Dr. Alexander Myasnikov – Endoscopy Department – Colonoscopy under anesthesia
Colonoscopy under anesthesia is one of the modern diagnostic methods that allow timely detection of problems with the large intestine. During a colonoscopy, specialists examine the condition of the large intestine and identify various pathologies - ongoing inflammatory processes, malignant and ulcerative. Colonoscopy under anesthesia is performed using a special device that allows you to study the mucous membrane of the rectum and colon.
As a rule, the procedure is well tolerated and rarely causes discomfort. A colonoscopy is a labor-intensive procedure, so you must strictly follow your doctor's and nurse's instructions.
To reduce discomfort during the procedure, doctors recommend performing a colonoscopy under anesthesia , or taking antispasmodic drugs.
Benefits of Colonoscopy
- highly effective diagnosis and prevention of intestinal diseases. This study makes it possible to prevent the development of cancer in the large intestine in the early stages.
- provides the most accurate information compared to alternative diagnostic methods.
- Using the latest digital imaging equipment, even the most difficult to reach areas of the intestine can be viewed. This is very important for the diagnosis and prevention of cancer.
- When performing a colonoscopy, it is possible to take a biopsy of intestinal tissue and detect cancer in the earliest stages.
- During a colonoscopy under anesthesia, the doctor can stop bleeding and remove malignant tumors without additional surgical intervention.
Indications for colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is usually performed for gastrointestinal bleeding, as well as for suspected development of inflammatory or malignant neoplasms of the colon.
Also, another indication for colonoscopy under anesthesia is a sharp decrease in hemoglobin in elderly patients.
Frequent abdominal pain and bloating, diarrhea are also reasons for a colonoscopy.
Before performing gynecological operations, it is necessary to do a colonoscopy under anesthesia.
A colonoscopy is also necessary to remove foreign bodies from the colon.
Colonoscopy
The relevance of early diagnosis.
Every year, more than 600 thousand new cases of colon cancer are detected worldwide. In Russia, the incidence is about 50 thousand new cases per year. Even in the later stages, colorectal cancer is detected in no more than 70% of patients. Due to unsatisfactory and late diagnosis, the mortality rate (mortality) from this disease remains high and reaches 40% within a year from the moment the disease is detected.
Symptoms that should alert you: unstable stools that appear for no apparent reason, the presence of mucus or blood in the stool, discomfort in the abdomen, a feeling of incomplete bowel movement.
Symptoms requiring urgent examination: unmotivated general weakness, loss of appetite, rapid weight loss without objective reasons.
If you are looking for where to have a colonoscopy in Moscow without pain and safely for your health , then the Central Clinical Hospital of the Presidential Administration is perhaps the best choice.
Our advantages:
- The best endoscopic equipment of the highest (expert) class from the leader - Olympus (Japan) with the ability to digitally zoom and examine in a narrow spectrum of light, allowing you to see early cancer with an area of 1 mm (not a typo - a millimeter!).
- Friendly and polite staff. Since its creation, the department's staff has been working with VIP patients.
- The equipment is processed after each patient in special washing machines (also manufactured by Olympus), which completely eliminates the possibility of transmission of infection from one patient to another. Processing in a washing machine is considered the gold standard for processing endoscopes, but leads to an increase in the cost of the study; however, the clinic’s policy is not to skimp on the safety of our clients.
- Affordable prices - essentially “business class” at an “economy” price.
- We don’t have hidden markups, like in private centers, where after research they will tell you that you owe another 5-6 thousand. Our doctors will discuss all pricing issues with you before the study begins. We are a government agency in which commercial activities are only a small part of our work.
- We conduct research on weekends and holidays - our service operates seven days a week.
Colonoscopy - what is it?
Colonoscopy (derived from Latin сolon - large intestine and Greek σκοπέω - look) is a diagnostic medical procedure, during which an endoscopist examines and evaluates the condition of the inner surface of the colon using a special instrument - an endoscope (colonoscope). Modern equipment makes it possible to detect even small changes in the intestinal mucosa during colonoscopy. The treatment capabilities of our department and the qualifications of our specialists allow us to remove polyps of any size without complications - from 1 millimeter to 8-10 centimeter giant polyps. Immediately after removal of the polyp, it can be examined and determined whether it is completely benign or has already begun to degenerate into cancer.
