Some patients worry when a corpus luteum is found in their ovary during a pelvic ultrasound. Such fears are unfounded - this formation appears in the body every month and its detection is considered a positive sign, indicating a normal ovulation process and the absence of female infertility.
Stages of development of the corpus luteum
The content of the article
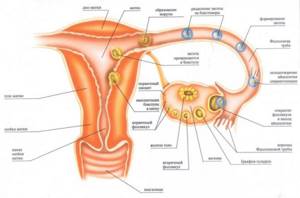
Although the VT appears instead of the follicle that released the egg into the fallopian tubes, its development begins long before the onset of the ovulation period. This complex process is controlled by the pituitary gland, ovaries and immune system.
- Initially, the follicle grows, increasing in size, and lutein accumulates inside it, a colored pigment that makes it yellow. The transformation process is called luteinization.
- After the release of the egg, vessels in the ruptured follicle begin to grow rapidly, penetrating into the luteal tissue. The corpus luteum gradually forms, the blood supply of which is higher than in other organs of the human body.
- The blooming stage of VT begins. During this period, iron is released up to 25 mg/day. progesterone. High doses of the hormone inhibit the development of other follicles, because the body adjusts to fertilization and pregnancy.
As a rule, there is only one corpus luteum, but when several eggs are released, two or three such structures are formed. If fertilization occurs during this menstrual cycle, twins or triplets will be born. These twins, called fraternal twins, do not look alike and may even have different sexes.
Progesterone not only inhibits new ovulation, but also prepares the uterus to “receive” the embryo. Even the work of the uterine muscles changes. Everything in the body is ready for pregnancy. If fertilization occurs, progesterone concentrations will increase until 16 weeks, until pregnancy maintenance functions are transferred to the developed placenta.
If conception does not occur, the corpus luteum will begin to sprout connective fibers, turning whitish. Gradually it will decrease in size and resolve. The concentration of progesterone drops, and new follicles begin to mature in the ovary.
But this “play with nature” does not pass without a trace. Ovulations that do not end in pregnancy lead to hormonal imbalances and gynecological pathologies. A burst follicle does not resolve, but begins to grow. Instead, a corpus luteum cyst is formed - a neoplasm that can exist for a long time.
It is better to turn off useless ovulation by taking hormonal pills that inhibit the development of eggs. The risk of developing a corpus luteum cyst in this case becomes zero.
Phases of the menstrual cycle
So, what phases generally exist:
- Menstrual
. The beginning of a cycle characterized by the detachment of the endometrium (the inner lining of the uterus) as a result of the lack of fertilization of the egg. Outwardly it manifests itself as bleeding, called menstruation. - Follicular (proliferative).
The next stage is the restoration of the damaged endometrial layer and the creation of conditions for the acceptance of a new fertilized egg. At the same time, a new egg matures as part of the dominant follicle - this process occurs in the ovaries. - Ovulation.
A short but very important phase, in the absence of which the pregnancy process becomes impossible. A mature egg is released from the follicle into the abdominal cavity in anticipation of fertilization. - Luteal (secretory)
. Includes two stages. During the first, the body’s restructuring to the conditions of pregnancy continues - it is here that the corpus luteum originates from the main, dominant follicle, which has been ruptured by the egg.
The second stage begins when there is no fertilization of the egg, therefore, there is nothing to penetrate the endometrium of the uterus. Then the size of the corpus luteum after ovulation decreases, transforms into a whitish hyaline body, then completely resolves, and the cycle repeats.
What is visible on ultrasound at different stages of development of the corpus luteum
During an ultrasound examination of the ovaries, the corpus luteum resembles a small sac located on the ovary. If it is not visible even after ovulation, it means that the woman has ovarian dysfunction. For example, during an anovulatory cycle, the egg is not released and the corpus luteum is not formed.
Sometimes it is not the ovaries that are to blame for the absence of the corpus luteum, but other organs - the pituitary gland, the thyroid gland. Such a woman needs to consult an endocrinologist and get tested.
The size of the VT depends on the day of the cycle:
- Before ovulation - on days 12-15 of the cycle, only the follicle is visible on ultrasound, but immediately after the release of the egg, the size of the corpus luteum can already be analyzed. Normally they are 12-20 mm. This is enough for the onset and maintenance of pregnancy. After this, the VT may “grow” a little more.
