As one of the 12 factors responsible for blood clotting, fibrinogen is essential for the body's healing processes that we often take for granted. However, elevated levels of fibrinogen can be harmful to your health. Fibrinogen is a very important marker for monitoring, especially if you do not lead a healthy lifestyle or have chronic diseases. The rest of the article will describe the capabilities of fibrinogen, its positive and negative roles, and how you can influence your fibrinogen levels.
The article is based on the findings of 87 scientific studies
The article quotes authors such as:
- Department of Anesthesiology, University Hospital RWTH Aachen, Germany
- Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Georgetown University Hospital, USA
- Department of Hematology, University Medical Center, Utrecht, The Netherlands
- Department of Cell Biology, University of Alabama at Birmingham, USA
- Department of Clinical Chemistry, University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden
- and other authors.
To view the research, follow the links in the text. []
What is fibrinogen?
Fibrinogen is a protein produced in the liver that is essential for a variety of processes, including blood clot formation, wound healing, inflammation, and blood vessel growth. [, ]
It circulates in the blood at a concentration of 2-4 g/l , which is the highest concentration of all blood clotting factors. This protein breaks down approximately 6 days after entering the bloodstream. []
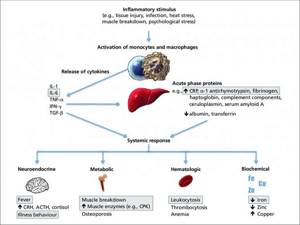
Acute phase reaction. The inflammatory stimulus leads to the activation of monocytes and macrophages, which release cytokines. Cytokines act on the liver to stimulate the production of acute phase proteins. Cytokines, together with acute phase proteins, produce a systemic response with neuroendocrine, metabolic, hematological and biochemical changes.
Fibrinogen is an acute phase positive , meaning its production increases during injury, infection, and inflammation. This occurs mainly through the mediation of cytokines (eg IL-6). [, , , ]
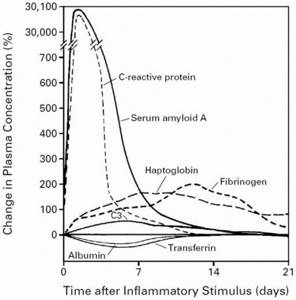
The characteristic patterns of changes that occur in the blood plasma through the concentration of certain acute phase proteins after moderate inflammation are shown. Pay attention to the duration of fibrinogen production (simultaneous increase in ESR).
The role of fibrinogen
Fibrinogen creates blood clots
Blood clots are very important for our health because they stop excessive blood loss and begin the wound healing process. []
During the process of blood coagulation (clotting), protein strands and cellular fragments (plaques) come together to form a solid blood clot. The formed clot is used as a plug at the wound site, preventing further bleeding from the damaged blood vessel. []
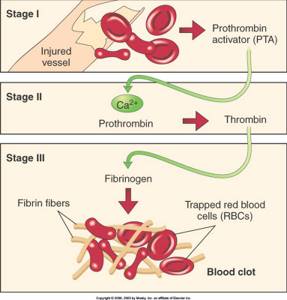
THE PROCESS OF FORMATION OF BLOOD CLOTTES (THROMBI) DURING A WOUND
Blood clot formation occurs through a series of steps
- Fibrinogen is metabolized by the enzyme thrombin into fibrin filaments.[]
- Next, an enzyme, coagulation factor XIII (activated by thrombin), cross-links these fibrin strands to create a network that, together with platelets, forms a clot. []
- Fibrin filaments also bind to thrombin to prevent its prolonged action on fibrinogen, thereby inhibiting the continuous formation of a blood clot. []
- Fibrinogen further promotes clot formation by binding to receptors on the surface of platelets. [, ]
Fibrinogen regulates the breakdown of blood clots
Fibrinogen and its successor fibrin influence the breakdown of blood clots (fibrinolysis). []
While fibrin activates plasmin (an enzyme that breaks down blood clots), fibrinogen blocks it. These opposing actions ensure that blood clots are broken up only after they are no longer needed and the wound does not bleed again. []
If the effect of fibrinogen increases with increasing levels in the blood, it can be dangerous to health because large numbers of clots become harmful and can block blood vessels , leading to a heart attack or stroke. []
Fibrinogen is involved in the body's immune defense
Fibrinogen binds and activates specific white blood cells (U937, THP-1, MAC-1) in mice and in vitro, indicating that it plays an important role in the immune response to infection or injury. [, , , ]
In a study of genes in 631 patients with sepsis, those people who had genetic mutations that lead to higher levels of fibrinogen in the blood showed faster recovery and reduced mortality. []
Another study conducted on mice with liver damage from acetaminophen found that fibrinogen improved liver tissue repair by activating white blood cells. []
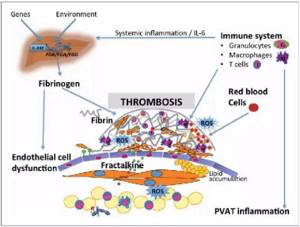
INTERACTION OF FIBRINOGEN, IMMUNE SYSTEM, VASCULAR ENDOTHELIUM AND ERYTHROCYTES IN THE REGULATION OF THROMBUS FORMATION AND BLOOD VESSEL DISEASE. (https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Interplay-between-fibrinogen-immune-system-endothelium-and-erythrocytes-in-the_fig1_230685490)
Normal fibrinogen levels
Blood fibrinogen values vary in the general population and range from 1.5 to 3.5 g/l , depending on the geographic region. [] The minimum fibrinogen required for body homeostasis is 0.5 g/l.
