Hormonal levels play a vital role in the life of any person, so its disorder leads to visible problems with health and well-being. Violation of this balance entails a large number of problems and leads to the development of diseases of varying severity. Despite the many hormones synthesized and circulating in the body, steroid hormones are considered one of the main ones. They are responsible for a number of important functions, including reproduction. One of the representatives of this group is progesterone; its level varies depending on gender and other related factors. Our modern medical center provides the opportunity to get tested for this hormone, receive accurate diagnostic data in the shortest possible time and receive medical advice from qualified specialists.
Progesterone, the norm of which will be indicated below, is produced in the female body by the ovaries, and in the male body by the testes (seminal vesicles). In addition, it is synthesized in small quantities by the adrenal glands. Many people mistakenly believe that progesterone is important only in women, but not in men. In fact, it plays a vital role in both organisms, so its increase or decrease leads to adverse effects and complications. First of all, it is responsible for reproductive ability, the ability to become pregnant, bear and give birth to a child. It has a significant effect on preparing the uterus for gestation, providing a sufficient level of thickening of the mucous membrane for the attachment of a fertilized egg to it. In addition, it contributes to:
- Increase in size of the uterus for the full development of the fetus;
- Partial suppression of the pregnant woman’s immunity, which is necessary to prevent rejection of the child;
- Development of some tissue structures of the embryo;
- Preparation of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus for childbirth;
- Normalization of the menstrual cycle;
- Stimulation of lactation (progesterone in women who prefer breastfeeding should be monitored in advance).
At the same time, progesterone plays an important role in the lives of men. First of all, it acts as a precursor to other hormones (it is from it that testosterone is produced). In addition, it performs the following functions:
- Strengthening bones;
- Regulation of estrogen;
- Prevention of prostate cancer;
- Control of blood sugar concentration;
- Sexual behavior (libido, attraction to a partner);
- Normalization of cardiovascular activity;
- Favorable effect on the functioning of the nervous system.
It is extremely important to monitor progesterone levels and promptly seek medical help if even minor deviations are detected. In our medical center you can get qualified medical advice, as well as undergo the necessary tests in a modern and accurate laboratory.
Progesterone norm: in women, men and children
Normal progesterone levels in men range from 0.35 to 0.63 nmol/L. A slight deviation from these indicators, as a rule, does not have a significant impact on men's health. Noticeable symptoms occur when changes are more than 100% (for example, when the analysis shows 1.3 nmol/l). It is worth considering that the synthesis of gesterogens can slowly decrease with age, which is a normal age-related restructuring of the body.
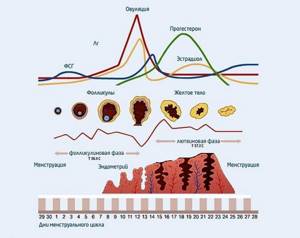
Progesterone in the female body has different normal levels, depending on several factors (menstruation, pregnancy, etc.). There are 3 phases of the menstrual cycle:
Follicular - the beginning of menstruation, characterized by the development of a follicle, from which an egg subsequently appears. It lasts about half of the entire cycle. In the follicular phase, the norm of the hormone progesterone is from 0.32 to 2.25 nmol/l.
Ovulatory - occurs after the rupture of the follicle and the release of the egg. This is the shortest phase, lasting 3 days. During this period, an increase in progesterone levels is observed and it reaches 0.49-9.41 nmol/l.
Luteal - the corpus luteum takes the place of the egg released from the ovary. It lasts from 12 to 14 days and is characterized by the most active hormonal synthesis. In the luteal phase, the normal level of progesterone in women is 6.95-56.63 nmol/l. This jump is associated with the body’s readiness for pregnancy. If fertilization does not take place, the progesterone level decreases again, and the corpus luteum dies after 14 days.
Progesterone is often called the pregnancy hormone, since its normal concentration is a prerequisite for bearing a child. Its deficiency in the early stages can lead to miscarriage and miscarriages, and its increase can lead to various health problems for the expectant mother and fetus. Until the 16th week of pregnancy, the hormone in a woman’s body is produced by the corpus luteum, and after that by the placenta. Progesterone levels begin to gradually increase, reaching the following levels:
- First trimester: 8.9-468.4 nmol/l;
- Second trimester: 71.5-303.1 nmol/l;
- Third trimester: 88.7-771.5 nmol/l;
It is important to note that the hormone progesterone has its own characteristics in children. Initially, this indicator is the same for both boys and girls. It is about 1.1 nmol/l. But upon reaching adolescence, active hormonal changes and the formation of reproductive function begin. As a result, there are differences in progesterone levels:
- For boys - from 0.7 to 3.5 nmol/l.
