdown, energy is produced, as well as ketones. If during this period the child does not receive enough fluid, ketone bodies are not excreted from the body and enter the blood. Due to irritation of the stomach walls with acetone, the patient experiences pain, vomiting, nausea and other negative symptoms.
The difficulty in treating this condition is that vomiting occurs in the baby due to a lack of glucose, and it is impossible to obtain glycogen due to vomiting.
mama-knowet.com
Your child is vomiting, has elevated levels of acetone in the urine, and you don’t know what to do? In this review I will try to clearly describe your actions.
The test is carried out using strips containing a special reagent. Upon contact with urine, which contains acetone, the active part of the strip changes its color depending on the concentration of acetone.

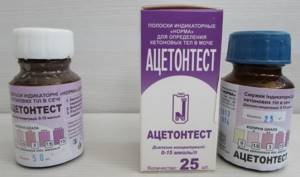
On the test packaging there is a scale with which the resulting test should be compared and the concentration of acetone should be determined by color.

In medical practice, it is customary to measure the acetone content in pluses. On the concentration scale, this corresponds to the following values (mmol/l is millimoles of acetone in 1 liter of urine): + 1.5 mmol/l ++ 3 mmol/l +++ 7.5 mmol/l ++++ 15 mmol/ l
The test is very simple and quick. The indicator strip should be dipped in urine, placed horizontally and waited for 3 minutes, then compared with the scale and determined which color is closest to the obtained one.

From personal experience I can say that tests that are not very late (half a year to be exact) also give the correct result.
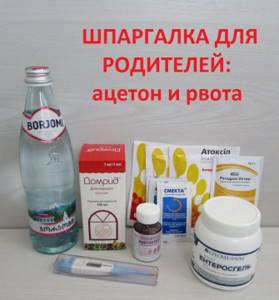
If the test shows the presence of acetone, it is necessary to take appropriate measures to prevent a further increase in its concentration. What to do if a child has acetone and vomits If the levels of acetone in the urine are not high (1-2 pluses), then the child can not be limited in anything, only actively watered, given glucose (in tablets or solution) and not denied sweets. With timely and correctly carried out actions, the increase in acetone in the body will stop and there will be no acetonemic vomiting. If acetone levels are above 3 pluses, and even more so if vomiting is involved, measures should be more drastic. Why does vomiting occur? Acetone accumulates in the blood, irritates the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract and the vomiting center in the brain. Acetonomia syndrome may also be accompanied by abdominal pain. Vomiting can be so severe that it is not possible to give the child water. Then it is necessary to use antiemetics. At home it can be Domrid in the form of syrup.

It is a suspension that tastes quite pleasant. Before use, the bottle must be shaken well.
The dose of the drug for a child weighing less than 35 kg is 0.25 ml of suspension per 1 kg of body. For example, if a child weighs 20 kg, then he should be given 0.25 x 20 = 5 ml of suspension. The packaging is equipped with a special measuring spoon, which has divisions of 2.5 ml and 5 ml. If you need a smaller dose, you can use a regular syringe without a needle.
The photo can be enlarged by clicking the mouse.

I advise you to carefully read the instructions before taking it , the drug is not simple. I can tell you from personal experience that half the age-appropriate dose was enough for us to stop vomiting. After taking the drug, you should wait 30 minutes and only then start drinking, otherwise vomiting may resume.
The maximum daily dose of the drug should not exceed 0.75 ml per kg of body weight, i.e. in our case, with a weight of 20 kg, the drug can be drunk no more than 3 times a day, 5 ml: 0.75x20 = 15 ml If you cannot stop vomiting yourself, you will have to seek medical help. In such cases, the child is given an intramuscular injection of an antiemetic drug, after which, while the medicine is working, they try to give him something to drink or resort to the help of a hospital, where fluid is administered intravenously (a dropper with glucose and other drugs). Doctors often use cerucal as an antiemetic, although not all doctors approve of it (I’m writing for myself - a child needs half a standard ampoule. From the instructions: “The drug is administered intramuscularly or intravenously slowly. Adults and adolescents are usually prescribed at a dose of 10 mg (2 ml drug) 3-4 times a day. Children over 3 years of age are usually prescribed at the rate of 0.1 mg/kg body weight, if necessary, the dose is increased to 0.5 mg/kg body weight." An analogue of cerucal is metoclopramide.
Attention! Do not use antiemetic drugs without a doctor's prescription. To reduce acetone, complex therapy is used, which includes:
- glucose preparations;
- sorbents;
- electrolytes;
- hepatoprotectors (or without their use);
- other drugs based on symptoms.
In this case, the so-called drinking : the child is given solutions of the above-mentioned drugs in small doses (usually 1 teaspoon) at short intervals. Soldering solutions should be at room temperature. Let's consider the listed groups of drugs in turn. Glucose preparations
Glucose preparations prevent the buildup of acetone in the body. For drinking, you can use pharmacy glucose (in powder, tablets, ampoules or bottles).

