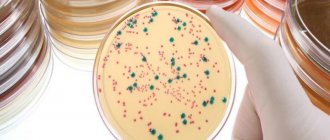
A smear on flora - biological purity or microflora - is one of the main research methods practiced in gynecology. Material for such a study is taken from the mucous membranes of the vagina, cervix and urethra. The main task of the gynecologist taking the analysis is to obtain information about the state of the microflora and the presence of pathogens of genitourinary diseases.
Appointment with gynecologist Ms. Diana
There are many microorganisms in the female genital organs, some of them are dangerous, others are harmless to the body, while there are few of them, and others are absolutely necessary for women’s health, as they help fight pathogenic bacteria that cause inflammatory processes. A flora smear (vaginal cleanliness smear) helps determine the composition of the flora and the quality of the environment in which it lives.
What can be detected in a smear to check the cleanliness of the vagina?
The content of the article
A smear to check the purity of the vaginal flora can reveal the following elements:
- Epithelium
. These are dead epithelial cells covering tissue organs, in particular the vagina and cervix. Normally there should be little of it. If there is a lot of biomaterial in the test sample, it means that an inflammatory process is occurring in the body. The absence of epithelium is observed in women with hormonal imbalances, with excess testosterone and lack of estrogen. This is an equally dangerous symptom, leading to early aging of the body and decreased sexual function. - Leukocytes
. These are special cells - protectors against infections, produced by the immune system. Leukocyte cells are white in color, which is why they are called white blood cells. Normally, there should be a small amount of them to resist attacks from pathogenic bacteria. A sign of inflammation is an increase in the number of leukocytes. - Red blood cells
. Red blood cells are part of the blood - they give it its red color. Their concentration in the smear depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle. However, if there are a lot of them, erosion, inflammation or damage to the vaginal mucosa can be assumed. - Slime.
This viscous substance is secreted by the glands of the vagina. Thanks to it, self-cleaning of the genital tract occurs. This means that mucus must be included in the smear for vaginal cleanliness. If mucus is found in the urethra, this is the first sign of a urinary tract infection. - Atypical cells
. These are cells that differ in structure from normal ones. Normally, they should not be there at all - they are a sign of a precancerous condition. - Gardnerellas
. These microorganisms belong to the opportunistic flora, which means they are harmless up to a certain point. It is conditional pathogenicity that allows them to be in the body without causing attacks by the immune system. Under some circumstances, such as weakened immunity or infection with other pathogens, the number of gardnerella increases, leading to gardnerellosis, which rarely occurs alone. Detection of these microorganisms in a smear in small quantities is normal. But an increase in the number of gardnerella indicates vaginal dysbiosis and bacterial vaginosis. - Key cells.
This is the name given to epithelial cells that stick together with microbes and viruses. They appear with gardnerellosis and weak immunity. - Cocchi.
Ball-shaped bacteria that are pathogenic (gonococcus) or opportunistic (staphylococcus) in nature. If cocci pathogens are detected, very serious treatment is required. - Candida
. This fungus can be found in small quantities even in healthy women. If there is more candida than lactobacilli, then candidiasis begins or, as this disease is called, “thrush”. This happens when taking antibiotics, pregnancy and decreased immunity. - Trichomonas
. This bacterium, the causative agent of the dangerous disease trichomoniasis, cannot always be detected when examining a smear for vaginal cleanliness due to its ability to change shape. To confirm its presence, an additional analysis is performed - bacterial culture (bacteria culture). But if it is detected, treatment cannot be avoided. - Dondrain's rods are lactobacilli
. The main female microorganisms that support the health of the reproductive system. Their presence in a smear for vaginal cleanliness is strictly necessary.
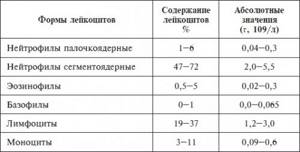
Normal indicators of various forms of leukocytes
Elevated leukocytes can demonstrate how the inflammatory process occurs. The more leukocytes in the smear, the more dangerous the inflammation is considered. An elevated white blood cell count may be associated with a disease such as thrush.
Enterobacters are gram-negative bacteria that are rod-shaped and covered with flagella. They do not form spores and develop under anaerobic conditions, but are able to survive in the presence of oxygen. Read more in the article: “Enterobacteria: what is it.”
