Is an anechoic inclusion in the uterus dangerous and what is it? These are polyps that may have malignant potential, and are essentially localized hyperplasia of the endometrium, that is, the inner lining of the uterine cavity. As a rule, they are located singly, but in 20% of cases there are multiple structures. They can have a wide base or a narrow vascular pedicle and occur in any part of the organ. They often have no symptoms and are an incidental finding during ultrasound diagnostics, for example, during pregnancy. May cause abnormal uterine bleeding.
Content
- Ovarian cyst - what is it?
- Forms of ovarian cyst
- At-risk groups
- Symptoms of an ovarian cyst
- Why do ovarian cysts form?
- What is an ovarian follicular cyst?
- Treatment of follicular cyst
- Corpus luteum cyst and its treatment
- Is a corpus luteum cyst dangerous during pregnancy?
- Dermoid cyst
- What is endometrioma (endometrioid ovarian cyst)?
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Cystadenoma
- Paraovarian cyst
- Carcinoma (malignant cyst)
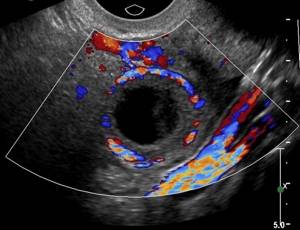
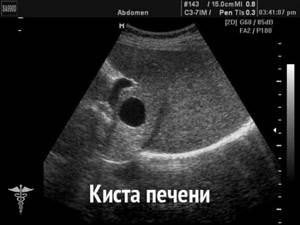
The anechoic formation in the left ovary is a round cyst with a homogeneous structure and a clear contour.
A woman receives a medical report “anechoic formation in the left or right ovary” after undergoing an ultrasound examination of the internal genital organs or the pelvis for various reasons. The conclusion may be, for example, this: “anechoic inclusion with a capsule (hyperechoic rim), signs of a corpus luteum cyst on the right.” Such a formation in the ultrasound “picture” looks light, almost white. For reference, similar inclusions (formations) are also hypoechoic (from other Greek - “lower, smaller”), they are detected on ultrasound as dark structures.
It should be understood that an anechoic or hypoechoic formation in the left ovary is a pathology that is not a diagnosis. This is a description of how the ultrasound beam was reflected from the ovary: the equipment emits ultrasound waves, human tissues and organs either transmit them unchanged (anechoic or echo-negative organs and formations) or reflect them to one degree or another. An anechoic structure is one that contains fluid.
In the case of the ovary, such a conclusion from a pelvic ultrasound means that the sonologist diagnoses a cyst. A woman’s next step after receiving such data about her health is to visit a gynecologist, since cysts can be completely different, and their therapy varies significantly.
It's time to decide how to treat a disease such as an ovarian cyst, and what impact it will have on pregnancy planning.
Anechoic formation: concept
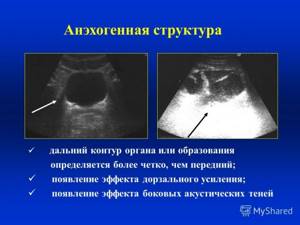
Echogenicity refers to the conductivity of ultrasound waves by tissues. High-density tissues, like bones, reflect ultrasound completely, and it is also reflected at the air-containing boundaries of organs and tissues. The denser the tissue, the higher the echogenicity; on ultrasound, such tissues look lighter.
If there is a large amount of fluid in an organ, including blood vessels, then its echogenicity is lower, therefore fluid neoplasms are considered anechoic and appear black on ultrasound.
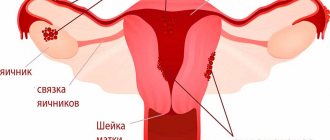
Ovarian cyst - what is it?
An anechoic formation - an ovarian cyst - is a single ovoid inclusion of a round or oval shape, with thickened walls. The anechoic structure must contain fluid, and blood can be added to it.
