CT scan of the intestine is most often used as a diagnostic tool in the gastroenterological area. This method is non-invasive and is based on the use of x-rays. Allows you to obtain very clear and detailed images of internal organs. Often, computed tomography of the intestines is also called “virtual colonoscopy,” since the effectiveness of the procedure allows you to examine the intestines no less accurately than invasive methods.
Computed tomography of the intestine
CT bowel
shows what is happening to the internal organ and allows not only to examine one section of it, but to study the condition of the large intestine along its entire length: from the cecum to the rectum. The three-dimensional image that is obtained makes it possible to carefully examine and determine the thickness, as well as the relief of the mucous membrane, and evaluate the entire structure of the walls. This method allows you to identify and study various processes associated with inflammation, tumors and erosive and ulcerative lesions.
The advantage of CT examination of the intestine is that the procedure is painless, unlike colonoscopy, it does not lead to complications, does not injure the mucous membrane and cannot lead to internal bleeding. Therefore, this method is considered as safe as possible for the patient, even in serious condition.
When is a bowel CT scan prescribed?
There are three main reasons for ordering a CT scan of the colon. This is a study of inflammation in diseases such as Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, the search for various neoplasms, and also to detect the source of intestinal bleeding. The method helps to detect polyps and metastases. It is also recommended that people over 40 years of age be examined every 5-8 years as a preventative measure.
What is this procedure?
This medical procedure is an examination of the large intestine (from the rectum to the cecum) without inserting an endoscope into the anus. It is performed using a modern multislice computed tomograph (MSCT). The doctor manages to obtain even the smallest anatomical structures of the intestinal wall and cavity on the screen, without causing discomfort or pain to the patient. This procedure has a similar principle of operation to endoscopic examination, so many people ask the question: “Virtual colonoscopy or regular colonoscopy - which is better?” The first diagnostic method is more accurate and informative, so most doctors prefer it. However, if there are contraindications to x-ray irradiation (pregnancy, childhood, some tumors), it is not recommended, which is why an examination directly with an endoscope is prescribed.
Virtual colonoscopy is indicated in the presence of the following pathological symptoms:
- Blood in stool.
- Stool disorder (constipation or diarrhea of unknown etiology).
- Pain in the abdomen for no apparent reason.
- Increased gas formation.
- Polyposis or neoplasms in the colon.
In addition, this study is recommended to be regularly carried out for all persons over 40 years of age and with a family history (oncological diseases in close blood relatives) for effective prevention of oncological diseases.
What does a CT scan of the intestines show?
What does a CT scan of the intestine show? The only difference between this method and colonoscopy is that it is less accurate, since with a CT scan it is impossible to see the color of the mucous membrane or take a biopsy from pathological lesions. However, with the help of three-dimensional scanning, you can view the organ from all sides, which is the great advantage of CT. The technique allows you to study the relief of the intestinal mucosa, the thickness and structure of its walls. If diffuse thickening is detected, it is easy to diagnose lymphoma, leiomyoma and leiomyosarcoma. It is also possible to examine the small intestine to determine its patency.
Contraindications
Pregnancy is an absolute contraindication to any CT scan. It is not advisable to do a CT scan for young children due to the presence of radiation exposure to the body. Patients with renal failure should have a blood test for creatinine before using contrast. If a person is sensitive to iodine, he needs to have allergy tests done to rule out intolerance to the components of the substance. Sometimes it is difficult to perform high-quality MSCT for obese patients. Most clinics in St. Petersburg provide diagnostics to patients weighing only up to 150 kg due to the throughput of the tomograph. When a CT scan of the intestine is not possible due to contraindications or weight restrictions, alternative scanning methods include MRI of the intestine and ultrasound using an expert-class device.
CT scan of the intestines: preparation for the procedure
Preparation for a CT scan of the intestines is usually the same for everyone, but you should always consult with your doctor in advance and follow all his instructions to achieve the best results during the examination.
Purgation
Since the study is carried out on an empty stomach, doctors usually prescribe the procedure in the morning. Computed tomography of the intestine requires preparation, namely, cleansing measures should be carried out. It is necessary to get rid of accumulated gases in the intestines; for this you should take Espumisan, as well as an enterosorbent such as activated carbon. The doctor should also prescribe an osmotic laxative, which is taken the day before the examination. It is advised to completely cleanse the intestines with an enema, and drink half a liter of still water an hour before the CT scan.
Diet
Of course, it is necessary to completely cleanse the intestines of feces; to do this, you should switch to a special diet for 2-3 days, which excludes from the diet foods that contribute to the formation of gas. These are fermented milk products, legumes, raw vegetables and fruits, sweets, and fermented foods. You should also not eat foods that promote constipation to avoid constipation, but it is also not recommended to eat foods with a laxative effect to prevent flatulence. The day before a CT scan of the intestine, it is best to consume liquid food, water, and broth.
CT diagnostic services at CELT
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| CT scan of the abdomen and retroperitoneum | 11 500 |
| CT scan of the hepato-pancreato-duodenal region and spleen | 11 000 |
| CT scan of the abdominal aorta and its branches and screening examination of the abdominal and pelvic organs | 14 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
How is the procedure done?
