What is ultrasound?
Ultrasound (ultrasound, sonography) is a procedure for examining the body using ultrasonic waves.
Their frequency is about 20,000 Hz, which is higher than what the human ear can perceive. This test is safe for the body and can be performed frequently if necessary. The thyroid gland produces iodine-containing hormones and stores iodine. It consists of two lobes and an isthmus and is located in the front of the neck. Its proper operation is extremely important for the normal functioning of the entire body, and violations lead to a number of diseases: cancer, Graves' disease, cretinism, adenoma, myxedema, etc.
An ultrasound of this gland allows you to find out what condition it is in, whether there are any pathologies or neoplasms. It shows changes in its structure, which can cause various health problems.
Interpretation of ultrasound of the thyroid gland
To obtain comprehensive information that reflects the condition of the thyroid gland, the diagnostician during the ultrasound procedure evaluates and enters into the protocol the following parameters:
- Location . The typical location of the gland is considered standard when it is within the anatomical norm. If there is a pathology, a record of its aberrant location is entered into the protocol, when the thyroid gland may be located behind the sternum, in the area of the root of the tongue, etc.
- Size . Determining this parameter allows one to judge the presence or absence of hypo- or hyperplasia of the thyroid gland.
- Structure . Normally, the thyroid gland consists of two symmetrical lobes, which are connected by a small isthmus. In the case of abnormal intrauterine development of the gland or its pathological acquired modification, tissue outgrowths, an additional lobe, and bifurcation may be absent.
- Form . Normally, the thyroid gland is flat, but may be slightly elongated. If it is greatly increased in volume, swollen, with thyroid tissue, diffuse goiter, viral or bacterial pathology is suspected.
- Outlines . The clear contours of the thyroid gland are taken as normal. Otherwise, if its contours are not clearly visualized, one can judge the presence of a tumor or inflammatory focus in the gland.
- Structure . If there is no pathological process in the gland, its structure is homogeneous and has a specific granularity.
- Echogenicity . Visually, this parameter can be defined as a gradation of gray shades over the entire area of the study area. Normally, the echogenicity of thyroid tissue should be visible in light gray shades.
- Focal formations . During ultrasound diagnostics, the doctor must examine the gland for the presence of pathological formations - nodes, calcifications, cysts or tumors.
- Blood supply to tissues . Impaired blood supply to the thyroid gland can lead to the death of its tissue. Normally, the multi-colored signals visualized on the ultrasound monitor screen should be uniform over the entire area of the thyroid gland. An increase in color and “pulsation” of shades indicates an increase in blood flow, which may be associated with an inflammatory process inside the gland.
- The structure of the cervical lymph nodes . To determine their condition, the following indicators are determined: structure, size, presence of pathological inclusions, cystic transformation, presence of the “gate” of the lymph node, assessment of blood flow.
How is ultrasound performed?
Long preparation is not required before the study, but there are several rules:
- It is recommended not to eat a few hours before
- If you plan to do Doppler ultrasound, you must take an iodine-containing drug 3-4 hours before
- Before lying on the couch, you need to remove all jewelry from your neck and free yourself from your collar, scarf and any other element of clothing or decor.
Doppler ultrasound is a type of analysis that allows you to combine a black and white image of the thyroid gland with a color display of blood flow. It allows you to determine:
- Patency of blood vessels
- Violations of their walls (thinning/thickening)
- Direction and speed
- Resistance index
The procedure itself goes like this:
- The patient lies down on the couch
- A special cream is applied to his neck
- The sonologist moves the device over the thyroid gland, and at this time the data is transmitted to the screen and recorded on the computer hard drive
The total research time is about 15 minutes.
How to carry out the procedure
Carrying out an ultrasound of the thyroid gland is a simple, painless procedure, its rules are simple:
- The patient lies down on the medical couch face up, throwing his head back and opening his neck as much as possible. A cushion or pillow is placed at the level of the shoulder girdle.
- A gel with good ultrasound conductivity is applied to the skin in the area of the gland.
- The sensor is applied to the neck. It emits ultrasound and then receives the reflected signal.
- The signal is processed by the program, the image is displayed on the screen.
