Colposcopy is a classic method for diagnosing gynecological diseases. When examining the condition of the vagina, vulva and cervix, the gynecologist uses a special device called a colposcope. Colposcopy is an effective tool for detecting many female pathologies, including precancerous conditions.
APPOINTMENT WITH A GYNECOLOGIST – 1000 rub. Extended colposcopy - 1500 rub. CONSULTATION WITH DOCTORS ON THE RESULTS OF ULTRASOUND AND ANALYSIS - 500 rubles!
CLICK TO SIGN UP
Many women experience great anxiety before a colposcopic examination. This happens due to simple ignorance. Colposcopic examination is a simple and painless, but extremely necessary gynecological procedure.
What is colposcopy
The content of the article
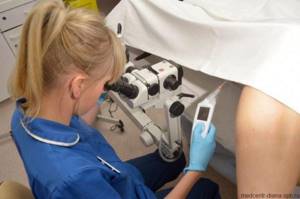
Colposcopy is a detailed examination of the internal female organs accessible to the gynecologist using a special microscope with built-in lighting - a colposcope. The procedure is similar to a regular gynecological examination - the vaginal walls are spread apart with a speculum, and the examination itself lasts no more than 20 minutes. Colposcopy is the choice of all modern medical centers.
To date, colposcopy is the only procedure that detects cancer in the early stages of development.
What does a colposcope show: why is colposcopy needed?
Using a colposcope, a gynecologist can examine the vaginal part of the cervix and the entire vagina - the organs most often suffering from infection, tumor processes and erosion.
Colposcopy reveals many diseases, even those at an early stage of development and occurring without any symptoms (latent, hidden), while providing extremely accurate research results. The device sees all changes in the mucous membrane, and the magnification of the image can be varied. In addition, problem areas can be removed and stored electronically, using the images later to compare the results of therapy, as well as for consultations with colleagues, without involving the patient.
The results obtained during colposcopy are already a reason to make a preliminary diagnosis. The gynecologist makes the final conclusion after receiving a response from the laboratory, where tissue samples taken during colposcopy are sent for cytological and histological examination. The diagnosis established during a complete examination is 100% reliable.
Abnormal colposcopic patterns
The presence of pathological changes may be indicated by detection during extended colposcopy:
- acetowhite epithelium;
- iodine-negative zones;
- signs of leukoplakia;
- punctuation;
- mosaics;
- atypical transformation zone;
- signs of invasive cancer.
All these cases require an individual approach and additional diagnostic procedures, including biopsy, PAP test, etc. Mild lesions are characterized by the detection of dense acetowhite epithelium with clear boundaries, delicate mosaics and punctures. With pronounced changes, rapid whitening of the treatment area is observed with the appearance of dense acetowhite epithelium and a rim around the open glands. Also in such situations, rough mosaic and punctation, signs of tuberosity, are observed.
Separately, mixed colposcopic patterns are distinguished, which are difficult to unambiguously classify. These include such “findings” as genital warts, inflammatory processes, atrophic changes in the mucous membrane, endometriosis, polyps, etc. In such cases, treatment is also prescribed, which can be either conservative or surgical, or additional examination.
Acetowhite epithelium
The appearance of areas of white or acetowhite epithelium when exposed to 3% acetic acid is one of the most important signs of pathology. Most researchers agree that the vast majority of areas in which the development of malignant processes is observed turn white with varying intensity under the influence of acetic acid.
Detection of acetowhite epithelium is typical for all degrees of CIN and makes it possible to diagnose the presence of changes at the earliest stages of development. CIN refers to cervical dysplasia, which is accompanied by the formation of cells with varying degrees of atypia in the covering epithelium. Untreated dysplasia can lead to cervical cancer, and each case of its development is the result of missed opportunities and ignoring the importance of regular colposcopy.

It is important to differentiate white epithelium from areas of dyskeratosis, i.e. leukoplakia. Some blanching of the mucous membrane can also be observed with:
- disturbances in the structure of epithelial cells;
- inflammatory process;
- papillomavirus infection;
- some other benign changes.
