Transferrin is a blood plasma protein that is produced in the liver. Iron from food accumulates in the epithelial cells of the small intestinal mucosa. Transferrin takes part in the transport of iron from the site of absorption to the bone marrow, liver, and spleen. At the Yusupov Hospital, all conditions have been created for the treatment of patients whose transferrin saturation coefficient is outside the normal range:
- Laboratory technicians determine the coefficient of transferrin saturation with iron using modern techniques;
- For patients who have an increased or decreased percentage of transferrin in the blood, hematologists individually select therapy with modern medications;
- The tactics for managing patients with severe disorders of iron concentration in the blood are developed at a meeting of the Expert Council with the participation of professors, associate professors and doctors of the highest category.
General information about the study
This test in medical practice is most often used for the comprehensive diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia. To establish an accurate diagnosis and choose treatment tactics, a doctor needs to know not only the concentration of transferrin, but also its saturation rate (normally it is about 30%). The transferrin blood test
determines both the protein level and the iron-binding capacity of the blood serum. It indicates how much protein is able to bind to iron. Based on this indicator, the protein saturation coefficient is calculated (in the absence of pathologies, it is 10-50). Protein binds to microelements formed during the breakdown of red blood cells and those that enter the body along with food. Iron is a component of hemoglobin and muscle protein. It is necessary for the normal functioning of the body. The total content of this microelement in the body is 4-5 grams. About 0.1% of all trace element reserves circulate in the bloodstream.
If iron levels are below normal, transferrin concentrations increase. Thanks to this, the protein can contact the trace element, even if its concentration in the blood is very low. Protein levels are also influenced by diet, liver condition, and gastrointestinal function. When liver function is impaired, it loses the ability to produce sufficient amounts of protein, and its levels decrease. Its synthesis will also be below normal if a person consumes insufficient amounts of protein foods and in a number of other cases.
Transferrin
Transferrin transfers iron atoms from the gastrointestinal tract to the cells of iron-depositing organs, between the erythroid elements of the bone marrow and macrophages, and regulates the transport of iron into hepatocytes. Like all transport proteins, transferrin is synthesized in the liver and is also produced in small quantities in lymphoid tissue, mammary gland, testicles and ovaries. It is a glycoprotein with a MW of 76–77 kDa and has significant genetic polymorphism (more than 20 variants of primary structure disorders). Each transferrin molecule is capable of binding two iron atoms; binding requires the presence of bicarbonates.
Iron atoms are transported into the cell through the interaction of the iron-transferrin complex with specific receptors on the plasma membrane. The iron-transferrin complex penetrates into the cytosol, where the iron atom is released, and transferrin leaves the cell into the bloodstream, remaining capable of repeated and multiple binding of iron ions. Reticulocytes have the highest density of transferrin receptors on the plasma membrane. Iron in these cells binds to protoporphyrin to form heme, which when combined with globin forms hemoglobin or myoglobin.
The intensity of transferrin synthesis correlates with total iron reserves according to the feedback principle - when iron reserves are depleted, transferrin synthesis is activated, and when it increases, it decreases. When transferrin saturation is below 16%, the supply of iron to the erythrocyte lineage of the bone marrow becomes insufficient for hemoglobin synthesis, which leads to microcytosis and hypochromia. There is also a decrease in cell proliferation, which entails a decrease in the number of red blood cells. It should be remembered that transferrin is one of the “negative” acute phase proteins, i.e. in various inflammatory diseases, its concentration decreases, which can lead to errors in the diagnosis of iron deficiency.
Indications for the study
- Differential diagnosis of anemia;
- detection of hemochromatosis;
- malignant neoplasms;
- chronic infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- liver diseases;
- kidney diseases;
- pregnancy.
Conditions for collecting and storing the sample.
Sample without signs of hemolysis.
Research method.
To determine the concentration of transferrin in blood serum, immunoturbidimetry or immunonephelometry methods are used.
Increased values
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- pregnancy (last trimester);
- taking contraceptives, estrogen therapy.
Reduced values
- Hypoplastic, hemolytic, megaloblastic anemia, hemochromatosis, repeated blood transfusions, iron therapy;
- conditions characterized by a decrease in the concentration of iron in the blood serum and inhibition of synthetic processes in hepatocytes (protein starvation, acute and chronic infections, chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver, surgical interventions, neoplastic processes);
- loss of protein in chronic nephropathy, diseases of the small intestine.
Interpretation of results
The test results are assessed by a doctor; their use for self-diagnosis is unacceptable. When interpreting the results, the fact that the amount of protein is determined by the condition of the liver is taken into account. With iron deficiency, protein levels are increased. When interpreting the results obtained, the gender of the patient must be taken into account. For women, reference values are higher than for men. During pregnancy, indicators can increase significantly in the absence of any pathological changes in the body. The decrease in hepatic protein synthesis with age is due to physiological processes.
Protein deficiency
may be observed in the following cases:
- in the presence of liver cirrhosis;
- with frequent inflammatory and infectious diseases;
- in patients with hemochromatosis;
- with uncontrolled use of hormonal contraceptives;
- in patients with malignant neoplasms.
Excess protein
may indicate anemia.
Reasons for decrease and increase in indicators
In the diagnosis of diseases, a calculated value is used - the percentage of transferrin saturation with iron. Normally this figure is 30%. Anemia may be the cause of a decrease in transferrin iron concentrations. If the iron saturation coefficient of transferrin is increased, low molecular weight iron appears in the plasma. It can deposit in the liver and pancreas, causing damage.
