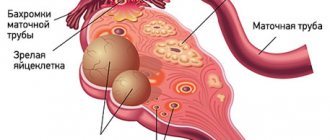
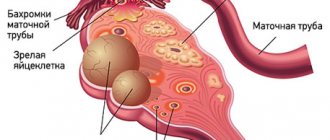
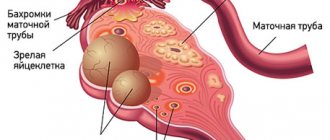
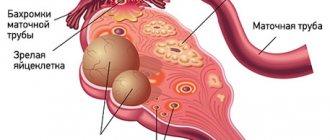
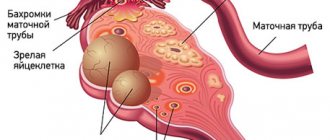
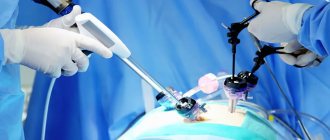
An ovarian cyst is a benign neoplasm filled with fluid and prone to the accumulation of secretions. With prolonged development of the cyst, women experience pain, menstruation is disrupted, and other signs of the disease appear. Laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, after which rehabilitation is faster, allows not only to eliminate the tumor, but also to preserve women's health.
The Yusupov Multidisciplinary Hospital is a modern medical institution where a woman can not only undergo examination and receive the necessary treatment, but also undergo rehabilitation after surgery. Recovery after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is carried out according to individually developed programs by a team of doctors.
Recovery after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst
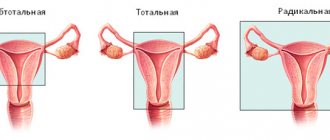
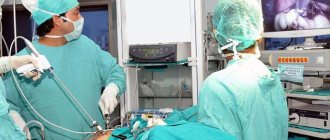
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that is used by specialists at the Yusupov Hospital in the treatment of various diseases, in particular, when removing an ovarian cyst. This operation is performed under general anesthesia, during which three punctures are made in the abdomen through which a small camera and instruments are inserted. To make the operation easier, the abdominal cavity is inflated with a special gas.
The next stage is recovery after removal of the ovarian cyst. The duration of early rehabilitation in a hospital does not exceed 7 days. Patients of the Yusupov Hospital are accommodated in comfortable rooms equipped with the necessary furniture, communications and necessary supplies.
After the ovarian cyst has been removed by laparoscopy, the postoperative period at the Yusupov Hospital takes place under the guidance of experienced oncologists, rehabilitation specialists, and surgeons. Particular attention is paid to the patient during the period of recovery from anesthesia, when she is at her weakest.
Laparoscopic hernioplasty with mesh implant
We perform all laparoscopic surgical interventions under endotracheal anesthesia and muscle relaxation.
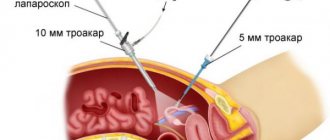
For standard laparoscopic hernioplasty, we use 3 accesses: 1st - 10 or 5 mm - at the paraumbilical point for insertion of the laparoscope, 2nd - 5 mm - the main working port in the right mesogastric region for insertion of the Protack herniostapler (Covidien), dissector, scissors , 3rd - 5 mm - in the left mesogastric region for inserting an instrument under the left hand - a soft or hard clamp (Fig. 1).
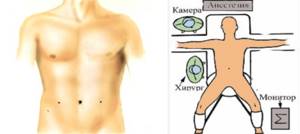
Fig.1. Location of ports and surgical team for laparoscopic hernioplasty.
Carboxyperitoneum up to 12 mm Hg. Art. is applied through a Veress needle inserted into the abdominal cavity. During survey laparoscopy, the diagnosis of a hernia is confirmed, its type and shape are established. Subsequently, diagnostic laparoscopy is performed. The organs of the upper floor of the abdominal cavity are examined (liver, gall bladder, anterior wall of the stomach, transverse colon, greater omentum, spleen), then the intestinal loops, after which the patient is transferred to the Trendelenburg position. This position ensures the displacement of the internal organs and frees up the area of the medial and lateral inguinal and femoral fossae on both sides. In women, the pelvic organs (uterus and appendages) are also examined. The diagnosis, the diameter of the hernial orifice and the degree of incompetence of the posterior wall of the inguinal canal (dislocation of the structures of the posterior wall) are clarified. The opposite side must be examined for a possible hernia.