The words endoscope and colonoscope are synonyms. A colonoscope is a flexible endoscopic device in the form of a narrow flexible tube, specially designed for examining the colon; it is slightly longer than a gastroscope (a device for examining the stomach) and slightly thicker. At the end of the colonoscope there is a video camera and lighting. The tip of the device is flexible and movable; the doctor controls it from the handle using a system of levers and rods located inside the endoscope.
The equipment in our department allows you to display images on a large monitor in high definition (HD) format, which allows the doctor to easily see the slightest changes in the relief or color of the intestinal mucosa. Our department uses the latest expert-class equipment, which, due to its high cost, cannot be afforded by the vast majority of private clinics.
This examination method allows visualization of the entire colon, including the final portion of the small intestine. Various intestinal diseases , colon cancer , rectal cancer , polyps in the intestines - this is just an incomplete list of the most common reasons to perform a colon examination - colonoscopy.
Colonoscopy of the intestines is a delicate procedure that can cause an uncomfortable psychological feeling even before the procedure itself. Especially for such cases, we have both female and male doctors on our staff.
If the doctor finds polyps during the procedure, he can remove them immediately* or take tissue samples for further histological analysis. Also, during an endoscopic examination, the doctor can indirectly assess the functional activity of the intestine.
In addition, colonoscopy is performed to remove early forms of cancer, identify and eliminate the source of bleeding, and also to remove foreign bodies.
In order to reduce discomfort, local anesthetic ointments and gels are used. The procedure is carried out using the most modern equipment from Olympus (Japan).
How to prepare for a colonoscopy.
The success and information content of the study is determined mainly by the quality of preparation for the procedure, so pay the most serious attention to following the preparation recommendations. Remember, in order for the doctor to be able to examine the mucous membrane of the colon in detail and thoroughly, it is necessary that there are not even traces of feces in its lumen.
Preparation schemes are given in the article preparation for colonoscopy. Choose any of the proposed ones.
Dietary recommendations are provided in the Diet Before Colonoscopy section.
Indications for colonoscopy.
The indication for a colonoscopy is the doctor's suspicion of any disease of the colon. Colonoscopy is the gold standard for diagnosing colon diseases. Any other studies provide only indirect information, which again can only be clarified by colonoscopy.
Most often, colonoscopy is performed when a tumor is suspected, as well as in inflammatory diseases of the colon.
In emergency situations (in case of intestinal bleeding, intestinal obstruction or in the presence of foreign bodies), it is performed for therapeutic purposes - to stop bleeding, install a unloading stent or remove a foreign body, respectively.
Contraindications.
If you are reading this section at home, then most likely there are no contraindications. The study is contraindicated only in cases of severe concomitant pathology that requires serious hospital treatment.
With or without anesthesia? Colonoscopy under anesthesia or “during sleep”.
We carry out quite a lot of research without anesthesia: the doctor’s experience, modern equipment with adjustable endoscope rigidity and the use of local anesthetic gels for the anus allow us to reduce discomfort to a minimum, and sometimes even avoid any pain.
Pain during a colonoscopy is usually “quite tolerable” and is caused by distension of the intestine by the injected air and/or distension of the intestine during difficult bends. At this point, the patient may experience short-term pain such as painful spasms.
After several operations or if the previous examination was very painful, we recommend performing a colonoscopy under general anesthesia. According to our observations, the pain in these patients is usually more intense than in others.
So that you understand: the words “sedation”, “general anesthesia”, “anesthesia” and “colonoscopy in a dream” are one and the same. “Sedation” (translated from English as “calm”, “peace”) is less “deep” than standard intravenous anesthesia, is carried out with a different drug and can leave memories, as you understand - unpleasant and painful. In addition, the dose of the drug for traditional “sedation” is more difficult to control and can cause respiratory arrest. Anesthesia looks like this: You fall asleep, then wake up - the procedure is completed, but you don’t remember anything and didn’t feel anything. We believe that this is the most optimal type of pain relief during colonoscopy. A safe drug is used, used in thousands of clinics in Europe, America and Israel; this drug has a clear dose-dependent effect - as soon as its administration is stopped, the patient begins to awaken.
Technique.
We will suggest that you remove all clothing below the waist, except for underwear, which can be left lowered to the knees. Then they will help you lie down on the examination table on your left side, with your knees better bent and pulled towards your stomach.