- For girls - from 0.3 to 41 nmol/l.
Indications for use
1. Component of the diagnosis of ovulatory dysfunction (corpus luteum insufficiency/luteal phase insufficiency), as a cause of infertility, miscarriage, abnormal uterine bleeding.2. Laboratory confirmation of ovulation that occurred in a given cycle.3. Component of diagnosis of developing and non-developing pregnancy, threatening spontaneous abortion.4. Evaluation of the effectiveness of therapy for luteal phase deficiency and progesterone therapy for the threat of spontaneous abortion.5. Pregnancy monitoring component
Low and high progesterone
Knowing what progesterone is responsible for, it is not difficult to guess that it is extremely important to monitor its concentration and promptly seek medical help if any discrepancies are detected. Despite the fact that this hormone is vital for both sexes, an increase in its concentration can be a sign of a variety of diseases. Often the cause of this pathological condition is progestin drugs that a person takes for therapeutic purposes.
Increase in men

High levels of progesterone in the male body often lead to a significant drop in libido. That is why medications with this hormone were previously used only when suppression of sexual desire was required (for example, for prison prisoners sentenced to a long term). But this is not the only problem associated with increasing the normal rate. A significant increase in the norm, persisting for a long time, leads to testicular atrophy - this is a condition in which they decrease in size and cease to perform their functions (produce sperm and testosterone). Elevated progesterone is quite common among professional bodybuilders, since many of them use a variety of chemical supplements, including anabolic steroids, that disrupt natural hormonal levels to achieve better athletic results.
Another equally important complication of increased progesterone is male infertility, caused by impaired production and maturation of sperm. It is extremely rare for such patients to be diagnosed with carbohydrate metabolism disorders. Scientists have proven a close connection between hormonal balance and a man’s mood. Thus, an increase in the level of progesterone prevents the formation of the paternal instinct, and instead of showing attention and care to children, such a man can easily ignore his paternal responsibilities. High levels of progesterone in the male body can be diagnosed when:
- Hormone-producing neoplasms in the organs responsible for secretion (adrenal glands and ovaries). Uncontrolled cellular growth in these organs affects hormonal levels and health. Both benign and malignant tumors can lead to this problem;
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. This is tissue growth that occurs against the background of hormonal imbalance. Such patients are distinguished by their characteristic appearance and the accumulation of subcutaneous fatty tissue, characteristic of the female type;
- Hypofunction of the thyroid gland;
- Pituitary tumor;
- Taking medications from the group of antipsychotics, antifungals, and phenothiazine medications;
- Surgery (in this case, high progesterone levels are extremely rare).
High progesterone in women
These pathological conditions indicate the presence of a disease that affects the synthesis of this hormone. This may be ovarian damage or malignant tumors, as well as other diseases: adrenal dysfunction, renal failure, corpus luteum cyst and much more. Among other possible causes, the use of certain medications, family history, chronic stress and the presence of bad habits are of diagnostic importance.
High progesterone in girls and women has clear symptoms that negatively affect the patient’s daily life. Such patients often suffer from headaches, which often develop into constant migraines. They experience decreased performance, chronic fatigue and a drop in the overall tone of the body. Quite often, visual impairment, skin rashes, menstrual irregularities and surges in blood pressure are diagnosed. Due to the fact that progesterone levels affect mood, its excessive production causes depression and mood swings. In addition, a particular sign of this condition is increased hair growth throughout the body.
Increased progesterone in pregnant women
Violation of the progesterone norm in this case may indicate improper functioning of the kidneys and adrenal glands. Since after the 16th week of bearing a child, the placenta is responsible for the production of this hormone, any disturbances in it can lead to excessive hormonal production. Another potential cause of the development of this pathological condition is multiple pregnancy.
A high level of progesterone during pregnancy is characterized by pain in the mammary glands, a sharp change in body weight (both weight loss and weight gain for no apparent reason). As practice shows, increased production of this hormone is not as dangerous to the health of the expectant mother and baby as its deficiency.
Low progesterone levels in men
A decrease in the rate of progesterone in the male body develops against the background of the following possible reasons:
- Malignant and benign tumors located in the brain;
- Diabetes;
- Hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- Inflammation localized in the organs of the reproductive system;
- Kidney failure;
- Disruption of the adrenal cortex.