The more intense the whitening of the tissue and the longer it persists after exposure to acetic acid, the more serious and profound the changes.
Iodine-negative zones
A typical sign of pathology is the identification of so-called silent iodine-negative areas of the mucosa after applying Lugol's solution. In most cases, they are represented by keratinized epithelium and require a more detailed examination by performing a biopsy.
Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia is a pathology accompanied by keratinization of the epithelium of the vagina, vulva or cervix. Colposcopically, it looks like a white spot of arbitrary shape with clear boundaries, which can be noticeable even before treatment of the mucous membrane with solutions. Most often, leukoplakia is observed in the area of the transformation zone and can have different sizes. The true size of the modified area is determined after treatment with Lugol's solution, since it does not turn brown. The main danger of leukoplakia is the inability to determine, without the use of invasive methods, what changes are located under the layer of keratinized cells. Therefore, if it is detected, a targeted biopsy is indicated.
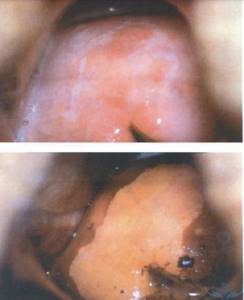
punctuation
Puncture refers to multiple red dots on the background of the epithelium, caused by its atypical vascularization, i.e., the formation of blood vessels. The degree of violation is determined based on the size and uniformity of the points. They are clearly visible after exposure to acetic acid, and sometimes have the appearance of papillae.
Mosaic
This term refers to the zone of the mucous membrane, which, after treatment with acetic acid, is delimited by red lines into yellowish-white segments. This area is devoid of open and closed glands. Based on the intensity of the mosaic, the degree of tissue damage is determined. Thus, with a rough mosaic, the mucous membrane takes on the appearance of a paved pavement, but more often a delicate mosaic is observed - the segments do not protrude above the level of the surrounding tissues and have a marble pattern. Most often, the mosaic is iodine-negative.
Atypical transformation zone
It is formed on the basis of normal ST, but differs in the presence of:
- atypical blood vessels;
- acetowhite epithelium;
- keratinized glands;
- leukoplakia;
- mosaics;
- punctuation;
- areas not stained with iodine.
This indicates the presence of significant changes in the structure of the epithelium and the likelihood of developing dysplasia.
Invasive cancer
The most distressing “finding” during colposcopy may be the discovery of signs of invasive carcinoma:
- atypical transformation zone with uneven tuberosity and the presence of a limited area rising above the level of surrounding tissues (plus tissue);
- ulcers;
- atypical vessels, characterized by fragility, which leads to bleeding.
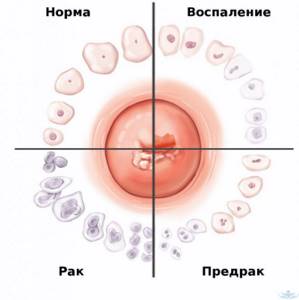
As a rule, oncology develops against the background of benign changes in the cervix, which were not diagnosed and eliminated in time.
Thus, the possibilities of colposcopy are truly wide, and its accessibility, low cost and ease of implementation are its indisputable advantages. Therefore, it is important not to ignore preventive gynecological examinations and doctor’s recommendations to perform colposcopy. Often this is what makes it possible to diagnose severe pathologies in the early stages, carry out the necessary treatment and save the patient’s life.
0 0 votes
Article rating
What diseases can be detected by colposcopy?
The main goal of cervical colposcopy
uterus - determination of the following diseases and pathologies:
- genital warts that can transform into cancerous tumors;
- cervical cancer;
- cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix);
- precancerous changes affecting the tissues of the vagina, cervix, vulva;
- vulvar cancer;
- vaginal cancer.
When is colposcopy performed?
