Symptomatic acute ulcers
A characteristic manifestation of an acute ulcer is necrosis and destruction of the epithelium of the mucous membrane, submucosal, and sometimes muscular layers. Healing of such an ulcer occurs by tissue regeneration, and not by replacing damaged layers with connective tissue, and scar formation does not occur.
Symptomatic ulcers occur against the background of impaired blood microcirculation in the mucous membrane, or, for example, as a side effect of taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hormones, and salicylates.
Causes of chronic ulcers
An imbalance between protective factors of the gastric mucosa and aggressive factors leads to increased secretion of pepsin and hydrochloric acid and an increase in their aggressive action. This process causes damage to the structure of the mucous layer.
The main cause of peptic ulcer development is infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori
. Intensively reproducing Helicobacter, producing specific enzymes, disrupts metabolic processes in the stomach, promotes increased secretion of hydrochloric acid and slows down the production of mucus, which leads to an imbalance of protective and aggressive factors and to the formation of ulcers.
Ulcers can be single or multiple. A typical picture for a chronic ulcer is necrosis of the glands of the mucous membrane, changes in the structure of the epithelium (benign) and proliferation of connective tissue. Scars form at the site of the ulcers.
Classification of reflux esophagitis
Rice. 1. Normal position of the stomach and angle of His (diagram).
Rice. 2. Moving part of the stomach into the chest cavity and changing the angle of His in case of hiatal hernia (diagram).
To unify and evaluate gastroscopic examination data, the Savary-Miller classification of the severity of esophagitis is used, distinguishing four stages of the disease:
- Stage I - round and longitudinal lesions that do not merge and spread from the Z-line to the mucous membrane of the esophagus;
- Stage II - merging transient lesions in the Z-line area, not covering the entire surface of the mucous membrane;
- Stage III - ulcerative lesions that coalesce in the lower part of the esophagus and cover the entire surface of the mucous membrane;
- Stage IV - chronic ulcerative lesions of the esophagus, fibrous stenosis, shortening of the esophagus (Barrett's esophagus).
Factors contributing to the occurrence of the disease
Neither gastric ulcer nor duodenal ulcer can appear without the influence of additional factors. As a rule, a combination of several components leads to peptic ulcer disease, the main of which are:
- Chronic gastritis, duodenitis or gastroduodenitis.
- Love for spicy dishes, constant consumption of monotonous or rough food. Food too cold and too hot.
- Violation of proper diet. Overeating, hasty eating with poor chewing. The body does not have time to secrete the required amount of enzymes needed to digest food; food is not evacuated from the stomach on time, but is retained in it, which leads to disruption of the digestion process.
- Impaired blood microcirculation. The mucous membrane has a dense network of blood capillaries. As soon as blood circulation in them is disrupted, the mucous membrane ceases to perform its protective functions in full.
- Constant overstrain of the nervous system, emotional stress, frequent anxiety states. In this case, the body’s protective properties are not simply reduced: the person’s appetite either disappears or becomes excessive, which, again, is a violation of the normal diet. At the same time, under stress, the functions of the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating the activity of the digestive organs, are disrupted.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Long-term use of certain medications (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, hormonal drugs, etc.).
- Excessive coffee consumption. The harmful effect of coffee manifests itself in stimulating the formation of excess gastric juice.
- Frequent or regular consumption of alcoholic beverages. Alcohol significantly reduces the protective properties of mucous membranes.
- Smoking. Resins containing carcinogenic substances enter the gastrointestinal tract along with saliva. Smoking increases the production of gastric juice, so smoking on an empty stomach is most harmful. If you do not stop smoking during treatment, this will significantly reduce the effectiveness of the latter.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs
- Cost: 3,800 rub.
More details
Treatment of stomach ulcers
Peptic ulcers are treated by a therapist or gastroenterologist. It aims to eliminate symptoms, heal ulcers and eliminate the cause of this disease through diet, lifestyle changes and medication.
Drug therapy
To get rid of Helicobacter pylori infection, the doctor prescribes antibiotics, and to reduce the acidity of gastric juice - acid-lowering drugs, etc. If a stomach ulcer is caused by taking painkillers (NSAIDs) or other medications that can provoke the development of an ulcer, the doctor selects other drugs for the patient, which do not have an ulcer-forming effect.