Abuse of diets aimed at consuming fiber while simultaneously reducing the consumption of meat and fat has been proven to have a negative effect on hormonal levels. Some laxatives, anticonvulsants, antibacterial drugs and dietary supplements can also lead to such an imbalance.
A decrease in progesterone levels in men manifests itself in the form of increased fatigue, which is difficult to eliminate even after a long rest. In addition, this pathology is manifested by frequent, causeless mood swings (starting with depression and ending with groundless aggression or nervous breakdowns). Such patients suffer from decreased or complete absence of appetite and fluctuations in body weight. These patients complain of loss of libido, resulting in sexual dysfunction, even incompetence. It is important to note that if progesterone is normal, then normal inhibition of estrogen production occurs. If a hormonal imbalance develops, the patient develops a female-type figure.
Deficiency of this hormone leads to such a serious complication as prostate hyperplasia. This occurs against the background of an obstacle to the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone, which stimulates the proliferation of prostate tissue.
Low progesterone in women
A deficiency of this hormone can be diagnosed both in pregnant women and in those who do not plan to give birth to a child in the near future. A separate group includes women in menopause, since during menopause, low progesterone in a woman is a natural phenomenon (due to the fact that the synthesizing function is transferred to the adrenal glands).
In non-pregnant women, a low concentration of this is enormous and manifests itself in the form of causeless mood swings. Patients complain of constant fatigue, which does not go away even after prolonged rest and sleep. They suffer from frequent headaches, hair loss and brittleness, weight gain and breast swelling. But, as practice shows, patients do not associate these pathological symptoms with a violation of the norm of progesterone in women. The most common symptom with which they seek medical help is the inability to become pregnant.
A temporary drop in progesterone levels may be associated with ovulation - a condition in which the maturation and release of the egg from their follicle does not occur. It can be natural (puberty, pregnancy or breastfeeding, menopause) and pathological (caused by various diseases: pathologies of the endocrine system, structural anomalies of internal organs, etc.). It is the latter type that often becomes the cause of female infertility.
Even if the ovulation cycle is normal, progesterone in women may be reduced. This occurs due to:
- Sudden weight loss or weight gain;
- Presence of bad habits (smoking and alcohol abuse);
- Therapy with drugs that affect hormone synthesis;
- Genetic diseases;
- Chronic stress.
If the decrease in progesterone levels progresses, this can lead to significant disorders of the menstrual cycle (failures, displacement, absence and uterine bleeding). It is important to note that such uterine bleeding is almost impossible to stop without timely medical intervention. They pose a serious threat to life, so if the first signs of this condition appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Progesterone in women during pregnancy is itself higher than in non-pregnant women. But there are a number of factors that can lead to a deficiency of this hormone. Among them:
- Disruption of the hypothalamic-pituitary system (can be caused by stress, vitamin deficiency, etc.).
- Uncontrolled use of medications.
- Pathologies of the thyroid gland.
- A decrease in progesterone in women leads to an increase in the tone of the uterine muscles, resulting in severe pain in the abdominal area, often accompanied by bloody discharge from the genital tract. The main danger of this condition is the threat of miscarriage.
Causes of progesterone deviations from the norm
A reduced level of progesterone during pregnancy indicates a delay in fetal development and the threat of miscarriage. In addition, a lack of the hormone is observed with anovulation, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, true post-term pregnancy, a short (less than 10 days) luteal phase, chronic inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system and excess estrogen. Low levels of progesterone are also observed with the use of certain medications (danazol, combined oral contraceptives, rifampicin, carbamazepine, prostaglandins).
Increased levels of progesterone in the blood are primarily observed during pregnancy. But there are a number of pathological conditions in which progesterone levels increase:
- corpus luteum cyst;
- malignant hormone-producing ovarian tumor;
- renal failure;
- dysfunctional uterine bleeding;
- pathology of the placenta during pregnancy;
- amenorrhea;
- disruption of the formation of sex hormones in the adrenal glands;
- taking pharmacological drugs (progesterone, mifepristone, tamoxifen, corticotropin);
- prolongation of the second phase of the menstrual cycle.
Analysis
It is important to understand that controlling progesterone levels is vital for any person. To do this, just contact our medical center, where there is a modern laboratory that allows you to quickly obtain accurate research results.