The colonoscope is inserted through the anus into the lumen of the rectum and gradually moves forward, straightening the intestinal bends and gathering the intestine; a small amount of air is supplied to straighten the intestinal lumen. During the examination, you may need to turn on your back to advance the colonoscope; the nurse will help - it is not difficult or painful. Sometimes it is necessary to hold the device through the anterior abdominal wall to avoid pain when pulling on a loop of intestine - the manipulation is performed by a nurse, lightly pressing on the abdomen with the palm of the hand in a place determined by the doctor.
Most pathological conditions require histological confirmation - a biopsy is performed - the doctor takes the smallest pieces of the mucous membrane with special forceps. It is absolutely painless - the mucous membrane simply does not have pain nerve endings.
Due to the supply of air to straighten the intestine during a colonoscopy, there is often a feeling of fullness of the intestine with gases, which causes the urge to defecate. There is no need to forcefully hold this air while contracting the anus - pain may appear - it is better to just relax and freely release the excess air. At the end of the study, the air introduced into the intestine is sucked out through the endoscope channel.
We would like to emphasize that colonoscopy is a technically complex procedure not only for you, but also for the doctor, so please try to help the doctor to carry out your examination as carefully as possible and at the same time painlessly. It's not difficult - just follow his instructions. You will likely experience some discomfort during the examination, but rest assured that our doctors will take every precaution to reduce any discomfort. As many of our patients note, strictly following the instructions of the medical staff makes the procedure much easier.
What is possible, what is not, and how to behave after the study?
If the procedure was performed without anesthesia, you can eat and drink immediately after the procedure.
If anesthesia was performed, it is better to postpone eating for at least 45 minutes.
If the procedure was therapeutic in nature, you may need to follow a certain diet - the doctor will tell you the restrictions.
Some of our patients note that air comes out more easily after the procedure when lying on their stomach. However, we recommend that after the procedure you walk for 5 minutes and then sit on the toilet for 10-15 minutes to relax and release any remaining air. If you just lie down, the excess air will come out much more slowly and the discomfort will persist longer. If the feeling of distension and/or bloating with gases persists for longer than 30-60 minutes, you can take 8-10 tablets of finely crushed activated carbon mixed in 1 /2 glasses of warm boiled water, or drink 30 ml of “espumisan” also diluted in 1/2 glass of warm water.
Complications.
During diagnostic colonoscopy, complications, the most dangerous of which is intestinal perforation, are very rare.
Alternative to colonoscopy.
The “golden” standard for diagnosing diseases of the colon and the most profitable examination in terms of price/quality ratio today is only colonoscopy.
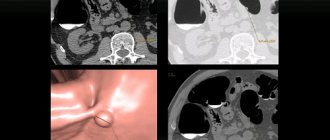
Virtual colonoscopy, irrigoscopy (x-ray with barium enema), video capsule endoscopy of the colon, computed tomography - none of these studies reaches the diagnostic level of colonoscopy and are used as auxiliary studies. In addition, they all have the main and most important drawback - during their implementation, not a single medical procedure can be performed, you can “only watch”.
________________________
* to remove polyps immediately during a diagnostic study, the patient must be examined in the same way as before endoscopic surgery to remove a polyp . The required minimum if the procedure is performed without anesthesia is an ECG (for patients 50 years and older), a blood test for HIV, blood type and Rh factor, a clinical blood test, and a coagulogram. When performing the procedure under anesthesia, a blood glucose (“sugar”) level test will be required in addition to the above. To avoid any complications, it is advisable to first consult and discuss all the nuances, including the preliminary examination and its scope, with an endoscopist in our department.
Colonoscopy price depends on the completeness of the examination. Prices for the current year can be found in the department of paid medical services of the Central Clinical Hospital by phone:
8 manager Olga Olegovna Rusakovskaya,
8 manager Natalya Ivanovna Rashkovskaya.
Anesthesia for colonoscopy
Despite the small size of the apparatus with which the procedure is performed, colonoscopy does not provide a pleasant sensation. In order to reduce pain symptoms and calm the patient, colonoscopy is performed under general anesthesia. The use of anesthesia is mandatory in the following cases:
- childhood - even mild pain and the presence of doctors in white coats can affect the psychological state of the child,
- adhesions on the intestines,
- low pain thresholds – even the sensation of mild pain can cause shock or fainting,
- patients who experience destructive processes in the intestines,
- Crohn's disease.
Painkillers are selected taking into account the patient's sensitivity to anesthetics. Many may be contraindicated for health reasons. Doctors recommend using anesthesia. Since discomfort and pain can be accompanied both during the procedure and after it. It is also difficult to predict the body’s response to the procedure and whether the colonoscopy will be painless.