In the third semester of pregnancy, the iron saturation coefficient of transferrin increases by 50 percent. The content of this protein decreases in older people. The percentage of transferrin saturation with iron is reduced in the acute phase of inflammation. Low transferrin and low iron saturation percentage lead to undesirable consequences.
What else is prescribed with this study?
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
1.21. Venous blood 1 day
290 RUR Add to cart
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
1.20. Venous blood 1 day
290 RUR Add to cart
Alcohol dehydrogenase 1B (class I) ADH1B: ADH1B*2 (Arg48His; Arg47His)
GN0007 Venous blood, DNA extraction 3 days
990 RUR Add to cart
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 ALDH2: ALDH2*1/*2 (Glu504Lys; E504K)
GN0017 Venous blood, DNA extraction 3 days
990 RUR Add to cart
Pancreatic amylase
1.23. Venous blood 1 day
440 RUR Add to cart
Urine analysis “Bad habits” (alcohol, nicotine, narcotic and psychoactive substances - more than 800 representatives)
1.91.1 Urine 6 days
RUB 3,500 Add to cart
Complete blood count without leukocyte formula (venous blood)
3.1.1. Venous blood 1 day
330 RUR Add to cart
When is a test ordered?
There are many indications, given the important role siderophilin plays. If we talk about the reasons for the examination:
- Frequent dizziness. Occurs in diseases for which an increase in free iron in the blood is typical. It is possible that the brain is affected. On the other hand, similar symptoms occur with element deficiency.
Since there is not enough iron, little hemoglobin is produced to carry oxygen to the central nervous system.
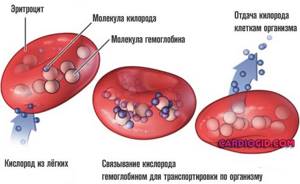
These tissues are very demanding on cellular respiration and nutrition. Therefore, neurological manifestations occur immediately.
Additionally, severe, regular headaches develop. Possible nausea and vomiting.
- Weakness. Asthenic syndrome. A natural continuation of the previous phenomenon. Drowsiness, a feeling of exhaustion - these symptoms are almost always caused by disorders of the brain.
Consequently, the cause must be sought in the poor supply of oxygen to cerebral structures. It may well be that transferrin is not the culprit. The doctor prescribes the analysis at his own discretion.
- Anemia. Most often iron deficiency. When the body does not receive enough substance, the production of siderophilin decreases. This is how the body saves energy.
If the element is supplied in sufficient quantity, but is not absorbed, the reverse process occurs. The concentration of free transferrin increases, which should not happen: most of the protein is in a bound state.
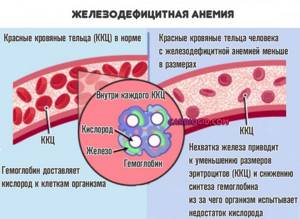
This is an informative technique for diagnosing anemia. But for determining its other forms: megaloblastic, etc., the method is not suitable.
- Heart rhythm disturbances. Especially if the reason for this could not be found earlier. We are talking about tachycardia (rapid heartbeat). This occurs against the background of insufficient cellular respiration of the myocardium. Muscle tissue is also extremely demanding of oxygen.
Gas transportation is impossible without hemoglobin. And the synthesis of this, in turn, without a sufficient amount of transferrin. Therefore, any rhythm deviations can occur due to siderophilin deficiency. Although this is relatively rare.
- Errors in other laboratory parameters. Especially if the number of red blood cells is changed.
- Pain in the liver.
- Disorders of the digestive tract. Occurs with excess iron. This is precisely a consequence of the fact that its toxic ions circulate freely throughout the body. Normally, almost the entire element is associated with transferrin. The disease is indicated by an excess amount of iron in the blood.
There are many indications. The list is far from complete. The doctor may order an examination for other reasons. This question is best left to the specialist himself.
References
- Mental and behavioral disorders caused by alcohol consumption. Alcohol dependence syndrome. Clinical recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 2018.
- Myagkova M.A. Determination of markers of chronic alcohol abuse using capillary electrophoresis. // Myagkova M.A., Pushkina V.V., Petrochenko S.N., Morozova V.S. — International Journal of Applied and Fundamental Research. 2015. No. 12-9. pp. 1640-1643.
- Sakran JV, Mehta A, Matar MM, Wilson DA, Kent AJ, Anton RF, Fakhry SM The Utility of Carbohydrate-Deficient Transferrin in Identifying Chronic Alcohol Users in the Injured Patient: Expanding the Toolkit. J Surg Res. 2021 Aug 17;257:92-100. Doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2020.07.027.
Additional examinations
Increased or decreased transferrin is an informative indicator; deviations indicate disorders: from liver pathologies to tumor processes.
However, it is impossible to say anything specific based on the level of siderophilin alone. We need auxiliary techniques.
- Oral interview and history taking. The very beginning of diagnosis. Based on the symptoms and lifestyle characteristics, one can draw conclusions about the origin and essence of the disorder.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. The liver is closely examined. To a lesser extent the intestines.
- Hormone tests. Biochemical blood test. With determination of ALT and AST.
- If necessary, MRI or CT is prescribed. Tomographic techniques are especially important in diagnosing cancer and oncology in general.
- Cardiography. ECHO-KG.
- This is just a small part. What exactly and how to examine is decided by the doctor, at his own discretion.
Transferrin is a special transport protein. It transports iron and makes cellular respiration possible. Many other functions also depend on this substance.
All deviations are grounds for in-depth examination of the patient. Treatment is prescribed as needed, if indications exist. With timely treatment, there is every chance to forget about the problem and fully recover.