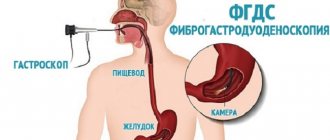
FGDS or fibrogastroduodenoscopy is the most informative gastroenterological diagnostic method. The examination allows you to identify diseases in the initial period of their development. Using gastroscopy, the presence of cancerous tumors, erosions, stenosis, and ulcers is diagnosed.
To obtain the most accurate results, special preparation for the examination is required. A few days before the procedure, the patient switches to a dietary diet, twelve hours before he stops eating, and an hour before he stops drinking liquids. The doctor informs the patient in detail about all preparatory measures when issuing a referral for examination.
FGDS gives the person being examined quite unpleasant sensations, which may accompany him for some time after the procedure. Therefore, many are concerned about questions related to the post-procedure period: how long after gastroscopy can you eat? How to eat properly? What complications may arise?
Basic principles of nutrition after gastroscopy of the stomach
It is rare that the study is performed on completely healthy patients. Therefore, the nature of the diet after fibrogastroduodenoscopy is determined by the nature of the patient’s disease .
Nutrition in the period after FGDS in most cases resembles Pevzner’s diet No. 1. The nature of the violation of secretory function (hyper- or hypoproduction of hydrochloric acid) is of greatest importance. But even regardless of this, nutrition after FGDS is based on several key principles:
- Reducing the amount of food at one time , and their frequency (up to 5-6 times a day). This reduces the load on the gastric mucosa.
- Chemical protection . It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that can damage the mucous membrane (for example, citrus fruits or alcoholic drinks).
- Thermal protection . All dishes served to the patient should be at a comfortable temperature (35-45°C). This prevents damage to the stomach wall from getting worse.
- Balance . Despite the exclusion of certain foods, the diet must maintain the required amount of nutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, fats), vitamins and microelements.
- Patient-oriented diet . The diet should take into account the patient’s preferences, since only then will he adhere to it.
Help The latest recommendations advise staying away from a strict diet.
It has not been proven that its use promotes faster recovery of the mucous membrane. Other factors play a much more important role - the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection, long-term use of certain groups of medications and concomitant diseases. These must be taken into account when preparing a diet after fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
Complications after FGDS
A correctly performed FGDS procedure and the patient's compliance with the doctor's recommendations practically do not result in complications. The most serious complication is a violation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus or stomach, infection.
To avoid unwanted reactions of the body, any complications, the doctor always asks about the presence of diseases, and the patient must tell about his individual characteristics, about his condition before the examination (if he does not like something about his feelings).
Complications after FGDS:
- body temperature rises to 38 degrees;
- black color of stool;
- gag reflex and blood in vomit;
- pain in the abdominal area.
If you have any undesirable symptoms, you should definitely consult a doctor.
When should you not eat or drink?
It all depends on the procedure used. Typically, FGDS is done under local anesthesia of the posterior wall of the oropharynx. Then (if there are no complications and surgery is not planned) you can eat 30 minutes after completion of the procedure.
If a biopsy of the mucous membrane was performed, then you need to refrain from eating for 2 hours after the procedure. All dishes should be warm, but not hot, as otherwise this will cause injury to the stomach wall.
, FGDS
has increasingly been performed (medicated sleep).
Considering the duration of action of the drug used for the procedure, the first meal is recommended after 90-120 minutes. Sometimes FGDS is done under general anesthesia. Then, after completing the procedure, the patient gradually withdraws from the administered medications and may complain of nausea, dizziness, and severe drowsiness for several hours. Therefore, the first feeding occurs after approximately 4-8 hours. At the same time, it should be as simple as possible (for example, buckwheat porridge) so as not to provoke vomiting.
FGDS is often performed on children under anesthesia or sedation. You can read about the features of this procedure by following the link.
Helpful tips for recovery
Gastroenterologists do not recommend rushing into the first meal after the end of FGDS. The time limits after which you can eat and drink vary from person to person, and their duration is influenced by many factors, including the method of pain relief. For example, local anesthesia may last longer than 2-3 hours, resulting in an increased risk of food and water particles entering the trachea and even the lungs: the body will not be able to recognize the threat, causing the larynx to allow them into the respiratory tract.
Physical activity can also be harmful, especially if FGDS was carried out with the collection of biopsy material or for the purpose of removing polyps. For 3-5 days, you should avoid lifting heavy objects, shaking in transport and straining the anterior abdominal wall.

Is it possible to drink alcohol after gastroscopy?
Much has been said about the fact that alcohol provokes diseases of the digestive tract, so the harm of alcoholic beverages after gastroscopy is obvious. Firstly, it provokes blood flow to the mucous membranes, and can cause bleeding after FGDS, even if there are minor injuries on the inner surface of the esophagus and stomach. Secondly, alcohol thins the blood, and this can lead to poor healing of wounds left after removing polyps and taking a biopsy.
Important! Doctors do not advise drinking alcohol until complete recovery from FGDS, that is, for 2-4 weeks depending on the type of procedure.
In addition to strong and low-alcohol drinks, you should avoid taking alcohol-containing drugs: tinctures of medicinal herbs, syrups containing ethanol, and the like. You should not eat sweets or confectionery products that contain cognac or alcohol.

