The use of magnetic resonance imaging is one of the most accurate methods for diagnosing human kidney diseases. This technique helps not only to identify pathology, but also to understand at what stage it is.
The examination will provide the attending physician with the maximum information necessary for making a diagnosis and subsequent successful treatment.
In this article we will talk about how MRI of the kidneys is done, when and who should be contacted for this diagnostic option. We will also touch upon the issue of preparation for the procedure and the main contraindications.
What does a kidney MRI show?
The kidneys are a paired organ of the urinary system. Located on both sides of the spinal column at the border of the lumbar and thoracic regions.
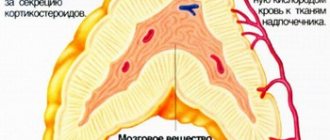
Each kidney is surrounded by fatty tissue and a fibrous capsule. The parenchyma (kidney tissue) is divided into the cortex (outer part) and the medulla (inner part). Inside the parenchyma there are cavities - cups and pelvis.
The organ has a bean-shaped shape, on the concave part there is an area where the ureter, renal vein, lymphatic vessels exit, and the renal artery and nerves (renal sinus) enter.
Kidney structure (frontal section)
MRI visualizes all these structures. The images in the transverse and frontal planes clearly differentiate the division of the parenchyma into the cortex (hyperintense signal) and the medulla (hypointense signal). The renal vessels, pyelocaliceal system and ureters are clearly visible.
Magnetic resonance imaging can also reveal:
- presence of stones;
- neoplasms and their structure;
- anatomical features and developmental anomalies;
- deviations in the condition of blood vessels;
- presence or absence of metastases.
LDC "Kutuzovsky": they trust us
- In our clinic, magnetic resonance imaging is performed using powerful equipment that shows the condition of the kidney with high accuracy. We perform highly targeted examinations - the doctor sets the minimum thickness of the sections in order to thoroughly examine the organ. The equipment is safe for the patient - there is no radiation.
- We employ qualified specialists with extensive experience who provide highly informative opinions. Images with MRI results allow the attending physician to make a decision on further treatment, including surgical operations. You can also get an extended consultation with a doctor on the same day of your visit.
- With a high level of service and the use of the latest equipment, we have an affordable MRI price. We guarantee a professional approach and a high level of service. We invite you to read reviews from our clients who have undergone the procedure.
- LDC "Kutuzovsky" has a convenient location, located at: Moscow, st. Davydkovskaya, 5. Detailed information on how to get to the clinic is provided on the website.
To find out how much a kidney MRI costs and to make an appointment, we suggest calling our managers. You can also fill out the feedback form and we will call you back as soon as possible.
How to do a kidney MRI
During the scan, the patient lies on a table located inside a magnetic tunnel. To obtain high-quality images, you must remain motionless throughout the entire session, which lasts about 30-40 minutes (up to 60 minutes when using contrast). The doctor, who is at this moment in the next office, can give commands to hold your breath via two-way communication. The tomograph creates noise and clicks during operation, so the staff suggests using headphones with pleasant music for better relaxation.
After the procedure is completed, the doctor prepares a description of the images within 15 minutes; they can be obtained in any convenient format.
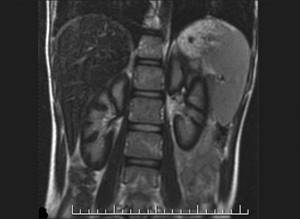
MRI of the kidneys is normal (in T2 mode)
Preparing for the study
Preparation for an MRI study of the kidneys does not imply any serious restrictions. 2 – 3 hours before the scan you must refrain from eating food, water, or medications. It is worth remembering that during the examination the presence of any metal jewelry, hairpins, watches, or glasses on the body is prohibited. Other contraindications to the study:
- presence of a pacemaker in the body;
- fixed dental, orthopedic prostheses, hearing aids;
- vascular clips;
- pins, spokes, fixing bolts, etc.
It is not recommended to apply decorative cosmetics that may contain metal microparticles. You must leave your mobile phone, any electronic gadgets, removable dentures, and hearing aids outside the doors of the diagnostic room.
If the patient suffers from claustrophobia and is terrified of closed spaces, on the eve of the study you can take light sedatives, such as Novo-Passit, tincture of valerian, etc. More serious drugs can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor.
This completes the preparation for MRI of the kidneys without contrast. If contrast enhancement is expected, an allergy test is performed immediately before the procedure, which will help assess the body’s reaction to the injected substance.