The contents of the cyst can not only be completely anechoic, but also have a cobweb-like or mesh-like structure, contain irregularly shaped septa or hyperechoic inclusions (which include contents such as blood clots) of various sizes and shapes.
An ovarian cyst can be single or multiple (several cysts on one ovary), as well as single-chamber and multi-chamber (two-chamber, three-chamber, etc.).
A single-chamber cyst is a simple vesicle in which there are no internal septa. A multi-chamber cyst has many partitions inside. It is believed that a single-chamber cyst is safer than a multi-chamber cyst.
Forms of ovarian cyst
- Follicular cyst
- formed from a follicle (vesicle) - a container for a maturing egg. Normally, the follicle, having reached a certain maturity, bursts and the egg is released into the abdominal cavity, which is called ovulation. If the follicle continues to increase in size and does not rupture in a timely manner, they speak of the formation of a follicular cyst, otherwise called an avascular formation. - Corpus luteum cyst
- formed when fluid and blood accumulate at the site of a ruptured follicle. - A simple (serous) cyst
is a bubble formed from serous tissue (covering the outside of the ovaries), filled with clear liquid. - A paraovarian cyst
is a dense, inactive formation near the ovary, which is a thin-walled chamber with a clear liquid with a small protein content. This cyst develops from the epididymis and is located between the fallopian tube and the ovary. During an ultrasound scan next to a cyst of this form, as a rule, the ovarian tissue is clearly visible.
Thyroid gland and its defects
An anechoic pathology of the thyroid gland is indicated if, during an ultrasound, the ultrasound signal is not reflected from some of its areas. It may be normal or require specialized treatment. In the gland, it occurs in normal tissues, its appearance is provoked by blood vessels, and the “black pattern” effect can also be caused by intranodular vessels.
Similar nodes in the thyroid gland can occur due to the appearance of accumulation of colloid in the follicles. The accumulation appears due to impaired blood flow in one of the lobes of the thyroid gland. In more than 90% of cases it is benign.
IMPORTANT! Colloid is a viscous pink liquid with a uniform structure.
Anechoic formation of the thyroid gland is as follows:
- A true cyst has clearly defined boundaries and is a cavity filled with fluid;
- Pseudocyst - is a transformed node or adenoma, occurs due to hemorrhage inside the node;
- Lateral cervical cyst is indirectly related to the gland, since it is located next to it; with active growth, it sometimes provokes compression of the organ.
Important! Anechoic formations diagnosed in patients over 50 years of age are malignant in most cases.
At-risk groups
Often, ovarian cysts are detected in young girls, as well as women of reproductive age (i.e., in patients who have not yet reached menopause). In addition, there is a small probability of the appearance of an ovarian cyst in girls before the onset of menstruation (usually a congenital cyst) and in women in the first five years of menopause.
It is important that every postmenopausal woman understands that ovarian cysts during menopause require much more serious attention than if they appeared in a woman of reproductive age. The fact is that after menopause the risk of developing a tumor (ovarian cancer) increases significantly. Therefore, all inclusions that may form in the ovary must undergo a thorough examination that can detect the presence of signs of cancer.
Development factors
The main reasons for the development of changes in the reproductive system are almost always pathological. Although natural moments cannot be excluded. The percentages are not entirely known. What causes the development of insecurity in the uterine cavity or ovaries?
Uterus
- Pregnancy
This happens in about half of all cases. Based on the results of the USG study, the presence of fetal eggs was found. It is a fertilized egg that moves through the oxide and is attached to the wall of the reproductive organ. You cannot always tell with any certainty whether a given situation is pregnant or not, even on the first try. Dynamic continuation of actions in a short time is necessary. At least for 2-3 weeks. No dynamics indicates the process of cancer or another, but excludes pregnancy. The development of the structure in accordance with all the rights of pregnancy, on the contrary, confirms the suspicion of a specialist. Typically there are no differential problems. Everything is obvious.