Prohibited Products
Carbonated drinks (including alcoholic drinks, kvass, lemonade and mineral water) from the diet that is recommended after FGDS It is also prohibited to drink strong tea or coffee as drinks, as they can stimulate the production of hydrochloric acid by the gastric mucosa.
Also, meat (chicken) broths can increase acidity, so they are also not included in the diet in the presence of hypersecretory conditions. Fatty meats (pork, duck, goose) have a similar effect. The diet also does not include soups with a large amount of spices, red borscht and okroshka.
Gels and suspensions will help cope with stomach pain. Which? This article will tell you about this.
Please note: Fresh baked goods negatively affect the digestive processes, as do pastry products. If a patient buys pies, then you need to pay attention to the nature of the filling.
With high acidity, fermented milk products (kefir, fermented baked milk) are not recommended. They can potentiate the effect of the aggression factor (hydrochloric acid) on the mucous membrane. Some types of hard cheese contain a large amount of spices and therefore should not be eaten.
If you look at vegetables, onions, radishes, rutabaga, cucumbers, spinach, and white cabbage are not included in the diet.

You should avoid eating peanuts, legumes, and nuts. All sour berries (blueberries, strawberries, lingonberries, gooseberries, currants) and citrus fruits are also undesirable.
Canned and pickled foods, most spices, mustard, tomato paste, horseradish, ketchup, and sauces are completely removed from the diet.
Additionally, in the first days after the study, it is advisable to avoid the following products :
- persimmons;
- grapes;
- fatty types of fish fillets;
- corn, pearl barley or barley;
- fried eggs;
- dried fruits;
- sweet products containing chocolate.
Indications for gastroscopy (FGDS)
Tests and x-rays do not always make it possible to make a diagnosis, but performing an FGDS allows you to see the picture of the disease from the inside, clarify or make a final diagnosis. The examination is mainly carried out to diagnose diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, especially its upper part.
When is FGDS performed:
- in the presence of nausea, heartburn, belching;
- cough for no apparent reason;
- pain when swallowing;
- swallowing dysfunction;
- bloating, gas formation;
- noticeable weight loss;
- abdominal pain, especially in the epigastric region;
- blood in stool;
- vomiting, blood in vomit;
- B12 deficiency anemia;
- with stomach bleeding;
- to deliver a medicinal product;
- remove polyps;
- take tissues, gastric juice for analysis, samples for gastrobacteria, for example, they often jointly perform a urease test for the presence of Helicobacter pylori (Helicobacter pylori);
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
FGDS reveals the following diseases: gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, stomach and esophageal cancer, inflammatory processes in the esophagus, reflux disease, polyps, duodenitis and other diseases.
A timely EGD of the stomach will help diagnose the disease at an early stage, which makes it possible to start treatment on time.
For chronic diseases, FGDS is performed once a year, in other cases - according to the indications and direction of the attending physician.
Authorized Products
Preference should be given to lean meats (for example, beef, turkey, horse meat, or rabbit meat). The most optimal preparation option is boiled (you can make zrazy, steamed cutlets, meatballs or soufflé). In this case, you need to ensure that all solid particles (bones, cartilage) are removed from the food. If the dish is prepared for older people, you can chop it more thoroughly to avoid possible digestive difficulties.
Do the same with fish. Low-fat types are recommended. You can cook pike perch, pollock, pike, flounder, carp, hake, cod, mullet. When cleaning fish, you should try to remove all bones and scales.
Bakery products in the diet include day-old white bread or buns without sour filling . It is also recommended to give preference to dry, unpalatable cookies, cheesecakes or biscuits without chocolate. If necessary, they can be dried a little at home.

Cereals are almost always found in the diet after FGDS. Many of them contain large amounts of mucus, which can cover the gastric mucosa and protect against various aggressive factors.
They give preference to buckwheat, rice, semolina and oatmeal. Rice water can be given as a separate drink. Pasta (provided it is thoroughly cooked) and mashed potatoes (without adding oil) are also left without restrictions.
If you look at drinks, it is recommended to drink still table water, sweet juices, weak tea (both traditional and from chamomile, St. John's wort or calendula), rose hip decoction.
Other products that are recommended are:
- hard cheese (mild);
- honey;
- baked fruits;
- soups with milk;
- soft-boiled eggs (smoked or quail).
If you feel constant discomfort in the stomach and mild heartburn, the cause may be an accumulation of bile. Timely neutralization will help avoid many problems. How to do this is written in this article.
What is recommended for decreased secretion?
If FGDS revealed atrophic gastritis with reduced secretory activity, then the diet has some features. It generally repeats the usual one, but the diet includes foods that stimulate the functioning of the parietal cells of the stomach and the production of hydrochloric acid :
- washed sauerkraut;
- weak coffee, cocoa with water;
- butter;
- meat pates;
- zucchini, beets, cabbage;
- citrus fruits (tangerines, oranges);
- fruit compotes.
When is alcohol allowed?

