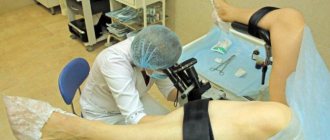
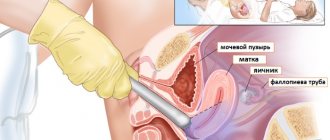
Approximately half of the world's female population suffers from various cervical diseases. If any pathological processes are detected in this area, the doctor usually sends the patient for additional examination - in particular, for a biopsy.
This procedure allows you to obtain samples of the epithelial layer of the cervical canal, which are used for histological examination. Experts recognize biopsy as one of the most accurate and informative methods for identifying inflammatory or infectious inflammatory processes in the uterus, as well as pre-cancer conditions.
In modern clinical practice, several types of biopsy procedures are used: conchotomy, colposcopic, loop, laser, circular, endocervical canal curettage, wedge-shaped, radio wave. Today, it is the latter option that is most popular.
Indications and contraindications
Radio wave biopsy of the cervix , the price of which in Moscow is very affordable, can be performed if any pathological changes in the cervix are suspected. Most often, this procedure is performed in the following cases:
- cervical erosion
- poor cytology results
- pathological changes in the cervix detected during colposcopy
A biopsy for cervical erosion allows you to diagnose the following diseases:
- chronic cervicitis (anti-inflammatory or antiviral therapy is prescribed)
- leukoplakia (treated with surgery)
- flat condyloma (antiviral therapy, if necessary, surgery)
- squamous metaplasia (does not require treatment)
- dysplasia (conservative or surgical treatment)
- cervical cancer
A cervical biopsy using the radio wave method is not performed if pregnancy is suspected, inflammatory diseases of the cervix or vagina, bleeding disorders, acute inflammatory processes, or during menstruation.
If it is necessary to carry out the procedure during pregnancy, experts recommend doing it in the second trimester.
Advantages of diagnostics in an international multidisciplinary health clinic:
- High quality of services provided. This is facilitated by many years of experience in performing various gynecological operations.
- Wide range of services. We have a laboratory and diagnostic service, an operating unit, and a hospital.
- Accuracy of diagnosis. High-precision equipment allows you to prescribe therapy for precancerous lesions - leukoplakia, dysplasia.
- Confidentiality. Only you and the doctor performing the procedure will be aware of the manipulation being performed.
- Delicacy of the staff. Any activities related to the intimate area require special delicacy, which we certainly take into account when providing services.
You can trust us to solve sensitive problems!
Advantages and disadvantages
This type of intervention has a number of advantages:
- short duration of the procedure
- almost complete absence of discomfort
- absence of postoperative scars on the cervix
- complete safety for tissues surrounding the affected area
- preservation of sexual and reproductive functions after manipulation
- minimal or complete absence of post-procedural bleeding
- impossibility of infectious contamination of the affected area (exposure to radio waves does not cause significant damage to the epithelium)
- short-term rehabilitation period
The main disadvantage of radio wave biopsy is the likelihood of coagulation damage to the material sample, which can affect the results of histological examination.
Tissue sampling methods
- Radio wave loop. The desired area of the epithelium is cut off with a radio wave electrode. This is a low-traumatic and quick diagnostic method. The radioknife seals the vessels at the site of impact, which eliminates bleeding.
- Case needle (circular scalpel). The required area of the vulva should be shaved and disinfected. A scalpel is applied to the affected area of the vulva and the tip is cut out. Cut off the cut fragment with small scissors.
- Traditional method with a scalpel. If the boundaries of the pathology are clear, a fragment of the mucous membrane and adjacent tissues is carefully cut off with a scalpel. The technique is used for superficial location of suspicious areas.
- With tongs. During the event, a small piece of tissue is pinched off from the suspicious area. The open forceps are immersed with the side surface into the tissue, and the problem area is between the jaws of the instrument; it is easily biopsied.
A biopsy is performed at the border of the lesion, including healthy tissue. The sample includes altered and healthy tissues. Their comparison allows us to objectively assess the existing deviations.
Preparation
Before performing a biopsy of the cervical uterus, the patient undergoes a number of studies:
- consultation with a gynecologist
- regular or extended colposcopy
- histological analysis of cervical tissue
- smears to determine the state of the flora and detect hidden infectious pathogens
- bacterial culture from the vagina
- general diagnostics (ultrasound, blood tests, etc.)
To reduce the likelihood of developing complications after a preparatory biopsy, the patient should follow a number of recommendations:
- refuse sex 2 days before the intervention
- do not introduce any medicinal substances into the vagina (except those approved by the gynecologist)
- avoid douching and the use of tampons 2 days before the biopsy
- on the evening before the visit to the gynecologist, you must take it in accordance with the rules of intimate hygiene
How to prepare?