The pharmaceutical preparation of glucose has the following concentrations (in descending order):
- 100% powder;
- less than 100% in tablets - 1 tablet contains 1 g of glucose monohydrate; (excipients so that a tablet can be formed: potato starch, talc, calcium stearate, stearic acid);
- 40% I am in ampoules;
- 5% or 10% in bottles.
The indicated concentration of 40% means that 100 g of solution contains 40 g of glucose. One teaspoon holds approximately 2.5-3 ml of liquid. Since 1 ml of 40% solution contains 0.4 g of glucose, then in a teaspoon of glucose solution there will be 0.4x(2.5-3) = 1-1.2 g. Thus, 1 teaspoon of 40% solution is equivalent to 1 tablet. From glucose powder you can prepare a solution of the desired concentration, for example 40%: dissolve 40 g of powder in 100 ml of drinking water. Give a teaspoon of glucose approximately every 5 minutes. It is not advisable to give large volumes so as not to provoke vomiting. It should be taken into account that the absorption of liquid in acetonemic syndrome is worse than in a healthy child and the drunk liquid can accumulate in the stomach and then be poured out in full during vomiting.
If the levels of acetone in the urine are high enough, then it is better to drink with a more concentrated solution, 40%. When reducing acetone, solutions of lower concentrations can be used. Please note that the child does not like the taste of a very sweet 40% glucose solution; it is cloying and can also cause vomiting. For drinking, you can use sweet uzvar (dried apples are best) and raisin decoction. From the experience of many parents, Coca-Cola (without gas) gives good results, but it can be recommended for older children (not for children under one year old, I would say not even up to 3 years old)
Sorbents
The appearance of acetone leads to intoxication of the body, to reduce which sorbents are used. Some sorbents work only in the stomach (activated carbon, white carbon, etc.), and some remain active until they enter the intestines (enterosorbents). For acetonemic syndrome, both coals and enterosorbents can be used, but the latter are more effective.
The most commonly used are atoxil and enterosgel, as well as smecta. It is easier for children to drink atoxil, it is more finely dispersed and less likely to provoke the gag reflex. Atoxyl is silicon dioxide with a high specific surface area, due to which it has the ability to “cling” to its structure, similar to a washcloth, various substances.

Enterosgel is more difficult for a child to drink, especially if it contains denser gel aggregates (depending on the form of the drug, it can be gel, powder, paste, and the manufacturer). Sometimes the structure of the enterosleg is homogeneous, such a drug is easier to take. There is a gel-like paste on sale, it comes in tubes. It seems to me that this is the best version of this drug.
Smecta is a sorbent of natural origin. The solution tastes quite pleasant. It is often used as a sorbent in pediatric practice.

There are quite a large number of sorbents. They have different points of maximum application and their effectiveness is also different. Also, the choice of sorbent depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. More detailed information about sorbents is the subject of another review.
Electrolytes
To quickly relieve acetone syndrome, you should ensure that the body receives fluids and mineral salts. For this purpose, when soldering, electrolytes are used, which contain physiologically necessary salts (electrolyte) and water. This will prevent dehydration and will help eliminate acetone and other toxins.
You can use Regidron or Humana Electrolyte as an electrolyte. They have approximately the same composition. Humana is more palatable.

Both drugs contain glucose, but in a much smaller amount (for example, 1 ml of Regidron solution contains 0.0135 g of glucose) than is needed for severe acetonemic syndrome, therefore additional glucose must be added. Solutions of electrolytes used for this purpose are also called alkaline drinks, since they have an alkaline reaction due to the presence of sodium citrate (a salt of a weak acid and a strong base, therefore it gives an alkaline reaction when dissolved)

For drinking, you can also use Borjomi mineral water, from which the gas has been removed by long-term settling. If you do not have a purchased electrolyte, you can prepare it yourself: to do this, dissolve 1 teaspoon of salt (NaCl) and 1 teaspoon of baking soda (NaHCO3) in 1 liter of drinking water. This recipe was recommended by Komarovsky. Hepatoprotective drugs
These drugs help remove end products of protein breakdown from the body, and also enhance the detoxification function of the liver.
Most often, with elevated acetone, the drugs used are Betargin, our analogue Hepargin, and also Citrarginine.