The main goal of a colposcopic examination is the timely diagnosis of cervical pathologies. Colposcopy is definitely prescribed if:
- Cervical cytology results show dysplasia. Colposcopy of the uterus in this case will show the specific area of the cervix where the modified cells are located. If foci of pathological epithelium (covering tissue) are detected during colposcopy, the gynecologist immediately performs a biopsy.
- During a standard gynecological examination, the gynecologist detects suspicious areas on the surface of the cervix. The method reveals areas of modified epithelium (upper integumentary layer), which cannot be detected without the use of video equipment.
In addition, indications for the procedure are:
- Control of local treatment.
- Genital warts detected on the cervix.
- The woman is worried about itching, unpleasant odor, discharge and rashes in the vaginal area.
- During sexual intercourse, pain is felt, then a discharge mixed with blood or pus is noticeable.
- Prolonged nagging pain in the lower abdomen, not related to typical menstrual ailments.
- Bleeding outside the cycle.
- Swelling, growths, ulcers in the genital area.
- Decreased desire.
- Difficulty conceiving;
- Missed pregnancies , miscarriages .
Colposcopy falls into the category of preventive procedures that every woman must undergo annually.
Types of calposcopy
There are five types of this survey:
- survey;
- with color filters;
- extended;
- chromocolposcopy;
- colpomicroscopy.
In the first case, the cervix is examined under magnification without chemicals.
The second method involves the use of light filters, most often green. It is this that makes it possible to thoroughly study the network of blood vessels in the uterine area. With an extended type of calposcopy, chemical reagents are used, which, depending on application to a particular area of the internal genital organs, may indicate certain pathologies. Speaking about the last two methods, it should be noted that:
- Chromocolposcopy is one of the options for advanced diagnostics, which involves changing the color of the cervical epithelium with hematoxylin, eosin or methylene blue. The presented dyes perfectly identify cells, which makes it possible to determine the presence of dangerous foci at the cellular level;
- Colpomicroscopy is the study of previously stained parts of the cervical epithelium under significant magnification. It can range from 160 to 280 times. Experts note that this method is a combination of two methods: histology and cytology.
How to prepare for the procedure
To obtain an accurate result, colposcopy is recommended to be performed in the first 2-4 days after the end of menstruation. It is not forbidden to carry it out on another day of the cycle, with the exception of menstruation, since the discharge will not allow a thorough examination of the organs.
An important point is that it is better to undergo colposcopy in the first phase of the cycle. After ovulation, a large amount of mucus accumulates in the cervical canal, so sometimes the results are distorted. In addition, in the second half of the menstrual cycle, tissue regenerates much more slowly, which increases the likelihood of discomfort during the procedure.
Preparation for colposcopy requires compliance with the following rules:
- Refusal of sexual contacts 2 days before the procedure;
- During this period, it is prohibited to use vaginal suppositories, sprays, tablets and creams, or douche. If a woman is undergoing therapy using them, she should consult a gynecologist about this.
- Do not take a bath, but temporarily switch to a shower.
- Personal hygiene should be carried out only by washing the genitals with water, without the use of special means.
Preparation for cervical colposcopy
Before the examination, you must abstain from vaginal sex for 48 hours and not use tampons for the same long time. It is recommended to take any over-the-counter pain reliever before starting the procedure. Let's say Ibuprofen or Paracetamol.
The date for the analysis should be chosen so that it does not fall during menstruation. A prerequisite for preparation is compliance with personal hygiene standards.
We recommend reading: what does Remens help with?
How is the procedure performed?
This procedure is painless and can be completed in just 5-10 minutes. The doctor conducts an examination as usual, on a gynecological chair. First, the vaginal speculum is inserted, then the colposcope itself. During the examination, the gynecologist takes swabs from the mucous membrane for study in the laboratory. To avoid discomfort and unpleasant sensations, the patient should sit in it as comfortably as possible and, most importantly, relax.
