- How is MRI fundamentally different from ultrasound?
- When is an ultrasound and when is an MRI prescribed?
The abdominal cavity contains many internal organs that perform vital functions. The spleen, stomach, pancreas, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters and most of the many intestines are located in a small area of the human body. Each organ takes its place in the anatomical region and does not interfere with the functioning of the others. But inflammation, tumor, and various pathologies often affect several organs at once, because everything in our body is interconnected. And since there are practically no people with 100% good health these days, doctors often recommend their patients to do an MRI of the abdominal cavity to check the condition and functions of the internal organs. But why does a specialist send for an MRI if you can do a more common and cheaper ultrasound? After all, the price of an abdominal MRI is much higher. How valid are such recommendations and why?
What is better and more accurate, ultrasound or MRI?
Ultrasound diagnostics is one of the classic ones. The most advanced techniques include magnetic resonance imaging. However, it is impossible to compare them without considering the differences in detail.
Difference between ultrasound and MRI
When it is necessary to diagnose and assess the state of health, we turn to these studies. Their most important difference can be seen in the name: the first is carried out using ultrasound, the second using magnetic fields.
- Mechanism
A tomograph, the main instrument in the MRI process, creates its own magnetic field, which “calls out” protons (hydrogen) in the patient’s body, notices their reactions and, on this basis, forms a holistic picture of the internal tissues. In some cases, in addition to the tomograph, a contrast agent is used - it is injected into a vein in order to increase the clarity and detail of the image.
- Ultrasound works on ultrasound waves that are reflected from tissues. Their reflection is the basis of the resulting image.
It is impossible to answer unequivocally which is better, ultrasound or MRI. Each technology is good in a specific case. For example, MRI is used to penetrate deeper into soft tissues (that is, the procedure “works” for cancer, when tumors form). The output images help provide an accurate picture of the condition of the organs.
- Ultrasound is prescribed when it comes to the organs of the digestive and excretory systems, heart, blood vessels, knee joints and gynecology.
- The errors of human and technical activity are also contrasted here: the ultrasound result is processed by the doctor, but the MRI lies entirely on the “shoulders” of the computer.
- Cost (MRI will hit your pocket harder).
- Equipment that will be in contact with the patient’s body (the ultrasound sensor is in contact with the skin, and during tomography it is necessary to lie in a capsule).
- Contraindications: MRI is harmful in the presence of artificial metal parts in the body (prostheses) and electronic devices that stimulate cardiac activity, insulin pumps.
Why do you need ultrasound and MRI?
These types of examinations have different purposes: ultrasound is used to confirm the disease or some pre-existing pathological changes, but if the clinical picture is not clear and the doctor has too many unanswered questions, an MRI is prescribed. Mostly, bone tissue is studied using MRI. In this aspect, tomography is really better and more accurate than ultrasound. Therefore, if you ever wonder what is better, ultrasound or MRI, say, of the knee joint or the spine, do not hesitate - MRI will be more productive.
Accordingly, ultrasound examination will give better results in diagnosing soft tissues: perinatal examinations (before, during and after childbirth), cardiovascular examinations, and so on. When deciding which is better, magnetic resonance imaging or ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, a good specialist will most likely refer you to an ultrasound scan first. If you have kidney problems, an ultrasound will also be preferable to an MRI. This is the first stage of diagnosis. MRI visualizes organs in more detail and clearly.
The question of what is more accurate, ultrasound or MRI, stands apart. If we look at it objectively, ultrasound provides only flat images in 2D format, and MRI provides full three-dimensional images, so much more information can be obtained using this study, and its reliability will be higher.
Methods
The study included 500 patients with non-ischemic heart failure. Patients were randomized to routine or selective cardiac MRI. The routine strategy involved echocardiography and MRI, the selective strategy involved conducting one or the other study, based on the clinical picture.
Heart failure classification and imaging review were performed 3 months after the study.
The total follow-up period was 12 months.
What to choose, ultrasound or MRI?
It all depends on the purpose and place of study. For oncology, diseases of the nervous system or musculoskeletal system, MRI is preferred. The main positive factor in oncology is the ability to monitor the condition of the tumor without undergoing painful procedures, such as biopsies.
In addition, there are areas that are inaccessible to ultrasound (spinal cord, inner ear).
During an MRI, a person is at rest for a long time (up to 40 minutes), so it is quite problematic to carry out this procedure on a child or a person who, due to health reasons, is unable to remain motionless for a long time.
When to choose tomography?
MRI is often confused with computed tomography (CT). Despite the similar output result - three-dimensional images - the mechanisms of the procedures are different. MRI, as mentioned earlier, works with magnetic fields, while CT uses x-rays. The advantage of CT over MRI is a better reflection of bone tissue. But if you take the price, there is no fixed difference.
When should you choose ultrasound?
Ultrasound has the following advantages:
- no contraindications;
- short procedure time (MRI takes about half an hour, ultrasound – 10 minutes);
- availability.
However, we should not forget that the correct interpretation of the result depends only on the specialist.