A pathological process in which endometrial cells, the inner lining of the uterus, move beyond the normal anatomical position and begin to spread along the cervical canal, fallopian tubes, and can invade the ovaries. There are several options. When assessing the condition of the reproductive system, it is necessary to determine, including the structures of all tissues surrounding it. At the initial stage, diagnosing endometriosis based on the results of the USG test is almost impossible. Regular follow-up is necessary.
- Tumor tumors
Uterine cancer is accompanied by the development of inexpensive creativity in the jam. Clinical variations vary, with cancer being the most common cause. The aggressiveness, rate of cell division and progression of the disease depend on the histological type of the tumor. Some cancers grow for many years without paying attention and do not metastasize until the last moment. There are also significantly more dangerous forms, especially those of embryonic origin. They can take the patient's life within months of exposure. So you can't do that.
Soft non-cancerous crayfish. They make up a small capsule, a fibrous sheath filled with fluid, blue blood, or over speech. Such abnormalities have little or no enlargement or progression. Restoration is carried out as needed if the cyst is large and distorts normal sexual life and reproductive activity.
- Soft cancer
You can talk about two types of structures. The first is the uterus. It is located in the uterine cavity. This is echosene, clearly different from the surrounding tissue. It grows slowly. In the first years of your youth, the intensity of proliferation in it is greater than after passing through menopause, because cancer is hormonally determined.
Another possible form is teratoma. This is an innate structure that, when examined, can show a completely different picture. Typically, ultrasound examination shows inclusions of various tissue types and an inhomogeneous signal.
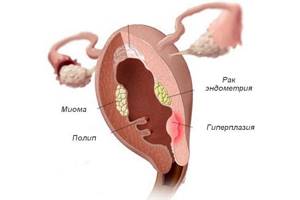
Uterine neoplasia
Ovaries
- Polycystic
What is this? Polycystic disease is the formation of a group of fluid-filled fibrous capsules, cysts. Anachogenic inclusions during ultrasound examination are small, multiple, and heterogeneously localized. This change is not life-threatening, but makes it difficult to conceive.
- Single cysts in the structure of an organ
They are observed somewhat less frequently. The size of the cyst varies from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
- Malignant neoplasms
Being in the ovaries, they are almost always dangerous and aggressive. The most dangerous teratogenic forms are dysgerminoma and others. They are very aggressive and multiply rapidly (cell division).
- Maturation of an excessive number of follicles in the ovary (multifollicular ovaries) more than eight.
In this case, scattered structures of small diameter are detected, darkened and in sharp contrast with healthy tissue, or large accumulations that can be mistaken for neoplastic. In this case, it is advisable to conduct a tomographic examination. With or without contrast enhancement.
The causes of deviations are almost always pathological. Especially if this finding is discovered during examination of the ovaries. Unfortunately, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based on one ultrasound result, and a comprehensive examination is necessary to determine the nature of the process.
Symptoms of an ovarian cyst
Usually, owners of ovarian cysts do not even suspect their presence, since small cysts do not provoke any symptoms. As the cyst develops, a woman may experience the following symptoms:
- Feeling of pressure and heaviness in the pelvis.
- Dull pain in the lower abdomen on the left or right, appearing or intensifying with physical activity and/or sexual intercourse.
- False urge to defecate.
- Pain when urinating and frequent urination.
- In case of complications of the cyst (its torsion, rupture), severe paroxysmal pain in the abdomen and groin area, high body temperature, vomiting, and nausea may occur. If such symptoms appear, you should immediately contact a gynecologist or call an ambulance.
Why do ovarian cysts form?
Today, the exact causes of the formation of ovarian cysts in the uterine cavity are not known, but some patterns have been identified:
- Congenital cyst (the girl already has it at birth): dermoid cyst.
- Cysts due to hormonal imbalance: corpus luteum cyst, follicular (functional) cyst.
- Benign ovarian cysts: cystadenomas.