The advantage of the method is simple preparation for the procedure, thanks to which endometrial biopsy pipette saves time and nerves of patients, as well as financial costs for tests and monitoring processes in the reproductive system.
Before the study you need:
- undergo an examination by a gynecologist;
- conduct laboratory tests for hepatitis, syphilis, HIV, sexually transmitted infections;
- take a smear for microflora.
24 hours before the examination, you should refrain from intimacy, the use of vaginal suppositories, tampons
Radio wave biopsy of the cervix: how it is performed
This procedure, which takes on average 7 to 10 minutes, is usually performed in the first phase of the menstrual cycle (up to the 10th day). At the same time, in some cases, the gynecologist may prescribe a biopsy on days 19-23 of the cycle.
Radio wave biopsy of the cervix, the low price of which makes this procedure widespread, is a virtually painless intervention: manipulations may be accompanied by minor discomfort in the lower abdomen (for example, a slight pain may occur when taking a sample from the affected area). Since patients differ in their level of sensitivity to pain, in some cases the doctor may use a local anesthetic (for example, lidocaine). When using painkillers, the patient should follow a gentle diet the day before the procedure.
Methods
There are several ways to carry out the procedure:
- Colposcopic;
- Radio wave;
- Conchotomnaya;
- Electroexcision;
- Laser;
- Wedge-shaped;
- Circular.
Colposcopic. The biopsy sample is taken without anesthesia and hospitalization with a special needle. The patient feels slight discomfort, but this is only a few minutes.
Endometrial aspiration biopsy
Radio wave. A radio wave apparatus is used. Minimal risk of scarring. Healing within a couple of days. It is carried out without anesthesia.
Conchotomnaya. This is done using a conchotome and special scissors. Local anesthesia is required.
Electroexcision. In this embodiment, a current is used, through which it is passed through special tools. Scar formation on the organ is possible. No anesthesia is required.
Laser. Performed in a hospital setting using general anesthesia. Use a laser knife. This method is considered low-traumatic.
Wedge-shaped. An advanced method: a scalpel is used to remove not only part of the problematic material, but also sections of healthy tissue. Anesthesia and hospital conditions are required.
Circular. This is also an advanced version of biopsy. The doctor uses a scalpel or radio knife. Anesthesia or anesthesia and hospital conditions are required.
Rehabilitation period
Healing of the cervix takes 3-4 weeks. During this period, many patients note the appearance of watery discharge. 10-14 days after the biopsy, the fibrin film is rejected, which may be accompanied by the appearance of scanty bleeding (disappears after a few days).
After the procedure, the woman must give up sex life and heavy physical activity for one month. Also prohibited are taking a bath, visiting a bathhouse, sauna, and swimming in open water.
After one month, a control gynecological examination is carried out to assess the healing process of the cervix, analyze histological examination data and develop further recommendations.
What is a loop biopsy
This biopsy method is also called electroexcision. The essence of the procedure is to excise pathological areas with a special instrument, which is shaped like a loop. The loop-shaped nozzle is mounted on a metal rod connected to a handle, which is attached directly to the main unit of the device.
A loop biopsy machine generates a high-frequency current that is conducted to the loop, heating it to high temperatures. It is with this loop that excision of tissue is carried out, which will subsequently be subjected to histological examination.
The main goal of the procedure is to confirm or refute an oncological disease, since a biopsy is primarily performed for histological examination of the changed tissues.
Among the advantages of the technique are the following:
- simplicity and accessibility;
- relatively low cost;
- sufficient volume of material obtained.
But loop biopsy has disadvantages. After manipulation, a large scar forms on the cervix, which can cause the inability to conceive and bear a child normally. Therefore, the procedure is not prescribed to nulliparous patients, as well as women who are planning another pregnancy. In general, this method is considered highly traumatic and is therefore used only in extreme cases.
Complications of cervical biopsy
Radio wave biopsy of the cervix is very rarely accompanied by complications such as infections or bleeding. If the following symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor:
- excessive bleeding (blood that is bright red or dark with blood clots)
- the duration of menstruation after the biopsy is more than a week
- light bleeding lasting more than 2-3 weeks
- increased body temperature (up to 37.5 degrees and above)
- the appearance of unpleasant-smelling vaginal discharge
Do you need a prostate biopsy?
Prostate biopsy (removal and examination of a piece of tissue) is a painful and insufficiently informative procedure; it is performed annually on more than a million men around the world. In most cases, cancer is not confirmed.
There are other diagnostic procedures that are less expensive and painful, but which can help specialists suspect prostate cancer at a very early stage.
Review
Most often, screening for prostate cancer begins with a blood test for PSA (prostate-specific antigen). An elevated PSA level may indicate the likelihood of prostate disease.
A PSA level, combined with the results of a digital rectal examination and ultrasound, can help your doctor suspect prostate cancer.
