What is bacterial seeding?
Bakposev - inoculation of biological material taken from the cervical canal. This type of analysis is widely used in gynecological practice. When sown on nutrient media, microorganisms and bacteria present begin to develop and their numbers increase. This gives the doctor a high chance of determining what pathological bacteria are in the body. Informative and inexpensive bacterial culture allows you to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Using culture, you can identify:
- Escherichia coli, enterococci;
- Staphylococci (aureus, epidermal);
- Gonococci, causative agents of gonorrhea;
- Gardnells;
- Proteus;
- Spirochetes (causative agents of syphilis), etc.
Bacteria that parasitize inside cells - ureaplasma, chlamydia, mycoplasma - cannot be detected by culture.
How to prepare for a bacterial culture and how many days it takes to do it
You need to understand that the accuracy of the analysis result largely depends on the woman. During the two days before the test, sexual intercourse, ultrasound using a vaginal sensor (since a gel is applied to it, which then remains on the cervix), douching, use of lubricants, etc. are prohibited. In addition, the result may not be accurate if the woman has just finished using local antibacterial treatment (suppositories or tablets), or less than a month ago she finished taking an oral antibiotic.
And another important point - you cannot take 2 smears on the same day, for example, bacterial culture and PCR, otherwise the result may not be reliable.
But alcohol taken several hours before taking a smear will not affect its accuracy. The duration of the analysis is 5-7 days, this is how long it takes for different microorganisms to grow in a nutrient medium and be discovered by laboratory assistants.
How to take bacterial cultures from the cervical canal
Many women are interested in what they need to take with them to the gynecologist, how to take a culture test, and whether it hurts. In fact, it’s like an ordinary “smear”. Taken on a chair. First, the doctor inserts a speculum into the vagina to open the cervix. Then, using a cotton swab, removes the so-called mucus plug from the external pharynx (vestibule of the cervical canal). And then he inserts a special thin brush there for a length of up to 1.5 cm. He turns it there and pulls it out.
A slightly unpleasant process, but quite tolerable. Does not require anesthesia. You don’t need to take anything special with you to the doctor. Unless you take a panty liner, as after taking a smear it may smear a little.
Preparation and execution
The procedure for taking biomaterial is practically painless, so it is performed without anesthesia. A day before the procedure, you should avoid sexual intercourse, do not use vaginal medications, or douche.
During the analysis, biomaterial for sowing is taken with a special brush-probe, which is inserted 1-1.5 cm into the cervical canal. Then it is removed and immersed in a test tube with a nutrient medium. The inoculated tube is kept in conditions favorable for reproduction for 2-3 days, and the resulting liquid is examined under a microscope. The analysis is deciphered by a microbiologist who identifies pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria. Having detected pathogenic microorganisms, the doctor can prescribe specific, effective treatment.
When choosing a clinic for testing, two points are taken into account - the equipment of the laboratory and the level of qualifications of the staff. The laboratory in which the analysis is carried out must be equipped in accordance with established standards - an air purification filter must be installed in the room. Personnel must be familiar with the instructions for collecting material and conducting research - this reduces the likelihood of diagnostic error to a minimum.
Microflora culture (agent identification and sensitivity to a/b)
Culture of upper respiratory tract secretions
Testing allows you to determine the causative agent of the infection and select the most effective antibiotic for treatment.
Quite often, the causes of diseases of the upper respiratory tract (in particular, rhinitis or sinusitis (nasal lesions), pharyngitis (throat mucosa)) are the effects of microorganisms:
- streptococcus, pneumococcus, staphylococcus – rhinitis;
- hemolytic (destroying red blood cells) streptococcus - pharyngitis.
Timely diagnosis with precise identification of the agent of infection facilitates adequate treatment, which in turn prevents the disease from passing from acute to chronic form.
The purpose of the study is to identify microorganisms:
main infectious agents, opportunistic bacteria:
- pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae);
- Haemophilus influenzae (Haemophilus influenzae);
- Moraxella catarrhalis;
- pyogenic streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes);
- Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus);
- gram-negative enterobacteria;
- some mushrooms of the genus Candida;
representatives of normal flora:
- viridans streptococci (Streptococcus viridans group);
- epidermal staphylococci (Staphylococcus epidermidis);
- non-pathogenic neisseria (Neisseria sp);
- non-pathogenic diphtheroids (Corynebacterium sp.);
- Candida mushrooms (Candida sp.) and others.
Bile culture
The purpose of testing is to isolate the following infectious agents:
- gram-negative bacteria of the Enterobacteriaceae family, of which Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli), Klebsiella sp., somewhat less frequently Enterobacter sp., Salmonella sp., and Proteus sp. are found;
- faecal streptococcus (S. faecalis);
- staphylococcus (Staphylococcus sp.),
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pseudomonas sp.), etc.