- Cysts in other diseases: cyst in polycystic ovary syndrome, endometrioid ovarian cyst.
- Malignant ovarian cyst: carcinoma (oncology) of the ovary.
Classification of anechoic neoplasms
Classification of incorrect test results occurs at several levels. The key one, which is used by ultrasound diagnostic specialists, is the size of the changed tissues. In this case, there are three forms of irregularity:
- Small anechoic formations of the uterine cavity. The size of the structure in this case barely exceeds 2 mm in diameter. Maximum value 3 mm. In the absence of a neoplastic component or hormonal factor, this disorder is detected extremely rarely. In some cases, the pathological structure does not allow normal conception. Infertility occurs due to the abnormal structure of the endometrium. The fertilized egg cannot stick to the tissue. Gynecologists consider cancer one of the main causes of impaired conception and primarily look for altered tissue in the uterus. Structures measuring 2-3 mm are not dangerous as such, unless it is a malignant tumor.
- Medium anechoic clusters. These are anomalies with a diameter of up to 6-7 mm and even up to 1 cm. It depends on the specific situation, location, design and shape. The problem is solved using special diagnostics. Such altered accumulations of cells are somewhat more dangerous due to the possible compression of surrounding tissues. Possible problems with conception, disturbances in the normal menstrual cycle, pain of unknown origin. Pathological forms additionally provoke a number of other symptoms. During an ultrasound examination, changes (so-called incidentaloma) may be accidentally detected.
- Large anechoic abnormalities. The diameter is more than a centimeter. They occur relatively often. In almost all cases we are dealing with a tumor process. Whether it's fibroids or cancer. A pathology such as a cyst is a somewhat more common occurrence. This is not a tumor, it is considered a non-neoplastic mass. He is not inclined to growth and progression. The need for treatment is decided by a gynecologist after additional examinations. When planning therapy, the main features of the pathology are taken into account and the problem is discussed, including with the oncologist.
Another way of classification is to determine the type of structure that is present. Aneogenous masses located in the uterine cavity can be as follows:
- Natural, non-marbet, abnormal accumulation. They are quite rare because there are not many development factors. This also applies to pregnancy. Fetal eggs in the initial phases of development appear as a darkened spot with different sizes (depending on the phase in which the pregnancy was detected and the location of the trailer). There are no other natural factors.
- Pathological, pathological changes. They happen much more often. This includes a wide range of possible problems. Cysts, cancer and non-cancer, neoplasia, consequences of endometriosis, other options. These types of changes require mandatory treatment. Probably promptly. Under the supervision of specialists in the field of gynecology, gynecological oncology.
There are other classification methods. For example, depending on the nature of the pathological process, the presence or absence of symptoms, and the clinical image. Methods for future recovery, additional pathologies in the interview.
Ultrasonic testing device
All methods are used to more accurately determine the essence of the disorder, its nature.
Treatment of follicular cyst

If we were talking about a disease such as a cervical cyst, it is customary to use the radio wave method for its treatment (the cyst is destroyed by high-frequency waves). As for ovarian cysts, usually a follicular or functional cyst does not need to be treated, since it completely resolves on its own in one to two months. If within three months the follicular cyst has not disappeared or its size exceeds five to seven centimeters, then such a cyst should be treated.
There are two main methods of treating ovarian cysts: with hormonal drugs and with surgery. Hormonal medications (birth control pills, oral contraceptives) help reduce the size of the cyst and prevent the formation of new ovarian cysts. When treatment with contraceptive drugs does not produce results, surgery is suggested. Also, surgical help will be needed when the size of the cyst is more than ten centimeters and it continues to grow, when a woman has severe abdominal pain, as well as in case of suspected twisted inflammation of the cyst, as well as other complications.
Kidney deformation
The kidneys, which are the main organ of the urinary system, are also subject to structural changes, which during ultrasound examination are diagnosed as an anechoic formation.