Therefore, it is advisable to completely exclude alcoholic beverages from the diet after the procedure for the period of clinical symptoms. If the study was carried out on a healthy person, then it is advisable to refrain from using them on the day of diagnosis.
Alcoholic drinks can be consumed in moderate doses only after the patient has fully recovered.
Features of diet No. 1
Pevzner's diet No. 1 is designed for diseases of the digestive system, which are accompanied by a sharp increase in acidity . It is the one most often prescribed after the procedure. Its main characteristics are presented in the following table:
| Indications | Hypersecretory gastritis (with increased acidity), gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastric or duodenal ulcer in the compensation phase |
| Target | Protect the mucous membrane from exposure to factors of chemical, temperature and mechanical aggression |
| Calorie content | 2800-3300 kcal (if necessary, it can be increased to 3500 kcal) |
| Cooking method | All solid particles are first removed from the products. Dishes are steamed, boiled or baked |
| Meal frequency | 5-6 times a day |
| Approximate composition of nutrients | Carbohydrates – 400-460 g, proteins – 85-130 g, fats – 90-120 g |
| Restrictions on salt intake | Moderate (no more than 12 g per day), it is necessary to take into account the presence of concomitant cardiovascular or renal pathology |
| Volume of fluid consumed | 1.5-2.0 l |
| Serving Size | Determined individually (based on age, gender and physical activity) |
The duration of the diet depends on the severity of symptoms. If FGDS was carried out against the background of compensation, to monitor the effectiveness of treatment or for preventive purposes, then dietary restrictions should not be maintained for more than 2 days.
Please note: If during an endoscopic examination the patient was found to have gastritis, erosions or peptic ulcers, then the diet remains for a longer period after FGDS.
On average, it must be observed for about 5-7 days for acute gastritis, 7-10 for chronic gastritis, and 14 for peptic ulcer disease.
In addition to following a proper diet, you can speed up the process of restoring stomach comfort with 10 recipes for treating gastritis.
Example menu
The daily menu after the diagnostic event looks approximately as follows:
- First breakfast (8-9 am) - includes oatmeal cooked in water, two soft-boiled eggs and a glass of still table mineral water.
- Second breakfast (11 o'clock in the afternoon) - consists of slightly warmed cottage cheese with sugar (but without butter) and tea with milk.
- Lunch (2 p.m.) – served rice vegetable soup (can be served with boiled lean meat), mashed potatoes, a steamed cutlet, several baked fruits (apples, pears) and weak tea.
- snack (5 p.m.) – enough dry biscuits (bagels) and a glass of non-sour yogurt.
- Dinner (20 pm) - the patient eats buckwheat porridge (without oil), boiled fillet of a lean fish, a glass of sweet juice.
- Before bed (22 hours) – baked apple with weak tea.
Water intake issue

This volume also includes water, which is included in soups, cereals and other dishes. But other factors also need to be taken into account.
For example, in a hot climate, the body's need for water increases. In the presence of decompensation of renal or cardiac function, fluid retention is often observed, so its intake must, on the contrary, be reduced. With an increase in body temperature (fever), active physical work, and playing sports, the patient's need for water also increases.
It is recommended to drink a glass of water 30 minutes before meals - this helps reduce the amount of acid in the stomach. It is important not to drink during meals, only 45-60 minutes after.
FGDS - what is this procedure, preparation, indications and contraindications, complications after
FGDS - what kind of diagnostic procedure it is, preparation for the study with important medical recommendations, indications and contraindications, possible complications, consequences - we will describe all this on the website alter-zdrav.ru.
Such detailed information is often necessary for those patients who are prescribed fibrogastroscopy of the stomach and adjacent organs for the first time. In modern medicine, various diagnostic methods are used to quickly and accurately make a diagnosis. These include radiation diagnostic methods (fluorography, X-ray, angiography, computer, magnetic resonance and nuclear magnetic tomography), direct visual diagnostic methods (fibrogastroduodenoscopy, esophagogastroduodenoscopy, duodenal intubation, coproscopy, etc.).
Quite often, any visual examination of the stomach, based on the insertion of a probe through the oral cavity, is called gastroscopy - FGS (fibrogastroscopy).
Gastroscopy examines the gastric mucosa using a flexible tube (endoscope) inserted into the stomach through the mouth and a camera at its end.
Another type of visual examination - EGDS (esophagogastroduodenoscopy) involves examining the stomach, esophagus, and duodenum with an endoscope.
Visual examination methods allow you to see the condition of the pharynx, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, small and large intestines, gall bladder, take gastric juice, bile, pieces of tissue for analysis, and deliver the medicine precisely. One of the visual inspection methods is the FGDS method.