Culture of wound fluid and tissues
The results of this testing are used to prescribe effective antibiotic treatment for wounds.
Often complex wounds are not treated properly, which in many cases is due to the inappropriate use of antibiotics.
Quite often, purulent-inflammatory complications of wounds arise due to the effects of opportunistic bacteria. However, even more common pathogens are bacteria that do not require oxygen (partially or completely) for normal functioning. The general name for such microorganisms is anaerobes. Complications of wounds are caused by some of their representatives - gram-negative (non-stainable during the characteristic Gram staining reaction) rods, gram-positive (stained) cocci, non-spore-forming rods. Even though the same symptoms of complications and the identity of the detected bacteria appear, their response to antibiotics in different people may have significant differences.
The effectiveness of antibiotic treatment currently leaves much to be desired. However, accurate identification of microorganisms and determination of their sensitivity to antibiotics makes the process much more effective.
The purpose of the study is to isolate the following infectious agents:
- pyogenic streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes);
- hemolytic (destroying red blood cells) streptococci of groups B, C, G;
- Haemophilus influenzae type B (Haemophilus influenzae), characteristic of cellulite;
- Pasteurella multocida, the presence of which is characteristic of complications after a bite;
- Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, the causative agent of an acute bacterial infection - erysipiloid, which usually affects the skin and is transmitted through contaminated animal products (one of the names of the disease is “erysipelas of pigs”);
- enterococci;
- gram-negative bacteria belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pseudomonas aeruginosa);
- Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus), the presence of which has been noticed in the infection of bedsores.
Important . When collecting a sample, you must have the transport medium ready.
Culture of discharge (scraping) from the eye
The study is carried out to isolate the following pathogens:
- staphylococci:
— Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus)
— epidermal staphylococcus (Staphylococcus epidermidis) and some other species;
- hemophilus influenzae (Haemophilus influenzae) (particular attention is paid to its presence when examining children);
- streptococci:
— pneumococci (Streptococcus pneumoniae);
— pyogenic streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes);
— streptococcus viridans (Viridans streptococcus);
- moraxella (Moraxella);
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pseudomonas aeruginosa);
- mushrooms:
— candida (Candida) (most often);
- Escherichia coli
- Neisseria species;
— protea (Proteus vulgaris);
- corynebacteria:
— Corynebacterium xerosis;
— Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum.
Sowing of genital discharge or scrapings from the vagina, cervical canal, urethra
The test is intended to identify bacteria that cause a nonspecific infectious-inflammatory disease (i.e., when the infectious agent that caused its occurrence is unknown), and to prescribe effective treatment using antibiotics based on its results.
In a normal state, the biocenosis (a set of microorganisms representing the microflora) of the human genitourinary system is represented by a more or less constant, sometimes age-dependent, composition. Thus, the vaginal microflora of women of reproductive age contains in significant quantities strict (obligate - dying when exposed to an oxygen environment) and facultative (which can exist both with and without the presence of oxygen) anaerobic organisms, most of which are lactobacilli. To a much lesser extent, it is inhabited by aerobic (requiring normal oxygen content for life) and microaerophilic (which require a reduced oxygen concentration) opportunistic bacteria. In the internal canal of the cervix and in the uterus itself, bacteria are normally absent.
The microflora of girls who have not entered the puberty phase is represented by cocci and diphtheroids (Gram-positive rods).
Small amounts of gram-positive rods and cocci may be present in the parts of the urethra (urethra) of healthy men closest to the external outlet. The proximal (distant from the exit) parts of the urethra, prostate and seminiferous tubules are normally sterile.
If the balance between the types of microorganisms is disturbed and/or bacteria unusual for a given place appear, this creates a serious precondition for the occurrence of an infectious-inflammatory process.
Diseases typical for women:
- vaginitis – inflammation of the vaginal mucosa;
- urethritis - inflammation of the urethra;
- Cervicitis is an inflammation of the cervix or the uterus itself.
Diseases common in men:
- urethritis - inflammation of the urethra;
- prostatitis – inflammation of the prostate gland.
The result of the study is the isolation of opportunistic bacteria (i.e. those that can be part of the normal microflora, but when the immune system is weakened they become pathogens): enterobacteria, streptococci, staphylococci, Haemophilus influenzae, non-fermentative gram-negative bacteria, enterococci, coryneform bacteria, yeast-like mushrooms (only the fact of their presence is stated, the species are not determined).
