Magnetic resonance imaging is a diagnostic method that allows you to obtain a detailed understanding of the nature of pathological changes in any area of the human body.
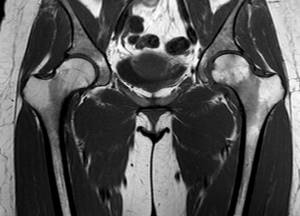
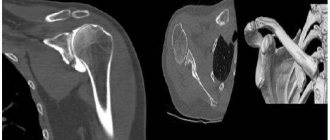
MRI scan of coxofemoral joints, normal variant
In orthopedic practice, MRI of the hip joint is often performed to clarify the causes of coxalgia - pain in the joint. The research method does not involve the use of ionizing radiation, which is especially important for children and pregnant women. The process of creating clear images that can be enlarged and viewed in volumetric form is based on the use of magnetic resonance and computer technology. Contrast is used to improve visualization capabilities. The diagnostic value of photographs obtained after gadolinium administration is comparable to the results of arthroscopy - an invasive study involving penetration of surgical instruments into the joint cavity.
How is an MRI of the hip done? Scanning is carried out on devices with different magnetic field strengths. The doctor can independently choose programs depending on clinical tasks. This is relevant if it is initially unclear what causes the pain syndrome: pathology of the pelvic organs or joints. In standard situations, multiparameter sequences are used.
Indications
The main indications for MRI of the hip joint are various disorders and deviations in the structure and structure, including:
- For traumatic injuries to the femoral region, MRI is prescribed to assess the extent of the damage. The images show areas of hematomas, damage or rupture of ligaments and tendons, bone fractures, etc.
- For dysfunction of the hip joint in children or adolescents, MRI is performed to identify congenital dislocation of the joint, dysplasia and other developmental abnormalities;
- If signs of an inflammatory or infectious disease appear, for example, osteomyelitis, rheumatoid arthritis;
- In older patients with complaints of pain in the hip area, an MRI scan is performed to identify degenerative processes, which will make it possible to identify and begin treatment of such serious diseases as osteoarthritis and coxarthrosis of the joint;
- If the nature of the pain is unclear and the presence of neoplasms is suspected, MRI is prescribed to confirm (or refute) the preliminary diagnosis.
- MRI of the hip joint is the best method in diagnosing both malignant and benign neoplasms; it allows you to accurately determine the nature of the tumor, its type, location, effect on surrounding tissues and other signs;
- When planning surgical intervention on a joint, as well as during subsequent monitoring of its results.
Preparatory activities
Preparation for tomography of the hip joint is directly related to how the MRI will be performed: in the classic version or using a contrast agent.
If contrast is not used, then no fundamental restrictions will have to be observed. The patient does not need to change his usual lifestyle or observe any strict restrictions on food intake.
But if the doctor ordered an MRI of the hip using a contrast enhancer, then you will have to make sure that there is no allergic reaction. To do this, a sensitivity test is performed at the medical center: a small amount of contrast is injected subcutaneously, and after 20-30 minutes the result is assessed.
If a rash, irritation, redness, itching or other allergy symptoms appear on the skin, the administration of contrast for scanning the hip joint to the patient will be strictly prohibited for safety reasons.
Such manifestations occur in people in exceptional cases, since contrast rarely causes such a reaction. It is advisable to carry out such a test once, and all subsequent diagnostics using contrast can be carried out with confidence without the need for a repeat test.
Every patient should remember that they must come for a study using contrast on an empty stomach. Otherwise, nausea and discomfort in the intestines may occur.
The radiologist should also conduct a conversation with the patient before starting the study in order to identify contraindications, which may include:
- pregnancy in women;
- the presence of a number of chronic diseases;
- existing metal objects in the body.
It is very important not to hide any important facts from the radiologist, as this will be the key to safety during the scan.
Immediately before starting the MRI, you will need to remove any jewelry. Personal belongings will have to be left outside the office. Gadgets and metal objects can interfere with the operation of the device, cause malfunctions and have a negative impact on the quality of pictures.
When is an MRI performed?
MRI of the hip joint in Moscow is performed on patients if indicated by the attending physician. The procedure may be prescribed to make a primary diagnosis (for example, after an injury). Tomography is also performed to confirm the existing diagnosis and monitor the dynamics of the disease. Older people whose hip joint is very vulnerable can also undergo the procedure. An MRI will allow you to most accurately determine the presence of injury in this part of the body after a fall or blow.