A CT scan of the intestine may be slightly uncomfortable because it requires filling the rectum with air or carbon dioxide. To do this, the patient should lie on the examination table in the desired position as recommended by a specialist. Afterwards, the limbs are secured with special belts to prevent unnecessary movements for clear diagnosis. A thin tube is inserted into the patient's anus, through which gas or air is pumped into the rectum. This is done in order to straighten the intestinal walls, since in its normal state it has many folds. The rectum allows for better diagnosis of the organ along its entire length, even in hard-to-reach places.
The procedure itself takes 15-20 minutes. During the images, the patient will need to hold their breath for 3-4 seconds.
Contrast enhancement
In some cases, contrast enhancement is required to diagnose the intestine. To do this, the patient must take the necessary medication several hours before the examination. Sometimes contrast is administered immediately before the procedure using an enema. This allows you to better visualize the contours of the intestines in the images.
Important!
X-ray diagnostic or therapeutic procedures involving irradiation of patients are carried out only as prescribed by the attending physician and with the consent of the patient, who is previously explained the benefits of the proposed procedure and the associated health risks. The final decision on whether to perform the appropriate procedure is made by the doctor. When performing medical x-ray radiological procedures, at the request of the patient, he is provided with information about the expected or received radiation dose and its possible consequences. (clauses 4.17 and 4.19 Basic sanitary rules for ensuring radiation safety (OSPORB - 99/2010))
.
Alternative Colonoscopy Methods
If a computer study is contraindicated for the patient or cannot be performed for other objective reasons, alternative procedures are prescribed:
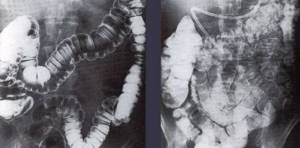
- Endoscopic colonoscopy. It is carried out invasively with the introduction of a thin hose, at the tip of which there is a miniature camera.
- Sigmoidoscopy. Not the entire length of the colon is examined, but only its lower part if abnormalities in this area are suspected.
- Irrigoscopy. It also involves the use of traditional X-ray equipment. Before the session, a coloring solution is injected into the intestinal cavity, which serves as a contrast in the resulting scans.
Another most informative research option is magnetic resonance imaging. Due to its high cost (compared to classical diagnostic techniques), MRI is prescribed secondarily if all other methods do not give correct results.
Virtual colonoscopy: features of the procedure
Ionizing radiation is used not only in traditional radiography. On its basis, computer diagnostic technology has been developed, called virtual or visual colonoscopy. This method allows for a targeted examination of all structures of the large intestine, which makes it possible to detect even complex pathological disorders in its functioning, including oncological processes. Screening requires special equipment and trained diagnosticians who can interpret the scans obtained.
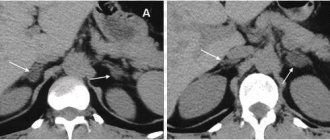
Decoding the received data
During the examination, the doctor receives a series of images, which are black and white images of sections of organs in the area being examined. Deciphering means determining which areas of the images correspond to which organs and tissues, what changes there are in the structure of organs and tissues, and what types of pathology these changes are typical for. A radiologist or radiation diagnostics doctor is responsible for describing the images. Decryption can take from 30 to 60 minutes. After this, the patient receives photographs on digital media or film, as well as a doctor’s report certified by signature and seal.
You should be prepared for the fact that the doctor will not be able to recognize the formations present in the images. This is why it happens that during a CT scan it is not possible to take a biopsy of a “suspicious” area of tissue. In this regard, after performing a CT scan of the stomach and intestines, the doctor’s conclusion may include a recommendation to continue the examination using fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) or colonoscopy with a mandatory biopsy.
How is a CT colonoscopy performed?
The session is carried out in two stages. In the first, the patient is placed inside the unit in a supine position. Then they ask you to turn over on your stomach. When the best angle for correct scanning is found, a full-fledged study begins. Colonoscopy involves preliminary filling of the intestinal tract with air. This does not cause pain, especially if the patient is in a relaxed state.
After preparatory manipulations, layer-by-layer shooting is carried out. The ring of the device moves along the table on which the subject lies. At some points you need to hold your breath at the doctor’s command. Once the screening is completed, the person is helped to their feet and escorted to the waiting room.
What can and cannot be eaten before an abdominal CT scan with contrast?
| Can | Not recommended |
|
|

Indications for examination
The scope of the examination depends on the presence of which pathology needs to be confirmed or excluded in the patient.
CT scanning of the stomach and intestines is rarely performed at the same time due to the fact that the large scope of the examination involves the patient receiving a large dose of radiation. To prescribe a diagnosis of the condition of the entire gastrointestinal tract, very serious indications are needed.
CT scan of the stomach is used for:
- detection of a cancerous tumor of the stomach walls;
- determining the location, size of the tumor, its spread to neighboring organs;
- identifying mucosal ulcers;
- searching for areas of bleeding.
Get a referral from your doctor for a CT scan of the small intestine:
- neoplasms (lymphomas, cancer);
- inflammation (colitis);
- mucosal ulcers;
- bleeding;
- damage to the walls of the small intestine due to celiac disease;
- foci of necrosis (death) due to thrombosis of the vessels of the intestinal mesentery.
CT scan of the large intestine is performed for the following indications:
- suspicion of the presence of polyps and other benign neoplasms;
- colon cancer;
- blood in the stool, pain in the rectum;
- preventive examination of the patient if intestinal cancer is detected in blood relatives;
- the presence of “minor signs” of cancer: alternating diarrhea with constipation, causeless weight loss, malaise, fatigue, etc.