When is a test for worm eggs prescribed?
The human gastrointestinal tract can be inhabited by various parasites - roundworms (nematodes) or flatworms.
The latter can also be tapeworms (cestodes) or flukes (trematodes). The most typical representatives of round ones: pinworms, roundworms, hookworms. Tapeworms: bull tapeworm, wide tapeworm, small tapeworm. Flukes - liver fluke. Parasitic worms (helminths) do not gnaw through wounds in the body, but are found primarily in the gastrointestinal tract. The exception is echinococcus, which can live in tissues. So what is the danger of parasites? Settling in the body of the “victim,” they absorb nutrients supplied by food and release their waste products (toxins) into the human gastrointestinal tract. As a result, significant harm is caused to human health - this is chronic intoxication, a decrease in the supply of nutrients and minerals.
Helminthiasis is suspected if the following symptoms are present:
- sudden weight loss for no apparent reason;
- causeless loss of appetite for a long period;
- various manifestations of gastrointestinal disorders: bloating, flatulence, constipation, or vice versa – diarrhea;
- skin rashes similar to allergic reactions;
- significant decrease in immunity for a long period;
- fatigue, dizziness, general poor health;
- itching of the skin around the anus;
- bad dream.
If several of the above symptoms are present, a stool test for worm eggs is prescribed. It is also performed during medical examinations and issuing health records and medical certificates.
Examination of stool for protozoa, helminth eggs
Examination of stool for protozoa and helminth eggs is a routine diagnostic test that has been used in laboratory diagnostics for many years. Helminths are widespread in all climatic zones, and children, pet owners and people who work with animals or work on the land are most susceptible to infection. Detection of helminth eggs is carried out by microscopy of a patient's stool specimen. Since helminths have certain reproduction cycles, for objective reasons it is not always possible to detect parasite eggs in feces in the presence of infestation. Often, several stool tests for helminths may be required to confirm the diagnosis of a parasitic disease.
In what cases is a stool test for helminth eggs usually prescribed?
Typically, tests for worm eggs are required for all children before attending school, kindergarten, swimming pool, sports sections, etc. This is a mandatory study during medical examination of healthy schoolchildren.
It is advisable to examine stool for protozoa and helminths if there are signs of a possible parasitic disease. Complaints of periodic abdominal pain, unstable stools, allergic manifestations, skin rashes, and fatigue may be symptoms of helminthic infestation. If a clinical (general) blood test shows a decrease in hemoglobin and an increased number of eosinophils, then this is also a reason to get tested for helminth eggs.
Important: when infected with pinworms - enterobiasis, stool examination for helminth eggs may not be informative, since these parasites lay eggs on the skin of the perianal area and the best diagnostic method is scraping for enterobiasis.
What exactly is determined during the analysis process?
During the analysis, the doctor examines the patient's stool samples under a microscope, visually determining the presence of eggs and body parts of parasites.
What do the test results mean?
A positive test result—“detected”—is issued when helminth eggs, protozoan cysts, or the parasites themselves are detected.
The result “not detected” does not exclude the presence of a parasitic disease, since the release of helminth eggs depends on the phase of their reproduction. If symptoms are present and the test result is negative, a repeat test should be done. If the number of parasite eggs in the stool is small, a new generation test, the stool test for protozoa and helminth eggs by enrichment method (PARASEP), may be more informative.
Typical test turnaround time
Typically, test results for helminths and protozoa can be obtained within 1-2 days.
Do I need special preparation for the analysis?
To identify protozoa, stool must be fresh and collected immediately before submitting the material to the laboratory. Helminth eggs are stable and remain in feces for a long time.
How to prepare for the test
Submitting biomaterial for coproscopy is quite simple, but it is important to follow a number of rules:
- exclude potent drugs, except for vital ones, a few days before the test;
- remove any foods that may cause gastrointestinal upset or have a laxative effect;
- do not eat foods containing large amounts of coloring substances, both natural (coloring berries, vegetables and fruits) and chemical (found in brightly colored sweets or drinks);
- refrain from fatty, spicy, sour foods.
Description
The study is aimed at identifying parasites living in the human gastrointestinal tract. This study allows you to identify helminth eggs, protozoan cysts and oocysts. A special feature of the study is the use of the sedimentation ether-formalin method in a special Parasep tube, which significantly increases the detection of helminth and protozoan eggs in stool, unlike other stool research methods. But it must be borne in mind that a single negative stool test does not rule out parasitic infection. For final verification of the diagnosis, three stool examinations are performed, at intervals of up to several days. Important! This study is not intended to identify adult helminths! The Parasep system allows you to detect the following helminths and protozoa: HELMINTHS: • Trematodes: opisthorchis (cat fluke), dicrocoelia (lanceolate fluke), fasciola (liver fluke), Nanophyet Shikhobalova; • Cestodes: pork (armed) tapeworm (tapeworm), bovine (unarmed) tapeworm (tapeworm), dwarf tapeworm, diphylobothria (wide tapeworm); • Nematodes: whipworm, pinworm, roundworm, trichostrogylids, hookworm (hookworm), necator (New World hookworm). PROTOZOOS: • Flagellate class: Giardia intestinalis (cyst form); • Class sercodae: intestinal amoeba (cyst form). The effect of parasites on the body is very diverse. They can cause toxic and toxic-allergic manifestations, have a traumatic effect on the intestinal wall and cause bleeding of varying degrees of intensity. Parasites can also cause obstruction (blockage) of the intestinal lumen and hepatic ducts - this leads to the development of intestinal obstruction and mechanical hepatitis. In addition, all helminths use nutrients from the host’s intestines, which leads to metabolic disorders and reduced levels of vitamins in the body. At the initial stages of infection, the clinical picture is nonspecific: general malaise, possible fever, eosinophilia, leukocytosis. Later, clinical manifestations associated with the localization and quantity of the pathogen appear. The routes of infection depend on the type of pathogen. One of the most common is the fecal-oral mechanism of infection, when a sick person, carrier, or animal releases parasite eggs into the environment (soil, water) with feces. Of primary importance are vegetables and fruits, salad greens on which there are particles of contaminated soil. Infection often occurs when ingesting water while swimming or drinking unboiled water from springs and reservoirs. Some parasites (opisthorchids) infect freshwater fish. Infection occurs after eating thermally unprocessed fish (sushi, tartare). It is also possible to become infected with tapeworm by consuming unprocessed meat from cattle or pork.