Significant disadvantages of ultrasound: distortion of the image in cases of obesity of varying degrees and meaninglessness in the early stages of diseases. MRI is more informative than ultrasound. For problems with the hip joints (which is often found in older people), preference is also given to magnetic resonance imaging, if possible, rather than ultrasound.
results
- Of the 500 patients, 344 were men. The average age of the patients was 59±13 years. The proportion of patients with HF with preserved ejection fraction was 7%; the mean left ventricular ejection fraction was 29%.
- 24% of patients in the selective management group underwent MRI.
- In the routine and selective groups, the rate of detection of a specific etiology of heart failure after 3 months was comparable (44% vs. 50%, respectively, p = 0.22).
- Re-interpretation of the image performed after 3 months did not reveal differences in the etiology of the disease (34% routine tactics vs. 30% selective tactics, p = 0.34).
- Patients with a specific etiology of heart failure had more clinical events than patients with a nonspecific etiology based on image classification, 19% vs. 12% respectively, p = 0.02, but not by clinical assessment, 15% vs. 14%, p = 0.49.
Cost difference
The difference in cost depends on the scope of the study and the number of zones. If you need an MRI of the whole body
, then the price will be high. However, this factor is not decisive. These procedures have different indications. In particularly serious cases, when it comes to, for example, problems with the spine, it is better to undergo a magnetic resonance examination rather than an ultrasound, because bone tissue cannot be viewed with ultrasound.
So, what is better, ultrasound or MRI? You can read a lot about these procedures, but the most rational option is to consult with a specialist and get a medically sound answer for your case.
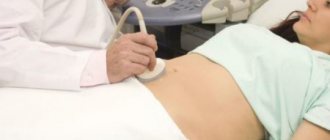
Abdominal ultrasound
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs is the most common diagnostic method, characterized by accessibility. With its help, you can get a good image of the internal organs located in the pelvic area, abdominal cavity, and also examine the hip joints. Formations containing large amounts of water will be clearly visible. These include thrombosis, abscesses, and infiltrates. Most often, abdominal ultrasound is used to view the condition of the fetus during pregnancy, as well as to monitor its development. In addition, ultrasound is widely used to diagnose diseases of the genitourinary system, gastrointestinal tract, and thyroid gland.
Benefits of Ultrasound
- It does not have a negative effect on the body, as is the case with X-rays or CT with contrast, therefore it has no contraindications;
- can be used to detect pathological changes in the fetus;
- does not give any side effects;
- the most affordable diagnostic method;
- the minimum preparation that is required when performing internal organs located in the pelvis (you need to fill the bladder in advance).
Disadvantages of Ultrasound
- Usually used only as a primary method of examination, based on the results of which other, more accurate diagnostic methods are prescribed;
- used to examine a specific organ;
- pathologies can be seen in the “picture” only when they have become noticeable, that is, the method is not very suitable for the initial stage of the disease;
- there may be an error when decoding the results;
- in case of flatulence and severe obesity, this method of examining the abdominal cavity is inappropriate, as it will not give an adequate result.
What are the purposes of cerebral vascular examination?
Regardless of which specific examination method is prescribed to the patient, his head and neck vessels are always checked for:
•Presence or absence of blockages in vascular narrowings;
•Identification of disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels in asymptomatic disease;
•Checking the effectiveness of treatment already carried out;
•Identification of congenital defects in the structure of blood vessels of the corresponding section;
•Checking the tone of the walls;
•Detection of disruptions in venous blood flow;
•Presence of aneurysms, spasms, deformities.
Breast MRI instead of mammography
Traditionally, mammography is used as a screening test for early detection of breast cancer. However, irradiation of glandular tissues with X-rays can itself cause a tumor, so mammography is indicated from 30-40 years of age (depending on the restrictions in force in different countries). Therefore, when there are indications for examination in women under this age, MRI of the mammary glands is most appropriate.
The second advantage of breast MRI is due to the development of aesthetic medicine technologies. Mammoplasty, which uses implants, on the one hand limits the use of mammography (the implant does not allow achieving the required degree of compression of the breast tissue), and on the other, creates a demand for regular examination of the condition of the implants themselves. Both problems are successfully solved by “targeted” MRI of the mammary glands, performed using special coils that are equipped at both MIBS MRI Centers in Moscow.
We have all the moves recorded...
A lesser-known, but much more widely used advantage of tomography over ultrasound is the ability to register (record) images of the current condition for monitoring over time (for example, the growth of a tumor with prostate adenoma or suspected prostate cancer) or to receive remote consultation with a doctor (the second opinion) without the need for a personal visit. Recording MRI images on a disk or flash drive, as well as storage options in the “cloud” (the network of MIBS Diagnostic Centers provides a “personal account” service), where the entire array of images will be available around the clock from any computer with Internet access, significantly speeds up obtaining a consultation after an MRI - you do not need to wait for the radiologist to draw up a report.
The main thing to remember is that a specialist should decide on the choice of examination method. If you are not sure which examination will be more informative in your situation, call us to get an expert answer.