This is how the Betargin ampoule looks original. The drug is expensive, but at the pharmacy you can buy it individually, one ampoule at a time.

To pour out the contents of the ampoule, it must be broken off at both ends. To use, dilute the contents of the ampoule in a glass of water and drink 1 teaspoon at a time. I will provide links to drugs of the same pharmacological group. If it is not possible to buy the drugs listed above, then you can use an existing drug from this list. https://www.medcentre24.ru/betargin-analogi https://www.medcentre.com.ua/betargin-analogi https://medbrowse.com.ua/citrarginin-analogi
Other drugs
Among the drugs that are effective and often used for acetonemia, the following can be listed:
Nicotinamide is a vitamin whose effects include regulating glucose metabolism. It comes in tablets and ampoules. Take a dose of 5 mg per 1 kg of weight 3 times a day; 1 ml of 5% solution contains 50 mg of the substance.
You can add ascorbic acid with glucose (white vitamins). In hospitals, cocarboxylase is almost always administered intramuscularly, but you can drink it at home.
To improve digestion and reduce the load on the pancreas, doctors often recommend taking enzymes: Pancreatin, Creon, Mezim, Festal, Enzisital, Somilaza, Panzinorm, Nigedaza, Oraza, etc.
They can be included in the treatment regimen immediately, or they can be added during the recovery period, when the acetone crisis has passed. Personally, I do not use them during acetone surges, so as not to increase the drug load on the body during this period.
The recovery regimen often includes probiotics and enzymes, for example, enterozermina, symbiter, etc. There will be more detailed information about enzymes, probiotics and enzymes in another review.
Let me give you a drinking regimen as an example:
This regimen includes drugs whose action is aimed at stopping the release of acetone, its sorption and excretion. Most often, this is the regimen I use to treat my children. 1. Glucose ampoule, 40%. Drink 1 teaspoon every 5-10 minutes. Then use lower concentrations of glucose. It is better to take glucose with water (a teaspoon) so as not to provoke vomiting.
2. Dilute a packet of Regidron powder in 0.5 liters of drinking water (boiled and cooled to room temperature). Drink 1 teaspoon every 3-5 minutes

3. Dilute Atoxil in 100-150 ml of drinking water (boiled and cooled to room temperature). Drink 1 teaspoon every 15 minutes.

4. Drink 1 teaspoon of Uzvar every 5 minutes. If the child does not like the taste of electrolyte or Atoxil, then you can try to drink it with uzvar. Uzvar has a diuretic effect, which is very useful in this case; acetone will be excreted faster. It is best to use homemade dried fruits without additives.

