In the first year of life, quite a lot of diseases, defects and anomalies in the development of internal organs do not have obvious manifestations.
Ultrasound allows you to correctly diagnose in the early stages of the disease, prescribe treatment in a timely manner, and often improve the prognosis and quality of life of the child.
The importance of timely ultrasound is emphasized by the fact that its use in young children is strictly regulated by the Orders of the Ministry of Health and Social Development, which allows its use in screening (that is, mass) diagnostic programs and detection of diseases at the earliest stages.
Absolutely every person has encountered an ultrasound examination. Currently, there are practically no organs that cannot be “seen” using ultrasound. Restrictions exist only for the lungs and bones.
Examination of children under 1 year of age
using ultrasound has a number of advantages compared to other types of examinations - it is not painful, not dangerous, quite fast and, most importantly, very informative. Even very premature babies weighing less than 1 kg can be examined.
Main research:
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, kidneys and urinary tract, hip joints, brain (neurosonography), ultrasound of the heart (echocardiography) and other organs.
How is the procedure done?
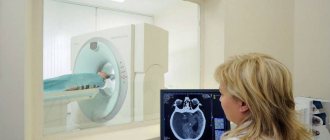
Neurosonography is a study of the brain or spinal cord using an ultrasound machine. The doctor who performs the ultrasound examination touches your baby's head and spine with a special soft plastic tip of the ultrasound machine, which emits nothing but high-frequency sound waves and a small amount of pleasant heat. The computer system builds a 2D or 3D-4D image of the structures of the central nervous system, obtained as a result of processing ultrasonic waves reflected from the brain structures. In order for the penetration of ultrasonic waves to be more effective, the doctor applies a special “acoustic gel” to the tip of the ultrasound machine, a water-based substance that is absolutely harmless, transparent, colorless and odorless, which can be easily removed with a sanitary napkin after the procedure.
In young children (from birth to 8-12 months), the brain is examined through a section of cartilage tissue on the head - the “fontanel”. At approximately 8-12 months, the child’s fontanel is overgrown with bone tissue, so in children older than one year, examination is used through the temporal, occipital and frontal bones.
Where to do NSG?
To conduct an ultrasound of the child’s brain, you just need to call our clinic’s one-stop help line. Preambula's highly qualified specialists have many years of practical experience and use the most modern equipment for their work. All this guarantees high accuracy of the information obtained during the study, which is then carefully deciphered by our doctors. Registration is made at a time convenient for you. The clinics are located close to your home, so you don’t have to travel long by public transport.
Neurosonography with Doppler - 2400 rubles.
How to reduce the cost? MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
When should an ultrasound scan of the brain be performed on a newborn baby?
As a preventive (screening) diagnostic method for early detection of possible pathology, neurosonography is carried out at the following times:
- Days 1-14 of a newborn’s life – in the maternity hospital. This study is aimed at diagnosing congenital pathologies that were not diagnosed in the fetus (malformations, cysts, tumors, etc.), as well as possible postpartum complications (hemorrhages, infection).
- When the baby is 3-4 months old - in the medical center. By the second month of a baby’s life, an increase in the volume of intracerebral fluid (CSF) is normal, and by the third month of life, pathologies that could have arisen during childbirth begin to appear. Ultrasound of the brain at this stage allows you to see signs of possible pathological conditions (hydrocephalus, etc.). Pathology that was not noticeable during the first ultrasound of the brain before the age of 1 month will appear precisely during the second study.
If additional diagnostics are necessary, the doctor may prescribe a computed tomography - CT scan or magnetic resonance imaging - MRI.
What parameters are determined during ultrasound examination?
During an ultrasound examination, a specialist examines the child’s brain and compares the information received with normal indicators. All data about the study is entered into a special form, and based on the diagnostic results, a conclusion is given about the absence or presence of pathologies. As a rule, during the ultrasound procedure of the child’s brain, the following parameters are determined:
- symmetry of brain structure;
- homogeneity of structure;
- area and size of the ventricles;
- the condition of large blood vessels supplying the brain;
- area of the subarachnoid space;
- clarity of the contours of convolutions and grooves;
- the presence of fluid in the ventricles of the brain and its quantity.
With the conclusion of an ultrasound specialist, the child is usually sent for a consultation with a neurologist, who, if necessary, prescribes treatment or additional examination.