Colonoscopy under anesthesia
Today, colonoscopy is the most modern method of instrumental research, which is used to provide the highest quality diagnosis of pathological conditions of the rectum and colon. Recently, the possibility of performing this procedure under general anesthesia has been increasingly used.
In accordance with the recommendations of the World Health Organization, it is recommended to undergo it as a preventive measure at least once every five years for every person over 40 years of age. In the event that a person comes to the doctor with certain complaints, a professional specialist must prescribe such a study without fail.
This procedure is carried out using a specialized colonoscope, with the help of which, within a matter of minutes, specialists will be able to assess the condition of the large intestine along its entire length. By carrying out this procedure, a specialist can study the condition of the intestinal mucosa in as much detail as possible and identify even the most minor pathological changes. Colonoscopy is simply irreplaceable for the timely detection and subsequent treatment of various intestinal diseases, as it has a number of important capabilities.
During a colonoscopy, the doctor has the opportunity to visually assess the general condition of the mucous membrane, determine all kinds of inflammatory changes, and also observe the functioning of intestinal motility.
On the monitor screen, the doctor determines even the most minor changes in the walls of the intestine, as well as all kinds of pathological formations, including polyps of the colon and rectum, cracks, ulcers, hemorrhoids, tumors, diverticula, or the presence of any foreign bodies.
Colonoscopy under anesthesia is preferred by specialists for the reason that during this procedure, if necessary, a small piece of tissue can be taken for histological examination.
A colonoscopy is necessary in the following cases:
- discharge of pus, mucus or blood from the large intestine;
- abdominal pain along the colon;
- stool disorders - both constipation and diarrhea;
- unexplained anemia or unmotivated weight loss of the patient, especially with a family history of intestinal cancer;
- suspicion of an intestinal tumor during irrigoscopy;
- foreign body of the colon;
- polyps or tumors detected during sigmoidoscopy. In this case, colonoscopy is necessary in order to exclude the presence of such formations in the overlying parts of the intestine.
This procedure is not recommended if:
- acute infectious processes of any localization;
- pulmonary and heart failure;
- pathologies of the blood coagulation system;
- pronounced exacerbation of ulcerative colitis;
- the presence of peritonitis;
- during pregnancy.
How to prepare for such a procedure?
First, you will need to prepare extremely responsibly for this procedure.
It is quite natural that a thorough, yet complete cleaning of the digestive tract must be ensured, and therefore it is recommended to follow a certain diet until a colonoscopy of the intestines is performed.
A slag-free diet requires the exclusion of foods rich in dietary fiber, which contribute to the formation of a large volume of feces. It is also necessary to remove what causes bloating. Exclude from the diet: brown bread, fresh greens and vegetables (beets, cabbage, carrots, turnips, radishes), fruits (peaches, bananas, apricots, oranges, grapes, dates), legumes, nuts, berries, oatmeal porridge, pearl barley and millet cereals, baked goods, as well as milk, carbonated drinks and kvass. Compliance with this diet is required in order to completely free the intestinal walls from all kinds of toxins, as well as to achieve complete removal of feces, which form obstacles during the advancement of the diagnostic probe. It is recommended to begin preparatory procedures approximately 2-3 days before the colonoscopy is performed.
The following foods are recommended for nutrition: lean boiled meat; wheat flour bread; cracker; all kinds of dietary broths; a variety of fermented milk drinks, such as yogurt, kefir or natural yoghurts. You can drink various liquids throughout the day, but the last meal must be taken no earlier than 20 hours before the examination. On the day on which the diagnosis is scheduled, eating is strictly prohibited; only drinking weak teas or water is allowed. When undergoing a colonoscopy under general anesthesia, you should consult your doctor about eating and drinking on the day of the test.
Among other things, it is imperative to carry out a complete cleansing of the intestines, which is done using a standard enema or specialized medications. The use of special laxatives makes the bowel preparation procedure for the examination more comfortable for the patient. The most commonly used products are Duphalac, Flit and Fortrans. They are diluted in a certain amount of water and started to be taken on the eve of the procedure, including the morning of the next day. In this case, the intestines are cleansed gently, efficiently and without any particular inconvenience for the patient.
After completion of the examination, the patient returns to his normal life. You can eat and drink immediately after the procedure, and nutrition after a colonoscopy does not require any restrictions. If the colonoscopy was performed under anesthesia, the patient is under the supervision of medical personnel for some time (15-20 minutes) and almost immediately returns to the normal rhythm of life.