We offer a promotional MRI of the hip joint. The minimum price is for both joints. For tomography, an open-type Siemens Magnetom C device is used, which allows examining patients weighing up to 170 kg. The MRI procedure on the hip joint lasts up to 30 minutes. After the examination, the doctor transcribes the data and records it on a digital medium.
Decoding
The doctor deciphers the images obtained during the tomography and issues a research protocol, which will indicate all joint parameters: tissue thickness, its shape and structure, location and size. Along with the protocol, the radiologist transfers to the patient all the images recorded on digital media. If desired, they can be obtained in printed form. The time required to compile a protocol can take about an hour on average, and in complex cases about 2 days.
Thus, the cycle from the start of the procedure to the receipt of results can be 2 hours. If the patient does not want to wait for the transcript results in the clinic, he can receive the data by email or come for an x-ray report the next day.
With the results of magnetic resonance imaging, you should contact your attending physician or a specialist who, based on the radiologist’s report, will make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
- If you have rheumatoid arthritis, you should consult a rheumatologist.
- A neurologist can help treat pinched tendons and the sciatic nerve.
- For complex joint injuries, arthritis and arthrosis, you need to make an appointment with an orthopedic traumatologist.
- If a tumor is detected, you need to go to an oncologist.
It is worth remembering that the radiologist does not make a diagnosis or prescribe treatment. This should be done by the attending physician based on the diagnosis.
It is difficult for an ordinary person to independently understand and interpret the results that, after an MRI, will be given to him on a digital medium. Therefore, with the conclusion of the radiologist and the photographs, he should go for a consultation with the attending physician, who will make a final diagnosis based on the summary data of the examination, medical history and tomography data. In our clinic , after an MRI, you can have a free consultation with a neurologist or orthopedist . Doctor
- will answer all questions based on the results of the research and the conclusion received
- Helps explain tomography results without using complex radiological terminology
- will conduct an examination and, if necessary, offer treatment.
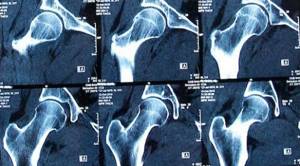
An example of decoding an MRI of the hip joints
On a series of MRIs of the hip joints, the relationships in the joints were not disturbed.
Free intra-articular fluid is not detected. The synovial membrane is not differentiated in native sections. No traumatic bone changes were detected according to the MRI examination. The bony contour of the articular surface of the femoral heads is not deformed, the heads are spherical in shape, centered within the articular sockets, and the arches of the acetabulum are formed correctly. Areas of increased MR signal on T1-weighted images from the bone marrow in the area of the proximal femurs and pelvic bones due to fatty degeneration. There are areas of unevenly expressed subchondral sclerosis of the articular surfaces of the acetabulum. The articular fibrocartilaginous lip has a homogeneous structure on both sides, without signs of rupture. The joint spaces are uniformly and moderately narrowed, the signal of the cartilaginous component of the joint is unevenly reduced, and the articular hyaline cartilage is moderately and uniformly thinned. There is an increase in signal intensity on Stir IP (swelling) in the area of the greater trochanter at the level of attachment of the tendons of the gluteus medius muscle on both sides, the structure of the tendons at this level is heterogeneous due to areas of increased signal, their integrity is not compromised. Conclusion: MRI signs of grade 1 deforming arthrosis of the hip joints. MRI signs of enthesopathy of the gluteus medius tendons on both sides. Author: Usenko Nikita Sergeevich
Orthopedist-traumatologist with 8 years of experience
What affects the cost and quality of MRI of the hip joints
The cost of a hip MRI may vary from hospital to hospital. Most often this depends on the equipment installed in clinics. Research using high-field tomographs is 1.5-2 times more expensive than medium- and low-field ones. If it is necessary to identify mechanical, gross damage to the joint surfaces, arthritis, arthrosis, then open-type tomographs can easily cope with this task, and in this case there is no need to overpay. But if there is a suspicion of tumor changes or systemic disorders, then a closed high-voltage (1.5 T and higher) tomograph is indispensable.
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| MRI of the hip joints | 5000 rub. | 3190 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| Appointment with an orthopedist | 1800 rub. | free after MRI | free after MRI |
| First aid program for joints (8 studies + appointment with an orthopedist + MRI of the joint) | 13000 rub. | 7500 rub. | 7500 rub. |
MRI of the hip joint: what does it show?
