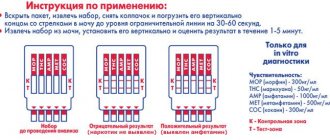
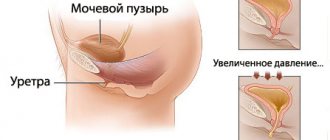
In the field of urology, urolithiasis is becoming an increasingly common and extremely serious problem. With this disease, the human urinary system is unable to remove salts of certain metals from the body, which crystallize and eventually turn into stones.
The greatest danger to health is posed by phosphate stones (or tripel phosphates) - compounds of calcium salts with phosphoric acid, which have the ability to quickly increase in size and cause the most destructive damage. Tripelphosphates in the urine - a need to quickly consult a doctor.
Problem Definition
Tripelphosphates are stones formed by calcium salts of phosphoric acid, formations that practically do not manifest themselves in terms of symptoms, but are clearly visible on x-rays. Phosphate is a smooth calculus, without sharp edges, so its movement through parts of the urinary system is not accompanied by tissue damage and, therefore, a characteristic symptom - bloody inclusions in the urine. Stones formed by calcium phosphate can grow very quickly, forming coral-shaped structures that can fill the entire kidney cavity within 2-3 weeks.
Crystallized tripelphosphate salts in the urine indicate the need to consult a doctor as soon as possible, as they are very aggressive formations. The only positive point is that the stones have a rather fragile structure, so they are relatively easily destroyed by crushing (lithotripsy). However, if a sick person seeks medical help too late, the enlarged stones will only allow themselves to be removed along with the removal of the entire kidney.
Modern methods of treatment
Leukocytes in the urine themselves are not treated in any way - they are a symptom of certain diseases.
Therefore, all treatment will be aimed at eliminating diseases or conditions manifested by leukocyturia. If these are acute inflammatory processes of the urinary tract caused by bacterial infections, antibiotics are used, which are selected taking into account the pathogen.
For non-infectious diseases, anti-inflammatory drugs, additional fluid intake, diet and medications are prescribed to eliminate the underlying cause of the disease.
In case of surgical pathologies, surgery is recommended, after which additional drugs are prescribed for tissue restoration.
Why are phosphates formed?
The main reason for the formation of tripel phosphate stones is a violation of the acid-base balance in the body, characterized by an increase in the alkaline reaction of urine. The acidity level is 5.5-6 pH, the level at which the formation of stones becomes impossible. If there is a “skew” towards increasing alkalinity, urolithiasis begins, leading to serious disruptions in the functioning of the urinary system.

The second factor in the appearance of tripelphosphates in the kidneys and, as a result, in the urine is infectious lesions of the urinary tract, such as cystitis and pyelonephritis, which is why the formations are often called “infectious stones.”
The causes are:
- infection of the body with gram-positive (staphylococci) or gram-negative (pseudomonas aeruginosa) bacteria, as well as fungi (candida);
- undergoing steroid therapy;
- problems with uncontrolled urination.
Also, tripelphosphates in the urine can appear in cases where the upper urinary tract is affected by injury or surgery.
Sometimes the cause of crystallization of calcium salts is an incorrect diet, that is, a predominance in the diet of:
- plant food;
- low-fat fish;
- milk and dairy products.
Violation of the alkaline composition of urine due to heavy consumption of the listed products is not a pathological condition - with correction of the diet, the problem with violation of the acid balance of urine will disappear by itself.
Recommended topic:
Stones in the ureter
Problems with tripel phosphates sometimes arise in expectant mothers - the “pregnant” body suffers from various malfunctions and disturbances in the most common processes. Among other things, women may experience kidney problems, leading to poor dilution of mineral salts and their crystallization.

Important: in a child, the detection of phosphate stones in the urine means the presence of pathology in quite rare cases; most often, this test result appears due to poor nutrition (especially with increased consumption of soda).
Tripelphosphates in urine in children
Doctors say that in children this disease usually develops against the background of a genetic predisposition. If one of the parents has an increased level of phosphates in urine, the likelihood of developing the disease will be about 35–40%.
And the development of the disease can also be triggered by poor nutrition and excessive consumption of foods with preservatives and carcinogens. As practice shows, the likelihood of developing pathology increases in children suffering from rickets, diabetes mellitus and pyonephrosis.
Symptoms of Phosphate Stones
Since the formation of tripelphosphates in the kidneys and their loss into the urine occurs mainly under the influence of infectious agents with accompanying predisposing factors, the main symptoms of the condition are characteristic of the inflammatory process:
- chills alternating with fever;
- nausea;
- loss of appetite;
- general weakness.