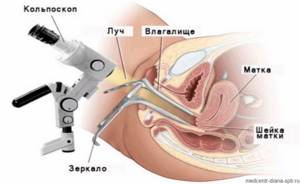
During the examination, a colposcope is used, which includes a lighting device and a binocular. To make the cervix accessible for examination, the vaginal walls are spread apart using a speculum (gynecological instrument), as during a standard examination in a chair. The duration of the procedure is on average 10 - 15 minutes.
Using the device, the doctor can see ruptures, tumors, deformations, and inflamed areas.
If there are indications, additional tests may be used: the use of optical filters, treatment of the cervix with a solution of acetic acid, and so on. This is required to diagnose tissue areas where dysplasia is suspected. Samples reveal hidden defects in the mucosa - the initial stages of erosion and other pathologies.
Is the procedure performed after childbirth?

After the birth of the baby, this examination helps to assess the condition of the cervix and vaginal walls, to identify possible problems in the process of their recovery after ruptures. You also need to take into account that after childbirth, ectropion may appear, which is precisely what colposcopy helps to assess.
As for the time of colposcopy, it should be carried out after the end of lochia discharge and after the cervix is fully formed after childbirth, that is, no earlier than 43 days. If changes are detected, a repeat study is scheduled after 6 months, or after completion of lactation and restoration of the menstrual cycle.
Extended colposcopic examination
An extended examination is carried out as follows:
- The gynecologist inserts an ordinary dilator and a speculum into the woman’s vagina, and a colposcope is installed 10-15 cm from the entrance to the vagina.
- Using a cotton ball, a weak solution of acetic acid (3-5%) is applied to the surface of the mucosa. Using the device, the gynecologist monitors the condition of the blood vessels: healthy tissues contract, but no pathological changes occur.
- The surface of the mucous membrane is treated with Lugol's solution or iodine (the patient may feel a slight burning sensation). The gynecologist evaluates the reaction of the tissues: healthy ones should turn the color of the solution, affected ones should not change color.
- If pathological areas of the mucous membrane are detected, the doctor takes a biopsy test - “pinches off” a particle of the affected tissue.
Women should not worry: the colposcope is not inserted into the vagina, and the procedure itself, although not particularly pleasant, is practically painless. Lasts no more than 30 minutes.
Extended examination gives great opportunities to the gynecologist. The doctor can
- Assess the condition of the mucosal surface.
- Take photographs and enlarge affected or modified tissues.
- Determine the nature of the neoplasm (benign, malignant).
- Take material for biopsy.
- Take a smear from questionable areas of the mucosa.
Despite a number of advantages, colposcopy is not a panacea. An accurate diagnosis can be made and treatment can be prescribed only after a comprehensive examination including tests for oncology.
Schiller test value
Of great importance in the differential diagnosis of normal and atypical patterns is the color shade and the clarity of the zone boundaries.
The presence of clear boundaries indicates an unfavorable situation. Benign lesions usually have less sharp, blurred contours.
Thus, the test expands diagnostic capabilities and allows:
- preliminary assess the degree of damage, size, depth and number of pathologically changed areas;
- determine patient management tactics;
- evaluate the effectiveness of treatment measures,
- to clarify the features of changes in stratified squamous epithelium under various physiological conditions (pregnancy, menopause, contraception).
What diseases can be detected using extended colposcopy?
This procedure is indispensable when detecting the following pathologies:
- Chronic cervicitis is inflammation of the cervix.
- Cervical erosion – changes in the structure of mucous areas on the cervix. If the pathology is not treated, then there is a great threat of infection of the uterus, infertility, and subsequent development of oncology.
- Ectopia (pseudo-erosion) is the result of displacement of endocervix cells beyond the boundaries of the external os. Under the age of 25, this is often a physiological norm, but in older women it is a fact of the presence of an inflammatory process as a result of infection.
- Genital warts (papillomas, condylomas) are benign formations that can develop into malignant ones if left untreated.
- Leukoplakia is a lesion of the mucosal surface, manifested in keratinization of the epithelium. There is a risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor.