Due to the high content of water in our body, the magnetic field causes a reorientation of hydrogen atoms in the studied structures of the hip joint. As a result, the specialist receives a series of images of a three-dimensional image of the joint with the ability to examine this area layer by layer.
The technique allows the radiologist to examine in detail the bone structures (the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvic bone), cartilage and ligaments, the joint capsule, the arterial and venous network, and even large nerve trunks. MRI will easily show the presence of hemorrhages and exudate in the joint, foci of inflammation and tumor growth, thinning of the cartilage layer, ruptures of the ligamentous apparatus, and abnormalities in the development of joint structures. Examination of the hip joint provides comprehensive information, which often allows one to refuse diagnostic arthroscopy.
Which diagnostic method should you prefer: computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging?
For the chosen treatment to be effective, it is important to determine the root cause of the pathology as accurately as possible. For this purpose, one of two diagnostic techniques is used: MRI of the hip or computed tomography.
In this regard, many patients wonder which method should be preferred. It is important to know that these survey methods have significant differences in the principle of operation.
MRI involves exposure to an electromagnetic field, while during a computed tomography the patient's body is exposed to x-rays. It is also worth taking into account the potential benefits for the patient:
- CT scans cannot be performed frequently, but magnetic resonance imaging can be used an unlimited number of times.
- A CT scan is much faster, but, as with magnetic resonance imaging, the patient cannot make any body movements during the examination.
- Magnetic resonance imaging cannot be performed if there are metal implants, stimulators, or prostheses in the body, but CT scanning can be done.
- People with injuries are most often referred to a CT scan, and to a magnetic resonance imaging scan for any signs of changes in nerves and soft tissues.
- A CT scan of the hip joint is indicated if there is a need to find out the size of the femoral head, identify foreign bodies, and determine the severity of fractures. Magnetic resonance imaging reveals ruptures and inflammation of ligaments, muscles, and pathological changes in bone tissue.
The final decision on the choice of diagnostic method should be made by a specialist on an individual basis.
Contraindications
MRI is contraindicated for patients with pacemakers, metal clips on cerebral vessels, middle ear implants, artificial heart valves, ferromagnetic metal structures and prostheses, insulin pumps, tattoos using metallic inks near the diagnostic area, and is also not recommended in the first trimester of pregnancy. After hip replacement, scanning depends on the material of the prosthesis. MRI with contrast is generally not performed on pregnant or breastfeeding women.
The result of the tomograph examination
The result of magnetic resonance imaging of the pelvic region is a series of layer-by-layer images, their description and the conclusion of a radiologist. Pictures can be recorded on any media (CD, USB drive, film, paper). The turnaround time for the results depends on the clinic – from two hours to a day.
The doctor's report describes in detail the hip joint, surrounding tissues and the pelvic area. If a pathological focus or neoplasm is detected, its characteristics are given - location, size, structure, degree of severity. The data obtained from MRI is used by the attending physician as the basis for making an accurate diagnosis.
If no preliminary consultation was carried out and the patient underwent the study independently, if signs of disease are detected, you should contact a traumatologist, rheumatologist, neurologist or oncologist, depending on the nature of the pathology.
You can choose a clinical diagnostic center for magnetic resonance imaging of the pelvic joints using our website. We have collected the most recent and necessary information about dozens of clinics, including low prices and discounts on the first appointment. By phone you can consult completely free of charge on any questions related to the work of the clinic and the equipment used for scanning.
How the procedure is performed
The patient takes off his metal accessories, takes out his phone and plastic cards from his pockets, enters the office with the device and lies down on the couch. Our center has open-type MRI scanners, so there is no need to stay in a confined space. To prevent random movements from interfering with the images, the person being examined needs to lie still. During the procedure, the patient hears tapping or humming of the device; if these sounds cause irritation, you can use earplugs or headphones. During the examination, the patient can communicate with the doctor. The MRI procedure is performed without pain or adverse reactions.
MRI of the hip joint with contrast
When an in-depth diagnosis of the condition of the hip joint is necessary, an MRI with contrast is performed. The main component of the contrast is gadolinium, a substance with paramagnetic properties that is safe and rarely causes allergic reactions. A gadolinium solution is administered intravenously immediately before the examination. The substance spreads quite quickly throughout the body, but accumulates differently in different tissues. In healthy areas, the amount of contrast is much less than in pathological areas. Gadolinium is excreted by the kidneys within 24 hours.