How to get tested for an adult and a child
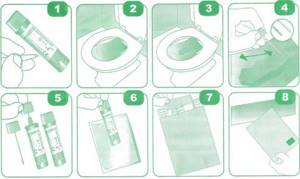
In the morning after waking up, defecate into a clean vessel, then take small samples with a spatula. It is important to take material from several areas of the stool. It is recommended to use a special container for collecting stool analysis, which is sold in pharmacies - it is equipped with a special spatula.
You should not perform hygiene procedures before defecation to collect a sample - this can give a false negative result, since the females of some worms lay eggs on the skin around the anus.
In some cases (to diagnose enterobiasis), in addition to stool analysis, perianal scraping is also prescribed. For children over 1 year of age, feces are collected as in adults.
Danger of parasites
If the number and size of parasites are small, their presence may go unnoticed for a long time. However, the rapid reproduction or growth of parasites and their movement throughout the body during their life cycle often causes serious health problems.
For example, roundworms that accumulate in the intestines can cause constipation and obstruction. Bovine tapeworm grows up to several meters in length and seriously damages the digestive tract, depriving the owner of nutrients and vitamins. Echinococcus forms cysts in internal organs, including the brain, liver, and lungs.
Rupture of such a cyst may occur unexpectedly, after a minor injury or during an examination. The contents of the cyst can cause anaphylactic shock or collapse. Trichinella larvae feed and live in the muscles, gradually destroying them. According to WHO, parasitic diseases account for about 14 million deaths worldwide per year.
Who is the analysis for?
Doctors recommend testing feces for the presence of helminth eggs in them, if there are a number of characteristic symptoms inherent in helminthiasis.
In adults, helminthiasis can be characterized by the presence of the following symptoms:
- itching in the anal area;
- pain in the intestines;
- problems with stool, bloating;
- fatigue and excessive irritability;
- sleep problems;
- vulvovaginitis;
- signs of an allergic reaction;
- increased levels of eosinophils in the blood;
- infectious lesions of the genitourinary system - a high probability of developing such a problem is present in older people, since their immune system functions poorly.
The child also has additional symptoms:
- an unending urge to defecate;
- crying at night, restless sleep, causeless whims;
- irritation in the anus;
- cough of unknown etiology.
If several of these signs are present, the doctor must refer the patient for analysis for worm eggs.
It is worth noting that the presence of helminths is just as dangerous for men as for women, but the frequency of their occurrence is several times reduced.
It is mandatory to collect stool for analysis for helminth eggs in the following cases:
- before visiting the pool;
- during inpatient treatment;
- to obtain a medical record;
- before registering a child for kindergarten.
Stool analysis for carbohydrates
Stool analysis for carbohydrates is used to diagnose congenital or acquired deficiency of the lactase enzyme in children of the first year of life.
Lactase is an enzyme that is produced by intestinal epithelial cells (enterocytes) and participates in the biochemical reaction of the breakdown of lactose, otherwise known as milk sugar. When consuming milk and dairy products, if there is not enough lactase, digestion is disrupted and unpleasant symptoms appear: diarrhea, flatulence, cramps, etc.
Causes of lactase deficiency:
- decrease in enzyme production by intact enterocytes due to genetic defects or physiological immaturity of enzyme systems in children of the first year of life - primary, or congenital, lactase deficiency;
- a decrease in enzyme production due to damage to enterocytes during an inflammatory or other (food allergy, tumor) process - secondary, or acquired, lactase deficiency.
Indications for taking a stool test for carbohydrates:
- the presence in children of symptoms such as flatulence, frequent regurgitation, diarrhea, cramps, abdominal pain;
- control of correct diet selection.
Types of examinations
Today, there are several methods for examining stool to detect helminth eggs:
- Microscopy of a native smear. A special glass is lubricated with glycerin, and then a little feces moistened with distilled water is placed on it. As a result, the feces are enriched with glycerol. The biomaterial is covered with a coverslip and examined using a microscope.
- Fulleborn test using a microscope - examines the film formed on top of a solution of salt water and feces. If the biomaterial contains helminth eggs, then after 1-2 hours they will emerge.
- Thalmann test using a microscope - a mixture of feces, hydrochloric acid and ether is examined.
How to properly collect feces
Doctors recommend collecting stool in the morning, since this biomaterial is considered the most informative. The collection of feces is carried out in a container purchased at a pharmacy using the tool that comes with it. It is recommended to take different stool samples (from the edge, center, inside).
The container is closed, signed and sent to the laboratory. The ideal option would be if the biomaterial is examined within an hour after the collection of feces; their maximum shelf life is 7-8 hours.
The sample should be stored at a temperature of 4-8 degrees. If stool is kept at room temperature for more than 60 minutes, it becomes unsuitable for analysis. Material that has been left in unsuitable conditions for a long time should be discarded.