The introduction into gynecological practice of such a diagnostic procedure as colposcopy gave doctors the opportunity to diagnose dangerous processes in the vaginal part of the cervix from the point of view of malignancy or malignancy at the earliest stages of development, which made it possible to significantly reduce the number of cases of cervical cancer and save tens of thousands of lives. Therefore, today colposcopy is performed everywhere as part of preventive gynecological examinations. This is a painless, easy-to-perform procedure, the cost of which is affordable for every woman, and the amount and value of the information obtained during it is difficult to overestimate.
Cervix and its features
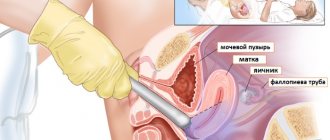
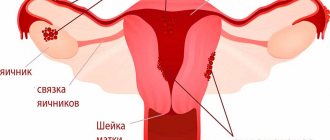
The cervix is the lower part of the uterus, connecting its body to the vagina. It has the shape of a tube, inside of which the cervical canal is located in the form of a spindle. At one end it opens into the uterine cavity, forming the internal pharynx, and at the other end into the vagina, thereby forming the external pharynx. It is the external os of the cervix that is examined during a gynecological examination, as well as colposcopy.
Along the entire internal surface, the cervical canal is covered with cylindrical (goblet) epithelium, secreting a special secretion that protects the uterus from penetration of pathogenic microorganisms, and also ensures the normal movement of sperm from the vagina into the uterine cavity. At the same time, the vagina and external os of the cervix are normally covered with stratified squamous epithelium. Typically, the border between the columnar and squamous epithelium, called the transition zone, is clearly visible and presents a clear edge. It is in this part that most often, namely in 90% of cases, pathological changes occur, which colposcopy is intended to diagnose.
In young girls, the presence of an area covered with goblet epithelium may be observed in the vaginal part of the cervix. If the transition boundary is clear and even, this is regarded as a variant of the norm. But such a condition should go away on its own by the age of 25, otherwise they say there is erosion.
Where to get a colposcopy in Krasnoyarsk?
In the city of Krasnoyarsk there are many public and private medical institutions where you can undergo gynecological examinations and colposcopy. However, it is important to understand that even an inexperienced gynecologist can conduct a routine examination, while only a professional should perform a colposcopic examination. It is the doctor’s experience that will determine how well he will conduct the examination and how accurately he will determine the diagnosis.
If you are scheduled for a colposcopy, where can you get it done with the most accurate results? Contact a trusted clinic and only an experienced specialist. The Center for Endoscopic Surgery employs professionals who will help you resolve this issue.
The clinic is located at Krasnoyarsk, st. Vesny, 14, room No. 75, tel., 258-18-54. Use the services of professionals and take care of your health!
What is colposcopy
Colposcopy is one of the methods of gynecological examination of the cervix from the vagina using a special apparatus (colposcope). It is an optical device similar to a microscope, in which a light source is installed for high-quality illumination of the most inaccessible and darkened areas. The colposcope does not contact the patient’s body and allows you to examine the cervix with a magnification of up to 40 times, thanks to which the gynecologist can notice even minor changes in the structure of its tissues, and carrying out various tests and samples significantly expands the diagnostic capabilities of the method.
With its help, the doctor evaluates the color, character, surface relief of the mucous membrane of the visible part of the cervix, vascular pattern, and the condition of the glands. All this makes it possible to accurately determine not only the size of pathological changes in the cervix, but also their origin, i.e., make a diagnosis and prescribe optimal treatment.
Previously, all colposcopes were mechanical, but today digital colposcopes are becoming increasingly common, allowing real-time image display on a monitor screen. This allows both the woman herself to see all the existing changes in the cervix, and creates a basis for comparing the results of treatment with the initial state and assessing its effectiveness. Therefore, if there is a choice, digital colposcopy is always preferred.
Colposcopy is a safe, painless, highly informative procedure that often takes no more than 5 minutes, although in some cases it can last up to half an hour. Only sometimes women feel slight discomfort when treating the outer part of the cervix with solutions of chemicals.