When should you take a smear test?
It is recommended to take a smear for flora at any visit to the gynecologist. Unfortunately, many women's diseases occur hidden, so this analysis is simply irreplaceable. In addition, there are direct indications for undergoing a gynecological smear to check the cleanliness of the vagina:
- Inflammation of the pelvic organs;
- Pregnancy planning;
- Pain in the lower abdomen;
- Itching, burning and unnatural vaginal discharge;
- Pregnancy;
- Taking antibiotics or hormones;
- Change of sexual partner.
In these cases, a smear to check the cleanliness of the vagina will help identify flora disorders.
Indications for undergoing a Pap test
A cytology smear is taken from all women from 18 to 65 years of age, regardless of whether there are any health complaints or no external signs of the disease. The only exception is for virgins: when taking a smear, a speculum is inserted into the vagina, which can damage the hymen.
The mandatory indication for a cytology smear is the beginning of sexual activity. The “risk group” includes young, inexperienced girls who have just entered into sexual relations with a man. Recently, a medical discovery was made, for which its author was awarded the Nobel Prize: in 99.9% of cases, cervical cancer was caused by 16 and 18 strains of the human papillomavirus. HPV is transmitted exclusively through sexual contact; douching after sex will not protect against infection.
With strong immunity, HPV may not manifest itself for a long time, but then it will make itself felt. The period 16-30 years is especially dangerous. Cytological analysis reveals the consequences of HPV in the early stages.
It is also recommended to undergo a Pap test in the following cases:
- to identify the causes of infertility;
- during pregnancy planning;
- for menstrual irregularities (helps identify hormonal disorders);
- when using oral contraceptives;
- if genital herpes is detected, leading to changes in epithelial cells;
- obese women;
- when HPV is detected;
- sexually active women who often change partners;
- before installing an intrauterine device;
- before surgery on the reproductive organs.
How to properly prepare for taking a smear to check the cleanliness of the vagina?
Before visiting a doctor, you should follow some recommendations:
- Do not use vaginal medications or douching;
- Refrain from sexual contact for a couple of days;
- Immediately before taking a smear, try not to urinate for 2-3 hours.
It is best to go for an examination after the end of menstruation, after 5-6 days. Direct collection of biomaterial from a woman is carried out by a gynecologist using a disposable spatula. The procedure is absolutely painless.
Ways to reduce white blood cells
First of all, it is necessary to normalize the microflora of the body and restore its balance. To do this, you can turn to folk remedies for help, namely medicinal herbs: aloe leaves, chamomile, oak bark. Douching can also help; for this, take a solution of chlorophyllipt. Warm baths (exclude hot baths) can relieve inflammation.
From drug intervention, the gynecologist can draw up a treatment plan, which may likely include medications such as special suppositories: Pimafucin, Terzhinan, etc.
Normal smear indicators for the purity of flora
| Index | V | WITH | U |
| Yeast | – | – | – |
| epithelium | 5-10 | 5-10 | 5-10 |
| Key cells | – | – | – |
| Slime | Moderately | Moderately | – |
| Leukocytes | 0-10 | 0-30 | 0-5 |
| Gonococci | – | – | – |
| Trihomonas | – | – | – |
| microflora | Many Dederlein sticks | – | – |
What does a cytologist see?
After the smear is taken for a PAP test, it is treated with a special solution, which allows you to see the structure of the cells under a microscope. Pathological changes indicate the onset of the disease.
| Identified changes | Possible diagnosis | What is he talking about? |
| Enlarged squamous epithelial cell nucleus | koilocytosis | Mild dysplasia (CIN1), signs of human papillomavirus |
| Change in the nucleus of multilayered epithelium | dyskeratosis | |
| Atypical ASCUS cells | HPV, STD | Occurs during menopause, can cause pathogenic microorganisms, dysplasia |
| Atypical squamous epithelial cells ASC-H | dysplasia | Moderate dysplasia (CIN2 and 3), early stage cancer |
| Few atypical LSIL cells | onset of dysplasia | Talks about HPV infection |
| Many atypical HSIL cells | advanced dysplasia | Speaks of the beginning of the development of oncology in situ |
| Changed glandular cells AGC | cervical cancer | The woman is sent for further examination |
| Pronounced changes in AIS cells | carcinoma | Early stage of cancer |
| High-grade SIL cages | squamous epithelial cancer | Stage 2 or 3 cancer |
| Modified cells | adenocarcinoma |
What is the degree of vaginal cleanliness?