This examination can be carried out at the request of the patient, both under general anesthesia and without it.
You can undergo the examination in endoscopic room No. 103, located on the 1st floor of the Medical Rehabilitation Center, at the address: Lermontov, st. Lenina, 26.
Make an appointment by phone +7 (87935) 3-43-68
Types of pain relief
To reduce discomfort and pain during the examination, specialists perform a colonoscopy under anesthesia.
The choice of one or another method of pain relief depends on the patient’s diagnosis and health condition. The decision about anesthesia is made by the doctor. In medical practice, 3 types of pain relief are used:
- local anesthesia,
- sedation,
- general anesthesia.
The use of one or another anesthesia can significantly reduce sensitivity to the procedure and perform it easily and quickly.
Local anesthesia
To reduce the sensitivity of the nerve endings, an anesthetic is applied to the tip of the device. It does not completely eliminate the pain, it only slightly reduces the pain. The patient still has a feeling of fear and anxiety, sensitivity.
To create more comfortable conditions during manipulation, on the eve of preparation for the procedure, antispasmodic and sedatives are prescribed.
Sedation
Sedation is a type of pain relief that involves putting a person into a state of medical sleep. This condition is caused by taking special medications. During sleep, a person does not feel anything, but at the same time he hears everything and can react to the doctor’s comments. The patient breathes independently; no special devices are required.
General anesthesia
Under general anesthesia, the patient falls deeply asleep and does not feel anything. There is a complete loss of consciousness. Therefore, after the procedure, the patient does not have any unpleasant memories. Using general anesthesia for this procedure is convenient for both the doctor and the patient. But sometimes there are quite a lot of consequences and complications. To avoid this, it is recommended that the procedure be performed in the operating room in the presence of an anesthesiologist.
What is this?
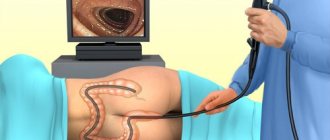
This procedure involves the use of endoscopic equipment equipped with a camera. The device is inserted through the anus, gradually moving along the entire length of the colon. The image is broadcast on the screen in real time, thanks to which the doctor can assess the condition of the walls and cavity, identify any neoplasms, obstruction, foreign body, areas of erosion or inflammation, and much more. Today, examination of the intestines without colonoscopy is practically not carried out. Only this technique is highly informative and safe.
Despite the absence of any harm to the patient's health, colonoscopy without anesthesia is performed infrequently. This is due to severe discomfort and slight pain that occurs during examination or performing medical procedures. In modern medical practice, 3 main types of anesthesia are used before this procedure:
- Colonoscopy of the intestines without anesthesia, in a dream
. In this case, sedation is used. The patient is injected with a sedative drug with a hypnotic effect, which, when activated, dulls his pain sensitivity. - Local anesthesia
. The tip of the endoscope is lubricated with an anesthetic, which eliminates discomfort after insertion of the tube. However, its action is ineffective during air injection, since it acts locally and only in the first stages of inspection. - Anesthesia sleep
. This method is used in an operating room. The anesthesiologist selects the composition and dosage of drugs, after the administration of which the patient loses consciousness. The duration of this condition exceeds the duration of endoscopy. As a rule, this method is prescribed to people with a low pain threshold and children under 12 years of age.
How to prepare for a colonoscopy
In order for the procedure to be successful, it is necessary to follow a toxin-free diet a week before the colonoscopy, as well as completely cleanse the intestines.
A zero-residue diet involves excluding high-fiber plant foods (for example, bread, fruits and vegetables) from the diet.
You do not need to take painkillers before a colonoscopy.
After a colonoscopy, you do not need to follow any special diet. There may be bloating in the abdomen, but this sensation quickly passes after the gas is released.
Preparing for a colonoscopy should be taken very seriously. It matters a lot. Failure to follow certain recommendations and advice from your doctor may lead to inaccurate test results. And a re-examination may be required.
Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the rectum.
Examination of patients with diseases of the rectum, anal canal and perineum begins with clarification of complaints, collection of anamnesis and general examination. The next stage is a local examination and instrumental diagnostics. In acute paraproctitis, acute hemorrhoids and acute anal fissure, when digital and endoscopic examination can be painful, the leading diagnostic methods are examination and palpation of the affected area, and digital examination of the rectum and sigmoidoscopy are carried out after the acute process has stopped.