Research result
After the diagnostic procedure, the ultrasound doctor will write a report. The interpretation of the provided report is carried out only by a qualified pediatric neurologist. Based on the study, the pediatric neurologist gives a conclusion, and if a pathology is identified, he will assess its nature, severity, make a diagnosis, determine what treatment will be required, and whether it will be necessary to constantly monitor it with a specialist. To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe additional diagnostic tests.
Features of the study
Neurosonography is in many ways similar to a regular ultrasound, except for the fact that the study is performed only on young children.
Age limitation is associated with the timing of fontanel closure. The largest fontanel (anterior) closes between 9 and 18 months after birth. The maximum period is two years. Sometimes the fontanel remains open for a longer period - this indicates pathology. After the bones have fused, ultrasound becomes impossible, since the bones do not allow ultrasound to pass through.
The study is indicated for all children aged one to one and a half months, even in the absence of symptoms of neurological pathology. If there are complaints and indications, NSG is performed several times in order to study the child’s condition over time. It is in the first year of life that the child’s brain and nervous system go through the stages of active development. The child’s body is susceptible to external influences and adequate treatment.
Ultrasound diagnostics are carried out using a special device equipped with a sensor. A gel is applied to the skin in the area of the fontanel, and the doctor moves a sensor along it. As a result, high-frequency sound is generated, which is reflected from the internal organs and displays an image on the monitor. Based on the data obtained, the specialist makes a conclusion about the patient’s condition.
Indications for the procedure
In the first month of life, neurosonography is recommended for preventive purposes. It is also very important to repeat the procedure at three months. This is explained by the fact that many pathologies of brain development may not appear immediately. If complications arise during childbirth or the baby is born prematurely, neurosonography is mandatory. Indications may also include:
- intrauterine hypoxia in the mother;
- infection of the fetus with toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, herpes, mycoplasmosis;
- low weight of the child;
- unusual head shape;
- breathing problems;
- head injuries;
- suspected chromosomal diseases, including Down syndrome;
- retraction of the fontanel;
- signs indicating neurological pathologies (tics, convulsions, facial asymmetry, increased excitability, developmental delay and others);
- post-term pregnancy;
- congenital brain defects;
- low Apgar score after birth;
- pathologies previously identified on ultrasound;
- long and difficult labor (more than 15 hours);
- severe illness of the mother during pregnancy (for example, hypertension);
- discrepancy between the Rh factors of the child and mother;
- high intracranial pressure;
- suspicion of intracranial bleeding, etc.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for the examination include:
- prematurity;
- birth injuries;
- irregular head shape;
- difficult childbirth;
- Rhesus conflict, newborn jaundice;
- bulging and pulsation of fontanelles;
- difficult pregnancy, lack of oxygen;
- inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system;
- signs of oxygen starvation during childbirth;
- suspected neurological pathologies;
- signs of intrauterine infection.
A pediatrician or neurologist prescribes an unscheduled examination if the child experiences regular convulsive twitching, frequent and profuse regurgitation, prolonged crying, and poor intermittent sleep.
An unscheduled study is indicated for head injuries in children of the first year of life. The use of NSG together with Doppler will allow us to assess the nature of blood flow and the condition of blood vessels.
Ultrasound of the brain in children has no contraindications. Limitations may include skin damage in the study area. In this case, you must first consult with your doctor. Ultrasound itself does not pose a danger to brain tissue. All research devices are manufactured under strict quality and safety control.
How the research is carried out
Neurosonography of newborns and infants is performed without special preparation. Your doctor may recommend taking a break from taking strong medications if they were previously prescribed. If treatment cannot be interrupted, then the specialist should be informed about this so that he takes this into account when interpreting the results.
In order for the child to behave calmly during the procedure, it is recommended to first feed him, calm him down, and provide him with a comfortable position. NSG can be performed while the patient is sleeping. Strong crying during the test may distort the results.
The procedure itself is carried out quickly and painlessly, without any discomfort for the child. It lasts 15-20 minutes. A special gel is applied to the scalp: it ensures maximum adhesion of the sensor to the surface of the body. The doctor turns the sensor in different directions, receiving an image of the brain from different projections on the monitor. If necessary, the resulting pictures can be printed and attached to the medical history.
