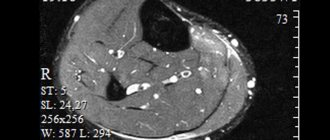
The most informative method for examining bone tissue is radiography. This examination will be the first to be prescribed by a traumatologist-orthopedist when it is necessary to assess the condition of the bones of the lower leg - their integrity, anatomical features, density and other parameters. In therapeutic and diagnostic radiography of the lower leg, a modern digital X-ray machine BrivoXR575Premium is used. This means that accurate high-resolution images will be ready in a couple of minutes, the procedure will be painless, and the resulting radiation dose will be minimal and safe for health.
What will a shin x-ray show?
During this study, photographs are taken in the direct and lateral surfaces. They show:
- Tibia and fibula.
- Adjacent joints: knee and ankle.
From the pictures you can see:
- Fractures, bone cracks.
- Number and location of bone fragments.
- Congenital or acquired bone deformation.
- Foreign bodies in the lower leg area.
- Neoplasms and metastases.
- Degenerative-dystrophic bone diseases: osteomyelitis, periostitis.
- Inflammatory processes in the soft tissues of the lower leg and foot.
How unsafe is an X-ray of the legs and how can you be treated with an X-ray?
Everyone knows about the dangers of ionizing radiation. However, everything depends on the degree of radiation and the total radiation exposure, because such radiation tends to accumulate in the body. That is why, after each X-ray diagnostic procedure, a note is made on the corresponding accounting sheet about the amount of radiation dose received. An average person who goes to the dentist several times a year and takes an X-ray and undergoes a routine fluorography procedure will receive, in addition to natural background radiation, exposure equal to approximately 15 mSv. And a dose of less than 10 μSv may not be taken into account at all.
Restrictions on the procedure may be associated with:
- severe condition of the patient, especially if bleeding occurs;
- pregnancy;
- under 15 years of age;
- significant total radiation dose received previously
However, given the insignificant radiation exposure of X-ray diagnostics of the legs, the information content of the method should prevail over the desire to avoid radiation.
Recently, thanks to the development of low-dose X-ray equipment, such a common disease as a bone growth on the surface of the heel bone in the form of a spike (wedge), also known as a “heel spur,” is effectively treated with the help of X-rays. Modern devices make it possible, firstly, to reduce radiation exposure, and secondly, to act purposefully, that is, without affecting the areas of other organs. This method makes it possible to very quickly remove pain and stop pathological processes. The dose of radiation received during the procedure does not exceed 10 μSv (0.01 mSv).
Indications
X-rays of the lower leg are prescribed only if there are indications; the examination is not carried out for preventive purposes.
Main indications for x-rays:
- Injuries, severe bruises and blows, when you need to evaluate the presence of a fracture.
- Pain, swelling, hemorrhages on the leg.
- Deformation of the lower leg, inability to stand on the leg.
- Suspicion of diseases such as tumors of various types and metastases, osteomyelitis, arthritis or arthrosis of the joints.
- X-ray control after osteosynthesis of tibia fractures.
An x-ray of the lower leg is required for fractures, when you need to understand its features - the presence and number of bone fragments, their location. X-rays are also taken after the treatment to evaluate the result - how correctly and completely the bone has fused.
In what cases will an x-ray of the lower extremities be prescribed?
This method of research is in demand due to its accessibility and information content. Another important factor is that the price of a leg x-ray will be lower than other non-invasive diagnostic methods. Typically, the reason for an X-ray examination is the referral of a specialist: a traumatologist, surgeon, orthopedist, or rheumatologist. The objects of study can be the hip joint, femur, knee joint, kneecap, shin bones, ankle joint, foot, heel bone, toes.
X-ray of the leg is not a preventative procedure. The doctor may prescribe such a referral if:
- there has been any mechanical damage and it is necessary to confirm the diagnosis of dislocation, sprain, tendon rupture, fracture;
- the patient complains of pain in the lower extremities of unknown etiology;
- there are complaints about difficulty moving, feelings of numbness;
- swelling of the lower extremities is observed;
- hyperemia of the skin of the legs (legs) can be observed;
- clinical signs give reason to assume the development of tumor processes, and primary diagnosis is required in order to further determine the nature of the tumor and the method of treatment;
- it is necessary to exclude malformations of the bones and joints of the lower extremities;
- there has been exposure to low or high temperatures and as a result there are signs of frostbite or burns (to determine the degree of bone damage);
- it is necessary to confirm the diagnosis of flat feet;
- it is required to visualize the process of bone fusion.
How is an x-ray of the lower leg performed at the Kutuzovsky Children's Center?
During an x-ray of the lower leg, two projections are used: direct and lateral. The pictures are taken in a couple of minutes, after which the radiologist prepares a report on the results. With it, the patient turns to the attending physician to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
The result complies with international protocols, and thanks to a convenient electronic form, it can be transferred to a doctor in any other clinic or even country.
The price of a shin x-ray can be found in the clinic’s price list, and you can make an appointment by calling the number. Don't delay your examination!
The essence of the examination
Radiography is a non-invasive type of examination. In practice, this means that it is not accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the skin, pain or any other unpleasant sensations. The study is based on irradiation of the supposed damaged part of the body, which allows one to obtain an image of the studied area, where bones are clearly visible, as well as indirectly ligaments and tendons.