In most cases, a full examination is necessary. After examining the perianal area, a digital examination of the rectum is performed. This method allows you to:
- assess the condition of the anal canal tissues, the function of the anal sphincter;
- assess the condition of the rectal mucosa and the organs and tissues surrounding the rectum;
- identify the pathological process;
- assess the nature of the contents of the rectum.
After a digital examination, sigmoidoscopy
– endoscopic examination of the rectum. Sigmoidoscopy allows you to visually assess the mucous membrane of the rectum to a level of 20-25 cm from the anus. The only contraindication to rectoscopy is the patient’s refusal to undergo the study. Sigmoidoscopy is an unpleasant procedure, but practically painless and therefore does not require general anesthesia.
Anoscopy
– examination using an anoscope, used to visualize the anal canal and lower ampullary rectum in case of chronic hemorrhoids, chronic paraproctitis and chronic anal fissures. A probe study is used by a proctologist to study the topography of rectal fistulas.
Sigmoidoscopy
- examination of the rectum and sigmoid colon with a flexible endoscope, can be performed without general anesthesia and is used mainly for dynamic observation when lesions are localized in the rectum and sigmoid colon.
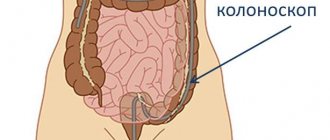
The standard and leading method for examining the colon and terminal ileum is colonoscopy. During colonoscopy
The entire large intestine is examined, as well as a small section of the small intestine above where it enters the large intestine.
Modern video colonoscopes are complex devices in which the image is transmitted from a miniature CCD matrix at the distal end of the endoscope directly to the monitor. Certain moments of colonoscopy are painful due to stretching of the intestinal wall, therefore in our clinic colonoscopy is performed mainly under anesthesia.
Colonoscopy is indispensable for detecting precancerous diseases and early colon cancer, for identifying inflammatory diseases of the colon, for follow-up of patients after removal of polyps, after conservative treatment and after operations on the colon.
If you are planning an appointment with a proctologist, then you need to prepare the rectum accordingly before rectoscopy. It is preferable to clean the rectum with Enema-klin. One microenema is administered in the evening before the study, the second - in the morning on the day of the study. An alternative is regular cleansing enemas, which also need to be given in the morning and evening. A cleansing enema is performed no later than 2 hours before examination by a proctologist, usually twice.
Indications for colonoscopy of the digestive tract are determined by the consulting physician: gastroenterologist, proctologist, surgeon, therapist, family doctor or other specialist.
Reasons for prescribing a colonoscopy
- signs of bleeding from the lower parts of the digestive tract (discharge of scarlet blood from the rectum, blood in the stool, a significant decrease in hemoglobin without obvious reasons, a positive stool test for occult blood);
- diarrhea lasting more than a week, incl. with mucus secretion;
- alternating constipation and diarrhea; abdominal pain;
- frequent flatulence (bloating) unexplained weight loss;
- unmotivated weakness;
- changes in stool analysis (coprogram);
- data from ultrasound, x-ray and other research methods indicating disease of the colon;
- control studies after conservative, endoscopic or surgical treatment, including for the purpose of dynamic observation after detection of diseases of the colon;
- unfavorable family history - the presence of benign or malignant colon tumors in close relatives;
- examination of a patient with a tumor of any location, incl. before surgical intervention on the pelvic organs in women;
- screening for colorectal cancer, i.e. performing a colonoscopy in the absence of complaints when a person reaches 45 years of age.
Preparing for a colonoscopy
The success of a colonoscopy is largely determined by the quality of the colon preparation. Insufficient preparation of the colon leads to a decrease in the information content of the study, lengthens the procedure time and increases discomfort in the abdomen after its completion. Incomplete colon examination due to inadequate preparation forces doctors to shorten the intervals between follow-up studies and increases the risk of detecting advanced colorectal cancer in the future. There are several methods for preparing for research. You can discuss the most suitable preparation option for you with the doctor who referred you for the study. You can also consult with an endoscopist about preparing for the study by contacting him at the call center.
Typically, the preparation plan for the study includes following a so-called slag-free diet and taking one or another lavage fluid. The most widely used drugs for preparing the colon are Fortrans, Endofalk, Lavacol, Flit phospho-soda. Depending on the time of the examination, the lavage fluid is taken either completely on the eve of the examination, or in two portions: in the evening before the examination and in the morning on the day of the examination.