After receiving the results of the examination, you must visit the doctor again. He will comment on the ultrasound and prescribe the necessary treatment to improve the patient’s well-being. Additional diagnostic measures may be required. The safety of the method allows neurosonography of the brain to be performed repeatedly, studying the dynamics of the condition.
Ultrasound results
Only a doctor deciphers the NSG; he evaluates the size of the brain, the asymmetry of its parts, the presence of fluid between the membranes and hemispheres of the organ, the shape of the ventricles, the softening or hardening of areas of the structure. The ultrasound conclusion does not indicate the diagnosis, but only the parameters and structural features of the brain. The final verdict based on them is determined by a neurologist or pediatrician.
What structures are studied during NSG:
- furrows and convolutions of the cerebral hemispheres (reflect the degree of maturity);
- ventricular system (their increase may be a sign of hydrocephalus);
- subcortical structures;
- cerebellum;
- liquor systems;
- brain tissue.
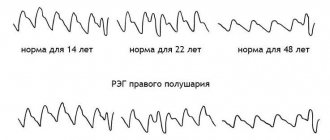
Normally, all brain structures are located symmetrically, the stem structures are not displaced, the contours of the convolutions are clear, the ventricles and cisterns have a homogeneous structure, the vascular plexuses are hyperechoic. Normal indicators change in accordance with the age of the child, which must be taken into account when interpreting the examination.
The results of ultrasound diagnostics will show a complete picture of the disease and allow the doctor to draw conclusions about the presence of pathologies. The specialist receives a picture of the condition of the patient’s soft tissues in real time. Timely diagnosis and detection of problems will allow a neurologist or pediatrician to begin effective treatment on time.
Benefits of the survey
There are several ways to get a picture of the state of the brain, but doctors recommend doing ultrasound examinations, especially if the baby is small. The advantages of the procedure are:
- harmlessness to the body;
- painlessness;
- good tissue visualization;
- the possibility of obtaining several projections of the study area;
- reliability due to real-time conduction;
- acceptable price.
There is an opinion that ultrasound is harmful to the body, but over the years of using the method, the negative impact of ultrasound has not been proven. It is for this reason that ultrasound examinations are preferred over CT and MRI.
How to prepare for an ultrasound
For young children, it is advisable to conduct the study while they are sleeping, since it is important that the child lies quietly. If the baby is awake, then it is recommended to feed him, calm him down, and give him a favorite or interesting toy before the ultrasound. You should take a diaper with you to the procedure, as well as napkins or a towel to wipe off any remaining gel from your head after the examination is completed. You can take some water with you, especially if your baby calms down with a bottle. Before an ultrasound, it is recommended to refrain from using drugs that improve brain trophism.
Indications for ultrasound in children over one year of age
On average, the fontanel is overgrown by the end of the first year of life. Once it closes, neurosonography becomes impossible. An ultrasound of the child's head is performed through the temples and the back of the head. The main indications for the procedure are:
- complaints of frequent and severe headaches;
- fainting;
- cognitive impairment (for example, problems with speech, memory, etc.);
- insomnia or, conversely, increased sleepiness;
- unstable emotional state (excessive tearfulness, excessive irritability);
- high blood pressure;
- inflammatory or immunological vascular pathologies;
- head injuries;
- previously established diagnoses, etc.
What does neurosonography show?
With the help of an ultrasound of the child’s head, it is possible to promptly identify changes that in the future can lead to the development of serious diseases. Changes in the size of the ventricles of the brain do not always indicate a deviation; gradually by twelve months the situation can normalize. However, if deviations are detected, constant monitoring by a specialist is required. Neurosonography allows you to diagnose pathologies such as:
- congenital malformations (porencephaly, Arnold-Chiari anomaly, Dandy-Walker anomaly and others);
- cysts and tumors;
- hydrocephalus and increased intracranial pressure;
- hemorrhages, aneurysms;
- complications from injuries and infections;
- cerebral ischemia and other diseases.
You can get an ultrasound of your child’s head using modern equipment from experienced specialists at the Dad, Mom and Baby clinic. Prices for head ultrasound depend on the chosen technique. You can view the prices on the website page or contact our consultants by phone. Use the “Make an Appointment” or “Order a Call” service, and the clinic staff will contact you as soon as possible.