First, pain is relieved with painkillers. Take medications only when you feel discomfort in the stomach. Enterosorbents are also prescribed, which neutralize the negative effects of toxins. In addition, the patient needs to take a course of vitamins.
Nutrition
If you have a stomach ulcer, it is important not to aggravate the symptoms with bad habits. You need to stop smoking and drinking alcohol. And also watch your diet. For stomach ulcers, a special diet should be prescribed.
It involves a complete diet, divided into 5-6 meals a day. The consumption of strong irritants of gastric secretion (ketchups, hot spices), coarse foods and dishes is limited. Food is prepared mainly pureed, steamed or boiled in water; fish and lean meats are served in pieces. Very cold and hot dishes are excluded from the diet. Limit your intake of table salt.
The appearance of an excess amount of hydrochloric acid in the stomach leads to pain and the patient suffers from heartburn. You need water that has an alkalizing effect - when used, the harmful effects of hydrochloric acid are neutralized.
The opposite problem is low acidity. In this case, little gastric juice is produced. Result: food is poorly digested, and there is a feeling of fullness in the stomach.
Alkaline mineral waters speed up the processing of food and promote its rapid movement through the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms characteristic of peptic ulcer
Very rarely, peptic ulcer disease occurs without any symptoms; mostly the symptoms are so pronounced that it is simply impossible not to notice them:
- Seasonal pain. In spring and autumn, during periods of exacerbation, the patient complains of cramping or aching pain in the epigastrium associated with eating. Pain appears half an hour to an hour after eating for a stomach ulcer, and two to three hours for a duodenal ulcer (early and late pain). Hunger pain and night pain may also occur. Pain can occur to the left or right of the midline of the abdomen, sometimes radiating to the chest area, the area of the left shoulder blade, and to the back. The localization of pain depends on where the ulcer occurs.
- Discomfortable sensations in the gastrointestinal tract. This may be heartburn, nausea, sour belching, vomiting. These manifestations are called dyspeptic syndrome. Dyspepsia also includes constipation, one of the characteristic symptoms accompanying peptic ulcer disease.
Complications of peptic ulcer
Complications of peptic ulcer disease usually require surgical intervention. The most common complications of peptic ulcer disease include:
- Bleeding. This is a dangerous complication that occurs against the background of ulcer damage to the walls of blood vessels. Blood may remain in the stomach or intestines, and is also detected in vomit (they look like coffee grounds) and stool (it becomes tarry).
- Perforation of the ulcer. The formation of a through hole in the wall of the organ with the entry of gastric contents into the abdominal cavity. It is fraught with the occurrence of peritonitis.
- Stenosis (narrowing) of the gastric outlet due to inflammatory and cicatricial changes.
- Ulcer penetration. If the process goes beyond the wall of the diseased organ and affects neighboring ones (for example, the pancreas), this can lead to their damage (pancreatitis, prancreatic necrosis).
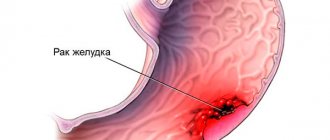
- Degeneration of an ulcer into cancer. A rarer but possible complication.
2. Reasons
The range of reasons for foreign objects entering the stomach is also very wide. Most often, foreign bodies (buttons, pins, fruit pits, beans, small toys, coins, etc.) are swallowed by small children during play, out of pranks, or simply by accident. As for adults, accidental ingestion is typical for workers whose profession involves constant contact with small parts or fasteners, provoking the bad habit of holding these parts in their teeth (needles, screws, insulating material, etc.). Sometimes there are cases of swallowing too large pieces of food (for example, a piece of meat with a large bone inside), which usually results from hasty “eating on the run.” Separate, and quite extensive, categories of victims are formed by mentally ill people who, in a psychotic state or for delusional reasons, can sometimes swallow a large number of different objects, or manage to swallow surprisingly large objects; persons in a state of alcoholic intoxication (in whom foreign bodies enter the stomach “on a dare”, out of drunken recklessness or without any clear motive at all); elderly and senile people, especially with senile or vascular dementia, parkinsonian syndrome, atrophic pathology of the central nervous system; patients with epilepsy; people who lost consciousness, were shocked by sudden news or fell into a semi-fainting state while eating or putting on dentures; suicides, swallowing nails, glass fragments, etc. for suicidal purposes.