Attention! A study of the presence of specific pathogens - chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis), trichomonas vaginalis (Trichomonas vaginalis), pale spirochete (Treponema pallidum), gonococcus (Neisseria gonorrhoeae) is not carried out as part of this test.
Culture of ear discharge
This test is intended for microbiological diagnosis of purulent-inflammatory diseases of the ear.
Purulent-inflammatory processes differ in localization and can be caused by various pathogens. The lesion is classified according to the location of the source of the disease:
- ear canal (boils, diffuse lesions);
- eardrum (this disease is called myringitis);
- middle ear;
- mastoid process (mastoiditis).
The following microorganisms cause diseases:
- Staphylococcus aureus – otitis media, boils;
- gram-negative rods – diffuse lesions;
- streptococcus – inflammation of the eardrum (myringitis);
- microplasma – inflammation of the eardrum;
- gram-negative Escherichia coli – inflammation of the middle ear.
For a quick recovery of the patient, as well as to prevent the transition of the disease from acute to chronic, it is very important to identify the pathogen and determine its sensitivity to antibiotics.
Cultures are carried out to check for the presence of gram-negative bacteria belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococci, streptococci (S. pyogenes, S. pneumoniae, S. viridans), corynebacteria, yeast-like fungi, Haemophilus influenzae ).
Culture of puncture material
The purpose of culture is to isolate the following pathogens:
- representatives of the enterobacteria family, namely Escherichia coli (E. coli), Klebsiella sp, species of enterobacter spp, Proteus sp and some others;
- fecal streptococcus (Streptococcus faecalis);
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pseudomonas aeruginosa);
- staphylococci, streptococci;
- yeast-like fungi;
- hemophilus influenzae (Haemophilus influenzae) - it is rare, mainly with infectious arthritis in children.
Samples taken for research:
- aspiration (selected by vacuum) fluid from the peritoneum or pleura;
- synovial fluid - a thick substance that fills the cavities of the joints;
- pericardial fluid - serous fluid located in the pericardial sac;
- amniotic fluid - amniotic fluid.
Sowing for anaerobic microflora
The purpose of the study is to detect the presence of microorganisms living and growing without access to oxygen during purulent-inflammatory processes.
Anaerobic bacteria live safely in the human body, making up a significant part of its microflora. However, certain conditions can make them the cause of purulent inflammation.
Regardless of what part of the body the focus is located, the action of anaerobes is not varied - this is rotting and gas formation. Most often, the target of microorganisms is the organs in which they live, resulting in damage to the genitourinary system, gastrointestinal tract, and upper respiratory tract. Carrying out an accurate diagnosis is vital - only this will help prescribe adequate treatment and neutralize the infection, which poses a mortal danger to the human body.
The infection is caused by prevotella, veillonella, clostridia, propionobacteria, eubacteria, peptostreptococci, actinomycetes, fusobacteria, gemella, bifidobacteria, bacteroides, porphyromonas.
During the examination, testing is carried out:
- aspirate (liquid with cells of the epidermis - the outer layer) from body cavities;
- biological fluids from the peritoneal cavity and pleura;
- purulent contents of abscesses;
- pieces of tissue due to inflammation of skeletal muscles (myositis) or tissue necrosis (myonecrosis - gas gangrene);
- discharge from the bottom of ulcers;
- bile;
- prostate secretion (seminal fluid).
What can culture detect?
It is the culture result that the vast majority of gynecologists rely on. It's all about its completeness and authenticity. There are several points, the analysis of which forms the result of sowing:
- Leukocytes. Their increased number in the field of view indicates an inflammatory process, which, in turn, could be caused by an infection.
- Mushrooms. For example, candidiasis involves the presence of candida fungi in the vagina. This disease is known to millions under the name “thrush”.
- Trichomonas whole or its particles. This microorganism is the causative agent of trichomoniasis. Thanks to the flagella, it is able to ascend the urinary canal and affect the entire genitourinary system. Fortunately, treatment for Trichomonas consists of a 10-day course of taking metronidazole or its analogues.
- Sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, cytomegalovirus.
- Cocchi.
These are the main indicators that are analyzed when considering sowing.
Useful information on the topic:
- Curdled discharge in women
- Thick discharge in women
- Green discharge in women
- Mucus discharge in women
- Transparent discharge in women
- Discharge with odor in women
- Causes of discharge in women
- Itching and discharge in women
- Odorless discharge in women
- White discharge in women
Why is sowing necessary?
It is worth saying that culture for infection and smear are different concepts. The differences in them are obvious and visible to the naked eye. The doctor takes a smear using a special plastic device with a widened tip. A mirror is also used. The gynecologist takes a smear from two or three areas of the vagina. A smear allows you to detect bacteria and fungi, but it is not at all a fact that the doctor will take a sample from the infected area.