MRI examinations (general preparation rules)
Indications and contraindications for MRI of the kidneys
Clinical symptoms of kidney pathology for which magnetic resonance scanning is prescribed:
- recurring pain in the abdomen and lower back;
- stone formation;
- urinary incontinence;
- urinary disturbance;
- hematuria (blood in the urine);
- dilation of the veins of the scrotum in adulthood;
- persistent increase in blood pressure.
MRI diagnostics are indicated both during the initial examination and to clarify the diagnosis made on the basis of other research methods, especially in doubtful cases.
Magnetic resonance scanning is justified for the following pathologies:
- infectious and inflammatory processes (pyelonephritis, abscesses and phlegmon of perinephric tissue);
- urolithiasis disease;
- hydronephrosis;
- developmental anomalies;
- benign neoplasms;
- malignant tumors and metastases.
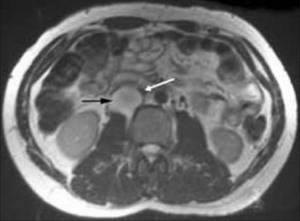
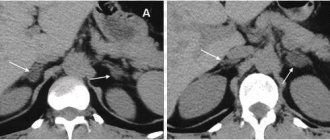
Magnetic resonance imaging shows a tumor located between the right kidney and the inferior vena cava (black arrow) that is compressing the overlying inferior vena cava (white arrow)
Hydronephrosis
This is a progressive expansion of the renal collecting system as a result of impaired urine outflow. May be congenital or acquired.
Causes of difficulty in urine flow:
- Internal - narrowing of the ureter due to changes in its wall.
- External - compression of the ureter from the outside.
Obstacles to normal urination can be created by:
- cicatricial changes in the ureters;
- tumors;
- post-inflammatory adhesive process;
- polyps;
- abnormalities in the development or location of the kidneys;
- BPH;
- enlarged lymph nodes of the retroperitoneum;
- intestinal diseases.
In young children, hydronephrosis is sometimes temporary, associated with the maturation of the kidneys, and can resolve without surgical intervention.
With this pathology, MRI makes it possible to assess the condition of the renal parenchyma and choose the optimal treatment tactics.
Polycystic kidney disease
This is a genetically determined pathology, manifested by the progressive formation of cysts in the kidneys.
Their volume and size can range from very small to gigantic.
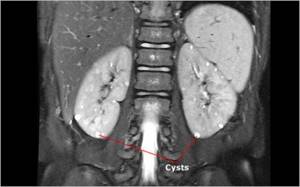
Multiple cysts on MRI of the kidneys (indicated by arrows)
Growing cysts replace the kidney parenchyma, leading to dysfunction of the organ. Inflammatory processes may develop in them.
In 60–75% of cases, the disease can manifest itself for a long time only in arterial hypertension, which manifests itself long before a significant decrease in renal function. The presence of such a pathology in relatives is a reason for a thorough MRI examination, even in the absence of complaints.
Pyelonephritis
This is an infectious-inflammatory disease of the kidneys, in which the parenchyma and pyelocaliceal system are involved in the pathological process.
There are acute and chronic pyelonephritis, as well as:
- primary - occurs in a normal kidney;
- secondary - develops as a complication against the background of abnormalities in the development of the kidney, urolithiasis and other pathologies.
Using MRI, a destructive process in the kidney and a possible cause are identified, even in cases where other diagnostic methods are ineffective (for example, inflammation against the background of an X-ray negative stone).
Contraindications to the MRI procedure:
- pregnancy in the first trimester;
- the patient has ferromagnetic implants or foreign bodies in the tissues;
- installation of non-removable electronic devices, such as a cochlear implant, pacemaker, insulin pump and others;
- age up to 5 years;
- weight more than 130 kg or waist size more than 140 cm.
Registration for the study
To book a tomography session, just contact the consultation service operators using the number at the top of the page.

Explore offers from MRI clinics, set your search criteria using the filter form, compare options and select the best. To ask any remaining questions or clarify information, please contact the portal’s hotline. Service administrators will advise you free of charge, advise you on prices, and make an appointment for a scan on a convenient day and with special discounts from the service.
Sources used:
- Diagnosis and treatment of kidney diseases [Text]: manual / N. A. Mukhin [et al.]. - Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2011. - 384 p.
- Ermolenko, V. M. Acute renal failure [Text]: manual / V. M. Ermolenko, A. Yu. Nikolaev. - Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2010. - 240 p.
- Radiation diagnostics and therapy in urology [Text]: national. hands / ch. ed. S. K. Ternovoy, A. I. Gromov, V. M. Builov; ASMOK. - Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2011. - 544 p.