Today the method has wide indications for use and is used for the following purposes:
- detection of areas of pathological epithelium on the surface of the vaginal part of the cervix, typical for erosion, dysplasia and cervical cancer;
- assessing the size and location of foci of pathological changes;
- choosing a treatment method for detected diseases;
- dynamic control over the condition of the cervix when choosing expectant management or active treatment of its pathologies;
- assessing the need for a biopsy followed by histological examination of the samples.
What happens if CIN 1 is not treated?
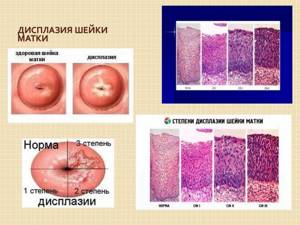
Any dysplasia requires constant monitoring and taking adequate measures. If the disease does not go away on its own, but recurs within 2-3 years, this means that it will develop into more severe forms and is highly likely to become malignant.
Grade 1 cervical dysplasia, according to experts, from the moment of detection without adequate treatment turns into invasive cancer in about 10-15 years. Stages 2-3 of the disease can also be treated, but it will be longer and more intense. It is important to take into account that bad habits, decreased immunity and other negative factors can significantly accelerate the period of transition from dysplasia to cancer.
Types of colposcopy
There are 3 types of colposcopy:
- simple (overview);
- extended;
- colpomicroscopy.
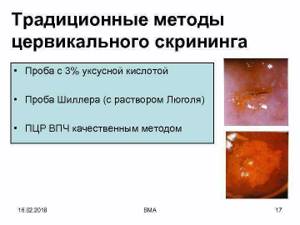
Initially, they always start with a simple colposcopy. If during the procedure the gynecologist discovers changes in the condition of the cervix, he will conduct an extensive study using chemicals: acetic acid and a 5% alcohol solution of iodine. After each stage of the procedure, the gynecologist carefully examines the cervix through a colposcope and records the detected changes.
Colpomicroscopy is performed extremely rarely and requires special equipment. It allows you to obtain an increase of more than 300 times, which is necessary for assessing the ratio of the size of the nucleus to the cytoplasm and detecting other features in the structure of cells.
Acid test
To carry out this test, use a 3% acetic acid solution or a 0.5% salicylic acid solution. Their treatment of the surface of the cervix leads to short-term swelling and pallor of the squamous epithelium, and narrowing of healthy capillaries. If the squamous epithelium is replaced by cylindrical epithelium, it does not react to the acid used and stands out against the healthy background as a bright red spot with clearly visible boundaries. Pathologically altered vessels also do not react to acetic or salicylic acid, so they retain their original shape and are clearly visible.
After 2 min. healthy mucous membrane returns to normal and becomes pale pink. A slight uniform whiteness of large areas is not regarded as a sign of the disease, but the more the epithelium whitens and the longer this effect persists, the deeper its damage. This is typical for inflammatory processes, in particular cervicitis, as well as mucosal atrophy. But if after application of acid the epithelium becomes thick and richly white, this is a sign of a precancerous condition.
Thus, the test allows you to obtain a lot of valuable information about the condition of the cervical mucosa, including:
- accurately determine the line between squamous and goblet epithelium;
- detect modifications of the squamous epithelium and assess the depth of the lesion, as well as areas modified by HPV;
- identify abnormal vessels;
- detect even small foci of leukoplakia and neoplasia (precancerous condition) and differentiate them;
- diagnose oncological diseases, in particular adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
Schiller test
The Schiller test is also part of an extended colposcopy and is performed immediately after the end of the test with acetic or salicylic acid. It involves treating the cervical mucosa with Lugol's solution or a 5% aqueous solution of iodine. The method is based on the ability of iodine to interact with glycogen, so its use makes it possible to detect areas of the epithelium whose cells lack this compound. Thus, after smearing with an iodine solution, the healthy mucous membrane is uniformly colored brown, and if pathological changes occur in it, it either remains unchanged or turns unevenly yellow or another color.