The development of kidney stones can be accompanied by such phenomena as an unpleasant odor of urine, as well as:
- urinary disorders (difficulty due to frequent urge);
- abdominal pain (not too intense, dull and aching);
- increased thirst;
- acute disturbance of urine outflow;
- malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract.
Important: the very first symptom from the above list should be the reason to consult a doctor, since the presence of phosphate stones in the urine is dangerous due to the stimulation of inflammatory processes and the active increase in size of the formations, followed by filling of the kidney.

Causes of crystalluria
Almost all types of urinary crystals can be detected in small quantities in a random urine sample from any healthy person. One should suspect any disease or pathological condition only if they are constantly present and in large quantities. The exception is crystals of cholesterol, amino acids and bilirubin, the detection of which always indicates the presence of pathology.
Oxalate crystalluria
The most common salts found in urine are oxalates. Normally, about 30 mg of oxalates are excreted in the urine per day in a dissolved state. They begin to crystallize when urine is left at room temperature for a long time. They have the shape of colorless octahedra, in appearance reminiscent of postal envelopes or pyramids. Oval-shaped oxalates, like hourglasses and gymnastic weights, are also found.
Sometimes it is difficult to differentiate ovoid oxalates and red blood cells based on morphology. To do this, add a drop of acetic acid to the urine sediment, which causes lysis of red blood cells. With parenchymal or obstructive jaundice, ovoid oxalates are stained yellow or dark yellow with bilirubin, while oxalates in the form of octahedrons remain colorless. Spherical oxalates, similar to fat droplets, are found in patients with chronic glomerulonephritis.
There are primary and secondary crystalluria. Primary oxalaturia (oxalosis) is a genetically determined metabolic disorder in which there is deposition of oxalates in the internal organs, their excretion in the urine increases, which contributes to the rapid development of calcium oxalate urolithiasis.
Secondary oxalaturia can have many causes:
- Eating foods high in oxalic acid (spinach, sorrel, potatoes) and ascorbic acid (citrus fruits, rose hips).
- Taking excess vitamin C.
- Vitamin B6 deficiency.
- Diseases accompanied by malabsorption syndrome - celiac disease, Crohn's disease, chronic pancreatitis.
- Dehydration.
- Previous operations on the intestines.
- Ethylene glycol poisoning.
- Oxalate urolithiasis.
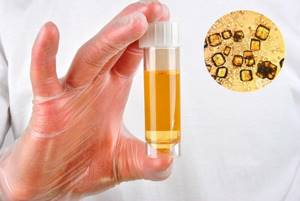
Crystalluria
Urate crystalluria
In second place in terms of frequency of occurrence is urate crystalluria. When present in large quantities, uric acid crystals turn urine brick-red. Most often, urates are diamond-shaped, yellow or brownish in color, and sometimes colorless. When taking acetylsalicylic acid, they may turn gray-violet or black. In some cases, urates have pronounced polymorphism - they can be presented in the form of a barrel, a grindstone, or a spindle.
Sometimes they resemble crystals of cholesterol, cystine, or red blood cells, which makes it difficult to identify them. The ability of urates to dissolve in sodium and potassium hydroxide, as well as information about the urine environment (must be acidic), helps in differential diagnosis. This type of crystalluria can be found in a healthy person whose diet consists mainly of meat foods.
Prolonged uraturia indicates a high concentration of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia) due to its increased formation. Uraturia can be observed in the following pathologies:
- Gout.
- Dehydration.
- Hemolytic anemia.
- Polycythemia.
- Tumor lysis syndrome when taking chemotherapy drugs (especially in patients with myelo- and lymphoproliferative diseases).
- Wilson-Konovalov disease.
- Diabetes mellitus type 2.
- Urate urolithiasis.
Phosphate crystalluria
There are 4 main types of crystals of phosphoric acid salts - amorphous phosphates, neutral magnesium phosphate, neutral calcium phosphate, tripel phosphates. The most common cause of phosphaturia is the consumption of dairy products, as well as large amounts of plant foods, which contribute to a shift in urine pH to the alkaline side. Other etiological factors:
- Urinary tract infection (tripelphosphates).
- Primary hyperparathyroidism.
- Vitamin D deficiency.
- Pathologies of the kidney tubules - renal tubular acidosis, aminoaciduria, phosphate diabetes.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Iron-deficiency anemia.
- Phosphate urolithiasis.
