Poor nutrition, frequent exhausting diets, and a predisposition to cancer often lead to serious problems with the gallbladder. In the presence of stones or tumor formation, surgical intervention is indicated.
For some time the person becomes incapacitated. It is important to understand how long sick leave is issued after gall bladder surgery. This will help you adjust your plans and use your time for rehabilitation more efficiently.
Is a certificate of incapacity for work opened and for what period of time?
Gallbladder surgery or gallbladder removal (cholicystectomy) is performed in a hospital. In this case, patients usually stay in hospital for 5-7 days. A sick leave certificate is opened by the attending physician on the basis of Law No. 255-FZ for the entire period of the patient’s stay in the hospital.
Carrying out the operation both open (abdominal surgery) and laparoscopically requires keeping the patient in a hospital. In both cases, the attending physician opens a certificate of incapacity for work. How long do they stay in the hospital?
- After removal using laparoscopy. Postoperative hospital rehabilitation for gallbladder removal using laparoscopy usually lasts less than a week.
- After abdominal surgery. An open operation requires a rehabilitation period in hospital lasting about a week, in some cases longer.
Sick leave opens on the day of admission and closes on the day the patient is discharged. In this case, the time of incapacity for work is paid according to the law. What is the maximum period for which a certificate of incapacity for work is given for laparoscopy and surgery? The duration of the initially issued sick leave must not exceed 10 days.
If the ability to work has not been restored within 10 days, the attending physician may decide to extend sick leave to 30 days. Usually this time is enough for rehabilitation and the person’s readiness to begin work duties.
How long do you stay in the hospital after surgery?
All types of gall bladder surgeries are performed in a hospital setting. The patient is admitted to the hospital several days before the planned surgical intervention. During this period, tests are taken and preparations for manipulation are carried out.
How long you stay in hospital after gallbladder surgery depends on the following factors:
- type of surgical intervention;
- type of existing pathology;
- general health;
- the success of the manipulation;
- presence of complications;
- age and individual characteristics.
Previously, stones were removed by performing abdominal operations.
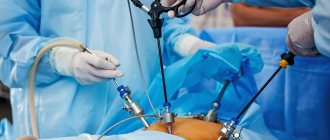
After such manipulations, the person had to stay in the hospital for quite a long time: from 10 to 15 days. Today there is a less traumatic method of treatment - laparoscopic. Its essence lies in the fact that a puncture is made in the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity and then all necessary manipulations are carried out through it (under the control of a special apparatus with a camera).
Laparoscopy relieves a person from excruciating pain in the postoperative period and shortens the period of hospital treatment. Most patients with cholelithiasis after cholecystectomy stay within the walls of a medical institution for a week. After surgery, the patient is taken to the intensive care unit.
Here the patient remains under the control of resuscitators until recovery from anesthesia and removal of the tubes with which artificial respiration is performed. After about three hours he is transported to a regular ward.
From the second day, the patient is allowed to get up and walk, drink and eat some foods. Children are kept in the hospital longer after laparoscopy than adults.
This is due to the fact that the body of babies reacts more acutely to the absence of an organ. The child may have a fever, severe pain and other unpleasant symptoms. Therefore, children should stay in the hospital for at least ten days after laparoscopy.
If you had to operate on a pregnant woman using the laparoscopic method, the patient’s stay in hospital will be long: from 10 to 15 days. While staying in the hospital, the woman will be under the supervision of a gynecologist.
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilyeva
Civil law expert
A sick leave certificate is opened on the day a person is admitted to a hospital. Its duration depends on the number of days needed to prepare for the operation and monitor the condition after it.
What influences the duration of BL?
The duration of sick leave depends on the complexity of the operation. In the case of any operations on the gallbladder, including cholecystectomy, laparoscopy is often used.
This option involves a more gentle intervention, the absence of large sutures and associated healing difficulties, and, accordingly, a significantly accelerated recovery period.
In addition, other factors influence the duration of sick leave:
- the condition of the person being operated on before and after the operation, determined by the general indicators of his health;
- the size of the diseased organ and the extent of surgical intervention;
- the occurrence of complications during and after surgery.
In what cases is sick leave extended?
A sick leave will be issued if the patient’s ability to work has not been restored or complications have arisen. When making a decision to increase the period of release from work, laboratory and instrumental indicators of the person’s health status and well-being are taken into account.
The certificate of incapacity for work is extended until full recovery. In some cases, the outcome of the disease is the assignment of a disability group. Then the certificate of incapacity for work is automatically closed on the day of the examination.
After laparoscopy and laparotomy, the following complications sometimes occur:
- bleeding;
- damage to the intestines, urinary tract;
- pneumonia;
- problems with the heart and blood vessels;
- thrombophlebitis;
- suppuration of postoperative sutures;
- allergy to anesthesia;
- peritonitis;
- omphalitis (inflammation of the tissue around the navel);
- bile leakage into the peritoneal cavity due to a poorly sutured stump of the cystic duct;
- postoperative infection due to weakening of the patient’s body’s defenses.
In severe conditions, the patient can be transferred from outpatient treatment to inpatient treatment. The length of stay in a medical institution is determined by the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of the therapy provided. Sometimes after laparoscopy it is necessary to perform a laparotomy (for example, in case of incomplete removal of an organ).
Most often, complications occur after laparoscopy. This is due to the fact that the surgeon does not have free access to the organ and may make mistakes.
Dear readers! To solve your problem right now, get a free consultation
— contact the on-duty lawyer in the online chat on the right or call:
+7
— Moscow and region.
+7
— St. Petersburg and region.
