Microalbuminuria (MAU) is the excretion of albumin in the urine in an amount of 30-300 mg per day. At the Yusupov Hospital, all conditions have been created for the treatment of patients who have been diagnosed with albuminuria:
- Chambers with European level of comfort;
- Use of modern expert-class diagnostic equipment, which allows you to quickly and accurately determine the cause of albuminuria;
- Treatment of diseases manifested by albuminuria using the latest drugs that are highly effective and have a minimal range of side effects;
- Attentive attitude of medical staff to the wishes of patients.
Severe cases of diseases, one of the symptoms of which is microalbuminuria, are discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council with the participation of professors, doctors of medical sciences, and doctors of the highest category. Depending on the cause of albuminuria, cardiologists, nephrologists, endocrinologists and other specialists are involved in the treatment of patients.
Microalbuminuria is an early sign of renal dysfunction and is one of the manifestations of target organ damage (an indicator of impaired endothelial function, insulin resistance and increased blood clotting - hypercoagulation). Diagnosis of microalbuminuria is carried out using special strips. They come in different sensitivities. If the result is positive, the presence of microalbuminuria is confirmed using quantitative methods.
general characteristics
Microalbuminuria is the excretion of albumin in the urine in the amount of 30-300 mg per day. Microalbuminuria is an early sign of renal dysfunction and is one of the manifestations of target organ damage (an indicator of endothelial dysfunction, insulin resistance and hypercoagulation). This early nephropathy is potentially reversible with strict glycemic control and adequate antihypertensive therapy. Persistence of microalbuminuria during antihypertensive therapy is associated with a worse prognosis.
Indications for prescribing a urine test for microalbuminuria
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe a urine test for microalbuminuria (MAU) for the following purposes:
- Screening for the initial stages of renal glomerular dysfunction (nephropathy, as a complication of hypertension, diabetes, atherosclerosis);
- Diagnosis of kidney and cardiovascular diseases;
- Monitoring the condition of the kidneys in diseases in which the kidneys may be involved in the pathological process (diabetes mellitus, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases);
- Monitoring therapy for arterial hypertension.
Microalbuminuria is a marker for assessing the risk of kidney pathology and cardiovascular diseases. A urine test for UIA is prescribed to patients suffering from glomerulonephritis, arterial hypertension, and sarcoidosis. The level of albumin in urine may increase with fructose intolerance and hypothermia. Microalbuminuria is determined in pregnant women who are at risk of developing nephropathy.
Patient preparation rules
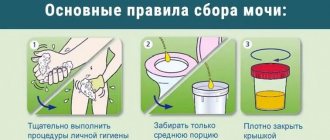
Biological material is accepted during the working day of the departments of ML "DILA". The morning portion of urine is placed in the toilet. All subsequent urine, including the morning portion of the next day, is collected in a clean urine collection container. During collection, store the container in a cool place, protected from light and children. After collecting the last portion, mix all collected urine, measure its volume and record it. Pour 30-40 ml and deliver to the nearest branch of the medical clinic "DILA" within 2 hours. Maybe:
To collect daily urine, the patient is asked to purchase a container with a volume of 2.0 liters at the price price (the cost of the container is not included in the cost of the study).
Random urine:
Any amount of urine, regardless of the time of day. Urine is collected after toileting the external genitalia.
You can add this study to your cart on this page
How to get tested for microalbuminuria
On the eve of the study, the patient is advised to avoid alcohol, salty and spicy foods, and foods that change the color of urine (beets, carrots). Before collecting urine, you should thoroughly clean the external genitalia. Men toilet the external genitalia after retracting the foreskin and exposing the head of the penis. Women are not recommended to test urine for microalbuminuria during menstruation. Before collecting urine, it is advisable to insert a gynecological tampon into the vagina.
For patients with incontinence, urine is collected using a catheter. In infants, a thorough toilet of the external genitalia is carried out, and urine is collected in a urinal. Urine squeezed out of a diaper cannot be examined.
Urine must be collected in a clean, dry glass or plastic container, well washed from cleaning agents and disinfectants, or a sterile disposable urine container. After collecting urine, the container is tightly closed with a lid, placed in a clean disposable bag and delivered to the laboratory center of the Yusupov Hospital.