It is very important to drink in small portions so as not to provoke another vomiting in the child. Even if the child asks for a drink and is ready to drink a lot, it is better not to do this, since a new attack of vomiting can worsen the situation. Drinking should be carried out as long as there are elevated acetone levels and vomiting, even when the child is sleeping. If you can’t drink from a teaspoon, for these purposes it is convenient to use any dosage syringe with measured divisions in ml from another medicine or a regular injection syringe (without a needle).
It should be noted that glucose works faster than an alkaline drink, so this is the first thing to do.
Additional measures should include a cleansing enema. Most often it is made with an alkaline solution. An alkaline environment (both drinking and enema) promotes the breakdown and elimination of acetone.
If vomiting continues for less than a day, then significant dehydration has not yet occurred and, following simple rules, the child can be quickly removed from this situation. In case of severe dehydration of the body with prolonged vomiting, diarrhea and large readings of acetone in the urine, more radical measures should be taken - it is better to go to the inpatient department and carry out deintoxication under the supervision of a doctor. Intravenous drip administration of drugs reduces acetone faster than orally taken drugs.
Children outgrow the tendency to acetonemia by about 7-10 years of age. But if acetone appears in a child over 7 years old, this is a reason for a serious examination. It is necessary to take a blood sugar test from a finger prick, as well as a urine test for sugar. Glucose deficiency and, accordingly, the appearance of acetone is one of the symptoms of diabetes mellitus. But with this disease, the problem is not that there is not enough glucose, but that it is not absorbed. Hence the completely different treatment methods.
Diet and prevention measures
Which foods can be eaten and which cannot be eaten, follows from the very definition of the source of acetone. Namely, it is necessary to exclude all products that contain animal fats, including broths and dairy products (with the exception of low-fat). You should also exclude foods that irritate the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines, so as not to provoke or aggravate vomiting. In this case, it is good to follow diet No. 5.
There is no need to completely deny your child sweets (except for chocolate and sweets that include animal fats), in this case such products are necessary, but do not overdo it, find the optimal middle ground and look at the child’s condition. It is good to replace sugar (sucrose) with fructose. It is wise to include baked apples in your diet; they contain pectin, which is a good sorbent and acts like, for example, atoxyl.
During times of high acetone and vomiting, a stricter diet should be followed. In the first days of a crisis, people often refuse food completely. As your condition improves, you need to maintain a diet for a certain time to allow the body to recover. Nutrition must be introduced very carefully, it should be in small portions and often. To support the pancreas, you can take enzymes.
When choosing which products are allowed and which are not, one must also take into account the presence of allergic reactions. After all, they can also cause an increase in acetone.
Full recovery from acetone syndrome occurs differently for everyone: it can take a week, maybe three, and sometimes much more. It all depends on the severity of the course, the state of the body, the specifics of metabolic processes, concomitant diseases, etc. The longer the child is kept on the correct diet after acetonemic syndrome, the less likely it is to return.
As an example, I will show one of the cases of an acetonemic crisis in my child - in test indicators. The above-described scheme was used for treatment.
The acetone rose sharply in the evening or at night, the moment of onset was missed, and at night there was severe vomiting with a large amount of liquid. There was no temperature. The test strip showed acetone over 4 plus (significantly darker than the last value on the color scale).

To stop vomiting, Domrid was used (one-time use). With constant desoldering according to the above scheme, by the evening of the first day the acetone practically did not decrease. In the evening the vomiting repeated. A half dose of Domrid was given and feeding continued.
At night, acetone began to decrease (3 pluses), this happened after about a day of active desoldering.

After a couple of hours it dropped to 2 pluses. There was no more vomiting. The child fell asleep.

In the morning there was a slight increase in the concentration of acetone. This always happens, since morning urine is more concentrated if the child did not go to the toilet at night.
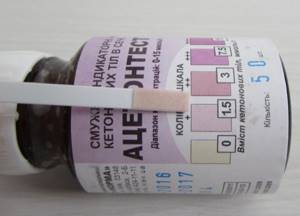
There was no acetone in the urine the entire next day and beyond.
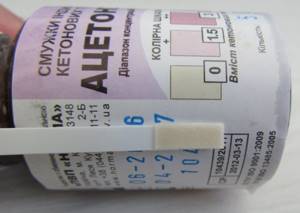
In our case, the increase in acetone was most likely provoked by the currently active intestinal flu virus (rotavirus). I hope that in the current unfavorable epidemiological situation, my review will be useful to parents, so I hastened to publish it.
Finally, I would like to thank Dr. Komarovskiy for the clarifications and recommendations, they were very useful to me https://video.komarovskiy.net/aceton-06-03-2011.html Thank you for your attention! Good health to everyone!
Reasons for rejection
Experts say that proper nutrition is the key to human health and well-being. Due to the fact that the digestive system of babies is not yet fully formed, children need to be fed only with the right and healthy foods. In a healthy body, ketone bodies are formed in small quantities. That is, if a child consumes carbohydrates within normal limits, then ketone will be released within acceptable limits.