- The further picture of the ultrasound depends on whether fertilization has occurred. If the female cell is not fertilized, the size of the VT gradually decreases, and its color changes from yellow to purple. The formation visually rises above the ovary. Gradually it is replaced by connective tissue.
- If after this the VT does not disappear, but, on the contrary, begins to increase, this means that the woman is growing a cyst, which can reach 40 mm. Sometimes, for unknown reasons, on the eve of the next ovulation, the cyst disappears on its own.
Treatment of hormonal deficiency
Treatment of corpus luteum pathology during pregnancy is symptomatic. If a woman’s body does not produce enough progesterone, it must be taken additionally. There are oral, vaginal or rectal preparations, as well as skin creams with progesterone as an active ingredient. Urozhestan and Duphaston are most often prescribed. Hospitals may prescribe progesterone in ampoules. Each medicine should be taken on certain days. But before prescribing hormonal drugs, it will be necessary to undergo a full examination.
During drug treatment, constant monitoring is carried out - the patient undergoes ovulation tests, progesterone levels are checked, and the corpus luteum is observed on ultrasound.
The Medicenter clinic network employs professional endocrinologists who have extensive experience in treating hormonal deficiency of the corpus luteum during pregnancy.
Ultrasound of the corpus luteum during pregnancy
At 8 weeks. the size of this formation is 10-30 mm. Normally, it should disappear by about 16 weeks, when the placenta has formed in the uterus. But sometimes VT resolves earlier or even remains until delivery. Pregnancy proceeds absolutely normally.
The corpus luteum, which for some reason lasted longer than expected, disappears before childbirth at 35-38 weeks, when the overall level of progesterone decreases. Sometimes it resolves after the baby is born.
Scientists have not yet fully studied the cause of such anomalies, but even earlier disappearance of VT does not always lead to miscarriage. Sometimes its functions are taken over by the adrenal glands, which also produce progesterone, and the fetus continues to develop. Subsequently, the adrenal glands transfer hormonal functions to the placenta.
In the absence or insufficient size of VT, it is necessary to take tests for progesterone. Its decrease is a bad sign, indicating the possibility of miscarriage, fading pregnancy or uterine bleeding.
In this case, the woman is prescribed medications that replace the hormones that VT synthesizes. Unfortunately, sometimes hormonal deficiency persists until childbirth, so the woman will have to take medication for the entire nine months.
How long does the corpus luteum live after ovulation?
It is necessary to consider in more detail the processes of formation, activity and purpose of this gland in order to understand how long the corpus luteum lives after ovulation. It is formed immediately after the destruction of the follicle from fragments of its cells and walls.
Then the process of growth of the corpus luteum begins - an increase in size due to an increase in the number of cells and the germination of blood vessels in them, providing the necessary nutrition. Upon reaching sufficient size, which will be discussed later, the growth phase ends (usually taking 2-3 days), and the corpus luteum turns into a functioning endocrine gland.
This stage is the peak of gland development, it is here that the most active production of progesterone occurs, and it occurs 7-8 days after the ovulation stage. In the absence of fertilization, the corpus luteum decreases in size, loses its function, and by the end of the cycle is completely reduced. The following conclusions can be drawn: the iron exists for 13-14 days after ovulation.
Types of ovarian cysts in women
There are main types of ovarian cystic formations:
Physiological cysts are normal
- Follicle
- Corpus luteum
Functional cysts
- Follicular cyst
- Corpus luteum cyst
- Thecal lutein cysts
- Complicated functional cysts: hemorrhagic cyst, rupture, torsion
Benign cystic tumors (cystoma)
- Dermoid cyst (mature teratoma)
- Serous cystadenoma
- Cystadenoma mucinous
- Cystedenofibroma
- Sclerosing stromal tumor
Malignant cystic tumors (cystomas)
- Serous cystadenocarcinoma
- Cystadenocarcinoma mucinous
- Endometrioid cancer
- Brenner's cystic tumor
- Immature teratoma
- Cystic metastasis
Other cysts
- Endometrioma (chocolate cyst)
- Polycystic ovaries (Stein-Leventhal syndrome)
- Postmenopausal cyst
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
Hormonal support
To treat insufficiency of the temporary gland, gynecology prescribes hormonal drugs that stimulate its functioning. They must be taken if a woman is having difficulty conceiving, before IVF, or if she has been diagnosed with insufficiency during gestation.