For kidneys, in the presence of such a diagnosis, a characteristic deformation of the organ itself is characteristic; in medicine, they speak of deformation of the renal collecting system.
Such a pathology can cause death of the kidney parenchyma, retraction of the renal papillae, and flattening of the renal tubules. Most often, the pathology manifests itself in adulthood; it occurs extremely rarely in children.
Changes in the structure of the kidneys occur due to the following pathologies:
- Hydronephrosis - bottom - or bilateral. The reason is a malfunction of the bladder valve and the reverse flow of urine or a disturbance in the removal of urine from the body. A hydronephotic sac forms in the kidney, and if it ruptures, sepsis can develop and, if not treated in a timely manner, can lead to death.
- Doubling of the heart rate is most often observed in women in labor, infants and children under 6 years of age. The kidney is divided into lobules, each with its own artery and ureter with an orifice, which can sometimes flow not into the bladder, but into the intestine. This pathology leads to disruption of the circulatory system. It can only be eliminated surgically.
- Neoplasms. Oncological pathologies occur in 8% of cases, usually in patients over 60 years of age.
- Genetic and congenital defects:
- narrowing and or complete fusion of the ureter,
- pyeloectonasia,
- nee doubling ChLS
IMPORTANT! Congenital kidney deformation can be caused by alcohol and cigarette abuse by the expectant mother.
Corpus luteum cyst and its treatment
When ovulation ends (the rupture of the follicle and the release of the egg), a piece of tissue appears in the ovary that produces progesterone, the pregnancy hormone. This area of tissue is called the corpus luteum. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum should normally resolve. But there are situations when the corpus luteum does not disappear, but fills with blood or fluid, thereby forming a corpus luteum cyst.
Typically, a corpus luteum cyst does not require treatment, since it resolves on its own within one to two months. To speed up the process of resorption, the gynecologist may recommend taking contraceptive medications that help reduce the size of the cyst.
In rare situations, a corpus luteum cyst reaches a large size (more than five to seven centimeters in diameter), spins around its axis or ruptures. In this case, the woman experiences severe pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies with exercise or sex. If any complication of a corpus luteum cyst develops, urgent surgery must be performed.
What is the danger: pathology or normal?
Anechoic formation can be either a physiological norm or a dangerous pathology; diseases are often diagnosed in women in the uterus or appendages. Their presence is a signal for a woman to undergo a more accurate diagnosis.
Depending on this, they may be:
- Serous cyst,
- Follicular cyst,
- Endometroid cyst , with a light-colored capsule filled with a heterogeneous mass
- Fetus during pregnancy,
- Corpus luteum.
IMPORTANT! The corpus luteum in the ovary in women is a physiological norm and evidence of the onset of ovulation.
An anechoic cyst is benign if there are vessels in its structure. A low echogenicity cyst during a period of up to 4 weeks of missed menstruation may indicate that a woman is pregnant.
Is a corpus luteum cyst dangerous during pregnancy?
No, such a cyst is not dangerous. Corpus luteum cyst is not a rare occurrence in the early stages of pregnancy. It not only does not interfere with the development of the fetus, but also helps maintain pregnancy by producing the pregnancy hormone - progesterone. When the need for progesterone disappears, the cyst resolves on its own. Often, this occurs after the twelfth week of pregnancy (in some cases at the eighteenth or nineteenth week).
Again, in extremely rare cases, there is a possibility of the cyst rupturing or torsion. In this case, the pregnant woman will feel severe pain in the abdomen. If this happens, emergency surgery may be needed.
About the clinical picture of the main processes of an anechoic finding
Anechoic implantation into the uterine cavity is not always unpleasant. In the clinic there are formations of at least 3-4 mm of non-malignant origin. Malignant neoplasms deserve a separate lecture; in most cases, the clinic is present.