When there is a nutritional disorder, there is often an imbalance. In addition, doctors identify the following reasons for the appearance of acetone in the blood and urine:
- Eating foods that are too high in calories (fatty, fried, sweet). An attack of increased levels of this substance in children can develop after a malnutrition, since the baby’s liver does not process fats well.
- Insufficient amount of carbohydrates in the diet. Like their excess, carbohydrate deficiency leads to a deterioration in metabolic processes. Against this background, metabolism is disrupted and fat oxidation and ketone production occur.
- Consuming ketogenic amino acids.
- Infectious diseases that cause symptoms such as diarrhea and vomiting. Such conditions lead to nutritional starvation, which causes the appearance of acetone in the blood.
- Diseases of a congenital or acquired nature associated with a deficiency of enzymes necessary for normal metabolic processes in the body.
- Diabetes mellitus of both types and neuro-arthritic diathesis.
Many parents, upon hearing about an increase in ketone bodies in their child’s blood, panic, but this should not be done. Having discovered this condition, it is important to look for its cause. Sometimes a regular diet helps to cope with the problem.
Recommendations from Amel Dental pediatricians
Parents should understand that if a child has ever had elevated acetone, then there is a possibility of a relapse. In this case you need to be prepared:
- always have sweets on hand in case of another crisis;
- have a glucometer and test strips in your first aid kit;
- Have glucose ampoules in your medicine cabinet.
Increased acetone in children (from infants to 11-12 years old) is considered the norm, associated with the age-related physiological characteristics of the child’s body.
The older the child, the lower the risk of a critical increase in acetone. Knowing the reasons and mechanism for the appearance of acetone, you can take preventive measures:
- provide the baby with a complete, balanced diet, and, if necessary, adhere to the diet recommended by the doctor;
- control the level of stress in the child (training, physical activity) - they must correspond to the age and capabilities of the child;
- avoid emotional, physical, mental overload, protect the child from stress;
- temper and strengthen the baby’s nervous system.
How much acetone is normal?
Normally, in children, the content of this component in the urine should be 0 mmol/l. If we take the entire volume of daily urine as a basis, then the content of this substance is allowed to be no more than 0.01 to 0.03 g. It is excreted from the body through urine and lungs. To check this indicator, the child needs to be tested, or parents can determine the presence or absence of acetone using a special test strip. It can be used to measure the level of harmful substances in the urine. For diagnosis, a special scale is used, with which you can determine traces of ketone bodies.

It is important to use a sterile container during testing. The study is usually carried out in the morning. If these recommendations are not followed, the indicators may be distorted.
Interpretation of results
Normally, the concentration of ketone bodies in urine should not exceed 1 mmol/liter. Modern laboratory analyzers do not determine specific numbers, but the presence of ketones. It is rated with a “+” sign and ranges from “+” to “++++”.
Norm
Acetone is normally always present in an insignificant amount, which is not detected. In this case, the research form will contain the inscription “denial” or “negative”.
Sometimes, after small errors in the diet, ketone bodies are determined to be “+” or “trace”, which means trace amounts. In most cases, this is also a normal variant that does not require any treatment. The exception is diabetes mellitus.
Deviations from the norm
If the analysis reveals acetone in quantities of “++” or more, then this is already a manifestation of trouble in the body. A doctor's consultation is required, possibly further examination and treatment adjustment. A result of “++++” in most cases will require hospitalization of the child.
What does an increase in this indicator in a child’s urine mean?
Many parents are interested in what acetone in urine means and what does this condition mean? Let's find out what diseases can provoke a disorder in which this indicator rises. Provoking factors include:
- Poor nutrition and lifestyle in general (insufficient sleep, low mobility).
- Diabetes mellitus of both types.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the body's immune defense.
- Endocrine pathologies.
- Kidney and liver diseases.
- Overeating or, conversely, undereating.
- Insufficient fluid intake.
- Intense physical activity.
- Frequent stress.
- Deficiency of vitamins and minerals.
- Transmission of infectious diseases.
In addition to the above, diseases such as oncology, congenital malformations of internal organs, diseases associated with the digestive system, injuries to internal organs, and more can provoke an increase in ketone bodies in the body.
The concentration of a harmful substance is determined by crosses or pluses. For example, three crosses or pluses indicate that the level of the dangerous component is quite high. One plus is the low amount of substance.
Recommendations when preparing for analysis
Of course, if the baby’s condition is serious, or complications of diabetes need to be excluded, then there can be no talk of any preparation. In other cases, for the reliability of the analysis, it does not hurt to follow some rules for collecting urine.
Diet and medications
Since the source of acetone is fats, 3-4 days before collecting the analysis, foods rich in fats, containing flavors, preservatives, and artificial colors are excluded from the child’s diet. It is recommended to comply with drinking regulations and avoid dehydration.
Parents should be aware that while taking certain antibacterial and other drugs in the form of syrups that contain flavorings and dyes, it is also possible to increase the level of acetone in the urine. In adults, a false positive result may occur while taking medications against Parkinson's disease.
Hygiene
Before collecting urine, rinse the child's external genitalia with warm water. You can use baby hygiene products with a neutral pH. Otherwise, it may be unreliable due to the entry of elements from the skin and genital tract.
How to collect urine correctly and is it possible to store urine for a long time?
To collect urine, it is better to use sterile containers, which are sold in pharmacies. If non-pharmaceutical containers are used, they should be washed well in running water and boiled together with the lid. Urinary bags have been developed for infants. They are also sterile and adhere to the skin, allowing mom and dad not to wait and the baby not to experience discomfort during the collection procedure.
It is unacceptable to pour urine from pots, plates, etc. In this case, the analysis will most likely be unreliable.
For children who control the process of urination, for a more reliable result, it is better to take a middle portion of urine for analysis, that is, skip the first streams.
The collected urine test must be delivered to the laboratory within 1.5-2 hours. Otherwise, decomposition processes begin. The analysis will be unreliable. In modern laboratories you can purchase special containers with a preservative. In such cases, the test can be delivered within a day.
The first signs of increased acetone in children
In most cases, an increase in ketone bodies in children is first detected at approximately the age of 3-4 years. Less common in children 1-2 years old or after 5, 6, 7, 8 years. By the age of 13-15 years, if the cause has not been eliminated, attacks may become more frequent. The most common sign of the pathological condition is vomiting. It can last quite a long time, from 2 to 5-7 days. The baby refuses to drink and eat; attempts to feed the baby cause him to vomit. With a prolonged illness, the patient may experience the following symptoms:
- Enlarged liver.
- Tachycardia.
- Weakening of heart sounds.
- Arrhythmia.
In addition, there is a decrease in blood glucose levels, an acceleration of erythrocyte sedimentation rate and an increase in leukocytes. With proper treatment, complete restoration of the body's activity occurs in approximately 7-14 days.