The table shows the characteristics of drugs:
| No. | Name | Active substance | Release form | Indications |
| 1 | Utrozhestan | Progesterone identical to that produced by VT | Capsules | Infertility due to luteal insufficiency. Threat of miscarriage due to progesterone deficiency, anovulation, hormone replacement therapy in pre-, peri- and postmenopause, prevention of premature birth, preparation for IVF. |
| 2 | Duphaston | Dydrogesterone, an analogue of natural progesterone | Pills | Indications are similar to Utrozhestan. |
The corpus luteum plays an important role in the reproductive function of the female body. It is thanks to him that it becomes possible to conceive and bear a child.
CT scan for ovarian cyst
CT and MRI are fairly accurate methods that allow you to determine the presence of a cyst, suggest whether it is benign or malignant, clarify its size and exact location, etc. In addition, in the case of a malignant cyst, diagnosis using contrast makes it possible to determine whether the tumor has metastasized to other organs and to accurately determine their location.
CT is performed using X-rays, which makes it possible to obtain sections of the organ in increments of approximately 2 mm. The collected and computer-processed sections are assembled into an accurate three-dimensional image. The procedure is absolutely painless, does not require complex preparation (all you need is to adhere to a certain diet for a couple of days before the procedure and, in case of constipation, take a laxative) and lasts no more than 20 minutes.
Given that the slice step is 2 mm, CT can detect formations of 2 mm in cross section or more. These are fairly small cysts and tumors that are at an early stage of development. Such accuracy of CT diagnostics allows you to begin timely treatment and avoid more serious consequences.
Contraindications to the method are pregnancy (due to exposure of the body to X-ray radiation) and allergic reactions to the contrast agent (in the case of CT with contrast). Such allergic reactions are not very common.
Dimensions
A pregnant woman must regularly undergo special ultrasound diagnostics. During the examination, the doctor carefully examines and evaluates the volume of the corpus luteum in the ovary. If there are any deviations from the norm, the specialist gives the expectant mother special recommendations or prescribes a course of treatment.
In the first weeks of pregnancy, the size of the temporary gland can be 15-20 mm. However, this formation gradually increases to 27-28 mm. After the 16th week of pregnancy, the functions of the corpus luteum begin to fade, and it again decreases in volume until it disappears completely.
Experienced specialists in the field of gynecology argue that a pregnant woman must have a corpus luteum in the right or left ovary. If it was not detected during an ultrasound, it means that outdated equipment was used for diagnosis, or it was carried out by an insufficiently qualified gynecologist. In rare cases, such a gland does not develop. Such patients are individually prescribed a course of hormonal therapy.
Functions and types
There are two types of corpus luteum: sexual cycle VT and gravidar VT. Why is VT needed? The main task of the corpus luteum is the production of the hormone progesterone. If pregnancy does not occur, the need for progesterone and, as a result, the gland itself disappears. During gestation, education is necessary until the placenta can produce the hormone on its own.
Progesterone performs a number of functions:
- prepares the endometrium of the uterus for implantation;
- thickens cervical mucus;
- reduces immunity during pregnancy;
- reduces the tone of the uterus.

The concept of the corpus luteum: what does it look like and what is it?
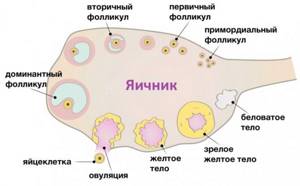
The corpus luteum (CL) is a temporary endocrine gland that is formed from an ovarian follicle after a certain period of time. During the menstrual cycle it is 2 weeks, and during the gestation period it is 10–12 weeks. Afterwards it degenerates into scar tissue. This area is called the white body, and over time it also disappears.
Why is VT called yellow? It got its name due to its appearance. This is a round formation of yellow ovarian follicle granulosa cells. In the left ovary it is smaller than in the right.