The most common diagnostic test for suspected prostate cancer is a biopsy: under ultrasound guidance, a doctor uses a small needle to remove a section of prostate tissue, which is then examined under a microscope for the presence of cancer cells.
A biopsy can not only show the presence or absence of cancer, but also determine its stage.
The patient should talk to the doctor about whether a prostate biopsy is necessary in this case or whether there is an alternative.
It is better to give preference to a biopsy in the following cases:
- The PSA level is significantly higher than normal, and the prostate is sharply enlarged during digital examination.
- Imaging findings suggest the likelihood of an aggressive form of cancer.
- The patient is at risk for prostate cancer.
Three alternatives to biopsy
Laboratory diagnostic methods
There are a number of tests that determine the presence in the blood of enzymes synthesized by cancer cells. One such test is the 4Kscore test, a relatively new way to diagnose prostate cancer. It does not replace a biopsy, but it can “weed out” those who do not need a biopsy.
The method for determining enzymes in the blood cannot be used as the only one; it can complement other studies.
Dynamic observation
Most often, after detecting high PSA numbers in the blood, the doctor immediately prescribes a prostate biopsy. However, it is equally important to know whether PSA changes over time. So, for example, if the PSA level is high but does not change over time, then prostate cancer most likely does not exist.
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an imaging technique that uses a magnetic field and radiofrequency pulses. Like a biopsy, MRI can produce false results, but is 98% accurate.
There are different options for MRI:
- Diffusion MRI – assessment of water absorption by molecules.
- MRI with contrast - assesses blood flow in and around the prostate.
- Magnetic resonance spectroscopy - allows you to distinguish cancer from other causes of prostate enlargement (for example, infectious diseases).
Each MRI technique has its own advantages and disadvantages. The optimal solution is to combine two different methods; then the picture will become more complete.
Advantages and disadvantages of prostate biopsy
Prostate biopsy, like any other research method, has its own characteristics.
The advantages are:
- Obtaining accurate information about the aggressiveness of cancer.
- Confirmation of cancer when there is evidence to suspect it.
- Possibility to begin treatment immediately after the biopsy.
The issue of early diagnosis of prostate cancer is very relevant, since the five-year survival rate with timely detection and treatment is 99%.
Disadvantages of Prostate Biopsy
- Discomfort. The material for biopsy is taken under local anesthesia, but pain is possible in the first days after the procedure.
- Insufficient information content. The probability of not finding cancer if it is present is approximately 20%. There is also a risk of false positive results. This means that some patients will have to have the biopsy done multiple times.
- Risk of hospitalization. The invasiveness of the procedure implies the likelihood of complications, primarily infectious. A 2011 study found that 6.9% of men were hospitalized within 30 days of a prostate biopsy. In addition, there is a risk of bleeding during the first days after the procedure.
Risk factors for prostate cancer
Elevated PSA levels in the blood are an important risk factor for prostate cancer.
Other factors include:
- age;
- family history (presence of prostate cancer in blood relatives);
- the presence of mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes;
- presence of Lynch syndrome (hereditary colon cancer);
- eating red meat and high-fat dairy products;
- obesity;
- smoking;
- history of inflammatory diseases of the prostate;
- history of sexually transmitted infections;
- exposure to certain toxic chemicals.
Some studies suggest that a vasectomy also increases the risk of prostate cancer.
What questions should you ask your doctor?
Below is a list of some questions you may want to ask your doctor who ordered your prostate biopsy.
- Am I at risk for prostate cancer?
- What treatments are there for prostate cancer?
- Are there other, more accurate and safer methods for diagnosing prostate cancer?
- Will a repeat biopsy be needed?
- How high is my PSA level?
- What are the results of digital and ultrasound rectal examination of the prostate?
Conclusion
The diagnosis of prostate cancer is often frightening for patients, but in fact, the disease is treatable and has a favorable prognosis if detected early. This does not mean that all men should undergo all kinds of diagnostic procedures. It is necessary to consult with a competent specialist who will prescribe the most suitable methods.
Aminat Adzhieva, portal “Eternal Youth” based on materials from Medical News Today: Are there any alternatives to a prostate biopsy?
Progress of the procedure
A loop biopsy is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. The procedure lasts on average 20 – 30 minutes. The technology includes the following stages:
- The patient is placed in a gynecological chair, after which the doctor performs sanitation of the genital organs and cervix.
- A dilator is placed on the vagina, after which a local anesthetic is administered.
- As soon as the anesthesia takes effect, the doctor inserts an electrocoagulator into the vaginal cavity.
- A biopath is collected using a loop, which is immediately placed under a glass slide.
- At the end of the procedure, the genitals and vagina are re-sanitized, and the dilators are removed.
If the woman feels normal, immediately after the operation she can return home, where she will undergo rehabilitation for 2.5 - 3 weeks. The rules of the recovery period must be agreed upon with the doctor during consultation before or after the biopsy.