This preparation scheme is called split and is used in all leading endoscopic centers in Europe and Russia. It is important to remember that lavage fluid intake should be stopped no later than 3 hours before the test. A slag-free diet involves excluding from the diet plant fiber, fatty foods, as well as foods and drinks that cause bloating.
Allowed:
- flour products and cereals: white bread made from enriched refined premium flour, muffins, biscuits, bagels (bagels) - without poppy seeds, simple crackers (without additives), oatmeal, vermicelli and noodles made from premium flour, including white rice;
- meat and soups: soups with low-fat meat broth, various, well-cooked dishes from lean beef, veal, boiled chicken, as well as in the form of cutlets, meatballs, soufflé; egg;
- fish: dishes from cod, pike perch, perch, pike (low-fat fish);
- vegetables: vegetable broths, mashed potatoes;
- dairy products: low-fat cottage cheese, cheeses, natural yogurt (without additives), no more than two glasses of skim milk;
- drinks: mousse, tea, weak coffee, compotes, jelly, clear juices without pulp, dried fruits, berries and grains) sweets: sugar, honey, syrup.
Excluded:
- all grain-containing products: whole grains, products containing crushed grains, bran, nuts, poppy seeds, coconut flakes, etc.;
- all fresh and dried vegetables and fruits, raisins and berries, all varieties of greens (parsley, dill, lettuce, cilantro, basil, etc.);
- cabbage soup and borscht, as well as cabbage in any form (fresh, pickled, heat-treated);
- milk soups, cream soups, okroshka;
- fatty meats, duck, goose;
- smoked meats and pickles, sausages, frankfurters;
- canned food;
- fatty fish;
- salted and pickled mushrooms;
- high-fat dairy products (yogurt with filling (fruit, muesli), pudding, cream, sour cream, ice cream, full-fat cottage cheese);
- hot seasonings (horseradish, mustard, pepper, onion, garlic, vinegar), as well as all seasonings and sauces with grains and herbs;
- alcoholic drinks, kvass, carbonated drinks, prune drinks;
- sweets not included in the list of permitted ones;
- legumes, peas, lentils, chickpeas, beans, black beans, etc.;
- black bread.
Directly during preparation, the so-called liquid diet is allowed, which involves taking clear liquids in unlimited quantities: clear broth, green tea, clear juices, jelly without berries, still water. It is forbidden to eat solid food.
If you are constantly taking medications, especially cardiac, antihypertensive, hypoglycemic, anticoagulant or hormonal medications, you must agree on the regimen and conditions for taking them with your doctor. As a rule, most drugs do not require discontinuation during the preparation and conduct of colonoscopy.
Performing a colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is performed by an endoscopist in the endoscopy room or in an operating room. A flexible video endoscope is inserted into the rectum through the anus and passed along the entire colon to the dome of the cecum and then inserted into the terminal ileum by 10 - 15 cm. When advancing the device, pain may occur due to stretching of the intestinal wall and its mesentery by an arc endoscope, as well as in connection with the introduction of air into the intestinal lumen to straighten the folds of the mucous membrane. Therefore, in our clinic, colonoscopy is performed mainly under anesthesia. In this case, the patient does not experience any discomfort and the procedure is completely painless. In selected patients who have previously had a colonoscopy without anesthesia and tolerated it well, it is possible to have a colonoscopy while numbing the anus with an anesthetic gel. The essence of the study is a visual examination of the mucous membrane, which is carried out both during insertion and removal of the endoscope.
If indicated, colonoscopy is complemented by diagnostic and therapeutic interventions:
- chromoscopy (coloring the mucous membrane with dyes);
- biopsy (taking a small piece of mucous membrane for examination under a microscope);
- removal of colon polyps, while small polyps (up to 5 - 6 mm) can be removed simultaneously during a diagnostic colonoscopy.
The duration of a diagnostic colonoscopy averages about 30 minutes, but can vary from 20 to 70 minutes depending on the anatomical features and the need for additional diagnostic interventions.
What anesthesia is used for colonoscopy?
In our clinic, colonoscopy is performed under intravenous anesthesia with propofol, a fast-acting anesthetic that provides total intravenous anesthesia while maintaining spontaneous breathing. Anesthesia is carried out by an anesthesiological team consisting of a doctor - anesthesiologist and a nurse - anesthetist. Oxygen inhalation, constant monitoring of pulse and ECG, blood pressure and arterial blood oxygen saturation levels are carried out. The advantages of performing a colonoscopy under anesthesia are its higher quality in conditions of maximum comfort for the patient. If you are planning to have a colonoscopy under anesthesia, you will need to take a clinical blood test (valid for 10 days), undergo an ECG and a preventive examination by a general practitioner or family doctor.