Anechoic formations in the uterus during pregnancy are accompanied by typical symptoms of the onset of the pregnancy process. At this stage, symptoms of toxicity, weakness, drowsiness, nausea, headaches, increased meteosensitivity and sensitivity to ambient temperature, etc. may be pronounced. Such signals from the body should be interpreted correctly.
In general, the presence of pathological structures in the uterine cavity of sufficient size is manifested as follows:
- Pain in the lower abdomen, in its lower part, on the side. There are several options. Discomfort intensifies during physical activity, during sexual intercourse, especially acute, after visiting the toilet, or changing body position. The feelings are strong and depressing.
- Menstrual irregularities. The type of heavy menstrual bleeding is called menorrhagia. They pose a huge risk to the health and sometimes even the life of the patient, as they can cause anemia and other abnormalities.
- Acyclic bleeding. This occurs between the main days of the cycle. Their intensity varies from a harmless minimum of weeping discharge to a critical maximum of full-blown life-threatening bleeding.
- Problems with conception. Relative infertility. Inability to implant the fetus in case of uterine disease or disruption of normal hormonal function in case of pathological damage to one or both ovaries.
- Emission from the genital tract. Depending on the character, it can be transparent or bloody.
There are also specific clinical signs that indicate a possible cause of the disorder.
When localized in the uterine cavity, symptoms of menstrual irregularities and prolonged pain are observed. Usually the clinic is limited to such signs.
Endometriosis causes severe pain in the lower abdomen. After the examination, the nature of the violations becomes obvious. It is possible to carry out diagnostic curettage at an early stage of suspected disease. This is the main method of checking the diagnosis. The inability to become pregnant is also clearly evident.
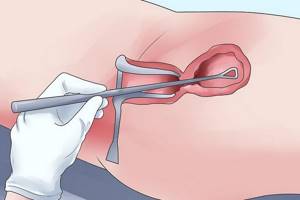
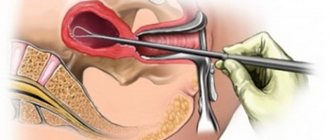
Carrying out diagnostic curettage of the uterus
As a rule, the muscle does not make itself felt until it becomes large enough. On ultrasound it looks like an anechoic parietal incision in the cervix, in the uterine cavity itself, in its mucous, submucosal and muscular layers.
Cysts and other formations do not show symptoms as such. All symptoms are associated with compression and mass effect. For their development, appropriate sizes of structures are required, from 4 mm and above.
Ovarian dysfunction is largely accompanied by hormonal disorders. Moreover, the imbalance of estrogen and progesterone is noticeable already in the initial stages of the deviation, regardless of the size of the tumor. The biggest problems arise when trying to get pregnant. There is a possibility of pregnancy, but the chances are low. There are no problems with artificial insemination and egg implantation.
The clinical picture differs from case to case. Assessing symptoms allows you to quickly assess the situation. It gives a lot of information about the essence of the phenomenon. Together with objective diagnostic data, this allows the doctor to quickly make a diagnosis.
How to behave when an anechoic mass is detected if the situation is not sudden?
If the doctor does not give specific recommendations on lifestyle, it is enough to minimize the risk of negative effects on the body from the outside. It's easy to do.
It is necessary to give up tobacco, cigarettes, and alcoholic beverages. Throughout the entire period of control care, you should monitor your well-being and record all changes in your health. Then, at your second visit, you'll let your doctor know about any changes to make diagnosis easier.
The woman's opinion will be used to decide what to do next. It is recommended to listen to your specialist.
Dermoid cyst
A dermoid cyst is a benign tumor-like formation in the ovary, which is present during the birth of a girl and can increase in size during puberty. It may seem strange, but sometimes completely unexpected tissues are revealed in this cyst: teeth, hair, bone tissue or cartilage. This can be explained by the fact that during the formation of this cyst (even during intrauterine development) it contained stem cells capable of giving rise to absolutely any tissue of the body.