Since the lower leg is a complex mechanism consisting of two bones, to obtain a complete picture of the condition, it is necessary to take into account the structure of the fibula and tibia. In medical practice, it is believed that the greatest difficulties for the patient and his attending physician are precisely the fracture of the tibia. The reason lies in the anatomical features, because it is on it that most of the load falls when distributing the weight of the body.
Content:
- The essence of the examination
- Main indications
- Preparation for the procedure
At the same time, the fibula is an attachment for muscle tissue, which explains the reduced load on this component of the lower leg.
To determine the exact location of the lesion, as well as to eliminate the risk of fragments getting into the surrounding tissue, you will need to take x-rays. Based on the data obtained, it will be possible to find out whether surgical intervention is required, or whether a standard cast or splint can be used.
Despite the fact that modern medicine offers many other types of diagnostics, the use of this type of imaging is still in consistently high demand. Doctors and patients value it not only for the relatively affordable cost of the examination, even when it comes to using the capabilities of a digital device in a private clinic.
And also because, unlike modern computed tomography, which even without the use of an additional stage of contrast, lasts about fifteen minutes, an x-ray examination will take, at most, five minutes.
If a digital camera was used for testing, the image is instantly displayed on the screen. It can be transferred to digital media or printed on paper along with an encrypted report from a radiologist. You need to hand over the official document to the attending physician yourself, or wait until it is delivered to his office, if we are talking about an inpatient department of a hospital.
New bone formation - symptoms and treatment
The diagnostic algorithm includes interviewing the patient, detailing complaints and clarifying the medical history. Particular attention should be paid to fever, weight loss, loss of appetite and other general symptoms. The time that has passed since the discovery of a bone tumor, the presence and intensity of its growth are also specified.[8]
During examination, the size of the formation, its structure, localization and skin changes are assessed. The areas of regional lymph nodes are palpated to assess possible changes - enlargement of the lymph nodes, their adhesion to the surrounding tissue and to each other.
A laboratory search begins with a general and biochemical blood test: determination of alkaline phosphatase, phosphate and calcium.[1] These analyzes provide evaluative information.
There are laboratory markers of bone resorption (dissolution) that confirm the predominance of bone breakdown (possibly at the tumor site).[9]
But their diagnostic value, unfortunately, is limited, since bone resorption can also occur in other conditions not associated with a bone tumor.
Instrumental diagnostics
The most accessible, fastest and most revealing instrumental diagnostic method is radiography. An x-ray taken in two projections gives an idea not only of the size and location of the bone tumor, but also of its type.[3]
A more detailed and sensitive visualization of new bone formations is computed tomography.[16] It is especially relevant for joint tumors and small bone tumors that are poorly visible on ordinary X-rays.[8]
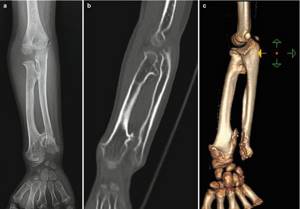
Scintigraphy is used as a screening (search evaluation method) - bone scanning after intravenous administration of a radioactive isotope. The isotope accumulates in the bone tumor, causing it to “glow” on the scanner screen. This method provides information about the presence of skeletal tumors and their number. It is also effective for the early detection of bone metastases in cancer patients.[6] However, it is impossible to distinguish a benign tumor from a malignant one, much less determine the type of tumor on a scintiogram.[16]
It is noteworthy that radiation methods for diagnosing neoplasms do not provide the right to reliably diagnose a specific type of bone tumor. Even with all the X-ray signs that speak in favor of a certain tumor, only examination of the tumor under a microscope is decisive.
For microscopy, cells are obtained using a biopsy - taking part of the tumor. For this, a puncture biopsy is used, when the bone is obtained with a wide needle, or an incisional biopsy - surgical removal of the tumor, i.e. cutting off part of it.[16]
Often a biopsy is performed immediately during surgery to obtain a preliminary result. This makes it possible to determine the volume of the operation.[2]
Contraindications
There are no absolute contraindications to digital radiography.
Relative ones include:
- Pregnancy – radiation exposure can have a negative impact on the developing baby.
- A situation where a patient needs emergency care.
- A highly agitated state or mental illness that makes it difficult to remain still while the X-ray machine is operating.
- Age up to 14 years.
In these cases, the doctor decides whether an x-ray is necessary. He may prescribe a different diagnostic method or perform x-rays with additional precautions. To minimize training, a lead apron is used to cover the genital area of an adult, or the entire body of a child.
Ankle diseases and injuries
The human ankle joint, along with the knee and hip, is one of the most complex joints. This is an area of increased risk of injury due to heavy workload. It bears the entire weight of the body when walking, running, jumping and other movements. And the greater the weight, and the more varied and active the movements, the higher the risk of injury and wear of joint tissue. Anyone can experience fractures and other injuries, but people who play sports professionally are at particular risk.
The ankle is responsible for the stability of the body and evenly distributes the load on the foot. It is characterized by both injuries from overload, bruises, and typical joint diseases. Deformation of the foot and joint occurs with flat feet, excess weight, as a result of hormonal imbalances and past autoimmune, infectious and other diseases.
If alarming symptoms appear, consultation with highly specialized doctors is necessary: orthopedist-traumatologist, surgeon. For diagnosis, the following are used: examination and palpation, history taking, laboratory and instrumental tests are prescribed. The most common method for examining bone structures is X-ray examination; if pathology in soft tissues is suspected, the doctor will prefer MRI; arthroscopy is possible.