The need for contrast enhancement arises when involvement of the hip joint in the tumor process is suspected. In addition to making a diagnosis, MRI with contrast allows you to evaluate the dynamics of tumor growth, the presence of metastases, and the results of treatment. This option of MRI lasts longer than a regular scan and its cost is higher.
Algorithm for proper preparation
It is imperative to determine in advance whether the patient is allergic to the contrast agent. Since patients do not always know how the body will react to a previously unused drug, a preliminary allergy test should be performed. If the reaction is positive, you can try replacing the drug with an analogue, using antihistamines, or using a CT scan instead of an MRI.
Another important stage of preparation is to notify the attending physician about pregnancy, since any stage of pregnancy becomes a contraindication to the use of magnetic resonance imaging with contrast, because the contrast can penetrate the blood-brain barrier and harm the fetus. Ignoring the ban can result in severe pathologies in the development of the unborn baby.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Young children are allowed to undergo such an analysis, with a serious outweighing of the benefits over the possible harm, when the choice is between the child’s life and conducting the study under general anesthesia.
As a rule, childhood is a relative contraindication, as are psychological disorders and uncontrolled motor syndrome. The categorical nature is explained by the fact that the victim must endure the entire procedure in complete immobility, when any movement displaces the three-dimensional image and requires repeated examination.
Other relative contraindications include diabetes mellitus, renal and liver failure.
All this is dangerous only when it is necessary to use contrast, since the elements of the drug must be eliminated naturally in a timely manner.
And with the final relative prohibition of claustrophobia, new generation devices with open side parts will help to cope. They are used both to examine the spine and to diagnose possible deviations of the hip joints.
Separately, you should take care to remove all metal elements from yourself before starting the study. We are talking about jewelry, piercings and metal elements on clothing. You need to warn the specialist in advance about the presence of any built-in electronic elements such as pacemakers and wires to support the bone skeleton.
MRI or X-ray of the hip joint: which is better?
The appointment of radiography or MRI of the hip joint depends on the diagnostic goals. Despite the outdated nature of x-rays, it has been and remains the primary method for diagnosing bone pathology of a given joint (fractures and dislocations). The advantages of radiography are its general availability and low cost, but in terms of information content and lack of radiation exposure, MRI wins. A high level of detail in the soft tissues of the joint makes it possible to identify even small morphological changes already in the early stages of development and assess the condition of the joint before endoprosthetics.
Conducting research
Scanning the hip joint is quite simple and does not cause any pain to the patient, which is a huge advantage over other diagnostic procedures.
The patient should change into a sterile hospital gown for greater comfort, then lie down in a horizontal position on the couch. To ensure immobility, the patient's body will be secured with straps during the MRI of the hip. This is also done to ensure that any involuntary movements of the legs and arms are completely eliminated.
The medical staff will explain how you can inform your doctor about changes in your health if it suddenly worsens. It is worth noting that any deterioration in well-being can only be caused by an unstable psycho-emotional state against the background of experiences. This is why it is so important to get ready to undergo the examination, especially since the procedure does not involve any risks for the patient.
After preparation, the couch is moved into the inside of the tomograph, and the scanner begins its work. Despite the fact that during the examination the patient is alone in the office, he is not left for a minute without the close supervision of the doctor, who monitors the progress of the scan from the next office.
As soon as the device starts working, the subject may hear specific sounds. This is a normal phenomenon and should not be alarming. An MRI of the hip joint lasts approximately 30 minutes without contrast and about 1 hour with its use.
As soon as the MRI of the hip is completed, the patient can immediately change into his own clothes and go to await the decoding of the images and the conclusion.
It is important to remember that with photographs of the hip joint and interpretation, it is imperative to contact a highly specialized specialist to prescribe appropriate treatment.
MRI or CT scan of the hip joint
Both computed tomography and MR imaging allow us to most accurately determine the cause of clinical symptoms of the hip joint. When choosing between these two methods, you need to consider:
- Patient safety (MRI has no restrictions on frequency).
- Type of pathology (CT is more justified for traumatic injuries of dense structures, MRI for inflammatory and degenerative changes in soft tissues).
- Execution time (for CT – up to 4-5 minutes, for MRI – up to half an hour per joint).
- Existing contraindications (CT is not performed throughout pregnancy, MRI is not recommended during the first trimester, as well as for patients with metal structures).