Possible complications
Colonoscopy in modern conditions is carried out as carefully as possible and is accompanied by a low level of undesirable effects (no more than 0.4%). However, like any endoscopic examination, colonoscopy is an invasive instrumental intervention and carries the risk of the following complications:
- perforation of the genital organ;
- pneumoperitoneum;
- bleeding;
- respiratory and cardiovascular disorders;
- local and allergic reactions.
If the above complications occur, there may be a need for emergency hospitalization, emergency intensive care, endoscopic and surgical treatment. Performing a colonoscopy in a multidisciplinary hospital, such as our clinic, allows for timely recognition and elimination of the complication that has arisen, which increases the safety of the procedure. If you experience unusual symptoms or other circumstances that worry you during the first hours or 24 hours after a colonoscopy, inform your endoscopist and your primary care physician.
After the end of the study, a feeling of bloating may persist, which goes away after visiting the toilet. If a biopsy was performed, then physical activity should be limited to household activities during the day. During the day after the study, it is not recommended to eat raw vegetables and fruits, drink natural juices and carbonated drinks. After performing a colonoscopy under anesthesia, eating and drinking are allowed no earlier than an hour after the end of the study; during the day you cannot drive a vehicle or other machines and mechanisms, engage in extreme sports or carry out activities that require a high concentration of attention.
Alternative to colonoscopy
Endoscopic examination is one of the most reliable diagnostic methods; moreover, it provides a unique opportunity to collect material for morphological examination and can be combined with therapeutic intervention. However, due to objective reasons, it is not always possible to perform a full colonoscopy and making an accurate diagnosis is not possible in all cases. A possible alternative to colonoscopy are radiation examination methods: irrigoscopy (X-ray), virtual colonoscopy (computed tomography) and MRI.
How does the procedure work?
To carry out the colonoscopy under anesthesia procedure, special prepared premises and equipment are required. The procedure goes as follows:
- first, the patient must undress to the waist and lie on his left side, bending his knees,
- then anesthesia is given,
- Afterwards, the device is inserted into the anus, and the doctor examines the inner surface of the intestine. If necessary, polyps are removed and material is taken for additional research,
- at the end of the procedure, the doctor carefully takes out the device and brings the patient to consciousness.
If local anesthesia is used, the patient can go home immediately after the procedure. When using sedation or general anesthesia, the patient is under the supervision of medical personnel for some time until consciousness is fully restored.
Ten years ago, colonoscopy was a fairly complicated procedure. Why?
The length of the human large intestine reaches 1.5-2 m (in some people 3 or more m), the intestine has several physiological bends along its length. During the examination, to ensure a good view, the intestine is inflated with air, which can cause intestinal spasms and severe pain. In addition, the very advancement of the probe through the intestine (especially in places of physiological bends) causes intestinal spasm and pain. The success of the procedure depends on the correct attitude of the patient, high-quality preparation for the procedure and the skill of the endoscopist.
Many patients undergo this procedure consciously, but during surveys, most of them note unpleasant (painful) sensations during the procedure, some of them are on the verge of tolerance. In some patients, the procedure causes severe pain, as a result of which it becomes impossible to move the probe through the intestines and the procedure has to be interrupted.
The modern approach in medicine is designed to ensure maximum safety and comfort during any therapeutic and diagnostic procedures. Unpleasant sensations during colonoscopy can be mitigated by performing the procedure while sleeping, i.e. under anesthesia.
Is it correct to carry out the procedure under anesthesia? The question is debatable. On the one hand, anesthesia is a fairly serious procedure, on the other hand, keeping the patient in a state of sleep eliminates the emotional and painful component of the manipulation, which significantly reduces the time of the procedure and allows the endoscopist to qualitatively examine the entire colon.
The safety and possibility of anesthesia during colonoscopy is assessed by an anesthesiologist. Taking into account your individual characteristics (weight, gender, age, concomitant diseases), the safest composition of anesthetics is selected, which allows you to fall asleep gently and wake up quickly after the procedure. After the procedure, the patient is observed in a comfortable room for an hour, finally recovers from anesthesia and leaves the clinic.