- The study takes place within 10–20 minutes. Discomfort can only be caused by an awkward neck position.
Indications for analysis for an adult patient
Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland is prescribed in the following cases:
- The patient is pale and does not feel well
- He experiences a sore throat/neck and does not have colds
- Hormone tests show abnormalities
- Arrhythmia
- Drowsiness, apathy and lethargy
- Sudden obesity or exhaustion
- Too frequent mood swings
When planning pregnancy, such a study should also be carried out.
Nodes in pregnant women
The diagnostic and treatment tactics for thyroid nodules in pregnant women are identical to the method for detecting thyroid nodules in non-pregnant women. If a nodule measuring 1 cm or larger is detected, the patient should be offered a fine-needle biopsy (FNA of a thyroid nodule).
A biopsy for pregnant women is not dangerous and can be performed routinely. If thyroid cancer is detected, it is important to seek an in-person consultation with an endocrinologist surgeon as soon as possible.
When is a thyroid ultrasound necessary for a child?
Children may also have problems with the functioning of this organ. Therefore, a doctor may prescribe such a study if the following signs occur:
- During the examination, the child was found to have a lump on his neck.
- He has difficulty breathing and shortness of breath
- Sudden weight gain/loss
- Arrhythmia
- If the patient has suffered a serious illness that may cause complications
There are several preconditions under which it is recommended that a child undergo a preventive examination of the thyroid gland:
- Living in an area with low iodine content in products
- In large industrial cities
- If the child has a genetic predisposition to problems with this organ
Causes of thyroid nodules
Currently, there is no clear answer about the cause of nodules in the organ. The main theory about the occurrence of nodules in the thyroid gland is a lack of iodine in food, as it is known that with insufficient amounts of iodine in drinking water and food, thyroid nodules are more often detected in the population of a certain region. In countries around the world where there are government programs to prevent iodine deficiency, nodules are detected less frequently than in countries without government support.
It is a known fact that ionizing radiation also adversely affects body tissues, including the thyroid gland, especially in early childhood. When exposed to radiation, nodes may appear in the organ, which, as a rule, are tumorous. There are cases where in early childhood children were treated with radiation to their tonsils and tumors of the oral region; subsequently, tumors and thyroid nodules were more often detected in this group of children.
There are examples of adverse ionizing radiation in the history of our planet, such as the nuclear bombing in Hiroshima and Nagasaki and the Chernobyl disaster. Over time, thyroid tumors began to be detected more often in residents of these regions, especially children.
In addition to external factors (lack of iodine, selenium, ionizing radiation), the formation of nodes is also influenced by heredity. If a nodule is detected in the thyroid gland, there is a higher probability that a relative will also have a nodule. There are known and described cases of inheritance of malignant tumors of the gland from generation to generation, in particular medullary carcinoma.
Sizes are normal
On the results of ultrasound of the thyroid gland, sizes and volumes are important. The maximum volume should be calculated in accordance with the patient’s weight and can range from 12.3 cm3 with a weight of up to 40 kg to 35 cm3 with a weight of 110 kg. Often in women it is less than in men, due to differences in some processes in the functioning of the endocrine system. If the gland is working correctly, but its volume is 1 cm3 or more larger, then this is also considered normal.
The parameters of shares are considered separately. On ultrasound of the thyroid gland, their normal sizes should correspond to the following categories:
- Width 1.5-2 cm
- Length 2.5-6 cm
- Thickness 1-1.5 cm
The isthmus can be from 4 to 8 mm. The size of the parathyroid glands is 2-8 mm. Normally, the right lobe may be slightly larger than the left (occasionally, the left lobe is larger than the right).
During pregnancy, the size of this organ may increase while maintaining normal functioning. 3-4 months after birth, he returns to his usual state.
In children under 16-18, the thyroid gland grows gradually from the moment of birth. May increase during puberty.
Are thyroid nodules dangerous?
Most thyroid nodules are not dangerous to humans, and if cancer is detected, the prognosis for their treatment is favorable; the main thing is to immediately seek an in-person consultation with an endocrinologist surgeon to determine further treatment tactics and examination.
When a benign process is detected in a gland node, surgical treatment is resorted to in the following situations:
- Symptoms of neck compression
- Cosmetic discomfort
- Excess thyroid hormones.
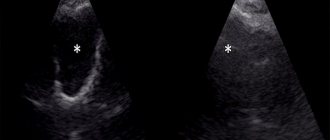
Echogenicity
This is a parameter that shows how much tissue reflects or does not reflect ultrasound. It is characterized by the density of a substance.
There are 4 types of echogenicity:
- Anaechogenic – tissues on the monitor are black, absorb ultrasound (blood vessels, benign formations)
- Isoechogenic – partially reflects, light gray on the screen (healthy tissue)
- Hypoechoic – little reflective, dark area (cysts)
- Hyperechoic – fully reflective, very light parts (connective tissue)
If the echogenicity of the thyroid gland is increased on ultrasound, this may be a sign of immune diseases.
How to prepare for an ultrasound
The method is accessible and simple, does not require special preparatory operations. You can eat absolutely any food product. But there are a number of restrictions:
1. Regardless of the feeling of nausea, older people are not recommended to eat before the procedure. Age-related changes may have an effect.
2. Women are recommended to undergo examination on days 7-9 of the menstrual cycle to avoid inaccurate results.
3. Immediately before the procedure, you need to free your neck from elements that interfere: jewelry, collars, etc.
4. Preparation for an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland in children is no different from the procedure for adults. The child must be psychologically prepared for the procedure so that he is not afraid of either the doctor or what he will do.
Doctors recommend that women undergo testing both during pregnancy and at the planning stage. If it is impossible to get pregnant, gland pathology may be one of the possible causes.
After the child has suffered stress, it is also worth going to the clinic so that an endocrinologist can perform an ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
Neoplasms
The analysis helps to identify various types of neoplasms. It can be:
- Benign colloid nodes, adenomas
- Cysts (contain fluid)
- Cancer tumor
When the echogenicity of the thyroid gland is reduced on ultrasound, the likelihood of a cyst or malignancy increases. This is indicated by the blurred boundaries of the spot on the sonogram.
If such seals are detected, other tests are performed to clarify the diagnosis.
Follicular tumor (FO)

Follicular tumor. The response from a FO biopsy implies an 85% probability of a benign process (Follicular adenoma) and a 15% probability of a malignant process (Follicular carcinoma). The fundamental difference between an adenoma (benign process) and carcinoma (malignant process) is only the presence of invasion (germination) of the tumor into the capsule of the node or into the surrounding vessels.
It is not possible to find out from the results of a biopsy of a thyroid nodule before surgery whether the nodule is benign or malignant. All over the world, when a diagnosis of “follicular tumor” is received, surgical treatment is recommended to the patient. After the operation, a specialist histologist determines exactly what exactly the patient has - a benign process (adenoma) or a malignant process (carcinoma).
What diseases can ultrasound help detect?
During ultrasound diagnostics, the doctor can detect a number of abnormalities. They are determined depending on the size, volume, tissue structure and echogenicity. Changes in these parameters may be a sign of diseases such as:
- Hypothyroidism – reduction of an organ
- Nodular goiter - the appearance of one or more foci of dense tissue
- Diffuse toxic goiter - excessive enlargement of the gland
- Inflammation – the appearance of swelling and, in some cases, pus
- Adenoma is a benign tumor formation
- A cyst is a cavity filled with fluid
- Cancer tumor
Adenoma can be distinguished from cancer by the clarity of the tumor boundaries:
- in benign they are clearly defined and clearly visible on the sonogram
- in malignant ones - vague, growing into a healthy area
To establish an accurate diagnosis in such cases, additional methods are used: blood tests, CT, MRI and others.
The thyroid gland and its functions
The thyroid gland is one of the organs of the human endocrine system, which is responsible for metabolism in the body and creates hormones important for life.
The thyroid gland has a small size and, accordingly, a total volume, which is measured in cm3. The organ is located in the neck and is shaped like a butterfly.
The thyroid gland produces hormones based on iodine, which a person receives from food; iodine deficiency leads to disruption of the organ and the development of various diseases. Also, the gland has a huge influence on the development of the fetus in the womb and its subsequent maturation.
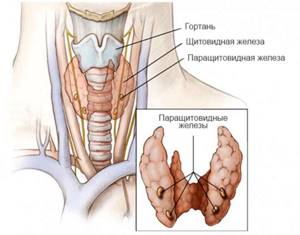
There are two main thyroid hormones that contain different amounts of iodine atoms: T3 and T4. There is another important hormone called TSH, which is produced in the pituitary gland and stimulates the production of T3 and T4 to maintain normal thyroid function.
Since the endocrine organ itself is very small and soft, it is usually difficult to detect it when palpating the neck, but if any changes occur: the formation of a goiter, an increase in the volume of the thyroid gland or one of the lobes, a specialist can detect this even by palpation in children, women and men.
The most common thyroid diseases are hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism and goiter.
In childhood, thyroid diseases are caused by a lack of iodine in the body. Therefore, it is so important to saturate your diet with foods containing this microelement.
With hypothyroidism, the gland produces insufficient amounts of T3 and T4, which is accompanied by many unpleasant symptoms:
- fatigue;
- infertility;
- allergies;
- sleep disturbance;
- lack of appetite;
- bad mood, apathy;
- swelling of the organ itself is observed.
The listed symptoms are typical for most diseases associated with thyroid dysfunction.
Hyperthyroidism is a pathology in which too much thyroid hormone is produced, which is also accompanied by serious symptoms.

Are there any ways to protect yourself from these formations?
The most important thing is a healthy lifestyle :
proper and nutritious nutrition, sufficient physical activity. You need to eliminate trigger factors - bad habits. Do not consult with “all-knowing” neighbors and friends, do not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication - but consult a doctor in a timely manner if you have complaints. It is also important not to take iodine preparations and other vitamins and microelements without a doctor’s prescription.
You can make an appointment with Tatyana Pugavko or another endocrinologist by calling the center: +375 29 311-88-44 ;
+375 33 311-01-44 ; +375 17 299-99-92 .
Or through the
online registration
on the website.
Frequently asked questions about the normal volume of the thyroid gland on my forum
Mom: Hello. Please tell me, is it necessary to carry out any treatment for elevated TSH (7.8 µIU/l)? T3 and T4, antibodies to TPO are normal. Ultrasound shows a cyst in the left lobe measuring 3.8 mm. Daughter is 21 years old, weight 53 kg. We were prescribed hormone therapy, but I doubt it.
Romanov G.N.: This is a picture of subclinical hypothyroidism. We treat when there are any problems or complaints.
Irina: Hello, doctor! Is there a lower limit for normal thyroid volume in women? What is the norm for a 25-year-old nulliparous girl? The ultrasound doctor, after conducting a study, suggested that the small volume of the thyroid gland is associated with low levels of the hormone; all the main indicators: the thickness of the isthmus, structure and echogenicity are normal.
Romanov G.N.: She’s gone! The main thing is that hormones are normal. And the size of the thyroid gland depends purely on human physiology. In women, the normal volume is up to 18 cm3. Exactly “up to”, which means 1 cm3 is also the norm. The main thing is a hormone analysis. A small gland can work perfectly, but a normal-sized gland may not work at all.
Marina: Hello, I have been doing an ultrasound of the thyroid gland for three years in a row and its volume is decreasing, it was 13, and now it is 9.2 cm3. Is it dangerous? Last year, when she was 11.2, her hormones were normal.
Romanov G.N.: The main thing is not the volume, but the TSH indicator.
Irina: Hello. Do I understand correctly that thyroid hypoplasia has nothing to do with subclinical hypothyroidism?
Romanov G.N.: Any amount of hypothyroidism with normal thyroid volume. I declare as a practicing specialist who constantly encounters this disease. (Hypoplasia is a condition in which disturbances in the structure of an organ and reduced size are observed).
Evgenia: Good afternoon. My daughter is 14 years old and had an ultrasound. Help me decipher: right lobe 14x13x42 mm, volume 3.7 cm3; left lobe 12x13x44 mm, volume 3.3 cm3, isthmus 2.5 mm, total volume 7 cm3. In conclusion, diffuse changes in the thyroid gland.
Romanov G.N.: The conclusion is about nothing. The volume is normal. I'll have to get my hormones tested.