One of the main tasks during survey laparoscopy is to clarify the type of inguinal hernia based on an assessment of the anatomical and functional features of the inner surface of the anterior abdominal wall and determine the method of laparoscopic hernioplasty (Fig. 2).
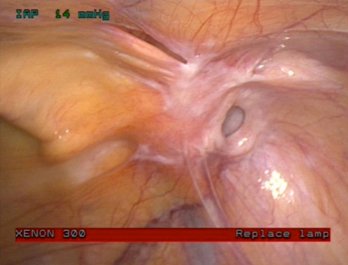
Rice. 2. View of a right-sided oblique inguinal hernia during survey laparoscopy.

Fig.3. Location of mesh implant for indirect inguinal hernia.
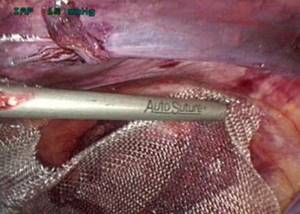
Fig.4. Fixation of the mesh implant with a Protack herniostapler (Covidien).
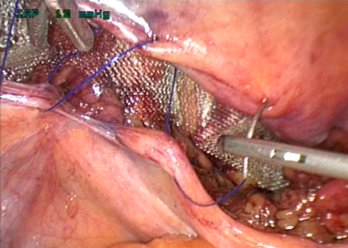
Fig.5. Peritonization of the implant with a detached peritoneal flap using a manual suture.
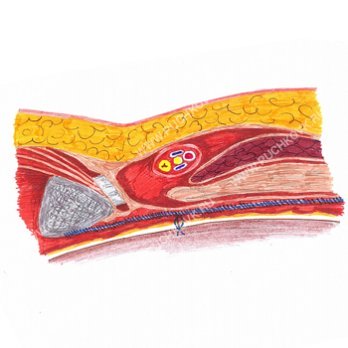
Rice. 6. Schematic representation of hernioplasty with a mesh implant performed by laparoscopic access.
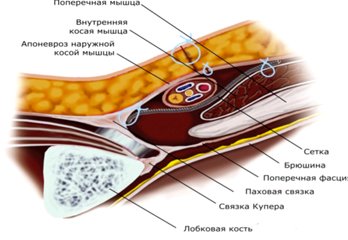
Rice. 7. Schematic representation of hernioplasty according to Lichtenstein.
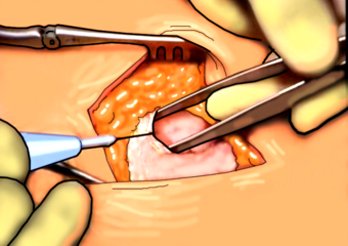
Fig.8. Dissection of the aponeurosis above the hernial protrusion
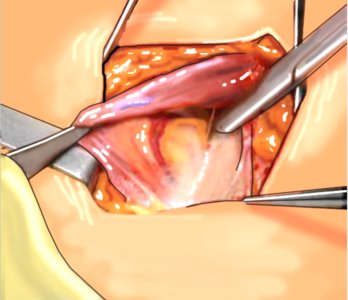
Rice. 9. Isolation of the spermatic cord
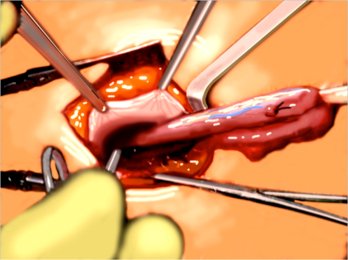
Fig. 10. Isolation of the hernial sac.
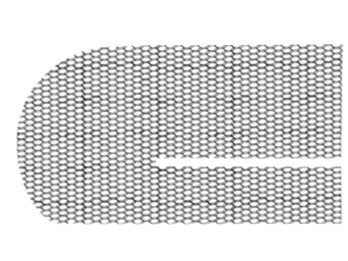
Rice. 11. Type of mesh implant for indirect inguinal hernia.