Sowing involves the use of a cotton swab. It is in a completely sterile factory jar. After being removed from it, it is immersed in the vagina, then removed and placed back in the jar.
While a smear test in Russian municipal medical institutions takes an average of a couple of days to prepare, a culture test can take up to a week and a half.
A smear is significantly inferior to a culture in terms of reliability, since a smear is the collection of secretions from a couple of areas, and culture is from the entire vagina. Despite this, in some cases it may be necessary to retake the analysis, but this will be discussed below.
Tank culture from the cervical canal during pregnancy
During pregnancy, bacterial culture of the cervical canal is one of the important laboratory tests.
The cervical canal is a part of the cervix in which a large number of microbes accumulate that can harm the unborn child.
Detection of the disease at an early stage makes it possible to immediately begin treatment and guarantee the birth of a healthy baby on time.
When registering, pregnant women undergo a routine vaginal smear. If deviations are detected in the list of outcome indicators, the expectant mother will be sent for additional examination of the cervical canal.
In pregnant women, the cervical canal reaches a length of 3–4 cm, the length of the cervix is up to 2 cm. Both ends of the pharynx are closed and represent a protective barrier for the fetus.
The collection of material is carried out only by an experienced professional, which guarantees the safety of the procedure and does not pose a threat to the life of the fetus.
How do you take a smear for bacterial culture?
If the patient does not take a number of preparatory measures on the eve of the analysis, bacterial culture will not be able to give correct results. For the analysis to be truly effective, you need to:
- Ensure complete sterility of the resulting smear. If foreign microorganisms get into it, the culture will be spoiled;
- Do not have sexual intercourse the day before the test;
- Do not douche, do not use anal and vaginal suppositories;
- Wait for the end of menstruation and wait 2 additional days after it stops;
- Wait at least 2 days after colposcopy;
- Refrain from bacterial culture if the woman has already taken any medications during treatment that could affect the result;
- Do not wash yourself before the analysis, and do not use hygiene products under any circumstances.
Decoding the culture tank from the cervical canal
A woman receives the results of a smear 4-6 days after submitting the material. During this period, colonies of bacteria grow. The resulting form indicates all microorganisms that populate the lining of the cervical canal.

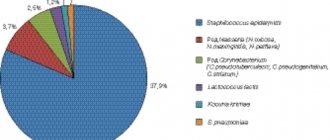
In the photo: an example of deciphering the analysis after a smear from the cervical canal - click to enlarge.
The norm is the presence of leukocytes and fungi in moderate quantities, lacto- and bifido-bacteria (107 CFU/mg, which corresponds to 300-400 million/g), creating a protective acidic environment. E. coli normally contains up to 102 enterococci.
An important indicator in decoding is the number of bacteria, indicating the degree of cleanliness of the cervical canal. In a contaminated mucosal environment, there is a minimal number of microorganisms growing in a liquid medium.
This category includes the minimum number of “resistant” bacteria that can develop in a dense environment (no more than 10 colonies). With the development of the inflammatory process, bacteria capable of multiplying in a dense environment (up to 100 colonies) are found in the smear.
Price
On average, prices for delivery of a sowing tank in Russia range from 800 to 1,400 rubles.
- Bacteria are detected using modern automated methods using new technologies. The sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics is determined by microbiological analyzers.
- The next stage is the selection of a drug depending on the identified pathogen. The results of the study are given to patients in accordance with standards that help the attending physician to easily navigate the information provided and make the correct conclusion.
Distorted analysis result
In some cases, culture analysis may not be accurate. This is quite possible if the sample is taken incorrectly or if antiseptic and aseptic standards are violated. A woman should always pay attention to what is being used for analysis. This should be a completely sterile package with a jar and a tampon. The doctor must carry out the procedure wearing freshly worn gloves. A smear and culture cannot be taken with a finger, this is a gross violation.
If a girl complains of discharge, itching or an unusual odor, but the analysis does not reveal any infections, then there is a serious reason to retake the exam. The reliability of the result also depends on the literacy of the laboratory assistant. Unfortunately, municipal institutions often employ qualified but not experienced specialists who lose sight of important aspects of the analysis.
Publication date: 2018-01-17
Useful information on the topic:
- Calling a gynecologist to your home
- Medical abortion
- Consultation with a gynecologist
- Surgical abortion
- HCG tests
- Ultrasound during pregnancy
- Intrauterine device
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted diseases
- Fetal ultrasound
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Ultrasound during pregnancy
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- Abortion pills
- Discharge in women