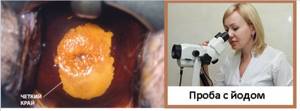
Thus, the Schiller test allows you to detect:
- atrophied epithelium (brown color is uneven);
- areas of metaplastic, columnar epithelium and other benign changes (such lesions are weakly stained and have blurred edges);
- foci of inflammation (partially painted over);
- cervical dysplasia, severe atrophy (colored yellow or pale);
- leukoplakia (no coloring occurs, and the affected area has the appearance of a light shiny film with a smooth or embossed surface);
- atypical cells (take on a gray, olive color and have pronounced contours).
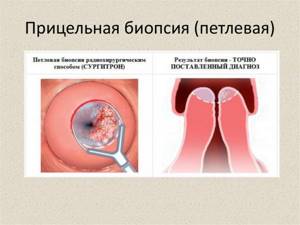
If, when performing a test with Lugol's solution, iodine-negative areas are detected, i.e., unstained, it is recommended to take a targeted biopsy from them and conduct a histological examination of the resulting biopsy. This is necessary to exclude cancer and establish an accurate diagnosis.
If the clinic where the colposcopy is performed has its own laboratory, the biopsy can be taken immediately.
Nutrition for mild dysplasia
The most important component for cervical neoplasia is dietary nutrition, which, in combination with therapeutic measures, significantly improves the prognosis for this pathology. Any disease occurs against the background of a reduced immune status. Therefore, to support immunity, the diet includes foods containing ascorbic acid, which helps stimulate metabolism, hematopoietic processes, and recovery. Black currants, kiwi, parsley, cabbage, citrus fruits, and walnuts are useful. You need to drink more decoctions of rose hips, dried fruits, herbs with an anti-inflammatory effect, add honey to drinks if there are no contraindications.
It is believed that homocysteine (an amino acid) aggravates dysplastic processes, and folic acid reduces the concentration of this substance. In addition, vitamin B9 improves hematopoiesis and promotes the restoration of epithelial tissue. Folic acid is sufficiently contained in cottage cheese, liver and beef, soy, lemons, beans, porcini mushrooms and Brussels sprouts, egg yolks, and hard cheeses.
According to medical research, beta-carotene reduces the risk of cervical cancer, is involved in cellular metabolism, and has an antiviral effect. There is a lot of vitamin A in orange-colored foods, natural butter, liver, egg yolks, and sea fish.
Tocopherol is a powerful antioxidant that is used to prevent the development of cancer against the background of cervical dysplasia, increases the concentration of red blood cells, helps with cardiovascular disorders, and slows down aging. The vitamin of youth is found in walnuts, almonds, brown rice, oils (corn, unrefined sunflower, wheat germ, soy).
If you have cervical neoplasia, you should not eat spicy and fried foods, smoked and pickled foods, processed and fast foods, foods rich in simple carbohydrates, dietary supplements, and alcohol. Optimal diet: cereals, nuts, dried fruits, vegetables, honey, decoctions, dairy products.
Indications for use
The procedure is performed both routinely once a year during a routine examination by a gynecologist, and upon receipt of the results of a cytological analysis of a scraping from the cervix, indicating the presence of dysplasia, namely atypical squamous or glandular epithelial cells:
- ASC-US;
- LSIL;
- HSIL;
- ASC-H;
- AGC;
- AIS.
It is the diagnosis of true cervical erosion and pseudo-erosion that has acquired signs of atypia and dysplasia that is one of the most common indications for performing colposcopy.