Physical manifestations of microalbuminuria
A patient with a high content of albumin in the urine goes through several stages of disease development. In the asymptomatic stage, the patient does not complain, but microalbuminuria is detected in the urine. At the initial stage of the disease there are also no complaints, but the glomerular filtration rate increases. Microalbuminuria does not exceed 30 mg per day.
The prenephrotic stage is characterized by an increase in the level of microalbumin in the urine to 300 mg. The patient's blood pressure increases and the renal filtration rate increases. Complaints associated with increased blood pressure (headache, nausea, and sometimes vomiting) appear. During the nephrotic stage of the disease, blood pressure increases, it is poorly controlled by taking antihypertensive drugs, and edema appears. The urine test results show a significant increase in the amount of protein and the presence of red blood cells. Glomerular filtration decreases, creatinine and urea levels increase.
The stage of renal failure is characterized by frequent increases in blood pressure. The swelling becomes persistent, and the number of red blood cells in the urine increases. The filtration rate decreases significantly, the concentration of protein in the urine increases along with creatinine and urea.
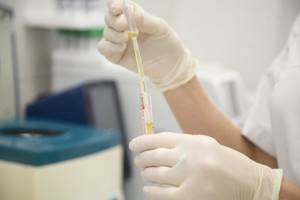
Clinical significance of microalbuminuria
Microalbuminuria is the most important early sign of kidney damage, which reflects the initial stages of vascular pathology (endothelial dysfunction, atherosclerosis). It is consistently correlated with increased cardiovascular disease incidence and mortality. Dissertations and articles devoted to the problem of microalbuminuria indicate that even a slight increase in the excretion of albumin in the urine is associated with a significant increase in the risk of cardiovascular events, including fatal ones. A progressive increase in MAU indicates deterioration of vascular health and causes an additional increase in risk. In this regard, microalbuminuria is recognized as an independent cardiovascular risk factor and the earliest sign of target organ damage (kidneys).
MAU is a consequence of increased loss of albumin from blood plasma through the endothelium and is defined as a marker for the development of systemic disorders of endothelial function. Endothelial dysfunction is characteristic of the early stages of atherosclerosis and is directly associated with increased cardiovascular risk.
Scientists have found that increased urinary protein excretion is clearly associated with left ventricular hypertrophy, regardless of age, race, gender, blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, smoking, or blood creatinine levels. MAU is especially often detected in heart failure and arterial hypertension. Microalbuminuria develops in 10-40% of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and in 15-40% of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The frequency of detection of microalbuminuria increases with the duration of the disease in both types of diabetes mellitus.
In order to get tested for microalbuminuria, call the contact center of the Yusupov Hospital. After the examination, doctors will treat the disease that caused the increase in protein in the urine.
Spontaneous remission and treatment with sartans
386 patients with insulin-dependent diabetes and microalbuminuria were observed for 6 years. In more than half (58%) of cases, microalbuminuria regressed spontaneously without treatment. Regression was more likely in patients whose HbA1c was less than 8%, systolic blood pressure less than 115 mmHg, total cholesterol less than 5.1 mmol/L, and triglycerides less than 1.6 mmol/L. Treatment with ACE inhibitors did not increase the number of remissions. Decisive for prognosis, however, is good control of cardiovascular risk factors.
Remission occurs more often in patients who lead a healthy lifestyle, the researchers noted. However, it is also important to take medications to reduce the risk of serious complications.
Although the beneficial effects of ACEIs on microalbuminuria in people with diabetes and normal blood pressure are well documented, this is not the case with angiotensin II receptor antagonists. A Dutch double-blind study that lasted just 10 weeks tested whether losartan could achieve the same effect. The study involved 147 people with diabetes and microalbuminuria, but with normal blood pressure. Losartan slightly reduced blood pressure, and creatinine clearance remained unchanged. As the study showed, losartan did not have a statistically significant effect, like other sartans, on the concentration of albumin in the blood plasma.

Losartan
Stages of nephropathy
Impaired kidney function occurs in stages that are characterized by certain features.
Initial manifestations
Analysis for MAU shows the presence of microalbumin. There are no external symptoms.
Prenephrotic changes
The patient experiences fluctuations in blood pressure, the kidneys filter fluid slowly, and in urine the protein concentration level is 30 - 300 MHz/day.
Nephrotic changes
The patient’s kidneys reduce their filtration capacity, resulting in edema, increased blood pressure, proteinuria, and microhematuria. Sometimes urea and creatinine levels increase.