The only treatment for dermoid cysts is surgery. It is impossible to cure this type of cyst with pills today.
How does an anechoic formation characterize the condition of the mammary glands?
During an ultrasound of the mammary glands, a doctor may detect a dark spot or a group of similar spots; as a rule, they are benign. If a woman has an anechoic formation in the mammary gland, an urgent consultation with a mammologist is necessary, as this may indicate the presence of a serious pathology.
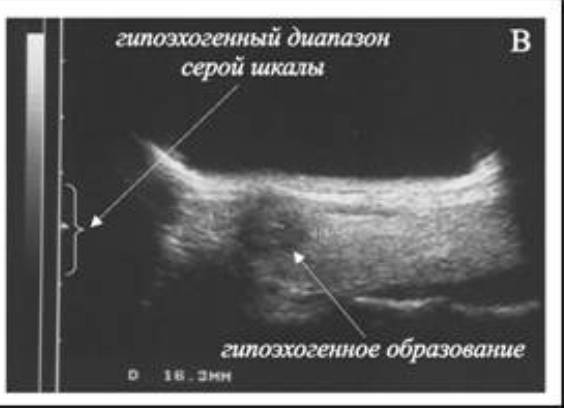
When dark spots appear, the doctor may talk about the following pathologies:
- Cyst. As a rule, it does not cause any discomfort to the woman and is asymptomatic. It is almost always benign, but without timely treatment it can develop into cancer.
- Fibroadenoma. Can occur at any age. Sometimes it appears in a leaf-shaped form, which is characterized by rapid growth.
- Malignant pathologies. It can be either single of different sizes or multiple; during examination, it is important to identify the level of its germination in the gland tissue.
- Oleogranuloma. A benign pathology that occurs as a result of injury to the gland. May lead to necrosis of glandular tissue.
ATTENTION! During lactation, women may develop a galactocele, a cavity filled with milk.
What is endometrioma (endometrioid ovarian cyst)?
Endometrioma forms in women who suffer from endometriosis. Endometriosis is a female disease in which the endometrium (the inner lining of the uterus) begins to develop in other organs. When the endometrium begins to develop on the ovary, an endometrioid ovarian cyst may appear. Since the endometrioid ovarian cyst is filled with dark brown fluid, it is often called a chocolate cyst.
Endometrioma (chocolate cyst) is treated exclusively with surgery.
Carcinoma (malignant cyst)
Ovarian carcinoma or malignant cyst is quite rare. There is an increased likelihood of developing ovarian cancer in women whose relatives had ovarian or breast cancer, as well as in patients who have never given birth. Symptoms of a malignant ovarian cyst are as follows:
- weakness;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- headache;
- weight loss.
Ovarian carcinoma is treated only with surgery. After removal of the tumor, drugs that destroy cancer cells (chemotherapy), as well as irradiation of the ovaries (radiotherapy), may be prescribed.
anechoic formation in the ovary, cyst
Polyp treatment
Treatment is surgical and involves removing the tumor. Recently, doctors have been trying, not entirely successfully, to invent an alternative to the surgical treatment of endometrial polyps. It is the possibility of a simple anechoic inclusion turning out to be cancer that limits the search for treatments for polyps without their removal and histological examination. If you use only ultrasound as a diagnosis, there is always a risk of missing cancer in the early stages. Therefore, simultaneously with the search for ways without surgical methods, the scientific process is moving towards improving surgical techniques in order to achieve maximum safety for patients.
Currently, in modern clinics, simple curettage of the uterus is replaced by endoscopic high-tech intervention - hysteroscopy, which involves immediate diagnosis and removal of any formations. This procedure is performed under anesthesia. A device with a camera is inserted into the uterus, allowing the entire endometrium to be examined. Hysteroscopy allows you to immediately remove the polyp.
To clarify the diagnosis of an anechoic inclusion in the uterus, distant formations are examined histologically. This allows us to exclude oncological pathology.