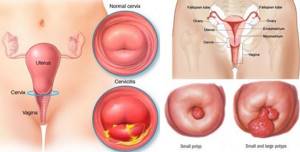
The procedure is also used to diagnose cervical pathologies such as:
- cervicitis is a disease accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervix;
- endometriosis is a pathology in which the endometrium covering the uterus from the inside extends beyond the boundaries of the inner lining of the cervix, which is often accompanied by bleeding of varying severity and nagging pain;
- polyps - are growths of the mucous membrane of the cervix;
- condylomas are small growths on the surface of the mucous membrane of a flat, papillary or pointed shape, which are a sign of infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV);
- erythroplakia is a disease accompanied by the formation of areas of atrophy and dyskeratosis against the background of infectious diseases, hormonal disorders, chemical and mechanical damage;
- leukoplakia is a pathology characterized by the formation of zones with increased keratinization of the squamous epithelium;
- cancer is the formation of a malignant tumor of the cervix, which often results from the development of dysplasia against the background of pseudo-erosion, the formation of condylomas and other pathological changes.
The procedure is necessarily performed as part of monitoring the condition of the cervix in patients with mild erosive changes that may turn out to be physiological, as well as to monitor the effectiveness of treatment of detected diseases.
Pregnancy with mild dysplasia
The presence of benign changes in the cervix is not a contraindication for natural conception, gestation and childbirth. They do not have a negative effect on placental function and fetal development. However, if you approach pregnancy responsibly and plan it, then if dysplasia is detected, you need to undergo appropriate treatment before conception. Although it is believed that pregnancy does not contribute to the worsening of dysplasia, it is impossible to say with 100% accuracy that hormonal changes during gestation will not affect the atypical process at all.
If a woman is diagnosed with epithelial changes for the first time during the gestational period and has never been tested for HPV and HIV, then these tests are performed at any time using a Pap test. Further actions depend on the results of the examination. If the test is negative, no therapy is carried out; a control test is prescribed one year after birth. If grade 1 dysplasia is detected, a colposcopy is performed and also a control test one year after birth.
Preparing for colposcopy
Colposcopy can be performed on absolutely any day of the cycle, with the exception of menstruation, since the presence of bloody discharge will not allow a full assessment of the condition of the mucous membrane of the cervix and will distort the test results. The optimal time for performing the procedure is considered to be the first 5 days after the end of menstruation.
There is no need to prepare specially for colposcopy, but to avoid getting false results, it is recommended that 2 days before your visit to the gynecologist you refuse:
- sexual intercourse;
- inserting tampons into the vagina;
- douching;
- use of vaginal suppositories and creams.
Douching, except when prescribed by a doctor for medicinal purposes, is harmful to the female body, as it leads to disruption of the microflora. Therefore, it should be abandoned in principle.

Before the procedure, you should empty your bowels and perform a standard toilet of the external genitalia. It is important to avoid getting soap solutions into the vagina.
Symptoms and signs of mild dysplasia
- itching in the vagina;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- spotting after sexual intercourse;
- change in the smell of vaginal discharge, its consistency;
- pain during sex.
As a gynecologist notices dysplasia: during the examination, the doctor sees redness, looseness of the mucous membrane, and there may also be spots on its surface of a color different from the surrounding tissues. Dysplasia is also characterized by small ulcerations of the mucous membrane and erosion.
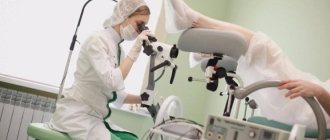
The essence of the procedure
Colposcopy is performed in a gynecological office equipped with a colposcope. The patient is placed on a gynecological chair, the doctor inserts a standard speculum into the vagina, expands it to the required parameters and fixes the cervix. If necessary, secretions and cervical cells are collected for laboratory tests. After this, the vaginal walls are cleaned of secretions with a tampon soaked in saline solution.
The doctor moves the optical device to the chair and places the colposcope at some distance from the vagina. It is equipped with two eyepieces and a magnification control, which allows you to view all areas of interest to the gynecologist in the required approximation. If a digital colposcopy is performed, a woman can monitor the progress of the procedure and see everything that the doctor sees on the monitor screen.
