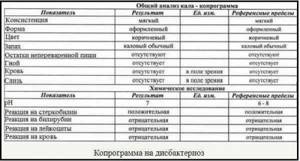
General stool analysis
A general stool test is a common study that includes macroscopic, chemical and microscopic analysis. Macroscopic examination involves assessing the consistency, smell, and color of stool. Using a chemical test, you can determine the acidity, the presence of protein, bilirubin, and serotonin in a sample of biological material. If we are talking about a microscopic examination, doctors have the opportunity to detect in a sample undigested muscle fibers, plant fiber, elements of connective tissue, neutral fat, helminth eggs, protozoan cysts and much more, on the basis of which one can judge the presence of a number of serious diseases.
If a person follows a normal diet, the nature of stool depends on the following factors:
- Enzymatic breakdown of food at different stages of digestion;
- Absorption of food digestion products by the intestines - various vitamins and microelements;
- The current state of the intestines;
- The vital activity of bacteria living in the intestines.
General stool analysis transcript
The norm for fecal excretion in a healthy person is approximately 100-200g per day. Normal stool composition is 80% water and 20% dry matter. If a person is a vegetarian and eats foods exclusively of plant origin, the amount of feces can increase to 400-500g per day. If a person eats only easily digestible foods, the amount of feces excreted daily may decrease.
Consistency and texture
With normal indicators, stool has a moderately dense consistency. The discharge of mushy feces is also allowed if a person consumes mainly products of plant origin. The normal shape of stool is cylindrical. The smell should not be pungent. It can increase significantly if food products of animal origin predominate in the human diet. If a person is constipated or follows a dairy-plant diet, the smell of stool usually decreases. The normal color of stool is brown. Different variations of brown color are allowed: if you follow a vegetarian diet, the feces will be lighter. If a person eats animal products, the stool will be darker. If certain plant substances or medications enter the body, the stool may turn different colors - from burgundy to black. All of these are variations of the norm. There should be no mucous impurities in the stool, as well as bloody ones. There should be no pus or undigested food in the stool.
To interpret other indicators of the results of a general stool analysis, the help of specialists is necessary. A sample of biological material is studied for dozens of parameters. A person who is not knowledgeable in medicine will not be able to independently interpret the results.
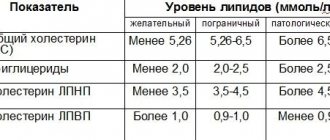
| Age and type of feeding | ||||
| Analysis indicators | Breast-feeding | Artificial feeding | Older children | Adults |
| 40-50 g/day. | 30-40 g/day. | 100-250 g/day. | 100-250 g/day. |
| sticky, viscous (mushy) | putty-like consistency | Decorated | Decorated |
| yellow, golden yellow, yellow green | yellow-brown | brown | brown |
| sourish | putrefactive | Fecal, not sharp | Fecal, not sharp |
| 4,8-5,8 | 6,8-7,5 | 7,0-7,5 | 7,0-7,5 |
| absent | absent | absent | |
| absent | absent | absent | absent |
| absent | absent | absent | absent |
| present | present | 75-350 mg/day. | 75-350 mg/day. |
| present | present | absent | absent |
| 20-40 mmol/kg | 20-40 mmol/kg | ||
| Various quantity | Various quantity | Various quantity | Various quantity |
| Small quantity or none | Small quantity or none | absent | absent |
| absent | absent | absent | absent |
| absent | absent | absent | absent |
| absent | absent | absent | absent |
| Drops | A small amount of | absent | absent |
| Crystals in small quantities | Crystals in small quantities | absent | absent |
| In small quantities | In small quantities | Minor amount | Minor amount |
| single | single | Single in the preparation | Single in the preparation |
Why are children prescribed coprogram?
Indications for research
Fecal analysis for coprogram is a mandatory test for children if they have signs of a functional disorder or pathological condition of the gastrointestinal tract:
- abdominal pain;
- heartburn, belching, nausea, specific taste in the mouth, vomiting;
- flatulence, constipation, diarrhea;
- abnormal appearance of feces - color, smell, volume, presence of suspicious impurities;
- mucus, pus, blood on underwear;
- pain, itching in the rectum;
- suspicion of neoplasm, helminthiasis, poisoning;
- allergies, intolerance to certain foods;
- significant, sudden weight loss for no identifiable reason.