- Urolithiasis disease. Modern methods of diagnosis and treatment [Text] / Yu. G. Alyaev [etc.]; edited by Yu. G. Alyaeva. - Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2010. - 224 p.
- Nephroptosis: diagnosis, treatment, prevention [Text]: textbook. manual / F. A. Sevryukov [etc.]; NizhSMA. - N. Novgorod: Publishing House of Nizhny Novgorod State Medical Academy, 2015. - 56 p.
- Urology. From symptoms to diagnosis and treatment [Text]: ill. hands / ed. P. V. Glybochko, Yu. G. Alyaeva, N. A. Grigorieva. - Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2014. - 148 p.
- Chekhoeva, O. A. Possibilities of ultrasound examination in diagnosing a kidney tumor at the planning stage of surgical intervention [Text] / O. A. Chekhoeva // Medical visualization. - 2021. - No. 3. - P. 44-52.
Kidney MRI with contrast
A drug based on gadolinium salts is used as a contrast. Unlike iodine-containing products, it extremely rarely causes allergic reactions, is non-toxic, and is completely eliminated from the body within 24 hours.
The use of contrast enhancement makes it possible not only to detect a tumor, but also to determine its stage, the condition of adjacent organs, and the presence of damage to blood vessels and lymph nodes. This is due to the fact that gadolinium actively accumulates in pathologically altered tissues.
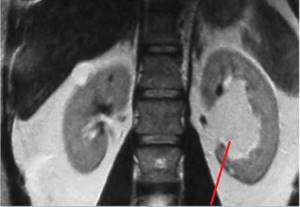
MRI of the kidneys shows a sinus tumor (left kidney)
First, an MRI without contrast is always performed, then, if it is necessary to clarify the data obtained, a scan is done against the background of intravenous administration of a contrast agent. This is especially true in the presence of any kidney tumors.
There is a classification of cystic formations based on the signs identified by the results of MRI with contrast. There are categories:
- The first (I) is a benign cyst with a thin wall, without septations or areas of compaction. Does not contrast, density is identical to water.
- The second (II) is a benign cyst with single septa and small compactions. The MRI signal intensity is lower than that of the parenchyma. Diameter less than 3 cm, accumulates contrast.
- IIF – in the cystic formation, thickening of the walls and septa is observed, focal densities are larger, but do not accumulate contrast. This category requires careful monitoring, as malignancy is possible.
- Third (III) - the walls and partitions are unevenly thickened and accumulate contrast. Surgical removal is indicated and in 50% a malignant process is detected.
- Fourth (IV) – the soft tissue contents of the cyst accumulate contrast well. As a rule, this is a malignant process.
The use of a contrast agent is contraindicated in:
- pregnancy;
- severe renal failure;
- allergies to the components of the contrast agent.
Contraindications
The medical procedure has a number of contraindications, among which it is worth noting:
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- The presence of metal elements and electronic devices in the body.
In addition, it is worth mentioning separately about scanning with contrast, regardless of which area is being examined &mdashl; kidney or adrenal gland. The procedure is prohibited if you have an allergic reaction to the drug, bronchial asthma, as well as an acute stage of renal failure; the doctor decides whether an MRI of the kidneys with contrast is performed in your case.
CT or MRI of the kidneys, which is better?
CT is a faster and cheaper method and is good at detecting radiopaque kidney stones. MRI shows small parenchymal tumors, their internal structure and capsule thickness more accurately and more clearly than CT.
When examining using CT, it is impossible to clearly determine the extent of damage to the inferior vena cava. Only magnetic resonance diagnostics will show the boundaries of the tumor thrombus with an accuracy of 95 - 100% and will assess the condition of the regional lymph nodes.
When choosing an examination technique, you need to take into account that MRI provides detailed data on kidney function and the anatomical features of the urinary tract and is safe when repeated several times. It is recommended to limit the number of CT procedures (no more than two per year) due to the high radiation exposure.
The high reliability of the information obtained as a result of MRI of the kidneys is confirmed by clinical studies in the largest research institutes - even in the most complex cases, the accuracy of the results is more than 98%.
What will the diagnostics show?
The procedure helps to detect the following kidney pathologies:
- cystic formations;
- tumors: malignant or benign;
- stones;
- jades;
- inflammatory pathologies of the kidneys and urinary tract;
- dilation of the renal pelvis;
- purulent damage to organ tissue;
- pathology of the renal vessels.
Timely diagnosed disease is the key to adequate and effective treatment. Using MRI, a doctor will be able to detect almost any pathology at the very initial stages of development, when it has not yet affected the functioning of the organ or caused its deformation.