Amorphous phosphates
The synonymous name is phosphate soils. Under a microscope, they look like colorless amorphous masses, consisting of small balls and grains, grouped into piles of different sizes. Their presence in the urine often causes it to become turbid, and after centrifugation, a white precipitate resembling leukocytes forms at the bottom of the tube.
Tripelphosphates
Synonym: ammonia-magnesium phosphate. They are transparent, colorless crystals that resemble coffin lids. If the patient has a pathology of the liver or biliary tract, with prolonged standing of urine, tripel phosphates turn yellow with bilirubin.
Magnesium phosphate
Synonym: neutral magnesium phosphate. Crystals can have different shapes - oblong tablets with strong light refraction, trapezoid, flat plate.
Calcium phosphate
Another name is neutral phosphate of lime. The crystals are colorless prisms with pointed ends. They can be located isolated or grouped, forming rosettes. Sometimes they look like plates or bundles of needles resembling tyrosine.
Carbonaturia
Calcium carbonate in urine is rare. Salts have the form of small balls, molded together, folded into the shapes of drumsticks or gymnastic weights. Often combined with tripelphosphates and amorphous phosphates. They are better visualized after urine has been kept in room conditions for a long time. Calcium carbonate can be seen in the urine of a person who eats a lot of plant foods.
Hippuraturia
A healthy person excretes small amounts of hippuric acid in the urine. An increase in its concentration with subsequent crystallization can occur with the consumption of fruits and berries (lingonberries, plums, pears), benzoic and salicylic acids. Hippuraturia is also characteristic of putrefactive colitis, liver diseases, and gall bladder. Hippuric acid has the form of colorless rhombic tablets with beveled ends.
Bilirubin crystals
Bilirubin is a bile pigment and is excreted in urine in minimal quantities. As the concentration of direct bilirubin in the urine increases, it crystallizes. This is observed when liver cells are damaged (alcoholic or viral hepatitis, cirrhosis) or when bile outflow is impaired (cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, primary sclerosing cholangitis).
Bilirubin crystals can also be detected in diseases accompanied by proteinuria (glomerulonephritis, nephropathy due to autoimmune pathologies or hematological malignancies). This is explained by the fact that when the glomerular apparatus of the kidney is damaged, indirect bilirubin is able to enter the urine, which is not normally observed. Microscopically, bilirubin is presented in the form of yellowish-brown granules or needles collected in bunches. They are often superimposed on leukocytes, cells of flat, transitional epithelium.
Cholesterol crystals
When cholesterol crystallizes in urine, it takes the form of very thin diamond-shaped tablets overlapping each other. Often, along with them, it is possible to identify drops of fat, renal epithelial cells in a state of fatty degeneration, and hyaline casts with fat deposits. Reasons for detecting cholesterol in urine:
- Glomerulonephritis with minimal changes (lipoid nephrosis).
- Nephrotic syndrome.
- Echinococcosis of the kidney.
- Amyloidosis.
Amino acid crystals
Cystine
Cystine crystals are hexagonal thin plates of regular or irregular shape. For the purpose of differential diagnosis, a test for cystine is used - 5% sodium cyanide and 5% sodium nitroprusside are added to the urine. Purple-red coloration indicates the presence of cystine. There are 2 clinical forms of hereditary cystine metabolism disorder:
- Cystinosis - characterized by the deposition of cystine in organs and tissues, increased excretion of cystine in the urine and the formation of cystine stones in the kidneys.
- Cystinuria is a more benign form. The release of cystine is increased, the risk of stone formation is increased, cystine deposition in tissues does not occur.
There is also secondary or acquired cystinuria. Its reasons are as follows:
- Viral hepatitis.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Hepatolenticular degeneration.
Leucine and tyrosine
Normally, these amino acids are excreted in urine in small quantities. Their crystallization occurs with increasing concentration. Leucine is represented by matte-shiny balls of various sizes with concentric striations, located separately or in clusters. Tyrosine has the appearance of thin, small needles grouped into bunches or asterisks.
Crystalluria of these amino acids is observed with genetic metabolic disorders or extensive tissue and cellular decay:
- Tyrosinemia.
- Leucinosis (maple syrup disease).
- B-12 deficiency anemia.
- Leukemia.
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Myasthenia.
- Phosphorus poisoning.
Drug-induced crystalluria
Detection of drug crystals in urine often occurs with long-term use or overdose. The formation of drug crystals can block the kidney tubules and cause acute kidney injury. Basically, drug crystals have the form of thin needles or small rectangles. Most often, drug-induced crystalluria develops while taking:
- Antibiotics – ampicillin, amoxicillin.
- Antiviral agents - acyclovir, indinavir.