What the analysis reveals
The coprogram allows you to detect:
- diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts;
- pathology of the pancreas;
- functional liver disorders;
- bowel dysfunction;
- stomach diseases;
- helminthiasis;
- celiac disease;
- cancer diseases.
Tests for coronavirus
- Test for coronavirus
- Coronavirus test for organizations
- Testing for coronavirus at home
- Testing for coronavirus at home in 12 hours!
- Testing for coronavirus in Lyubertsy in 12 hours!
- Testing for coronavirus in Nekrasovka in 12 hours!
- Testing for coronavirus in Korolev in 12 hours!
- Test for coronavirus on the Sokol metro station
- Coronavirus test at Kolomenskaya metro station
- Coronavirus test at Voykovskaya metro station
- Test for coronavirus in Nekrasovka
- Coronavirus test in Korolev
- Test for coronavirus in Lyubertsy
- Test for coronavirus in Mytishchi
- Test for coronavirus at home Mytishchi
- Test for coronavirus at home Korolev
- Test for coronavirus at home Lyubertsy
- Test for coronavirus at home Nekrasovka
Any tests can be taken at clinics in the East Clinic network.
Patient preparation rules
Standard conditions:
Feces are collected after spontaneous defecation, should not contain foreign impurities and are delivered to the ML “DILA” in Kiev within 2 hours. Material for research collected after an enema, taking medications that affect peristalsis, taking castor or vaseline oil, after administering suppositories, or drugs that affect the color of stool (iron, bismuth) is not accepted. The biomaterial is accepted according to the biomaterial collection schedule at the ML department “DILA”.
You can add this study to your cart on this page
What is a coprogram?
Fecal examination is performed to clarify the state of digestion and identify detritus. Such a check is called a coprogram. With its help, deviations in the performance of the gastrointestinal tract are identified, and the number of harmful bacteria in the organs is determined. In addition to the level of detritus in the coprogram, other indicators of substances contained in fecal matter and their condition are established. Increased or decreased readings confirm problems in the digestive organs. This happens with inflammation, diarrhea, problems with the pancreas, etc.
Coprogramming of detritus is performed using a microscope. The test drug is prepared, a small fragment of it is placed between a pair of glass slides, its structural structure is studied and its composition is assessed. The laboratory technician adds a small amount of water or sodium chloride to the feces when the fecal masses have a dense consistency.
Hemorrhoids are a disease in the treatment of which not only a conservative approach with medications is important. For successful treatment, special exercises for hemorrhoids are very important, which tone the pelvic vessels, improve blood circulation, and prevent stagnation of venous blood and the formation of varicose nodes. Read more in the article: “exercises for hemorrhoids.”

Before the start of the study, the biomaterial is subjected to centrifugation. In this case, detritus is considered to be everything that is in liquid fractions. Large particles are classified as impurities. It is allowed to use different dyes during the study to help identify certain impurities or microorganisms.

General information
The coprogram method evaluates the enzymatic (digestion of foods) and acid-forming (secretion of gastric juice) functions of the stomach. Also, this study allows us to identify dysfunction of the pancreas and liver, inflammatory processes in the upper or lower gastrointestinal tract, dysbacteriosis, the presence of parasites in the body, etc.
The color of feces is given by a special pigment, stercobilin. A number of pathological conditions are determined by changes in the shade of stool:
- transparent - reflux of bile into the intestines, a sign of obstructive jaundice (impaired outflow of bile, resulting in staining of the mucous membranes, skin, etc.);
- black, resembling tar in appearance (in medicine - “melena”) - bleeding of the upper gastrointestinal tract;
- red – bleeding from the lower gastrointestinal tract (large intestine).
Also, the color of stool may change as a result of the addition of pathological impurities: blood, proteins, pus, mucus, parasites, etc.