How else does the disorder manifest itself? During the next attack, the child may experience the following symptoms:
- Nausea.
- Repeated vomiting (sometimes without it).
- Protein in urine.
- Plaque formation on the tongue.
- Pain in the abdominal area.
- Weakness, apathy.
- Dry dermis.
- The stool smells like acetone.
- Temperature increase.
- Odor from mouth and nose. Many parents note that their breath smells like baked apples.
- Decreased amount of urination or complete absence of urine.
Often, ketone bodies have a negative effect on the brain, which leads to weakness and loss of consciousness. In this case, the patient must be urgently taken to a medical facility, since staying at home is quite dangerous. If an attack occurs for the first time, the doctor prescribes the necessary tests to find out the cause of this condition. If a patient experiences several attacks of acetone vomiting over the course of a year, the child is diagnosed with acetone syndrome.
Features of treatment of the disease
Like many other disorders in the body, acetonomia syndrome should be treated in a timely manner. This applies to newborns, infants, as well as older children, for example, a one-year-old or four-year-old baby. An acetone crisis is dangerous at any age. More often, therapy consists of such simple measures as following a diet, drinking plenty of fluids, gastric lavage, and taking sorbents.

With moderate severity of the condition, if the acetone rises slightly, you can reduce it at home. If the child refuses to eat and drink, weakness and loss of consciousness are noted, therapy should be carried out in a hospital setting under close medical supervision.
How to remove acetone at home?
In infants and older children, a pathological condition can develop due to vomiting, for example, due to poisoning, intestinal infection, colds, ARVI, or rotavirus. You can understand that ketone bodies have increased in the body by symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and the smell of baked apples on the breath. In severe cases, breathing becomes intermittent, the heart rhythm is disturbed, and the patient loses consciousness.
If parents discover such signs, they should not waste a minute, since excess acetone, even in small quantities, poses a serious danger to the baby. Despite this, the patient does not always need hospital treatment. Sometimes therapy can be done at home.
Gastric lavage
If the baby has increased acetone, intestinal lavage should be performed. For this, a regular enema is used. This will help reduce the concentration of ketone bodies in the body and normalize the condition. To perform an enema, boiled warm water and ordinary soda are used.