In all of these cases, the foreign body penetrates the esophagus and stomach in the most expected way: through the pharynx. However, there are also situations when a foreign or, rather, an object inaccessible to enzymatic decomposition is formed in the body itself - such as, for example, gallstones in gallstone disease (penetrating into the stomach through a cholecystogastric fistula) or gastric bezoar stones, which can reach significant and even gigantic sizes.
Finally, traumatic penetration of foreign bodies into the stomach from the outside is relatively rare (in peacetime) - with open thoracic or abdominal trauma, explosions, road accidents, industrial accidents, as well as during surgical operations (the notorious “forgotten scalpel inside”, packing material and so on.).
Visit our Gastroenterology page
Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of disease
Diagnosis of peptic ulcer disease is carried out by a gastroenterologist using a general examination of the patient and special laboratory tests, including video esophagogastroduodenoscopy, X-rays, blood tests, and diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection. If necessary, a biopsy of the mucous membrane is performed during gastroscopy.
In case of bleeding and perforation of the ulcer, urgent surgical intervention is necessary. The Helicobacter bacterium is destroyed with the help of antibiotics - the so-called eradication of the microbe is carried out using standard treatment regimens. Taking medications is also necessary to restore the mucous membrane. Treatment is prescribed by a gastroenterologist taking into account the clinical picture, medical history, previous treatment, the characteristics of the individual patient and many other factors.
At the CELT clinic, you can undergo a full examination and receive advice from a highly qualified gastroenterologist if you suspect or have a peptic ulcer.
Treatment of hiatal hernia
Puchkov K.V., Filimonov V.B. Hiatal hernia: monograph. - M.: MEDPRACTIKA - M., 2003. - 172 p.
Treatment of hiatal hernia is 99% consistent with the treatment of its complications - reflux esophagitis and, unfortunately, the therapeutic treatment of hiatal hernia is purely symptomatic: as long as the patient takes medications, limits himself in diet, and strictly follows all the doctor’s instructions and prescriptions, his condition is relatively satisfactory. As soon as the course of treatment is stopped, all the symptoms of hiatal hernia (constant belching, painful heartburn) return. Patients with small, unfixed hiatal hernias without a pronounced clinical picture and only if the patient is ready to take medications for life that prevent the occurrence of reflux esophagitis or reduce the symptoms of the disease are subject to conservative (therapeutic) treatment by a gastroenterologist. But it is worth noting that with the systematic use of drugs that reduce the acidity of gastric juice, for example, omeza, quamatel, ranetidine and others, after 5 years the risk of developing stomach cancer increases by 350%, and after 12 years it increases by 560% compared with persons without hiatus of the same age. At the same time, the lack of acid in the stomach prevents the normal digestion of food, as a result of which its remains enter the large intestine, causing putrefactive processes and the development of severe intestinal dysbiosis.
Folk remedies and methods of treating traditional medicine for hiatal hernia
I would like to especially note the folk remedies and methods of traditional medicine used in the treatment of hiatal hernia. Folk or pseudo-folk remedies and methods for the treatment of hiatal hernia recommended by various herbalists, collections of advice for patients and other popular literature lead to a temporary improvement in the patient’s condition and relief from the symptoms of reflux esophagitis, which is perceived by patients as a cure. All folk remedies for the treatment of hiatal hernia are comparable in their mechanism of action to medications - they either reduce the acidity of gastric juice or change the acidity (neutralize) the gastric juice itself. But as a rule, the effectiveness of folk remedies for hiatal hernia is 50–70% lower compared to medications.
Rice. 3. Hiatal hernia before surgery (diagram).
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Gastroscopy (videoesophagogastroduodenoscopy) | 6 000 |
| Breathing HELIK test (urease activity of H. Pylori) | 1 100 |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen) | 3 800 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions