Author Marina Lebedeva
09/24/2003 13:08 (Updated: 07/02/2021 23:05)
Health
Hemoglobin level is one of the most important indicators of a blood test. It may vary depending on age, lifestyle and health status. What is the normal hemoglobin level in men, what can cause deviations from the norm and how dangerous are they?
Causes of increased hemoglobin levels
Hemoglobin levels can be influenced by a variety of functional and pathological factors. Their list includes:
- a long period of stay of people in high mountain areas, among the characteristic features of which are low atmospheric pressure, insufficient amount of oxygen from rarefied air for the normal functioning of the respiratory system
- passion for mountaineering
- living in industrial urban areas characterized by increased smoke and gas contamination of the surrounding environment with harmful substances
- high physical activity that causes tension in the male body due to performance of work duties, amateur or professional sports
- dehydration caused by irreplaceable loss of fluid due to work in hot climates, lack of opportunity to organize proper drinking regime
- disruption of the absorption of B vitamins
- addiction to alcohol and smoking, which impairs the supply of oxygen to tissues
- diagnosing oncology, endocrine diseases, intestinal obstruction, pathologies of the cardiac and vascular system
- manifestation of side effects after the use of medications, anabolic agents
Such reasons are prerequisites for determining hemoglobin levels. Timely adoption of measures to reduce it provides an opportunity to avoid the development of serious complications such as thrombosis of blood vessels, myocardial infarction, stroke and other diseases that pose a threat to the lives of patients.
Reasons for increased hemoglobin in men
Functional and pathological factors can influence hemoglobin levels. Normal physiological, adaptive and compensatory mechanisms operate under certain conditions of climate, altitude, latitude, etc.
These include:

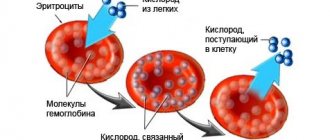
Long-term presence and residence of a person in high mountain areas. Low atmospheric pressure causes a response from the body, which consists of deepening and increasing breathing in order to compensate for the lack of oxygen supply from the rarefied air. This is a short term reaction. Then a longer adaptive mechanism develops, which increases the number of red blood cells in the blood and, accordingly, hemoglobin. The duration of its formation is from a week to 2 months. After a transition period, breathing evens out and slows down again. The process plays a role in the development of mountain sickness in climbers. This unpleasant pathology develops in the case of a sharp rise to a high altitude without adaptation;

excessive physical stress. From a one-time load, the adaptive mechanisms of increased gas exchange will not have time to work, but if the overload lasts a long time, then the blood will react by increasing the number of red blood cells and the hemoglobin content. This reaction of the body aims to relieve the respiratory system and cardiovascular system. Therefore, often in men associated with constant heavy physical labor, hemoglobin numbers are higher than normal. A similar phenomenon occurs in athletes experiencing monotonous daily overload. For example, long-distance runners, cyclists, skiers, etc.

functional types of dehydration are intermediate between physiological and pathological causes of increased hemoglobin;- living in conditions with insufficient water. For example, working in a hot climate and without proper drinking conditions. In this case, an irreplaceable loss of fluid occurs, leading to “thickening” of the blood. These types of work are more typical for men, so functional dehydration is more common among them.
Please note: the longer a person works and lives in such conditions, the more hyperhemoglobinemia develops and the risk of complications increases.
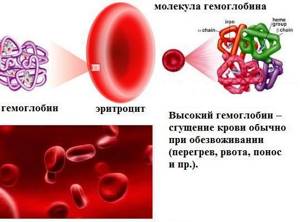
An increase in hemoglobin in men can develop as a result of diseases:
- occurring with debilitating and prolonged diarrhea, especially accompanied by concomitant vomiting (infectious diseases);
- with excessive urination due to diabetes, chronic stress, kidney disease;
- chronic heart failure, causing swelling of the body and a compensatory increase in fluid secretion by the kidneys;
- malignant polycythemia vera (Vaquez disease).
Long-term use of diuretics and a number of other drugs, and deficiency of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) can lead to dehydration and thickening of the blood.
Symptoms of elevated hemoglobin in men
An increased level of hemoglobin in the male body can cause nonspecific symptoms, which can manifest themselves with the development of many other pathological conditions. These include:
- redness, peeling of areas of the skin and their alternation with pale areas on the patient’s body
- loss of appetite
- the appearance of lethargy, weakness, increased fatigue
- decreased performance of hearing and vision organs
- problems getting proper rest at night
- pain in muscles, joints, bones
- the appearance of headaches, dizziness, feeling of fullness in the abdominal cavity
- high incidence of constipation and diarrhea
- constant drowsiness
- disruptions in the functioning of the genitourinary system
An increase in blood viscosity complicates its circulation within the male body, intravenous injections and infusion of medications. There is a danger of blood clots, and the risk of heart attacks and strokes increases.
Diagnosis of elevated hemoglobin

Detection of an increased number of red blood cells and hemoglobin is determined during a routine clinical blood test. If the doctor suspects the cause of this process, he may order additional tests. After establishing a diagnosis or functional state, a plan of treatment measures, drug therapy is drawn up, and a diet is prescribed.
Please note: before you start sounding the alarm, compare the test results with the reference values - they are different for men and women!
| Age | Men (g/l) | Women (g/l) |
| Hemoglobin norms in adults | ||
| Over 65 years old | 126 – 174 | 117 – 161 |
| Over 45 years old | 131 – 172 | 117 – 160 |
| Over 18 years old | 132 – 173 | 117 – 155 |
| Hemoglobin norms in adolescents | ||
| 15 – 18 years old | 115 – 165 | 115 – 155 |
| 12 – 14 years old | 120 – 160 | 115 – 150 |
Diagnosis and treatment of high hemoglobin levels in men
High hemoglobin levels are determined by performing a routine clinical blood test. After collecting anamnesis and identifying the causes of this pathological phenomenon, a treatment plan is drawn up aimed at reducing hemoglobin to 140 g/dm³ - 170 g/dm³. The main activities include:
- carrying out drug therapy based on the use of anticoagulants, blood thinning drugs that have vasodilatory properties, and also prevent red blood cell aggregation
- the use of traditional medicine recipes based on cranberries, honey, lemon, meadowsweet root, herbal infusions of mint, birch buds, willow bark, sweet clover
- hirudotherapy or bloodletting procedures
- organization of the correct water regime and dietary nutritious diet, excluding iron-containing foods and based on the use of dill, cinnamon, legumes, vegetables, fruits, seafood, sea fish and algae, garlic, horseradish, radish
- giving up bad habits, playing sports, walking
A healthy lifestyle, calmness and an optimistic mood are the key to a successful solution to the problem of increased hemoglobin levels in the blood of men!
Causes
Low hemoglobin levels can be associated both with the cancer itself and with its treatment.
- Chemotherapy with cytotoxic drugs destroys rapidly dividing cells in the body, not only cancer cells, but also bone marrow cells. They are responsible for the process of erythropoiesis - the formation of red blood cells (erythrocytes). The production of red blood cells decreases, their volume in the blood (hematocrit) decreases, and anemia develops.
Chemotherapy with platinum drugs inhibits the functioning of the kidneys and their production of the hormone erythropoietin. This hormone stimulates the process of erythropoiesis - the formation of red blood cells. Its level decreases, erythropoiesis slows down, hematocrit decreases, and anemia develops.Radiation therapy can negatively affect the bone marrow, which also leads to decreased red blood cell production.
- Many types of cancer metastasize to the bones, affecting the red bone marrow. Cancer cells replace normal, active bone marrow cells, resulting in decreased red blood cell production.
- Anemia is associated with internal bleeding. For example, for intestinal and stomach cancer. Constant blood loss causes a decrease in the volume of red blood cells and the development of oxygen starvation.
- Functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and/or poor appetite lead to a deficiency of vitamin B12 and iron, which are necessary for normal hematopoiesis and maintaining hemoglobin levels in the blood.
- A malignant tumor has a poisonous effect on the body. Cancer intoxication leads to damage and destruction of red blood cells - pathological hemolysis. In addition, intoxication negatively affects the functioning of the bone marrow, which leads to impaired erythropoiesis.
- A person’s own immune system, reacting to a malignant tumor, can provoke a decrease in hemoglobin. Its active cells - cytokines inhibit the production of erythropoietin by the kidneys. In addition, cytokines attack red blood cells - erythrocytes, reducing their life expectancy by one and a half to two times. This leads to a decrease in hematocrit and the development of anemia.
Often the cause of low hemoglobin and anemia in cancer is a combination of several of these factors.
What do deviations from the norm indicate?
In addition to the physiological and completely natural reasons for the increase in hemoglobin in the blood, of course, there are also pathological ones caused by serious diseases. Therefore, for each deviation from the norm, consultation with a specialist, analysis of existing symptoms and, possibly, an extensive examination of the body are required.
Pathological causes of increased hemoglobin levels include:
- Dehydration as a result of serious poisoning or intoxication. Prolonged vomiting and diarrhea can cause such a dangerous condition as increased blood viscosity. In this case, appropriate therapy may be required to restore the water-salt balance;
- Diabetes mellitus: this phenomenon is accompanied by frequent urination, which partly causes an increase in hemoglobin;
- Erythrocytosis is a condition that results in increased production of red blood cells and increased blood viscosity;
- Presence of cancerous tumors;
- Hypovitaminosis (vitamins B9, B12);
- Problems with the heart and blood vessels;
- Lung diseases;
- Diseases of the hematopoietic system.
In general, the whole danger of increasing hemoglobin levels is an increase in blood viscosity, which can lead to events such as stroke, myocardial infarction and blood clots. All of these are serious pathologies of the cardiovascular system, which are not only dangerous, they can be fatal.
As mentioned above, the cause of low hemoglobin can be an improper diet with low iron content, but there are also more dangerous causes of low hemoglobin that require medical intervention. One of these pathological causes is helminthic infestations. Parasites absorb microelements and nutrients important for the body, as a result of which a person begins to experience their deficiency.
Also, low hemoglobin may indicate the presence of hidden bleeding and large blood loss due to this. This phenomenon requires urgent medical intervention, as it seriously threatens the patient’s life.
Due to the reduced level of hemoglobin, increased blood circulation appears, which is still fraught with problems with the cardiovascular system and can lead to the development of cardiomyopathy and heart failure.
Preventive measures to prevent increased hemoglobin in men
Regular clinical blood tests will help to recognize hyperhemoglobinemia in time and make the right decision to prevent its development.
Examinations by a doctor will allow you to suspect a possible disease leading to an increase in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin and begin its treatment.
A proper lifestyle and diet will help prevent the development of dangerous blood thickening processes.
Stepanenko Vladimir, surgeon
109, total, today
( 53 votes, average: 4.62 out of 5)
Iron supplements for anemia: a review of remedies
Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia): symptoms, causes, treatment
Related Posts
Treatment methods aimed at reducing hemoglobin in men

If the load is excessive, it is recommended to reduce its intensity. This should be done if the patient has the complaints outlined above.
For diseases of the cardiovascular system, it is necessary to identify the pathology and carry out treatment, which will lead to the normalization of hemoglobin analysis data.
If hemoglobin increases due to diabetes mellitus, it is necessary to reconsider the nutrition plan and introduce correction of insulin doses.
If the treatment does not reduce the level of hemoglobin in the blood, then you should consider prophylactic administration of anticoagulants and antiplatelet medications. These include acetylsalicylic acid, the dose of which must be selected by the doctor.
Insufficient absorption of vitamin B12 should be compensated by prescribing the medication in injection form.
Please note: if the main cause of increased hemoglobin in men is caused by an existing disease, then its treatment, if the tactics are chosen correctly, will itself normalize the deviation of indicators from normal numbers.