First, a survey colposcopy is always performed, during which the gynecologist examines the cervix at different magnifications for abnormalities. If they are not detected, the procedure ends there. But if the doctor sees pathological changes, he proceeds to conduct an extended colposcopy in the absence of allergies to iodine and acetic acid preparations.
At this stage, the gynecologist initially carefully treats the entire surface of the external os of the cervix with a tampon moistened with a 3% solution of acetic acid, holding it on the surface of the mucous membrane for 30-40 seconds. Afterwards, the tampon is removed and the cervix is examined again using a colposcope. As a result of the action of the drug, the changed areas of the mucous membrane become white, which is called acetowhite epithelium.
After this, a Schiller test is performed, which involves the use of an aqueous solution of iodine (Lugol's solution). A tampon soaked in it is used to treat the visible part of the cervix, which can sometimes lead to a slight burning sensation that causes slight discomfort to the woman. Areas with healthy mucosa are uniformly dark brown in color, while areas with pathological changes acquire lighter shades.
If during colposcopy areas with signs of pathological changes are detected, to accurately diagnose their nature, samples can be taken immediately after colposcopy for histological examination, i.e., biopsy.
Contraindications
Colposcopy is a safe and highly informative diagnostic method. But its implementation is impossible if:
- acute inflammatory process in the cervix, which reduces the diagnostic information and leads to discomfort in the patient during epithelial and vascular tests;
- menstruation;
- allergic reaction to iodine preparations and acetic acid solution.
In such situations, you can limit yourself to a simple colposcopy.
Decoding the results
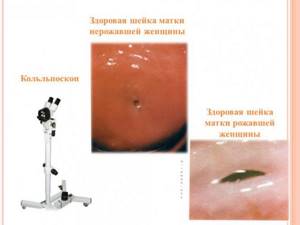
Normally, in a healthy woman, the cervix has a uniform, shiny, pale pink surface. If the patient consults a doctor in the 2nd half of the menstrual cycle, the mucous membrane may acquire a bluish tint, which is not a sign of pathological changes. The presence of the disease is indicated by bright red mucous membrane, which may also have a bumpy or velvety surface.
The external pharynx in nulliparous women has a rounded shape, and after natural childbirth it takes on the appearance of a slit and retains it until the end of life.
When the cervix is treated with acetic acid, the normal mucous membrane lightens for a while and after a couple of minutes returns to its normal pinkish color. The receipt of acetowhite epithelium after treating the cervix with a 3% solution of acetic acid, i.e., areas with an intense white color, may indicate HPV infection and the development of dysplasia, which requires further examination.
When performing the Schiller test, the degree of brown coloration of various parts of the cervix is assessed. If the entire surface has a uniform brown color, this indicates the absence of pathology. The presence of changes is indicated by the coloring of various areas in:
- yellow color – dysplasia;
- white color – atypia;
- lack of staining (the mucous membrane remains pink) – pseudo-erosion, i.e. covering the vaginal part of the cervix with an atypical columnar epithelium.
Thus, a healthy cervix has a conical shape, its mucosa is not swollen, pale pink or bluish, the border between the stratified squamous and goblet epithelium is clear. There are no glands, cysts, signs of keratosis and epithelial atrophy on the surface of the cervix. The vessels have a typical shape, the punctuation is gentle, and there is no mosaic. There is no acetowhite epithelium, the Schiller test is positive, i.e. there are no iodine-negative areas. Any deviations from these values are regarded as deviations from the norm, based on the nature of which the doctor can immediately make a diagnosis or refer the patient for a biopsy and other examinations to clarify the nature of the detected changes.
The diagnostic results are announced to the patient directly during the procedure or after completion of the examination. Additionally, they can be presented in the form of a schematic image of the cervix indicating the area and size of the affected area, photos or videos (only possible with digital colposcopy).
Normal colposcopic picture
If there are no abnormalities during colposcopy, the following will be observed:
- Original squamous epithelium or genuine MPE. Normally, it covers the vagina and the vaginal part of the cervix and has a light pink tint. But on the eve of menstruation or during pregnancy, it becomes bluish as a result of active blood filling of the blood vessels. When exposed to acetic acid, blanching is observed, and when exposed to Lugol's solution, a uniform dark brown color is observed.