Uremia
Blood pressure reaches high levels that cannot be treated. Edema, hematuria and proteinuria appear. In the analysis, the number of red blood cells, creatinine, and urea increases. With heart pathology, the patient experiences chest pain, sometimes on the left side.
If, when analyzing for UIA, the norm is too high, you should adhere to proper nutrition and undergo regular examinations by specialists who will prescribe restorative and corrective medications. The earlier the disease is diagnosed, the more effective therapeutic measures are.
A urine test for microalbumin content (MAU) is one of the most informative tests that allows you to assess the patient’s health status.
This type of examination is important if there is suspicion of damage to the kidney tissue.
In this case, the concentration of microalbumin reflects the degree of damage to the excretory organ.
Letters from our readers

My grandmother has been suffering from diabetes for a long time (type 2), but recently there have been complications in her legs and internal organs.
I accidentally found an article on the Internet that literally saved my life. They gave me a free consultation over the phone and answered all my questions and told me how to treat diabetes.
2 weeks after completing the course of treatment, my grandmother’s mood even changed. She said that my legs no longer hurt and the ulcers are not progressing, next week we will go to see a doctor. I am sending a link to the article
How to prepare for a daily UIA
This type of examination provides the greatest accuracy, but will require the implementation of simple recommendations:
- the day before the collection and during it, avoid taking diuretics, as well as antihypertensive drugs of the ACE inhibitor group (in general, taking any medications should be discussed with your doctor in advance);
- the day before urine collection, you should avoid stressful and emotionally difficult situations, intense physical training;
- at least two days in advance, stop drinking alcohol, energy drinks, and, if possible, smoking;
- maintain a drinking regime and do not overload the body with protein foods;
- The test should not be performed during non-infectious inflammation or infection, as well as critical days (in women);
- the day before collection, avoid sexual contact (for men).
Diagnostics
To determine the amount of albumin in urine, the following methods are used:
- Linked immunosorbent assay;
- Isotope immunological;
- Immunoturbidimetric.
For analysis, urine collected during the day is used, but you can also take morning urine or urine that was collected in the morning within 4 hours. To do this, take the ratio of albumin and creatinine. When performing an analysis, you can use test strips, but if they show a positive result, the tests will need to be repeated in the laboratory.
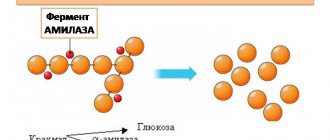
The role of albumin in the human body
Proteins, in particular albumins, are the main material for all cells of the body. They maintain the balance of fluid and microelements between cellular and extracellular structures. Albumin is necessary for the functioning of all organs and systems.
Most proteins are synthesized from amino acids in liver cells. After this, they enter the systemic bloodstream and are distributed throughout the body. The synthesis of some proteins requires essential amino acids from food. The loss of such proteins in the urine is observed in serious pathologies and threatens the body with serious consequences.
Interpretation of urine test results for UIA
Albumin excretion in urine may increase with dehydration, heavy physical activity, or following a high-protein diet. Microalbuminuria is determined in patients suffering from diseases that occur with an increase in body temperature, inflammatory processes of the urinary tract (cystitis, urethritis).
A decrease in the level of albumin in urine occurs in the following diseases:
- Dysmetabolic, reflux, radiation nephropathy;
- Pyelonephritis;
- Early stage of glomerulonephritis;
- Renal vein thrombosis;
- Polycystic kidney disease;
- Nephropathy in pregnant women;
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (lupus nephritis);
- Amyloidosis of the kidneys;
- Multiple myeloma.
Urinary albumin excretion decreases with excess hydration, a low protein diet, taking angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (enalapril, captopril), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and hypothermia.
Treatment and normalization of microalbuminuria in diabetes mellitus
Diabetology has achieved significant results in the development of diabetes treatment methods. New drugs are constantly being created to replace endogenous insulin.
This section of medicine also deals with the selection of individual diets and primary prevention, which aims not only to treat diabetes, but also to reduce its occurrence.
At the stage of microalbuminuria, which is already a complication of the disease, it is necessary:
- closely adjust the carbohydrate metabolism of drugs (mainly by switching to insulin options);
- even with a slight increase in blood pressure, use ACE inhibitors or an analogue group (if they are intolerant), as they have nephroprotective properties;
- use statins in therapy;
- undergo a course of treatment with angioprotectors and antioxidants.