- Dysplasia is a precancerous change. Mild pathology rarely develops into a tumor, unlike grade 2 and 3 dysplasia.
- Oncological diseases.
Common Causes
The appearance of vaginal mucous secretion of unusual color and consistency after colposcopy most often means that during the examination the doctor used medicinal solutions to identify the boundaries of the affected areas on the cervix. Since iodine or Lugol, which have a dark tint, is mainly used for this purpose, this helps to change the characteristics of the discharge. They may become brown, yellow, orange, reddish, and thicker than usual.
It is for this reason that, after completing the examination, the specialist recommends that his patients use a sanitary pad to avoid getting the medicine on their underwear. He warns in advance that such discharge can be observed for up to 5 days and there is nothing to worry about.

You should contact your gynecologist again if, after this time, the production of vaginal secretions does not stop, but, on the contrary, intensifies, or other symptoms appear, for example, abdominal pain, weakness and bleeding.
The presence of spotting a few days after colposcopy is harmless only if the procedure was carried out on the eve of menstruation. When there are more than 9-14 days left before menstruation, the appearance of blood should alert the woman and force her to visit a doctor.
After colposcopy: complications
After a simple examination, no consequences or restrictions are expected, since the gynecologist did not come into any contact with the uterus. After dilation, a woman may experience dark brown discharge, but one should not be afraid of them: this is the remnants of Lugol’s solution. Also characteristic is nagging pain in the lower abdomen for 4-10 days.
There are cases when an infection gets into a woman’s vagina, resulting in inflammation and accompanying symptoms. But this fact does not directly relate to colposcopy; this occurs due to the negligence of the gynecologist who allowed the infection to occur. Or the infection may have been picked up before or after colposcopy, but until now it has not actively developed.
Some patients continue to bleed for 2 days after the procedure. In this case, only pads are allowed, tampons are prohibited. This happens quite rarely and is not a reason to contact a gynecologist. The exception is pregnancy.
As a rule, there are no other consequences after the procedure.
Colposcopy during pregnancy
Colposcopic examination is prescribed for pregnant women only in extreme cases. It is mainly carried out due to suspicion of cervical erosion, which is now common in young women. In this case, the procedure should be performed by the most experienced gynecologist. In addition to erosion, colposcopy will help identify many other diseases in a pregnant woman, the timely diagnosis of which is important both for the unborn child and for the woman herself.
The examination should be carried out as carefully as possible, otherwise there is a high probability of dire consequences - bleeding, miscarriage in the first trimester or premature birth at a later date. A biopsy during pregnancy may produce the same result. Without a threat to health, it is recommended to carry out it in the postpartum period (after 1.5-2 months).
Recommendations after the examination
After a simple colposcopy, you are expected to lead a normal lifestyle. But the extended one, especially in combination with a biopsy, requires compliance with the following rules for 1-2 weeks:
- personal hygiene using detergents is prohibited;
- refuse to visit the bathhouse, sauna, or take a bath;
- take a shower only;
- sexual activity is prohibited;
- do not use tampons (only pads), do not douche;
- limit yourself from heavy physical activity and sports;
- Do not take acetylsalicylic acid or medications containing it.
- You should immediately consult a doctor if:
- body temperature has risen above 38°C;
- heavy bleeding does not stop for more than a day;
- there was severe pain, chills, dizziness, the general condition deteriorated sharply;
- purulent discharge appeared;
- discharge with blood continues for more than 5 days.
Where to get a colposcopy in St. Petersburg
This diagnostic technique is classified as subjective, since the medical opinion is made based on what is seen, without confirmation by tests. Therefore, in order to accurately assess the situation, the gynecologist must have extensive experience and high qualifications. These are the specialists who work at the Diana Clinic (St. Petersburg). Specialists have a new colposcope with powerful magnification at their disposal. In the clinic you can undergo colposcopy at any time convenient for you.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter