Hysterectomy is an operation during which the uterus is removed. Its other name is uterine amputation . Every year, Russian gynecological surgeons perform hundreds of thousands of hysterectomies, of which only 10% are related to cancer. The remaining 90% are carried out for benign pathologies, primarily uterine fibroids.
Hysterectomy accounts for up to 38% of all gynecological operations in Russia. The average age of women operated on is 40 years.
And this despite the fact that currently there are other organ-preserving methods of treating fibroids. They can be used in most cases. Unfortunately, many gynecologists still operate the old fashioned way. Let's talk about under what conditions it is actually necessary to remove the uterus, what complications this poses, and how you can get rid of fibroids while preserving an important organ of the female reproductive system.
- Indications and contraindications for hysterectomy
- Types of hysterectomy surgeries
- Preoperative examination
- Preparing for surgery
- How is a hysterectomy performed?
- Postoperative period
- Risks and complications of hysterectomy
- Rehabilitation after hysterectomy
- Non-surgical treatment methods
Indications and contraindications for hysterectomy
Among the indications for hysterectomy, fibroids are still often mentioned in first place. According to some estimates, up to 40% of all hysterectomies are performed for this disease.
This is primarily due to a misunderstanding of the nature of fibroids and the functions of the uterus in the past. Previously, it was believed that fibroids were a benign tumor that occurred as a result of hormonal imbalance. The uterus was perceived as an organ intended exclusively for bearing a fetus. Therefore, gynecologists often preferred to act radically and suggested immediately removing the organ, especially to women who did not plan a pregnancy in the future. It has now become clear that the causes of fibroids are much more complex, and the uterus is an important organ that affects the overall health of a woman. According to modern approaches, in most cases of fibroids, hysterectomy is not indicated. This is a last resort. You should always try to preserve the uterus - and today there are effective organ-preserving treatment methods. We will talk about them below.
By and large, for fibroids, there are only two absolute indications for removal of the uterus:
- If there is a suspicion of a malignant tumor.
- If a woman with fibroids has prolapse or prolapse of the uterus.
Other indications for hysterectomy (according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists):
- Endometriosis.
- Uterine prolapse.
- Abnormal uterine bleeding.
- Chronic pelvic pain.
- Malignant tumors of the uterus and ovaries.
Not all of these indications are absolute. For pathologies not related to cancer, other organ-preserving treatment methods are available. Hysterectomy is indicated when other measures do not help, and surgery is needed to prevent complications and save the patient’s life.
The main contraindications to elective hysterectomy: severe disorders of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, bleeding disorders and the risk of severe bleeding during surgery, peritonitis, inflammation, infectious processes of the abdominal wall.
Conservative treatment of uterine fibroids
In modern medicine, the most commonly used hormonal drugs are androgens, progestins and GnRH antagonists, antiandrogens and 17-ethynyl-testosterone derivatives, which cause “false” menopause. This approach allows you to slow down the growth of fibroids and reduce the size of the tumor. But, as a rule, the growth of education resumes if hormone therapy is stopped.
Progestins are a group of steroid hormones that are produced by the ovaries. Their main task is to help the female body regulate the reproductive system. For example, transforming the endometrium of the uterus after fertilization.
Tranexamic acid is another popular hormone therapy drug that helps reduce blood loss during heavy menstruation in patients with fibroids. Tranexamic acid prevents the occurrence of anemia, which is a common side effect of fibroids.
Treatment with hormonal drugs is advisable only in two cases:
- If the patient is elderly;
- And as a wait-and-see approach (for example, when surgical treatment is contraindicated for the patient for certain reasons)
When hormonally treating a patient with uterine fibroids, it is important to have regular ultrasound examinations, tests and examinations with a gynecologist, which will help assess the effectiveness of treatment and adjust it if necessary.
Types of hysterectomy surgeries
Depending on the extent of the surgical intervention, there are three types of hysterectomy:
- Radical . As a rule, this operation is performed only for cancer. The surgeon removes the uterus, its cervix, part of the vagina, surrounding tissue, and lymph nodes. Often the ovaries and fallopian tubes are excised at the same time - a salpingo-oophorectomy .
- Total . This is the most common intervention option. The uterus and its cervix are removed, the ovaries are left.
- Subtotal . Only the body of the uterus is removed, the cervix is left behind.
Indications
Minimally invasive surgery using laparoscopic equipment is prescribed for the following indications:
- rapid growth of myomatous formation;
- uterine bleeding leading to anemia;
- inability to become pregnant or bear a child (provided that other causes of infertility on the part of both partners have not been identified or eliminated);
- functional disturbances in the work of nearby internal organs that are under pressure from the formation;
- intensive adhesive process.
Preoperative examination
Preoperative examination before hysterectomy includes:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Study of blood clotting (coagulogram), blood group, Rh factor, biochemical blood test.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs and kidneys.
- Flora smear, cytological smear.
- Ultrasound of leg veins.
- ECG.
- Blood test for infections: syphilis, viral hepatitis, HIV.
- Fluorography.
- Mammography.
- Biopsy of the endometrium (uterine lining).
- Consultation with a therapist and, if indicated, other medical specialists.
If necessary, the gynecologist may prescribe other diagnostic methods.

Classification of laparoscopic hysterectomies
At the present stage of development of laparoscopy, there are several classifications for hysterectomy. The most popular among them is the classification proposed by H. Rich.
<р3>The following methods of laparoscopic removal of the uterus are distinguished:
- Diagnostic laparoscopy in combination with transvaginal removal of the uterus - this technique allows us to first evaluate the possibility of transvaginal access and its further use;
- Vaginal hysterectomy under laparoscopy control - first, laparoscopic removal of adhesions, tissues damaged by endometriosis, removal of the appendages and ligamentous apparatus of the uterus is performed, and at the second stage, ligation of the arteries and removal of the uterus are performed, like a classic vaginal hysterectomy. It is believed that true laparoscopic hysterectomy is difficult to perform, therefore, in order to avoid possible death and complications, specialists are recommended to perform this particular type of uterine laparoscopy;
- True laparoscopic hysterectomy - performed only using laparoscopic access and instruments, including ligation of the uterine artery;
- Total hysterectomy – a gynecological surgeon removes the uterus and ligates blood vessels, as well as creating a stump through a laparoscope;
- Supravaginal laparoscopic removal of the uterus (subtotal hysterectomy);
- Laparoscopic restoration of the pelvic floor and vaginal hysterectomy - if it is impossible to reconstruct the perineal muscles, eliminate genital prolapse or urinary disorders when performing a classic hysterectomy through the vaginal access, then laparoscopy is used in parallel;
- Laparoscopic removal of the uterus and lymph nodes;
- Hysterectomy according to the Semm method with removal of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal.
Preparing for surgery
The woman is hospitalized in the hospital the day before surgery. Before this, no preparation at home is needed; the doctor will only recommend a diet so that the intestines are emptied in a timely manner.
A cleansing enema is performed the day before and in the morning. An anesthesiologist first talks with the woman and finds out whether she has chronic diseases or allergies to medications. On the day of surgery, you will need to shower and shave your genital hair. Then premedication - medications are administered that help to calm down and relax. Need to pee. The woman is then taken on a gurney to the operating room.
Causes of fibroids
Why fibroids occur has not yet been precisely established. Only a few factors are known that can stimulate the appearance of a neoplasm.
Common reasons include:
- Hormonal disorders;
- Heredity;
- Late onset of menstruation;
- Abortion;
- Diseases of the pelvic organs;
- Excess weight.
An ordinary ultrasound helps to detect fibroids. It is impossible to do this on your own. But you need to know the symptoms that accompany the growth of fibroids in order to consult a doctor in time.
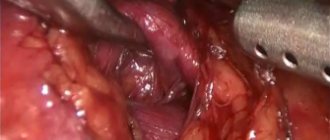
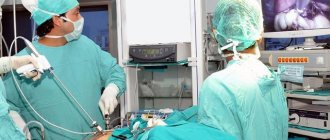
How is a hysterectomy performed?
The most common open surgery is through an incision that can be horizontal along the bikini line or vertical along the midline. The average incision length is between 12 and 17 cm. The advantages of this approach are that it provides a good view for the surgeon and does not require complex equipment. Disadvantages: relatively high risk of complications and long recovery period.
The uterus can be removed laparoscopically, through punctures in the abdominal wall. This operation is less traumatic, after it the risk of some complications is lower, and the woman returns to her normal life faster. But laparoscopic hysterectomy cannot always be performed; factors such as the size of the uterus, the presence of scars from previous operations, obesity and concomitant diseases play a role.
Some clinics perform robot-assisted interventions. Instruments connected to the robot’s “arms” are inserted through punctures in the abdominal wall, and the doctor controls them using a special remote control and monitors the process on the device’s screen.
In some cases, a vaginal hysterectomy is possible. The incision is made inside the vagina, leaving no scars on the skin. Sometimes laparoscopy is performed simultaneously for control.
Carrying out surgery
Laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia and lasts from 40 minutes. up to 2 hours. A trocar is inserted into the abdomen, pumping carbon dioxide, lifting the peritoneal wall and improving visibility of the operated area. Then a second trocar is installed, equipped with an LED and a camera. Afterwards, the surgeon inserts 2 more trocar tubes (4 in total). Through them, using an endoscopic instrument, adhesions are dissected, the tissue above the node is cut, the formation is removed, the vessels are sealed, and sutures are applied. The order of manipulations may vary at the discretion of the surgeon. If the fibroids are large and it is impossible to remove them through the tube, a morcellator is used - a grinding device that is inserted instead of a trocar. Thus, the entire operation is performed through 4 punctures without additional incisions. At the end of the intervention, the holes are sutured, disinfected, and isolated with napkins soaked in a sterilizing composition. No drainage needed.
The optimal time for the operation is the period between the 15th and 25th day of the cycle.
Postoperative period
After the operation, the doctor monitors the woman’s condition, periodically performs dressings, administers painkillers and other medications. A catheter, a tube for draining urine, remains in the bladder for some time. After abdominal surgery, a drainage tube is installed in the abdominal cavity for 1-2 days - a tube for the outflow of blood and ichor. After a vaginal hysterectomy, a gauze pad is left in the vagina for 24 hours.
In the postoperative period, it is important to prevent deep vein thrombosis of the legs. To do this, they try to get the woman back on her feet as soon as possible (the timing depends on the type of operation), and wearing compression garments is recommended.
Why is it better to have myomectomy done at the MEDICA Center for Reproduction and Family Planning?
- In our Center, myomectomies are performed using a state-of-the-art laparoscope with a diameter of less than 5 mm;
- We use only the most modern, high-tech tools and equipment, only the most effective and safe materials and medicines;
- The experience and knowledge of our specialists is a guarantee of performing diagnostic and surgical procedures with impeccable quality;
- All procedures in the clinic are carried out in comfortable conditions;
- With the highest quality of services, our prices do not exceed the city average.
Risks and complications of hysterectomy
A hysterectomy is a major surgery and carries some risks.
Ability to have children
After a hysterectomy, a woman is deprived of an organ designed to carry a fetus, making pregnancy impossible. There will be no more periods. If the ovaries are removed along with the uterus, menopause occurs.
Posthysterectomy syndrome
The uterus is an important organ of the female reproductive system; after its removal, a number of disorders develop in the body. They are combined with the term “posthysterectomy syndrome” . Even if the ovaries remain, blood circulation in them is disrupted, and this affects their function.
Posthysterectomy syndrome includes the following symptoms:
- Emotional disorders, depression.
- A disorder of the autonomic nervous system, which manifests itself in the form of hot flashes, sweating, poor tolerance of high temperatures, palpitations, chills, poor sleep, and increased blood pressure.
- Increased fatigue, low performance.
- Increased anxiety, fear of death.
- Tendency to swelling.
- Deposition of adipose tissue in the abdomen and waist.
- Bone loss, osteoporosis.
- If a woman previously suffered from arterial hypertension, the course of the disease is aggravated.
Sex after hysterectomy
Typically, after a hysterectomy, a woman can have sex as before and enjoy it. Many women note that their sex life has even improved. Most likely, this is due to the fact that the pain and other painful symptoms that the disease caused are no longer bothersome.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Contraindications
Due to possible complications, the laparoscopy method for removing a benign uterine tumor is not recommended for use in:
- assumption of a malignant nature of the neoplasm;
- the presence of cancer tumors of other organs of the reproductive system;
- the size of neoplasms exceeding 60 mm;
- acute infectious diseases (surgical intervention is impossible until complete recovery);
- pathologies of the kidneys and liver;
- weight discrepancy with standard indicators (obesity or underweight);
- heart disease;
- disorders of the respiratory system.
Rehabilitation after hysterectomy
The length of hospitalization depends on the type of surgery. After laparoscopic hysterectomy, the woman is discharged from the hospital after 1–4 days, after open surgery - after 5 days.
Full recovery after laparoscopic surgery occurs after 3-4 weeks, after open surgery - after 6-8 weeks. During this time, you must observe some restrictions:
- Rest more, do not engage in intense physical work.
- Do not lift heavy objects.
- Maintain moderate physical activity as recommended by your doctor.
- Refrain from sexual intercourse.
Recovery after surgery
After laparoscopy, the patient is left in the hospital for 2-3 days, under the supervision of doctors. To avoid complications, it is recommended to get out of bed and move as early as the day of surgery.
For the period established by the attending physician, after discharge, the patient must exclude:
- Bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool, hot baths, swimming in open water;
- Being in the hot sun;
- Sport;
- Sexual contacts;
- Vaginal tampons and suppositories, tablets;
- Douching.
If all recommendations are followed, health will quickly recover, and after the operation the long-awaited pregnancy will certainly occur.
Non-surgical treatment methods
For some diseases, removal of the uterus is necessary. But with fibroids this is an outdated approach. Most women do not need such essentially mutilating surgery. There are other types of treatment that allow you to save the organ and the opportunity to have children in the future.
Organ-conserving surgery, during which only the myomatous node is removed, is called myomectomy . It can be performed, depending on the location of the nodes, open, laparoscopically or through the vagina. This is an effective treatment method, after which pregnancy can occur. But myomectomy also has some disadvantages.
First of all, there is a high probability of relapse. After 4–5 years, fibroids are re-discovered in half of the operated women. A scar remains on the uterus, which can lead to complications during pregnancy; many women have to have a caesarean section. Adhesions form and can lead to obstruction of the fallopian tubes and infertility.
Myomectomy can be performed under three conditions: if the woman plans to become pregnant in the near future, and not later, if there is no risk of opening the uterine cavity and the likelihood that the organ will have to be removed during the operation.
A modern non-surgical alternative to hysterectomy and myomectomy is uterine artery embolization (UAE) . The procedure is performed using a thin catheter inserted into the femoral artery through a puncture in the upper thigh. The doctor inserts the end of the catheter into the vessel feeding the fibroid and injects an embolic drug. It consists of particles that clog small vessels, as a result of which the fibroid dies and turns into a small scar.
Many scientific studies have been conducted on the use of UAE in the treatment of fibroids, and they have shown the advantages of the method over myomectomy and hysterectomy:
- Low risk of relapse - less than 1%.
- In case of recurrence of fibroids, the procedure can be repeated.
- It is possible to preserve the uterus and the ability to become pregnant.
- 98% of women do not need any additional treatment after UAE.
- There is no incision, severe blood loss, the woman quickly recovers and returns to her normal life.
At Euroonko in Moscow, the EMA department is supervised by the famous Russian gynecologist Dmitry Mikhailovich Lubnin. He defended the first dissertation in Russia on the use of this technique for the treatment of uterine fibroids.
What to do if you were diagnosed with fibroids and the gynecologist suggested removing the uterus? Don't rush to make a decision. Get a second opinion from Dmitry Mikhailovich. Hysterectomy is a last resort; most women are indicated for follow-up or UAE.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Bibliography:
- Fateeva A.S., Petrov I.A., Tikhonovskaya O.A., Logvinov S.V. Morphofunctional state of the ovaries after hysterectomy. Bulletin of Siberian Medicine, 2014, volume 13, no. 1, p. 145–152.
- M.M. VYSOTSKY, V.F. BEZHENAR, M.A. OVAKIMYAN. Total or subtotal hysterectomy: time to dispel myths?. doi: 10.17116/endoskop201622652-56.
- DI. Gaivoronskikh, A.A. Koval, V.G. Skvortsov. Posthysterectomy syndrome: clinical manifestations and methods of their correction. Military Medical Academy named after. CM. Kirov, St. Petersburg.
Other methods for removing fibroids
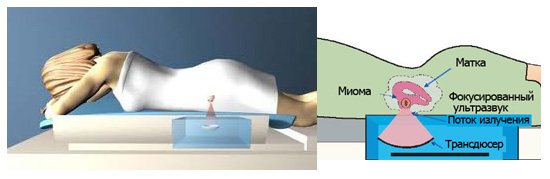
FUS ablation
FUS ablation is a modern method of removing uterine fibroids using a powerful and focused flow of ultrasound radiation. FUS ablation allows you to cure a tumor without a single incision, since ultrasound energy is directed exclusively to the fibroid tissue and does not cause any trauma, does not provoke suppuration or swelling.
Nowadays, such a procedure is increasingly performed using an MRI scanner. This makes it possible to control the location of ultrasound radiation and the heating temperature of tumor tissue.
How does FUS ablation work?
A concentrated beam of ultrasound is directed to the place where the formation is located. Penetrating through the skin, organs and tissues, the beam focuses on the fibroid and cauterizes it, since the connective tissues of the tumor are able to accumulate heat. Thus, thermal necrosis of myomatous nodes occurs.
It should be noted that this method copes well with tumors, which consist mainly of connective tissue. And for the removal of fibroids from muscle tissue and the treatment of multiple fibroids of combined localization, FUS ablation does not bring the expected result.
Uterine artery embolization (UAE)
UAE is a method of treating fibroids that reduces (or completely stops) the blood supply to the myomatous node. Naturally, without stable blood flow, tumor growth and development stops.
How is the UAE procedure performed?
The patient is given a catheter through the femoral artery, which penetrates the artery in the uterus and stops the blood supply to the fibroid node. The advantage of uterine artery embolization is that the patient does not need to undergo open surgery.
With all the “advantages” of UAE, laparoscopy is much more effective for removing uterine fibroids.
Myomectomy with temporary occlusion of the internal iliac arteries
Quite often, when performing a myomectomy, there are risks of serious complications. For example, removal of myomatous nodes can lead to heavy blood loss, due to which the surgeon will immediately need to switch to an open surgical procedure.
Severe bleeding and poor visibility of the operated area forces doctors to use coagulation, which can lead to scarring and other complications.
To avoid negative consequences, nowadays an additional technique is used - temporary occlusion of the internal iliac arteries.
Advantages of the method:
- Ability to avoid bleeding
- Ability to avoid excessive tissue coagulation
- Reduces surgical time
After myomectomy, the patient can leave the hospital within 2-3 days. To prevent infectious diseases, a course of antibiotics is prescribed, and for pain in the first few days, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
Removal of uterine fibroids: abdominal surgery (laparotomy)
For multiple uterine fibroids or large nodes, open (laparotomy) treatment is used. To do this, the surgeon makes an incision in the abdominal cavity in the pubic area or the middle of the abdomen.
During laparotomy, an incision is made along the midline of the abdomen or above the pubis. All manipulations are also carried out in compliance with the basic principles: minimizing blood loss, minimal trauma to the myometrium, preventing adhesions, etc.
The basic rules of laparotomy boil down to minimizing:
- Adhesive process;
- Damage to the myometrium;
- Bleeding.