As mentioned above, the sex hormone in women fluctuates depending on the menstrual cycle, so it is necessary to take the test on certain days. The optimal period is considered to be the 22nd day of the cycle (subject to stable menstruation). If there are any failures or delays, you will need to be tested for progesterone levels several times: a week after the start of menstruation, on the 14th and 20th day. Thanks to this, it is possible to effectively assess the dynamics of changes.
This analysis does not require complex preparation. To obtain the most reliable diagnostic data, it is necessary to donate blood on an empty stomach (refuse to eat at least 8 hours before the procedure) in the morning. The day before blood sampling, you will need to limit the consumption of foods that stimulate the central nervous system (coffee, strong tea and dishes with a lot of spices). It is also strongly recommended to stop drinking alcoholic beverages and take a break from smoking. These preparatory measures will be enough to accurately identify normal, decreased or increased progesterone.

This test is often prescribed to patients suffering from infertility. In addition, its use is advisable when diagnosing increases in the menstrual cycle and uterine bleeding of varying intensity of unspecified etiology. In men, decreased or increased progesterone may indicate testicular pathology, increased functioning of the adrenal glands or thyroid gland.
Typically, results can be obtained from our laboratory within 1-2 business days. The interpretation of diagnostic data is carried out exclusively by the attending physician. Based on the information received, he prescribes additional diagnostics, makes the correct diagnosis and selects the optimal therapeutic course aimed at achieving the progesterone level and improving the current condition. In most cases, medications are used for treatment. Modifying the patient’s lifestyle is no less effective. This combination of treatment measures allows you to achieve better results in the shortest possible time.
Indications for determining progesterone levels
A blood test to determine the amount of progesterone is prescribed to women:
- in case of infertility,
- with metrorrhagia,
- if there is a threat of miscarriage,
- to determine the cause of post-term pregnancy,
- in the absence of ovulation,
- with a short luteal phase of the menstrual cycle,
- if you suspect an ovarian tumor,
- with premenstrual and menopausal syndromes,
- with severe side effects from taking progesterone-containing drugs (edema, increased blood pressure).
How to maintain the hormone progesterone
Progesterone in women and men is an important component of health, so it is necessary to carefully monitor its concentration. In the absence of hormonal imbalance, a number of effective measures can be taken to prevent preventive action. To a large extent, prevention lies in maintaining a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition.
According to medical recommendations, to achieve and maintain progesterone levels, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Complete rest and sleep. Lack of sleep leads to fatigue, stress and decreased performance. Therefore, it is extremely important to monitor the correct alternation of sleep and wake cycles.
- Adequate physical activity. Playing sports that do not involve intense physical activity has a beneficial effect on normalizing hormonal levels. The safest and most effective are breathing exercises in the fresh air.
- Balanced and varied diet. To maintain progesterone levels, you need to consume enough proteins, fats and carbohydrates daily. It is strongly recommended to increase your intake of fresh fruits and vegetables, fish and lean meats. To achieve better results, you will need to give up fat and junk food. You also need to monitor your water balance and drink at least 1.5 liters of clean water daily.
- Take oral contraceptives and other medications containing hormones with caution. Before starting such a therapeutic course, it is necessary to consult with your doctor, who will select the correct dosage in accordance with the individual characteristics of each patient.
- It is impossible to achieve normal levels of progesterone without eliminating concomitant somatic diseases. Therefore, you need to carefully monitor your own health and promptly seek medical help if even minor pathological symptoms appear. Also, do not ignore preventive examinations, especially by gynecologists (at least once a year if there is no serious medical history).
- Timely visit to the doctor. Often, the onset of the disease or a symptom of a deficiency of certain hormones are signs that patients mistakenly do not pay attention to: frequent mood swings, fatigue, hair loss and brittle nails, headaches, depression. It is almost impossible to completely get rid of them without medical intervention. Moreover, self-medication can only worsen the current situation. Therefore, if these symptoms persist for a long time, it is necessary to urgently consult a specialist, undergo diagnostics and receive treatment from a qualified doctor.
Controlling progesterone levels is a guarantee not only of physical health, but also of procreation. The implementation of reproductive function in both men and women depends on this hormone. Even a slight hormonal imbalance can lead to a significant deterioration in a person’s well-being, as well as to serious health problems, including infertility. Therefore, maintaining the level of this hormone in the normal range and timely treatment of any disorders is the key to success for those who care about their own health and family well-being.