In addition, it is necessary to follow a certain regime in:
- nutrition (limiting simple carbohydrates, fried, spicy, salty);
- work and rest (do not overexert);
- physical activity (regular physical exercise with dosed exercise);
- healthy functioning (without harmful addictions).
Expert opinion
Guseva Yulia Alexandrova
Specialized endocrinologist
Following all recommendations for treatment and prevention at the stage of microalbuminuria will significantly improve the condition and prolong life.
Epidemiology
In 20-40% of diabetics who develop kidney disease, microalbumin can be detected in a urine sample. In 2-2.5% of diabetic patients with normal albumin excretion, microalbuminuria first appears in the first year of the disease. Type 1 diabetics are especially susceptible to the disease.
Advice! It is not recommended to “remove” excess protein using folk remedies or untested methods (diets). If you have high blood sugar and hypertension, you should consult a doctor.
Interesting:
- What are the blood sugar standards in young children, types of tests, causes of hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, methods of prevention and treatment of deviations from the norm
- Indications for tests for diabetes mellitus, their information content and potential complications of the disease
- Is the presence of sugar in urine dangerous during pregnancy and what to do in this case?
- Reasons for the increase in the concentration of antibodies to the substance GAD, indications for the examination, preparation, contraindications and interpretation of the results
- Indications for analysis of blood sugar levels, information content of studies, interpretation of results and normal indicators
- Insulin rate 2 hours after a glucose load, indications, contraindications for the study, preparation and interpretation of results
- Preparation for the analysis of glycated hemoglobin in young children, the norm, information content of the study and interpretation of the results
Standard indicators
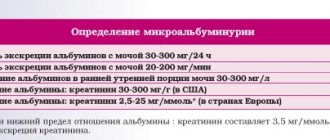
In an adult, the norm of UIA in urine should not exceed 30 mg/day. They should be practically absent in the urine of children. If albumin is released in quantities greater than 30 mg/day, this means that the patient develops mild nephropathy.
If more than 300 mg is excreted per day, this indicates that the kidneys are significantly affected. After 6 weeks, you need to retake the test to confirm the diagnosis. After this, the specialist prescribes treatment.
Prevention and recommendations
An increased amount of protein in the urine always indicates damage to the kidney tissue.

To avoid this, preventive measures should be taken:
- Monitor blood pressure values regularly. The tonometer readings should be checked especially for those patients who have a genetic predisposition to hypertension.
- Monitor the concentration of glucose, the concentration of which should not exceed 3.5 - 6.0 mmol per liter. Systematic measurements should be carried out on an empty stomach, since food intake can change quality indicators.
- Complete smoking cessation, since nicotine can negatively affect the condition of the vascular system. Nicotine addiction is especially dangerous for the arteries that feed the liver and kidneys. According to statistics, a person with a long history of smoking is at 21 times higher risk of developing proteinuria than a non-smoker.
- Every quarter it is necessary to conduct a lipid profile, which will allow you to control the level of cholesterol in the blood.
With the help of prevention, protein loss is reduced and the risk of developing serious diseases is reduced.
What is albuminuria?
Albumins are one of the types of proteins produced in the liver and present in the blood plasma. Their volume makes up about 60% of all proteins.
The functions that albumins perform are important for:
- stable osmotic pressure in body systems;
- transportation of products produced both by internal organs (bilirubin, fatty acids, urobilin, thyroxine) and coming from outside;
- creating a protein reserve.
Albumin molecules are small in volume, have the greatest mobility and are the majority.
Therefore, when the filtration function in the kidneys is impaired, they are the first to be lost. The appearance of a small amount of proteins in the urine - microalbuminuria - is characteristic of the initial level of diabetic kidney damage.
The insidiousness of this stage is the absence of external manifestations of the lesion, but the pathological process continues to develop. After a few years (12-15) from the manifestation of diabetes, the stage of proteinuria begins - a clear loss of protein by the body.
Here the symptoms of the disease are already obvious: swelling, increased blood pressure, weakness. The progression of the pathology leads to the uremic stage - renal failure develops.
Thus, kidney damage in diabetes goes through the following stages:
- microalbuminuria;
- proteinuria;
- uremia.
The loss of even a small amount of proteins already indicates significant kidney damage. But at the first stage, with timely treatment, it is possible to stop the process.
Expert opinion
Guseva Yulia Alexandrova
Specialized endocrinologist
It is important to identify the pathology at an early stage, even before clinical signs, when therapy is effective.