Pathologies
In some cases, during the formation of the corpus luteum, a pregnant woman may experience certain disturbances. In this case, the volume of the gland is less or much more than the established norm. In the first case, doctors diagnose insufficiency of the corpus luteum, and in the second - a cyst.
The generally accepted norms for volumes and, accordingly, hormonal activity of the corpus luteum can be considered:
- 18-22 mm. Iron reaches this size in the second half of the monthly cycle. This means that ovulation has occurred and the female body is completely ready for fertilization.
- 20-30 mm. If the corpus luteum has reached such volumes, then the woman is pregnant, and the gland is actively producing hormones to support new life.
- 23-30 mm. Such sizes of the corpus luteum may signal the development of a follicular cyst. With this pathology, ovulation does not occur, which means the woman has virtually no chance of becoming pregnant.
- 30-40 mm. A clear symptom of cyst formation in the ovary. This is especially true for women who have not become pregnant.
A corpus luteum cyst can occur even during pregnancy. This is an unpleasant disease that needs to be treated, but, nevertheless, it does not affect the development of the fetus.
Cyst
If the corpus luteum exceeds 30 mm in volume, this may indicate the development of a cyst. If you were diagnosed with this during pregnancy, there is no need to panic. Pathological changes in the gland do not affect the production of progesterone in the development of the fetus. A cyst in the shape of a bubble, similar to a blister, can form not only in women in an interesting position, but also in very young girls.
There are several main reasons for the development of this pathology, namely:
- Frequent stress and emotional overstrain;
- Work in hazardous production;
- Smoking, drinking alcohol and other bad habits;
- A strict diet with a minimum content of vitamins and other substances necessary for normal life;
- Severe physical fatigue at work or during sports training;
- Taking dangerous drugs to urgently prevent conception;
- Puberty too early;
- Infectious pathologies of the genital organs;
- Improper functioning of the thyroid gland;
- Taking hormonal medications immediately before conception;
- Pathologies of the circulatory or lymphatic systems.
The patient may not know that she is developing a corpus luteum cyst in the ovary. The thing is that such a disorder is not accompanied by obvious symptoms, such as pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen. This disease does not require any special treatment; over time it disappears on its own. However, a gynecologist may advise a pregnant woman to give up excessive physical activity and intimate life for a while.
The condition of the corpus luteum in the ovary is monitored by doctors during an ultrasound. If, due to a cyst, the corpus luteum reaches a large size (up to 5 cm), the girl may experience complications. To prevent this, the problem is solved by surgically removing the formation. With a normal prognosis, the cyst resolves along with the corpus luteum by the 20th week of pregnancy. This formation is benign, so there is no need to worry. A cyst has never turned into cancer.
Cyst rupture
If you are diagnosed with a corpus luteum cyst in the ovary while carrying a child, be sure to strictly adhere to all the recommendations of the gynecologist. If this problem is not taken seriously enough, serious complications can arise. With intense physical activity or during passionate sex, the cyst may burst. The consequences of such a rupture must be immediately corrected surgically.
There are several main symptoms of a ruptured cyst:
- Severe pain in the abdominal area;
- Attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- Tension and excessive unpleasant sensitivity in the lower abdomen;
- Pain on palpation, false contractions;
- Fall in blood pressure (as a result of hemorrhage in the abdominal cavity).
If you notice several of these symptoms, call an ambulance immediately. This condition can be life-threatening for the expectant mother and the unborn child.
Downsizing
A reduction in size is also possible normally during the reduction phase: in the absence of fertilization, the iron gradually decreases in size to 2-3 mm, and then completely resolves. Therefore, it is important to know at which stage of the menstrual cycle the examination is carried out, so as not to confuse the norm with pathology.
A pathological decrease in the size of the corpus luteum will be its insufficient development. Insufficiency of the gland leads to a lot of problems and is a serious pathology. The normal course of pregnancy in this situation is physically impossible, since the gland is not capable of producing the required amount of hormones.
A deficiency of sex hormones leads to disorders of the menstrual cycle, as well as the process of conception. In the case of a successful fertilization process, the risk of placental abruption remains throughout pregnancy, since the embryo is initially not able to attach well enough.
In this regard, the woman will be forced to take progesterone in dosage forms in order to prevent all risks of problems with pregnancy and avoid miscarriage.