Normal feces is considered to be a biological mass consisting of food residues. In healthy patients, particles of muscle and epithelial tissue are found in small quantities in the stool. If the proportion of the above components in the stool increases, then pancreatic insufficiency or impaired secretion of gastric juice should be suspected.
The presence of fiber or starch may indicate diseases of the small intestine.
Neutral fat in the coprogram indicates insufficiency of the lipolytic function of the pancreas (the ability to digest fat), a violation of the outflow of bile.
The presence of leukocytes in stool allows one to diagnose intestinal inflammation (colitis, ulcers, dysentery).
Collection of material
Required volume of stool
For research, you should collect 3 - 5 cm 3 (approximately a teaspoon) of feces.
Procedure for collecting stool
You should wash your hands thoroughly and put on latex gloves before collecting stool from a child.
It is necessary to place a polyethylene film under the rim of the toilet, then collect a fecal sample from it. This film can be used in the diaper of a baby who has not yet used the toilet. It is impossible to remove feces from the diaper for analysis, as it absorbs liquid.
It is unacceptable for urine to get into the collected stool, but if contamination has occurred, the sample will have to be taken again. Feces should be collected before they touch the inner surface of the toilet.
You cannot remove feces after a cleansing enema.
How to store and transport coprogram material
Experts recommend donating feces “fresh.” But when it is not possible to provide the material to the place of its research immediately, feces can be stored in a well-closed container at a temperature of +3 oC -+5 oC for up to 8 hours.
It is best to carry the container in a cooler bag or thermal bag. If this is not possible, then the container should be wrapped in several layers of paper and then wrapped in a towel; thick fabric will also work. However, the material must be delivered to the laboratory within 2 - 3 hours.
Why is the material not collected in the evening?
It is not recommended to remove feces for analysis in the evening, since most laboratories are closed and it will not be possible to immediately deliver feces for analysis. You will have to store the material until the morning, as a result of which the results may be false.
Analysis period
The results of the study will be ready 5–6 days after the material is provided. At this time, the laboratory assistant is engaged in microscopic and macroscopic examination of fecal matter, checking them for the presence of foreign impurities, harmful microorganisms and other pathogenic elements.
What is detritus?
Detritus refers to small particles of food digested by the human body, as well as a certain amount of bacteria killed as a result of the action of digestive enzymes. And in fact, the more detritus in the stool, the better. That is, the presence of this substance in the proper amount is a signal about the normal functioning of the digestive system. By the amount of detritus in the coprogram, one can judge the state of the gastrointestinal tract and the human body as a whole.

The feces of a healthy person (child or adult) have a fairly dense consistency, and when carrying out tests, a large amount of detritus can be detected in it. And this is the norm.
If you examine detritus under a microscope, its structure will be generally shapeless; the particles, vaguely reminiscent of grains, have different sizes. Its formation largely depends on what foods a person consumed, on the composition of gastric juice, on the amount of digestive enzymes and much more. Also in detritus, in addition to dead bacteria and dietary fiber, pieces of dead epithelium of the intestinal walls, dead blood cells and other components may be present. During the digestion process, they change their structure so much that it becomes very difficult to distinguish them from each other.
Poor nutrition and alcohol abuse lead to organ failure, which is indicated by corresponding pain and discomfort in the abdomen. Read more in the article: “reasons why the pancreas hurts.”
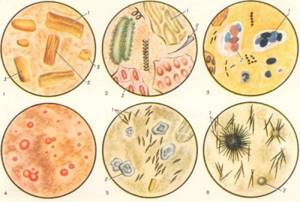
Why are the indicators violated?
If there are disruptions in the digestion process, food is not absorbed in full. Therefore, waste products in their primary form are detected in feces. With heavy consumption of meat dishes or offal, muscle tissue fibers and fat clots are detected in the feces. Recognized visually by oblong clots resembling cylinders.

If a certain food product is not completely digested, it is detected in the stool by thin threads. If we compare detritus with fat particles, the first component is distinguished by its smooth surface. Normally, the lumps are identical in size and homogeneous in structure.
Deviations from the norms appear due to a lack of gastric juice or inflammation. A reduced level of detritus, especially in infants, indicates that the body’s immunity is not coping with its task.