Detailed description of the study
Every year, up to 1.3 million new cases of breast cancer are registered worldwide. To diagnose a tumor, its metastases, as well as to monitor the effectiveness of therapy and early detection of a possible relapse of the disease, dynamic determination of tumor markers - tumor markers - is carried out.
Tumor markers are specific substances that are secreted by cancer cells or healthy cells associated with tumor growth.
The following are often used as markers of malignant tumors: enzymes, glycoproteins, antigens, hormones, lipids. As a rule, their content increases as the tumor grows.
Tumor markers are specific to a certain type of cancer and its location. If there is a history of cancer or hereditary forms of cancer, then monitoring changes in the concentration of specific tumor markers helps to detect tumor formation earlier than other diagnostic methods.
Monitoring the concentration of tumor markers is also used in cancer therapy. By measuring this indicator over time, one can judge the effectiveness of treatment or, conversely, its ineffectiveness. This is important if therapy uses a drug or method to which tumor cells may develop resistance, or resistance, in this case it becomes possible to replace the drug or treatment method in a timely manner.
Tumor marker CA 15-3 is a glycoprotein that is normally synthesized in small quantities by breast cells. A significant increase in its synthesis is observed in breast cancer (BC).
Testing the level of this tumor marker is generally ineffective for detecting early stages of breast cancer, but is successfully used to monitor the development of cancer and the effectiveness of its treatment.
The tumor marker level depends on the stage of the disease, as well as on the duration of the relapse-free period.
The concentration of CA 15-3 in blood serum serves as an indicator of the effectiveness of cancer treatment. Dynamic determination of tumor marker concentrations is justified for early detection of relapses or metastases in the long term after surgical treatment.
A moderate increase in tumor marker concentration may indicate pathologies not associated with breast cancer. The concentration of CA 15-3 may be increased in malignant tumors of other locations (colon, ovaries, cervix, etc.). A slight increase in the level of tumor marker is observed in liver diseases, during a normal pregnancy, as well as in benign breast formations.
However, in this case, the level of the marker is significantly lower than in breast cancer, and after clinical improvement during treatment of these diseases, it decreases or normalizes.
As a rule, it is recommended to determine CA 15-3:
- During breast cancer therapy (allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy and make timely adjustments to the prescribed treatment, as well as assess the likelihood of metastasis);
- During the period of remission (prediction of tumor relapse).
An increase in concentration indicates a recurrent tumor or indicates the ineffectiveness of cancer therapy.
Indications for analysis
The CA 15-3 cancer antigen test is considered auxiliary among specialists and is prescribed for the following purposes:
- confirmation or refutation of a malignant process in the mammary glands;
- differential diagnosis of benign and malignant tumors, mastopathy, other inflammatory or infectious processes of the mammary glands and internal organs;
- dynamic assessment of the effectiveness of surgical or conservative treatment of confirmed breast cancer;
- assessment of the likelihood of metastasis and relapse;
- making a prognosis for the course of the disease, remission, monitoring the rehabilitation of patients;
- obtaining data regarding the shape and volume of the tumor, its location and extent of spread (the greater the specific gravity of CA 15-3 in the plasma, the greater the volume of malignant cells produced by mammary tissue).
The need to prescribe this test as part of a comprehensive examination of the mammary glands may be indicated by the following clinical signs:
- the appearance of lumps, lumps or other formations in the breast tissue, which is determined visually or during palpation;
- pain in the chest, feeling of fullness or heaviness;
- pathological discharge from the nipples (including in males);
- change in the shape of the nipple (retraction, hardening, redness), the appearance of cracks or wounds on it that may bleed;
- changes in the structure of tissues and skin (redness, generalized swelling, roughness, “lemon peel” effect);
- immobility of the mammary gland (the tumor has grown into the sternum, which leads to deformation of muscle tissue and glands);
- inflammation of regional lymph nodes, their enlargement.
You can read more about breast self-examination techniques for women in our separate article.
The study is also prescribed to patients at risk for oncology:
- the presence of direct relatives who have a history of being diagnosed with cancer of internal organs;
- age over 40-50 years;
- long-term hormonal support, oral contraceptives, hormone replacement therapy;
- chronically elevated levels of estrogen in the blood;
- chronic menstrual irregularities, secondary amenorrhea;
- earlier onset of menstruation;
- late menopause;
- history of ovarian cancer.
Interpretation of the test results for cancer antigen CA 15-3 is carried out by an oncologist, mammologist, surgeon or functional diagnostician.
How and under what conditions is it produced?
CA 15-3 is a highly specific antigen, so it is used as a tumor marker. The antigen is found in 95% of cases of malignant breast lesions. In rare cases, the appearance of a specific protein in the blood is associated with other types of cancer, for example, when a tumor grows in the intestinal area.
CA 15-3 tumor marker
It is synthesized by the membranes of cancer cells located in the mammary gland. In addition to blood, the antigen can be detected in the secretion of the mammary gland.
Possible complications
If abnormalities are detected in the blood, self-medication is prohibited.
A high volume of tumor markers in the blood is observed in advanced forms of cancer and developing mammary glands.