Fig. 12. General view of plastic surgery according to Liechtenstein.
If surgery is performed for an indirect inguinal hernia, a hole is formed in the center of a 10x15 cm Surgypro (Covidien) polypropylene implant for the spermatic cord. The lower edge of the cut implant is brought under the cord, the mesh is straightened, covering the medial and lateral inguinal, as well as the femoral fossa (Fig. 3).
The prosthesis is fixed with a herniostapler, starting from the cut part along the perimeter, avoiding accidental stitching of vascular structures. The optimal stapler for fixing the mesh is Protack (Covidien), since it fixes the implant quite reliably with a spring-shaped clip, excluding nerve structures from getting into the seam. The spring of the Protack herniostapler enters the tissue at any angle of placement of the stapler rod in relation to the anatomical surfaces, up to an almost parallel position (Fig. 4). However, for better fixation and control of the entry of the staple, especially into dense structures along the upper edge of the attachment (the area of the connected tendon aponeurosis and the edge of the sheath of the anterior rectus muscle), it is advisable to recreate the location of the stapler rod and the underlying area close to the perpendicular. To do this, we recommend using the following technique. When bringing the herniostapler to the place where the mesh is fixed, it is necessary to change the direction of the tissue plane with the fingers of the left hand from the side of the skin of the anterior abdominal wall and create from them a perpendicular surface to the position of the stapler. This way, you will feel the pressure exerted by the hernia stapler with your left hand and will be able to securely fix the implant. It should be noted that the staples penetrate into the tissue depth by only 3-4 mm and are located in it freely without causing ischemia.
It is possible to secure the mesh using sutures and extra- or intracorporeal tying of a knot, but this is less reliable and significantly lengthens the operation time. In our practice, we rarely used this method of implant fixation, explaining this not by the complexity of the manipulations, but by the possibility of a greater number of neurological complications when the nerve is captured in a manual suture. In case of a direct inguinal hernia, fixation to the Cooper ligament is mandatory, then along the perimeter of the mesh.
It should be remembered that fixation in the “fatal” triangle area is inadmissible. The number of staples and fixation points used varies from 4 to 10 depending on the nature and size of the hernia (most often we use 5-6 staples). In case of a direct inguinal hernia, the implant is directly placed in the projection of the inguinal fossae and fixed with staples (without isolating the spermatic cord). After control of hemostasis, peritonization of the implant is performed with a detached flap of the peritoneum using a manual suture (Fig. 5).
The emergency drainage is not left in the abdominal cavity, so there are no wound surfaces and ligated vessels in the free abdominal cavity. Suturing 5 mm trocar wounds is not necessary. If the patient has asthenia, we additionally place one suture on the aponeurosis at the site of puncture with a 10 mm trocar using Polysorb 1-0 thread.
Complications after laparoscopy of ovarian cysts
The laparoscopic method is the most gentle in comparison with other methods, therefore, if medical recommendations are followed, recovery is carried out in the shortest possible time. However, due to various circumstances, patients may experience complications after removal of an ovarian cyst.
Negative consequences that may occur after laparoscopic surgery are:
- damage to neighboring tissues and organs as a result of insufficient visibility;
- intense bleeding;
- vascular damage;
- allergies to anesthesia or gas;
- increased body temperature;
- development of infectious diseases as a result of body weakness.
Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital are fluent in laparoscopy techniques and perform precise movements during tumor removal without damaging nearby tissues. If a patient at the Yusupov Hospital has pain in her ovary after laparoscopy of a cyst, specialists not only take the necessary measures to improve the woman’s condition, but also find out the causes of the pain.
Structure of the knee joint
The knee joint is formed from the base of the femur and the top of the tibia. The patella is located on the front surface of the knee joint. Around the joint are muscles, ligaments and tendons. A huge role is played by the joint capsule, in which the natural production of fluid occurs for normal gliding of the joint. Most often, diseases and damage to joints occur in athletes or people leading a sedentary lifestyle. As a rule, any pathology is accompanied by pain and impaired motor activity; a person cannot independently extend the lower limb and move normally.
Pain after removal of an ovarian cyst
Patients are most often bothered by pain after laparoscopy of ovarian cysts, the duration of which can reach 7 days. This symptom is a natural reaction of the body to damage; it occurs after the sutures have healed.
If a patient has pain in the ovary after removal of a cyst, she is advised to rest in bed; in addition, it is recommended not to make sudden movements and adhere to certain dietary rules. Medicines are prescribed by the attending physician if the pain intensifies.
Discharge after laparoscopy of ovarian cyst
After surgery to remove an ovarian cyst using laparoscopy, many women report intense vaginal discharge consisting of mucus, blood and clots, which can last up to two weeks. After laparoscopy, the discharge from ovarian cysts is intense for a week, but in the second week the discharge decreases.
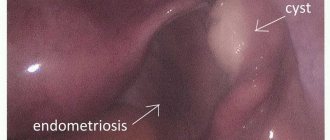
Pathological discharge that occurs during complications is distinguished by an unpleasant odor and a green or yellow tint. Curdled abnormal discharge indicates the development of an infectious process in the genital tract.
Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital pay close attention to each patient, so when pathological signs and complications appear, their signs are identified and therapeutic measures are prescribed, and the condition after laparoscopy of the ovarian cyst is assessed. Diagnostics carried out at each stage of treatment make it possible to identify possible disorders and determine the effectiveness of therapy.
Doctor's answers to common questions
Is it possible to practice swimming during the rehabilitation period? Swimming is a great way to speed up the recovery process and develop the knee joint. Doctors approve breaststroke swimming when the patient's brace is removed. It is important that swimming does not cause pain or discomfort. How should you eat during recovery? It is recommended to change your daily diet slightly. Be sure to include Omega-3, protein, and vitamins C and B in your menu. Please note that due to reduced physical activity, weight gain may occur. Therefore, it is recommended to exclude fatty, smoked and high-calorie foods. We recommend giving preference to low-fat varieties of fish and meat, fresh vegetables and fruits, as well as fermented milk products. What physical procedures will speed up the healing of the joint? Experts recommend after arthroscopy to undergo a course of electrical stimulation, magnetic therapy and laser therapy. These physical procedures improve blood circulation and ensure speedy rehabilitation of the knee joint.
| Therapy from leading medical specialists at the GarantClinic center in Russia |
| Orthopedics from leading medical specialists at the GarantClinic center in Russia |
| Cosmetology from leading medical specialists at the GarantClinic center in Russia |
| Phlebology from leading medical specialists at the GarantClinic center in Russia |
— Does the bone near your thumb hurt in November 2021?
The leading clinic on the basis of the Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University is GarantClinic Moscow.
Sports after laparoscopy of ovarian cyst
Recovery after laparoscopy of an endometrioid ovarian cyst requires adherence to a mode of moderate activity. Thus, in the first days after surgery, physical activity is strictly limited. After a week of recovery and bed rest, the woman can take short walks and do light exercises. Physical activity helps eliminate stagnant processes in tissues and strengthen muscle tissue.
For a woman who has undergone laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, training and serious sports activities should be postponed for 4 months in the postoperative period. Specialists at the rehabilitation clinic, together with the patient’s attending physician, draw up an individual recovery program, one of the components of which is physical therapy.
Rehabilitation after removal of an ovarian cyst in Moscow
Some patients underestimate rehabilitation after removal of an ovarian cyst by laparoscopy. However, a set of measures selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient allows not only to prevent the development of complications, but also to preserve reproductive health.
Yusupov Hospital is located in the historical center of Moscow. In this medical institution, a staff of experienced specialists helps patients improve their quality of life and maintain health. Oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital diagnose and treat both malignant and benign tumors of various locations.
The key principle of the work of specialists at the Yusupov Hospital is the use of organ-preserving techniques and minimally invasive technologies for the treatment of various pathologies. So, if a woman has an ovarian cyst after removal of the uterus, the specialist will select treatment methods aimed at preserving the ovary. Medical care provided to patients at the Yusupov Hospital meets international standards.
Women who have had an ovarian cyst torsion, rupture or other complications can go to the Yusupov Hospital for emergency help at any time of the day. Pre-registration for a consultation with specialists at the Oncology Clinic is carried out by calling the Yusupov Hospital.