Removal of uterine fibroids using the laparoscopic method does not in any way affect a woman’s ability to become pregnant, carry and give birth to a child. For example, they now use a special device - a hysteroresectoscope, which allows you to remove sumbucous nodes with minimal trauma and a quick recovery period.
Treatment of subserous uterine fibroids
Subserous uterine fibroids are most often detected only during an ultrasound examination, since the disease practically does not give any symptoms in the form of cervical dysfunction, pain or lack of pregnancy. This occurs due to the fact that myomatous nodes grow towards the peritoneum.
The absence of symptoms is not a reason to start the disease. A woman with this diagnosis should contact an experienced specialist who will determine the treatment method for subserous fibroids.
In any case, in pregnant patients with subserous myoma, compelling reasons for surgical treatment are:
- The presence of subserous nodes near the cervix, which can cause serious complications in the last weeks of pregnancy.
- Large nodes that compress neighboring organs.
- Presence of signs of necrosis (tissue death).
To normalize the general condition after surgery, the patient is prescribed a course of drug therapy with hormonal drugs, as well as herbal medicine (chamomile, boron uterus, sage, etc.).
Treatment of submucous uterine fibroids
Sumbucous fibroids are one of the most difficult types of neoplasms for surgical treatment, since myomatous nodes are located immediately under the uterine mucosa, protruding into its cavity.
Sumbucous fibroids lead to the following complications:
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Blockage of the fallopian tubes;
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- Infertility.
If some time ago, complete removal of the uterus was required to cure sumbucous fibroids, now the tumor can be removed using a conservative method. For example, for small nodes, drug therapy has a good effect.
Hysteroscopy is another method of removing sumbucos nodes, in which the tumor is excised using a hysteroscope. Small myomatous nodes, which mainly consist of connective tissue, are removed using the UA method (uterine artery embolization).
Treatment of intermuscular fibroids
According to statistics, interstitial fibroids are the most common. It forms inside the muscle tissue of the uterus, making this type of tumor very difficult to diagnose and remove.
Intermuscular fibroids can be treated with both medication and surgery. Everything is determined by the patient’s age, the size and location of the nodes, and the presence of signs of tumor malignancy.
Intermuscular fibroids rarely give obvious symptoms. A woman with this diagnosis is usually not bothered by pain, but she should be wary of excessive menstruation, which often leads to a complication such as anemia. It is noteworthy that such fibroids do not interfere with the functioning of the productive system, so a woman can become pregnant.
For intermuscular fibroids, both surgical and drug treatment are used. The effectiveness of a particular method is determined by the attending physician based on the size of the formation, the age of the patient and the nature of the tumor (malignant or benign).
Tests required for laparoscopy of uterine fibroids
Before any surgical intervention, the patient must undergo a series of examinations. For planned laparoscopy of uterine fibroids in our center in Moscow, the list of required tests is as follows:
- General and biochemical blood test;
- Test for hepatitis B and C, syphilis;
- HIV test;
- Coagulability test;
- ECG (for patients over 40 years old).
These tests will help assess the patient's overall health and determine if there are other medical conditions that could cause complications during surgery and recovery.
Prevention of the development and growth of fibroids
The factors that provoke the occurrence of uterine fibroids have not yet been thoroughly studied. Therefore, it is difficult for doctors to make clear recommendations for the prevention of the disease.
If a woman has small myomatous nodes that do not give any complications or painful symptoms, then the doctor independently makes a decision based on the specific situation. The best option in this case would be actions aimed at preventing the growth of fibroids. For example, the patient should avoid foods high in carbohydrates and fats, maintain a healthy lifestyle and balance her body weight (if overweight).
Intense exposure to ultraviolet rays can also cause the growth of myomatous nodes, so the patient is prohibited from visiting a solarium or staying in the sun for a long time. Massage, thermal and physiotherapy procedures can lead to pathological tissue growth.
Even if fibroids do not require urgent surgical or drug treatment, a patient with a similar diagnosis must undergo regular examinations with a gynecologist and undergo a series of tests.