- This means that breast tissue is being destroyed. A growing tumor compresses and destroys healthy tissue that forms the mammary gland and milk ducts, which leads to the development of severe inflammation, even necrotic changes.
- There is a high probability of metastases occurring in organs and systems located far from the mammary glands. Cancer cells travel through the blood throughout the body and serve as the basis for the emergence of new malignant tumors. In this case, doctors give an extremely unfavorable prognosis.
First of all, metastases germinate:
- Into the lung tissue, which is actively supplied with blood and nutrients. In this case, signs of suffocation will be observed, often occurring against the background of ongoing pneumonia.
- Into liver tissue. When metastases form in the liver, symptoms of hepatitis appear.
- Into the brain. When metastases grow in the brain, vision, hearing, and sleep deteriorate, convulsions appear mainly at night, consciousness is impaired and the thinking process changes.
When metastases form, the probability of death is always high. CA 15-3 is a tumor marker, the norm in women without pathology is quite low, in this case it will be many times higher than normal values. Most of the methods used in the treatment of cancer at this stage of cancer are ineffective. Treatment of such patients is carried out in specialized hospices.
Indicator table is normal
| Tumor marker level | |
| normal amount | up to 20 units/ml |
| threshold limit | 30 units/ml |
| high level | over 30 units/ml |
| very tall | above 50 units/ml |
CA 15-3 is a tumor marker; the norm for women is not the same and depends on the laboratory in which the study was carried out. It is necessary to compare the existing result with the standards accepted in this medical institution.
Reference values
Important! Standards vary depending on the reagents and equipment used in each particular laboratory.
Therefore, when interpreting the results, it is necessary to use the standards adopted in the laboratory where the analysis was carried out. You also need to pay attention to the units of measurement. Below are the most commonly used ranges:
- less than 31.3 U/ml (Invitro)
- 0 - 25 U/ml. (Helix)
- Less than 30 U/ml (European standard)
The average norm for CA 15-3 is 0-27 U/ml. Alternative unit of measurement is IU/ml, threshold value is 0-22. The indicated range indicates the absence of a malignant process or its tendency to decrease with successful therapy.
A value from 22 to 30 U/ml is borderline, so additional studies are used to interpret them, for example, cytology or CEA analysis. The higher the level of CA 15-3 in the blood, the greater the likelihood that the process of metastasis has begun, and the tumor itself occupies a significant proportion in the body. Moreover, with a high level of tumor marker, metastases are more often found in liver tissue and bones.
Exceeding the norm by more than 40 U/ml is critical and suggests breast cancer.
Preparing and conducting analysis
Collecting material for research is a completely safe procedure. Its task is to obtain the most accurate result.
To do this, a number of conditions must be met:
- Blood sampling is carried out in the morning strictly on an empty stomach.
- The last meal should take place twelve hours before the examination.
- At the last meal, dishes containing large amounts of fat and spicy seasonings are completely excluded from the diet.
- A few days before the visit to the laboratory, the consumption of alcohol, alcohol-containing drinks, and energy drinks with high levels of caffeine is prohibited. These substances can affect the composition and condition of the blood.
- Smoking is prohibited for several hours prior to your visit to the laboratory.
- On the eve of the examination, avoid stress and limit the level of physical activity.
- For several days before the examination, it is recommended not to take medications, especially those that suppress the immune system, as well as drugs belonging to the group of corticosteroids and tranquilizers. An exception is made for essential medicines. Their name and dose must be indicated on the directions.
- If necessary, drinking still water before analysis is allowed.
- Receiving material
- The material is collected in a treatment room under highly sterile conditions.
- Blood is taken from the antecubital vein only by a medical professional.
- Minor discomfort may appear if the patient’s pain threshold is elevated.
How to determine
Chemiluminescence immunoassay is used to detect tumor markers in serum. This method is similar in its method to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The essence of immunochemiluminescence research lies in the use of specific magnetic particles that have a high degree of sensitivity.
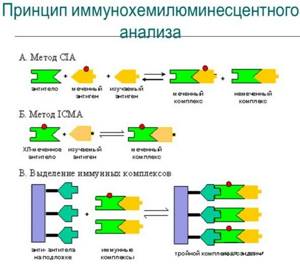
During the study of serum, immune reactions are detected combining a specific antigen with a specific antibody. Such reactions are unique, which makes it possible to prove with high accuracy the presence of pathological changes.
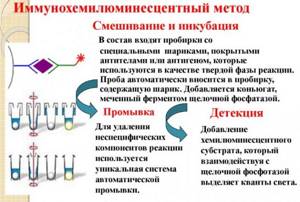
Plasma testing is carried out using an automatic chemiluminescence immunoassay analyzer.
The likelihood of receiving false data is low.
The cause of the error may be:
- incorrect actions of the laboratory assistant when drawing blood;
- failure of the patient to comply with the conditions of preparation for the examination.
For a more accurate diagnosis, an additional blood test for carcinoembryonic antigen is performed. If the test is negative and there are visible signs of breast cancer, the examination is repeated.
In the initial stages of pathology, the concentration of antigens may be low and specific proteins will not be detected by traditional laboratory tests. In this case, a repeat analysis is carried out after a short period of time.