- Sulfonamides – sulfamethoxazole.
- Vitamin C.
- Barbiturates – phenobarbital.
- Antitumor drugs – methotrexate.
- Potassium-sparing diuretics – triamterene.

Urates under a microscope
How are they diagnosed?
After identifying tripelphosphate stones in the urine samples being tested, the doctor will refer the patient for additional diagnostic examinations, which begin with the following procedures:
- examination and questioning of the patient (lifestyle, professional activity, diagnosed diseases, medications taken, diet and fluid intake);
- palpation of the abdomen;
- general health assessment.
Next, the patient is sent for urine and blood tests for a biochemical study, which reveals:
- inflammation in parts of the urinary system with an increased content of leukocytes and protein metabolic residues;
- weakened immunity with a low platelet count.
A urine test (bacterial culture) is also carried out, the results of which make it possible to identify the specific pathogen that caused the infectious disease and, as a result, increased crystallization of phosphates.
Additionally, the urine test checks the following factors:
Recommended topic:
Ultrasound crushing of kidney stones
- volume of nitrogen, magnesium, phosphorus ions;
- concentration of substances that inhibit stone formation;
- acidity level.
If a pathological process is detected in the urinary system, the doctor will refer the patient to additional instrumental procedures - ultrasound, CT or MRI.
To prescribe optimal measures to combat the increased formation of tripelphosphates, the following diagnostic tools are needed:
- X-ray diffractometry;
- infrared spectrophotometry.
The procedures are necessary so that specialists can identify the composition of the formation and analyze it (doctors have a special table of the qualitative and quantitative content of components in various formations), thereby accurately determining the pathology for prescribing therapy - conservative or surgical.
Diagnosis is carried out by a urologist with the involvement, if necessary, of a nutritionist, endocrinologist and gastroenterologist.
2. How to prepare and how is the analysis carried out?
How to prepare for a urine phosphate test?
Various medications may change test results, so tell your doctor about all the ones you take.
How is a 24-hour urine test performed?
To test your urine for phosphates, you will need to collect all of your urine for the day except your very first morning urine. Record the time you collect your first urine. The next day at the same time the collection must be completed. All urine should be collected in one large container. Try to keep blood, feces, toilet paper, hair, and other foreign substances out of the container.
Treatment and prevention
An increased amount of tripelphosphates in the urine of a child and an adult is treated with medication and surgery. Conservative therapy allows you to dissolve the stone and suppress the infectious inflammatory process in the body. Surgery is used in cases where the phosphates have become large in size and have led to impaired kidney function.
Treatment and at the same time prevention of lesions of the genitourinary system is a diet followed during and after therapy. Doctors recommend:
- drink plenty of liquids – mineral water, fruit drinks, berry juices;
- add sour berries, poultry, beef to the diet, exclude milk and dairy products, fish and seafood, cereals, fatty meat and lard;
- eat small meals several times a day;
- limit the consumption of salt and foods containing starch.
- eliminate bad habits, including drinking carbonated drinks.
All therapeutic measures and prevention of relapse of the disease must be prescribed by a doctor who can monitor the patient’s condition.
An additional preventive measure is maintaining personal hygiene and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, which will help prevent the crystallization of calcium salts.
Unlike stones formed by salts of other metals, phosphate stones do not cause unnecessary pain to their “carrier”. Moreover, their danger lies in their rapid growth, due to which the patient has no chance of a quick and easy cure after just a few weeks. If tripelphosphates are detected in the urine, you should consult a doctor and begin taking medical care immediately.
Decoding the results: norm and deviation
An analytical assessment of bacterial culture is given after 48 hours of incubation. It is important that the laboratory test data be interpreted by the attending physician.
Interpretation of results
- The microbial concentration threshold of less than 1000 CFU/ml is “negative” (no microbial growth is observed);
- The number of bacteria more than 100,000 CFU/ml is “positive” (microbiological forms are present in the urine and can be pathogens).
- The concentration of microorganisms ranges from 103 to 105, indicating various clinical symptoms and is interpreted depending on the patient’s condition and general history.
Some people have multiple types of bacteria. If their number is more than 3, and the concentration in the crop is the same, then this indicates a mixed flora and no further identification is carried out.
In what cases is a false answer possible?
It is not recommended to take the test earlier than 2 weeks after completing the course of hormonal and antibacterial therapy. In such cases, there is a high probability of a false research result.
Also, an incorrect result can be obtained if the purity of the biological material is compromised. Or if it was provided to the laboratory later than 6 hours after collection and was stored at a temperature above +15 ˚С.