Enema proportions with soda:
- Take 1 teaspoon of baking soda per glass of warm water and mix the solution thoroughly.
- For babies under one year of age, 50-150 ml of solution is administered using a syringe.
- Children from 12 months to 9 years are administered 200-500 ml of solution.
- Patients over 10 years of age are given 500 ml of liquid.
The procedure should be performed until clean water begins to come out of the intestines. Infants from birth and adults can remove acetone in this way.
Drink plenty of fluids
Drinking plenty of fluids will help quickly remove harmful substances from the body. The patient should drink an alkaline drink. To do this, you should use mineral water, Regidron or a solution of salt and sugar prepared independently. After the vomiting stops, the patient can be offered a sweet compote. This will help the baby recover faster.
What should not be given during an attack? It is forbidden to give your child drinks such as soda, Coca-Cola and other sweet carbonated drinks.
Ready solutions
In case of acetone syndrome that has developed due to rotavirus, poisoning or other diseases, it is very important to stop vomiting and prevent dehydration. To do this, you need to give the baby plenty of liquid. This will help prevent dehydration and dangerous complications associated with it. To do this, you can feed your baby breast milk, regular or mineral water, or you can use ready-made solutions that are sold in pharmacies.
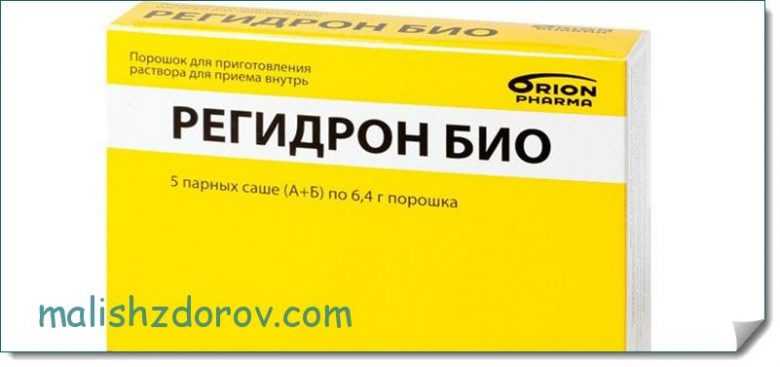
These include Betargin and Regidron. They contain the selected content of salts and minerals necessary for a person to prevent dehydration. Before starting to use the drugs, parents should carefully study the instructions for use. The dosage should be selected by the doctor depending on the weight, age of the patient and the characteristics of the course of the disease.
Nutritional Features
Proper nutrition helps remove acetone. If during an attack the baby refuses to eat and constantly vomits, you cannot force it. It is enough to give the patient plenty of water. As a rule, appetite appears after the condition has stabilized.

If the attack has not happened for the first time, the diet must be followed on an ongoing basis. In the table we look at healthy and unhealthy foods that can be used in your diet on a daily basis.
| Recommended dishes | Prohibited Products |
| Rice, oatmeal, buckwheat, corn, wheat porridge cooked in water. | Pasta and cereals with plenty of butter. |
| Vegetable soups, steamed vegetables. | Fatty meats and fish. |
| Dietary meats (rabbit, chicken, beef, turkey), prepared by boiling, stewing or steaming. | Sausages, cheeses, cottage cheese and sour cream with a high percentage of fat. |
| Biscuits, dry biscuits, dried fruits (raisins, dried apricots). | Rich soups with meat. |
| Non-acidic raw vegetables and fruits (banana, apples, cucumbers, carrots). | Mushrooms, sauces, marinades, preservation. |
| Herbal teas, compotes, mineral water. | Sour vegetables and fruits (tomatoes, tangerines, oranges). |
| Steam omelettes, cottage cheese casseroles. | Strong tea, coffee, sweet carbonated drinks. |
| Low-fat dairy and fermented milk products. | Nuts, chips, hot dogs, hamburgers, pizza and other fast food. |
Reviews from parents and doctors indicate that the right menu helps to quickly cure the pathological condition and prevent serious consequences. To create a daily menu, you should use only high-quality products and healthy recipes.
Recipes for children with metabolic disorders
Food for a baby should not only be healthy, but also tasty. We offer you to consider several recipes that will certainly please your child.
Oatmeal with dried fruits and milk
To prepare this dish you will need the following products:
- Milk – 1 glass.
- Oatmeal – 0.5 cups.
- Sugar – 1 tablespoon.
- Raisins – 1 tablespoon.
- Dried apricots – 1 tablespoon.
- Walnuts – 3 pcs.