8
- Other regions of the Russian Federation
You will not need to waste your time and nerves
- an experienced lawyer will take care of solving all your problems!
Grounds for extension and possible extension periods
There are difficult cases when 30 days are not enough for the patient to regain working capacity. In such situations, sick leave can be extended for up to 12 months. However, the attending physician in this case cannot decide on an extension. This decision is made by a committee of doctors, which has the necessary powers and acts on the basis of data and arguments in favor of longer treatment presented by the attending physician.
Every 15 days the patient must visit the doctor to confirm the need to continue treatment. If at the next visit the doctor is convinced that the patient’s condition is normal and he can start working, the certificate of incapacity for work is closed.
Indications and contraindications for laparoscopy
Today, laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the “gold standard” and is indicated for:
- any form of symptomatic gallstone disease
- gallbladder polyps
- Cholelithiasis complicated by choledocholithiasis
Contraindications for laparoscopy are the same as for other types of operations:
- terminal state;
- decompensation of the functions of the cardiovascular system and lungs.
Where it is better to have laparoscopic cholecystectomy in Moscow, the patient chooses himself. It is better to give preference to a clinic with good recommendations and reviews, highly qualified surgeons, and modern equipment. The average cost of laparoscopic cholecystectomy as a service depends on these same factors.
Preparing for surgery
The methods of preparing for surgery are similar and do not depend on where laparoscopic cholecystectomy is performed in Moscow.
Before the procedure, the patient undergoes a full examination at the medical center. Laboratory and instrumental diagnostic measures are prescribed - blood and urine tests, ultrasound, and, if necessary, MRI. Their goal is to determine the patient’s health status and identify concomitant pathologies that require correction before surgery. If pathologies that impede the operation are identified, treatment will be prescribed to compensate for the disease.
In the absence of contraindications, cholecystectomy is prescribed. Preparation for the procedure:
- Follow a special diet the day before surgery. You can only eat light foods that do not overload the digestive tract.
- Dinner the day before is allowed no later than 19:00.
On the day of surgery, you should not eat or drink. If the patient regularly takes any medications, their use should be coordinated with the surgeon and anesthesiologist. In most cases, therapy is not interrupted.
Hospital stay
After completion of the operation, the patient is transferred to the surgery department, where he is under the supervision of the attending and duty doctor.
After 2-3 hours, the patient can get up under the supervision of a nurse.
Eating is prohibited before the operation. After - after 2 hours you can drink still water, and in the evening - a light dinner.
On the first day after surgery, the patient can walk around the department. After an ultrasound examination and obtaining the results of control blood tests and the absence of pain, the patient can be discharged home. Elderly patients are recommended to be observed in a hospital for up to 2–3 days.
Upon discharge, you are given a certificate of incapacity for work, test results and detailed recommendations for further management of the postoperative period. If you need to extend your sick leave, you should contact the clinic at your place of residence. If necessary, the operating surgeon is available via mobile phone 24/7.
Possible complications
Although laparoscopic cholecystectomy has a number of advantages, there are still risks and complications.
In most cases, the operations are successful, but sometimes the following may occur:
- damage to the bile ducts;
- development of internal bleeding;
- allergic reactions to medications used;
- inflammation and suppuration of the places where punctures were made.
In most cases, after surgery, the body exhibits good compensatory abilities, and the process of assimilation and digestion of food is rebuilt and adjusted to new conditions. Normally, the health status is restored within a period of 6 months to 2 years, the patient returns to the pre-operative lifestyle.
How to remove the gallbladder
The laparoscopic cholecystectomy operation is performed under general anesthesia. Its duration is from 40 minutes to 3 hours, which depends on the diagnosis, form and severity of the disease, and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Operation stages:
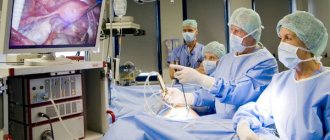
- Puncture of the abdominal cavity with a special atraumatic needle through which carbon dioxide is injected. For this purpose, a special device is used - an insufflator. There is a constant supply of gas, and its constant pressure in the abdominal cavity is also maintained.
- Next, small punctures are made in the abdominal wall, through which laparoports are inserted. These are special devices for inserting surgical instruments into the abdominal cavity and preventing carbon dioxide from escaping.
- A laparoscope is inserted into the puncture in the navel area. This is a device in the form of a tube with optics at the end, which transmits images of internal organs to a monitor. The device magnifies the image several times, which makes the visualization of anatomical structures and tissues as clear as possible. Manipulations performed inside the abdominal cavity can be seen by all medical professionals present in the operating room.
- Through other laparoports, clamps are inserted to hold the gallbladder and other instruments are inserted to isolate structures and perform other stages of the operation.
- The most critical stage of the operation, the precision of which largely determines the success of the operation, is the isolation and intersection of the cystic duct and the artery supplying the gallbladder. We use the principle of critical safety view before crossing these structures, which minimizes the risk of damage to the main bile ducts and bleeding.
- Using the electrocoagulation method, the surgeon separates the gallbladder from the liver
- Next, through one of the punctures in the abdominal wall, the gallbladder is removed out into a special container.
- Surgical instruments and trocars are removed from the punctures (always under visual control to prevent bleeding from the trocar wounds. Sutures are placed on the incisions. We use intradermal sutures with absorbable material, which gives maximum cosmetic effect.
Sometimes, to prevent and early diagnose complications, drainage of the abdominal cavity is performed - a silicone tube is installed through one of the punctures. We are not supporters of this approach and resort to drainage only in extremely difficult cases, monitoring the postoperative condition using ultrasound.