- Columnar epithelium (CE). It lines the cervical canal, but during the development of the organs of the reproductive system it can protrude beyond the external os, which indicates congenital ectopia. In other cases, it should be absent on the surface of the exocervix. CE has a red color due to the thinness of the layer of epithelial cells and an uneven papillary surface. Since its cells are practically devoid of glycogen, it almost does not interact with Lugol's solution, but is more clearly released after treatment with a solution of acetic acid.
- Normal transformation zone (NT) or transformation zone. It is formed when the CE is replaced by a multilayer flat one and is located at the junction of the CE and natural MPE, which is found both on the outer part of the cervix and inside its canal. It contains metaplastic epithelium of varying degrees of maturity, as well as open and closed glands, areas of columnar epithelium with blurred contours.
Ectopia (erosion) refers to areas of columnar epithelium on the surface of the vaginal part of the cervix. Some of its types are considered normal and do not require invasive treatment.
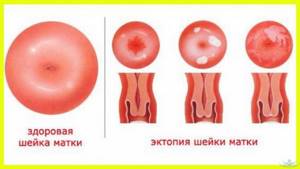
Most women who exhibit a normal transformation zone are considered healthy and do not require treatment. But many patients of reproductive age have a transformation zone and signs of ectopia. Although the transformation zone is considered a benign process, some experts find differences between the stratified squamous epithelium of the ST and conventional MPE. This, in their opinion, can be the basis for the development of cancer and requires monitoring over time.
If large nabothian cysts (closed glands of the cylindrical epithelium) are detected during colposcopy, their opening, removal of contents and coagulation of the bottom are indicated, since they can act as a depot of infections.
Actions after colposcopy
Since colposcopy is not a traumatic procedure, no restrictions are imposed after it is performed. A woman can continue to lead a normal life, including sexual intercourse, as well as play sports and perform her usual work. After the manipulation, there is no need to use any medications or perform procedures.
If extended colposcopy was used, brownish discharge may occur in the first 3 days after the procedure. This is normal, and the brown color of vaginal mucus is not caused by blood, but by leaching iodine residues. Therefore, these days it is worth using panty liners to protect your underwear.
Refraining from sexual activity, physical activity and visiting open water bodies, swimming pools, saunas, baths for 1-4 weeks will be required in cases where during colposcopy a biopsy was immediately taken or polyps and condylomas were removed. In such cases, the doctor may also prescribe the use of certain medications to speed up the healing of the wound surface. After such procedures, discomfort may occur in the lower abdomen or directly in the vagina, as well as spotting bleeding. This should not cause concern to a woman, as it is a normal reaction of the body to the intervention.
Thus, colposcopy is a simple, cheap, safe and at the same time very informative method for diagnosing a huge number of cervical diseases. Therefore, it is recommended to carry it out at least once a year for every woman.
0 0 votes
Article rating
Causes
Most often, the causes of grade 1 cervical dysplasia lie in a woman’s infection with HPV, which is a highly oncogenic type 16 or 18. According to research, after infection, cell changes are observed within 1-2 years.
All factors that contribute to the development of the disease are divided into:
- Exogenous.
- Endogenous.
The first include HPV strains, sexually transmitted infections, herpes virus type 2, which causes the development of herpes on the genitals.
Endogenous factors include:
- Chronic inflammation of the reproductive organs.
- Hormonal imbalances during pregnancy, use of hormonal pills.
- Injuries to the internal genital organs.
- Sexual intercourse without using a condom.
- Frequent change of sexual partners.
- Early onset of sexual activity.
- Abortion.
- Long-term use of hormonal drugs.
- Decreased immunity due to chronic diseases and aggressive medications.
- Congenital predisposition.
The occurrence of the disease can be influenced by neglect of hygiene, unhealthy lifestyle and other factors.