The dish is very simple to prepare. To do this, you need to boil the milk and pour cereal and sugar into it. After boiling, simmer the porridge over low heat for 2-3 minutes. Pour boiling water over dried fruits and chop. The finished dish is decorated with nuts, raisins and dried apricots. Serve warm or cool.
Pumpkin fritters
Pumpkin is rich in vitamins and minerals that have a beneficial effect on the digestive system and the entire body as a whole. To make pancakes you will need the following products:
- Fresh pumpkin – 300 g.
- Sugar – 2 tablespoons.
- Egg – 1 pc.
- Flour - a tablespoon.

Peel the pumpkin, wash it well, pass through a meat grinder or grate it on a fine grater. Add sugar, flour and egg to the resulting product, knead thoroughly. It is better to fry pancakes in butter. You can add sour cream before serving.
Salmon fish soup
You can pamper your baby with healthy salmon soup. To prepare it you will need the following products:
- Salmon – 150 g.
- Potatoes – 3 pcs.
- Carrots – 1 pc.
- Onion – 1 pc.
- Butter – 20 g.
- Greenery.

To prepare the dish, you need to peel the potatoes and place them in boiling water. After 15 minutes, add carrots, onions and salmon. Five minutes before readiness, add oil and herbs. Serve the soup warm. If desired, you can add sour cream.
Apple and Pumpkin Casserole
Most kids are delighted with various casseroles. An excellent option would be a dish of pumpkin and apples. To prepare it you will need the following products:
- Apples – 2 pcs.
- Pumpkin – 200 g.
- Milk – 0.5 cups.
- Sugar – 2 tablespoons.
- Egg – 2 pcs.
- Flour – 1 tablespoon.
- Sunflower oil for greasing the baking sheet.

Peel the apples and pumpkin and grate them on a fine grater. Place the resulting mass on a baking sheet greased with sunflower oil. In a separate bowl, combine milk, egg, flour and sugar, mix the products thoroughly. Pour this mixture over the pumpkin and apples and place in the oven to bake for 20-25 minutes at 180°C.
Diet
An important component of effective therapy for acetone in children is the correct diet. Basic principles of nutrition with increased acetone:
- 1
The first day you cannot feed the baby. - 2
From the 2nd day, provided that the attacks of vomiting have decreased, you can give the child liquid rice or buckwheat porridge, white bread croutons, lean vegetable soups, baked apple, banana. Meals are fractional - often, in small portions.
- 3
After a week, you can give your baby boiled eggs, turkey meat, heat-treated fruits and vegetables (boiled, steamed), porridge from various cereals, and fermented milk products.
Products that should be strictly excluded from the diet:
- any meat except turkey meat;
- broths;
- some vegetables (tomatoes, cabbage);
- legumes;
- kiwi;
- any sausages, smoked meats;
- marinades, dishes with added spices.
You need to follow the diet for at least 2-3 weeks.
Drug therapy
So, we found out where ketone bodies come from. It's time to find out what medications are used in medical practice to normalize metabolic processes in the body. For children suffering from increased acetone, the doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Korilip suppositories are a metabolic product based on vitamins and coenzymes.
- Stimol is a medicine that has a positive effect on the human digestive system.
- Cocarboxylase - the medicine has a coenzyme effect and normalizes carbohydrate metabolism.
- Dimephosphone is an anti-acidemic medication that restores water-alkaline balance.
- Polysorb and Enterosgel are sorbents that help remove harmful substances from the body.
Any medications should be used in children only as prescribed by a doctor. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. This can lead to serious consequences.
An increase in acetone is a rather dangerous condition. His treatment with medications and folk remedies must be carried out under strict medical supervision.
Prevention
Is it possible to prevent surges in the growth of ketone bodies in the body? Discussion of this issue today is quite relevant in many forms among parents. Most experts believe that to avoid relapse, the following preventive measures should be observed:
- Proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle.
- Avoiding large amounts of high-carbohydrate foods.
- Regular exercise and sufficient physical activity.
- Frequent walks in the fresh air.
- Taking vitamins.
- Hardening the child.
- Adequate and quality rest and sleep.
- Minimizing stressful situations.
- Timely treatment of infectious and other diseases.
- Refusal to self-medicate at home.
This memo for parents will be useful for mothers and fathers of children who have already been diagnosed with acetone syndrome, as well as for the prevention of primary cases of the disease.

A healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition are the key to excellent health for children. Don't neglect this rule.