Based on the result of the vaginal cleanliness smear, the degree of vaginal cleanliness is determined. There are only 4 of them:
- Grade 1
is characterized by a normal number of leukocytes in the test sample. Lactobacilli make up the main part of the general microflora. Epithelium and mucus - in moderate quantities. If, after examining the biomaterial, the 1st degree of vaginal cleanliness is assigned, this means that the body’s immunity is strong, the microflora is in perfect order and there is no threat of inflammation or infections. - Grade 2
is also determined by the normal leukocyte count. The vaginal microflora contains cocci and fungi along with lactobacilli. Mucus and epithelium - within acceptable concentrations. These indicators are considered normal, but the microflora is not ideal. This can cause inflammation due to decreased immunity. - 3rd degree
: the number of leukocytes is increased. Most of the microflora consists of pathogenic and pathogenic microorganisms: fungi, cocci. There are very few lactobacilli, but there is a lot of mucus and epithelium. These are all signs of infection or serious inflammation that require immediate treatment. - 4th degree
: a large number of leukocytes and pathogens. Lactobacilli are not observed. There is a lot of mucus and epithelium, which indicates a pronounced inflammatory process. Urgent medical examination and treatment is required.
If the first two degrees are considered normal and do not require special attention, then the third and fourth degrees indicate an infection of the internal genital organs. Various gynecological procedures for such indications cannot be performed without preliminary treatment and re-examination.
Analysis of a smear for vaginal cleanliness is of great importance for studying the functioning of the immune system and identifying infections and inflammations, especially chronic ones. If necessary, the doctor can conduct an extensive examination of the discharge using special analysis methods: cytomorphological and bacterial.
CLICK TO MAKE AN APPOINTMENT, TEST OR ULTRASOUND
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
What tests should a sexual partner take if there is an increased level of leukocytes in urethral smears?
If an STD is detected, then the sexual partner needs to do the necessary testing to detect such an infection.
First of all, for very contagious infections - Trichomonas, gonococcus and mycoplasma.
They are often asymptomatic and the sexual partner may not even know that they are sick.
Testing for the presence of these infections must be carried out using the PCR method.
No earlier than three months after unprotected sex, it is necessary to donate blood for the presence of HIV infection, treponema pallidum and hepatitis B and C viruses.
Other sexually transmitted infections are not all classified as STIs and tests for their presence are not necessary.
It is advisable to repeat the HIV test six months after unprotected sex.
Since three months after unprotected sex, there may still be no specific antibodies.
Reasons for increase in women
Deviation from the norm can be caused by several groups of reasons, primarily inflammatory processes in the reproductive or urinary organs (if a smear is taken from the urethra):
- Cervicitis is an inflammation of the cervical canal of the uterus. Symptoms may include: the presence of cloudy discharge, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, discomfort during sexual intercourse and urination.
- Colpitis is an inflammatory process that develops in the vagina. Among its signs: itching, discomfort in the affected area of the mucous membranes, pain in the lower abdomen, copious whitish discharge.
- Endometritis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the inner uterine layer. It manifests itself in the form of various discharges, aching pains, discomfort during intimate contacts. An acute course may be accompanied by fever and requires immediate attention to a gynecologist.
- Adnexitis is the appearance of a focus of inflammation simultaneously in the ovaries and appendages. Exacerbation is expressed in pain in the lower abdomen, sometimes on one side, fever, weakness, and menstrual irregularities. The chronic course includes periods of quiescence and relapse of symptoms.
- Urethritis is inflammation of the urethra. Noticeable manifestations will be pain during diuresis, purulent discharge from the urethra, swelling and redness of its edges.
The pathogenic microflora that causes the listed diseases can also be represented (but not necessarily) by infections that enter the body through sexual contact. These same pathogens can also cause their own specific pathologies (STDs). They can be divided into 4 groups. In group 1, bacteria can cause:
- Gonorrhea (gonococcus) and chlamydia (chlamydia) - can cause cervicitis, endometritis and proctitis.
