Detailed description of the study
Minerals are necessary to maintain normal functioning of the body. They do not provide energy, but ensure the normal course of metabolic processes, being part of enzymes, transport proteins (including hemoglobin), ensuring the strength of teeth and bones, the normal functioning of the nervous system, and the functioning of muscles and the heart.
Mineral metabolism analysis is a comprehensive study that identifies excess or deficiency of minerals and evaluates the usefulness of metabolism. Metabolism should be understood as a combination of processes of transfer, absorption, secretion and assimilation of substances that are present in the body in the form of inorganic compounds. Even if you get enough minerals from your diet, malabsorption can occur at all levels, from intestinal absorption to cellular uptake.
Microelements essential for human life can be divided into groups listed below. It is important to understand that trace elements are needed by the body in very small quantities - in high doses they are toxic.
- Structural elements: calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, phosphorus.
- Essential (vital) elements: iron, copper, zinc, cobalt, chromium, molybdenum, nickel, selenium, manganese, arsenic, lithium.
- Conditionally necessary element: boron.
- Other important elements: cadmium, lead, aluminum.
- Ultramicroelements: beryllium, mercury, antimony.
Urine is a biological fluid that is formed in the kidneys when blood is filtered through them. The end products of metabolism, water, salts and minerals, as well as toxic substances are removed from the body with urine. In case of pathologies of internal organs (kidneys, liver, heart, digestive system, endocrine glands, etc.), a change occurs in the chemical composition of the blood and, accordingly, the composition of urine. The mineral molecules are small enough to pass through the kidney filter. A chemical analysis of urine allows us to identify even minor disturbances in metabolic processes in the body, including mineral ones.
The study includes analysis of 23 elements involved in mineral metabolism.
Iron. It is part of hemoglobin, allowing the transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. Iron is also part of myoglobin, a hemoglobin-like protein found in muscles and the heart that stores oxygen, creating a reserve. In the blood and some organs there is a similar “reservoir”, ferritin - an iron-protein complex that contains this metal in reserve form. If there is not enough iron in the body, ferritin will ensure its additional supply into the blood.
Copper. Part of the enzymes that ensure cellular respiration. Cytochrome c oxidase transfers electrons in the respiratory chain to produce energy, and superoxide dismutase neutralizes toxic reactive oxygen species.
Zinc. This metal is necessary for the synthesis of growth hormones: insulin, somatotropin growth hormone, testosterone. It is part of the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase, which breaks down alcohol, and is also necessary for the absorption and use of the most powerful antioxidant - vitamin E. Zinc is especially important for the health of men: only with it is possible the production of sperm and most male hormones. In addition, the health of the prostate gland depends on it.
Cobalt. It is part of vitamin B12 (cobalamin), which is necessary for DNA synthesis and normal hematopoiesis - its deficiency can cause anemia. It also provides protection and maintenance of the viability of nerve cells and the detoxification function of the liver.
Chromium. It is part of the gastric enzyme trypsin, which breaks down proteins. It also takes part in the metabolism of carbohydrates and lipids. Its deficiency can lead to increased blood cholesterol levels.
Molybdenum. It is part of the enzymes involved in tissue respiration and the metabolism of uric acid nitrogen, which, if disturbed, can cause gout. Enhances the effect of antioxidants (vitamins C and E), supports the activity of the immune system.
Nickel. Strengthens the effect of insulin on the body's cells, preventing excessive increases in blood sugar levels. Enhances the effectiveness of ascorbic acid and ensures the functioning of enzymes involved in the neutralization of toxic substances.
Selenium. It itself is an antioxidant, since it protects cells from the action of reactive oxygen species - one of the causes of aging of the body. The authoritative medical journal Lancet reports that it showed significant anticancer activity against tumors of the rectum, colon, prostate, and lung, overall reducing cancer mortality by 39%. Selenium has an antiallergic effect, improves tissue healing, and supports the functioning of the cardiovascular and immune systems.
Manganese. A trace element important for hematopoiesis, development and maintenance of the health of the gonads.
Arsenic. The body needs it in very small doses and is considered an ultramicroelement. Participates in hematopoiesis and maintaining immunity. It also promotes the growth and strengthening of bones in childhood and adolescence.
Lithium. Plays a very important role in the functioning of the nervous system, reducing its excitability. Lithium preparations are used in psychiatry and neurology to treat epilepsy. Takes part in the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats, has mild antiallergic properties.
Mechanism of protection against stone formation
If there are disturbances in the metabolic process, urine begins to acidify or become alkalized. When the acid-base balance shifts, salts in the urine are converted into crystals. To prevent crystallization, the body produces special antagonist substances. They control biochemical processes and, in case of any disturbances, bind individual components. Elements that have this effect:
- enzymes;
- magnesium ions;
- pyrophosphate compounds;
- citrates.
They prevent crystals from attaching to the mucous membrane of the urinary system (bladder, kidneys, ureters).
References
1. Seregina I. F., Lanskaya S. Yu., Okina O. I., Bolshov M. A., Lyapunov S. M., Chugunova O. L., Foktova A. S. Determination of chemical elements in biological fluids and diagnostic substrates of children using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry / Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2010, Vol. 65, No. 9, p. 986-994. 2. Skalny A.V. Chemical elements in human physiology and ecology. – M.: Publishing house “Onyx 21st century”: Mir, 2004, 216 p. 3. Singh N, Gupta VK, Kumar A, Sharma B. Synergistic Effects of Heavy Metals and Pesticides in Living Systems. / Front Chem. 2017;5:70. 4. Chen SX, Wiseman CL, Chakravartty D, Cole DC. Metal Concentrations in Newcomer Women and Environmental Exposures: A Scoping Review. / Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. 8;14(3) 5. Rayman MP. Selenium and human health. Lancet. 2012;379(9822):1256-1268. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61452-9
Daily analysis
A daily urine test helps determine the functionality of the kidneys and determine the amount of substances excreted per day. This prevents the development of diabetes mellitus and urological pathologies.
24 hours before the test, urine is collected in one large container. Such a study can be carried out on people of any age category, even newborns.
Elements that determine the composition of urine:
- water (approximately 97%);
- xanthine, indican, creatinine;
- potassium, sodium, magnesium, phosphorus, traces of calcium;
- uric acid, its compounds;
- phosphates, sulfates, chlorides.
The amount of urine collected is 1-2 liters. Depending on the age and gender of the patient. An accurate interpretation of the analysis is carried out by a specialist.
Preparation
In order for the analysis results to be accurate, it is necessary to prepare for it. 2-3 days before delivery you need to do the following:
- When collecting biomaterial, monitor the hygiene of the external genitalia;
- the day before collecting the analysis, exclude coloring foods (carrots, berries, beets, etc.);
- remove everything spicy, salty, fatty and very sweet from the diet;
- maintain proper drinking regimen throughout the day (at least 1.5 liters);
- do not take synthetic drugs.
If the use of medications cannot be excluded, then you need to inform the laboratory employee about this. Also provide him with information about the name of the medicine, dosage.
How to collect material correctly?
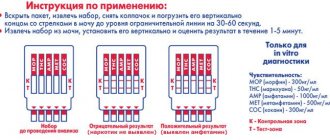
It is necessary to collect material for analysis within 24 hours. Therefore, it is recommended to postpone any trips for this day. Collection rules:
- Prepare a 2-3 liter container with a wide neck and a well-closing lid. It must be pre-sterilized and dried. You can also purchase a special plastic container at any pharmacy chain. Its volume is 2.7 liters.
- Remember the start time of urine collection. Exactly 24 hours must pass between the first and last procedure.
- Wash your genitals well without using products with additives. You can use a weak solution of potassium permanganate or furatsilin.
- When you go to the toilet for the first time in the morning, do not collect urine, just record the time.
- The analysis is first collected in a small sterile and dry vessel and immediately poured into the main container. After this, close the lid tightly.
- After the last urine collection (on the day of the test), mix the material well and pour 150-200 ml into a special jar.
Before collecting material for analysis, you need to ask your doctor how much urine you need to bring. In some cases, a larger capacity may be needed.
What diseases does the test detect?
The deposition of salts in urine may indicate the formation of:
- Kidney pathologies: pyelonephritis, nephritis (if urates, oxalates are detected). Concomitant symptoms may include fever, pain in the lumbar region, discomfort when urinating, cloudy urine, nausea and general weakness.
- Urolithiasis (with elevated levels of creatinine and urate). Acute pain occurs in attacks in the lower back, frequent false urge to urinate.
- Diabetes mellitus (with high oxalate content). There is an increased level of glucose in the blood, the patient is constantly thirsty, and the urge to go to the toilet becomes frequent.
- Joint diseases: gout, arthritis (urate is observed not only in urine, but also in the joints). In the affected area, stifling pain occurs in attacks, an inflammatory process and swelling in the joints appears.
Based on the results of a urine test for the presence of salts, an accurate diagnosis cannot be made. Therefore, differential diagnostic methods are additionally prescribed.
Choice of treatment depending on results
When removing excess salts from the body, an integrated approach is required. Conservative treatment will not bring results if you do not start leading a healthy lifestyle and eating rationally. To eliminate crystals, you can also use alternative medicine, but only as part of the main therapy and after the recommendation of your doctor.
Nutrition
To remove excess salt from the body, you need to change your usual diet.
- Drink at least 1.5-3 liters of fluid per day (its volume depends on gender, weight category and physical activity).
- Reduce salt intake (it is advisable to eliminate it completely for the first days, after 2-3 days, consume no more than 1-2 g per day).
- Eat sea salt, as it is healthier than table salt.
You need to eat regularly. Portions should be small. Excluded from the diet:
- fatty and fried, with a high content of spices and seasonings;
- fast food;
- canned and pickled;
- semi-finished products;
- carbonated drinks;
- coffee Tea.
Products with a diuretic effect also help eliminate salts. These include any green vegetables, citrus fruits, beets, and onions. It is best to consume them without heat treatment. You can make juices, salads, or eat them raw from fruits and vegetables.
Folk remedies
To remove salts using folk remedies, you can use regular rice:
- 3 tbsp. l. rice pour 1 liter of cool water. Let it sit overnight. In the morning, drain off the excess liquid and add new liquid. Cook over low heat for 5 minutes. After this, rinse the cereal and put it on the stove for another 5 minutes. Repeat these steps 4 times. The resulting porridge is consumed warm. Approximately 3 hours after preparation.
- Pour 1 tbsp. l. rice with cold water. Let it brew overnight. After this, cook over low heat without adding salt. Eat the resulting porridge on an empty stomach. After this, you can have breakfast only after 4 hours.

This treatment lasts 10 days. During this period, it is necessary to include fruits, dried fruits, and vegetables in the diet.
What will it reveal?
Daily urine analysis reveals the presence of the same salts as in OAM.
Urats
These are sodium and uric acid salts that have precipitated. Their occurrence in urine is not dangerous. Most often, this occurs when drinking alcohol or eating a poor diet. Urates can also form as a result of heavy physical exertion and systematic fasting.

To bring this indicator back to normal, you need to reduce your alcohol consumption (or better yet, give it up completely) and start eating rationally. Carefully ensure that the body receives all the nutrients it needs.
Phosphates
If there are phosphates in urine, the collected material has a cloudy tint. A burning sensation occurs during urination. This pathological condition indicates the development of cystitis, alkaline diathesis (uraturia).
Oxalates
Elevated levels of oxalates indicate the occurrence of urolithiasis. Sometimes such deposits can be manifestations of infectious pathologies, cystitis, pyelonephritis.
If oxalates are detected in the urine, a repeat test is prescribed. If it gives the same results, the doctor conducts a full diagnostic examination and makes an accurate diagnosis. Only after this the necessary therapy is prescribed.