- Syphilis (pale spirochete) , lymphogranuloma venereum and inguinal granuloma (Klebsiella) - common to these venous diseases are specific skin manifestations (ulcers).
- Ureaplasmosis and mycoplasmosis – cause vaginitis and may be accompanied by inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs. Characterized by copious gray or whitish discharge with a “fishy” odor.
- Tuberculosis of the genital organs (Koch bacillus) - the infection can enter the body not only sexually, but also through the lymphogenous or hematogenous route (in the presence of other foci). It can be asymptomatic, or manifest itself in the absence of menstruation and sudden weight loss, low-grade fever, acute pain and night sweats.
Group 2 are protozoal infections represented by Trichomonas. It ranks first in prevalence among sexually transmitted diseases. Trichomoniasis is characterized by pain (during sexual intercourse and urination), copious yellow-green discharge with a fishy odor, swelling, itching and burning of the external organs and vaginal mucosa.
Group 3 consists of viral infections:
- HIV – causes the course of AIDS and other related diseases;
- herpes simplex viruses type 2 and human papilloma – pathologies have pronounced skin manifestations;
- cytomegalovirus - develops almost imperceptibly, causeless fever is possible.
Group 4 (fungal infections) should primarily include thrush. The main cause of candidiasis is a decrease in general immunity, but the disease is also transmitted to a sexual partner, which allows it to be included in the list. Symptoms include itching, burning, cheesy discharge, a strong odor from the vagina, as well as pain during urination and intimacy.
The cause of deviation from the norm may be oncological diseases of the genital area - the key symptom will be bloody discharge without physiological reasons. However, routine inspections are a more effective detection measure.
The reason for the increase in leukocytes in the smear may also be vaginal dysbiosis, which develops against the background of active reproduction of conditionally pathogenic microflora - Escherichia coli, gardnerella, fungi. If the disease is not accompanied by other inflammations, the woman may have no complaints at all, or there may be a foamy, dirty-white discharge with a fishy odor, which intensifies after sexual intercourse or before the onset of her menstrual period.
The causes of dysbacteriosis can be:
- hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy or its interruption, menopause, as well as endocrine disorders;
- decreased general and local immunity;
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics;
- passion for douching;
- physical and mental fatigue;
- chemical and radiation therapy methods;
- frequent change of partners, oral contacts, intimate microtraumas;
- foreign bodies in the vagina (hygienic tampons);
- frequent use of local spermicidal contraceptives;
- deformations of the vaginal vault due to anatomical features, difficult childbirth or surgical interventions;
- intestinal dysbiosis.
Allergic reactions can also cause an increase in white blood cells; mucous membranes can react to:
- intravaginally administered dosage forms or douching, including their organic components (herbs);
- intimate cosmetics (lubricants);
- partner's sperm (infrequently).
A general allergic reaction of the body, regardless of the cause, can provoke an increase in the level of white blood cells.
Also, irritation of the external genitalia, causing local inflammation, can occur against the background of:
- poor hygiene;
- hypothermia or overheating;
- wearing uncomfortable underwear;
- using chemicals without consulting a doctor;
- systemic diseases (diabetes, hepatitis, genitourinary pathologies).
A noticeable increase in leukocytes during pregnancy requires more attention, as it may indicate hidden pathologies that have worsened against the background of restructuring of the body and a physiological decrease in general immunity.
A functional increase in leukocytes can be provoked by intimate contact, less than a day before taking a smear, taking certain medications or a recently installed intrauterine device (7-10 days before the test).
Oncology of the glandular epithelium of the cervical canal
The gynecologist deciphers the smear analysis for cytology. If deviations from the norm are detected, the woman will be invited for a consultation and further research will be prescribed.
The greatest danger is the human papillomavirus. If a woman is infected with the virus, the chance that she will develop cervical dysplasia or cervical cancer increases 400 times!
In addition to atypical cells, a cytology smear reveals:
- Chlamydia is an STD that does not manifest itself for a long time and does not cause concern in a woman, but leads to the development of serious diseases.
- Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted disease, which is similar in manifestation to thrush and cystitis. Timely detection will help avoid serious health consequences.
- Candida yeast (thrush), which leads to inflammation and dysplasia;
- Gonorrhea is an STI that leads to infertility.