During pregnancy, in the 2nd and 3rd trimester, there may be an increase in fibrinogen values up to 5.6 g/l.
Naturally, the reference values for analysis will depend on the laboratories and diagnostic systems used. Often, reference values for fibrinogen analysis are shown in the range from 2 to 4.5 g/l .
Causes of low fibrinogen
Injury
Acquired hypofibrinogenemia, defined as fibrinogen deficiency, develops later in life and most often causes severe blood loss . This decrease in fibrinogen levels occurs because the body has already used most of the fibrinogen to stop bleeding from an injury. []
An experiment involving blunt liver trauma in pigs resulted in decreased fibrinogen production and blood levels. []
Medicines
Medicines used to reduce blood clots , such as streptokinase, urokinase, and tissue plasminogen activator, reduce fibrinogen levels in the blood in laboratory and clinical studies. [, , ]
The drug urokinase is able to reduce the level of fibrinogen in the arteries by an average of 35% after 24 hours from the moment of administration (study involving 204 patients with stroke). []
Anti-seizure drugs valproic acid (meta-analysis of 11 studies, 967 participants) and phenobarbital reduce blood fibrinogen concentrations in humans and animals, but the mechanisms of this effect remain unclear. [, ]
Numerous studies have found that certain types of chemotherapy can reduce fibrinogen levels in a person's blood, probably by inhibiting the production of proteins in the liver. [, , ]
A 2-week study of anabolic steroids reduced fibrinogen levels by 22% in a clinical study of 14 healthy adults. []
For muscle pain, the drug pentoxifylline lowers fibrinogen values in a study of 427 patients with stage 2 peripheral vascular disease, likely due to suppression of fibrinogen production. [, ]
Diseases
Liver disease can cause low levels of fibrinogen, either impair the body's ability to produce fibrinogen, or greatly stimulate the breakdown of blood clots and the use of fibrinogen to do so. [, , ]
Leukemia may reduce fibrinogen levels in the blood by promoting clot formation and fibrinogen degradation (from studies involving 1,304 patients, 17 patients and 379 patients). This means that hypofibrinogenemia (fibrinogen deficiency) can serve as an early marker for the diagnosis of leukemia. [, , ]
Other diseases with low fibrinogen:
- DIC – syndrome (stages II and III)
- bone marrow lesions (leukemia, tumor metastases)
- deficiency of vitamins B12, C
- Infectious mononucleosis
- defeat by snake venoms
- chronic myeloid leukemia
- polycythemia
Genetic diseases
Congenital hypofibrinogenemia
Congenital hypofibrinogenemia is characterized by a low level of fibrinogen in the blood (from 0.5 to 1.5 g/l) and prolongation of the blood clotting process. []
This condition is caused by either dominant or recessive mutations, and the incidence is estimated at 1 in 100 people . Many of these people are asymptomatic and fibrinogen levels are maintained at sufficient levels to allow clotting in small lesions (study of 100 patients; genomic analysis databases, including about 140,000 people). [, , , ]
Congenital afibrinohemia
Congenital afibrinohemia is characterized by an extremely low level of fibrinogen in the blood (less than 0.1 g/l). Blood clotting time cannot be determined because blood does not clot. []
It is a recessive disorder, meaning both parents must have the genetic mutation passed on to their child. This disease affects approximately 10 people per million of the population. The disease is usually diagnosed in infancy (survey among 155 study participants; genomic database analysis, including about 140,000 people). [, , ]
Fibrinogen storage disease
This genetic disease is characterized by low levels of fibrinogen in the blood, as well as liver disease. [, , ]
Liver disease, caused by excess storage of fibrinogen in liver cells, is associated exclusively with dominant mutations in the FGG gene. [, , ]
The disease usually appears in childhood and is estimated to affect 1 in 100 people (genomic database analyses, including about 140,000 people). [, ]
Below normal
Why did the biochemical blood test show a low protein level? The reasons may be the following:
- genetic predisposition;
- polycythemia;
- myeloid leukemia;

- intoxication with poisons;
- severe liver disease: cirrhosis, hepatitis;
- anorexia and extreme diet, which provokes vitamin B12 deficiency;
- blood transfusion.
After receiving the test results, the specialist will prescribe further examination and treatment.
If deviations in the biochemical composition of the blood are detected in time, it is possible to quickly normalize the patient’s condition and improve well-being. Regular testing will help prevent the development of the disease.
Negative effects of low fibrinogen
Low fibrinogen levels promote bleeding
The most common symptoms of low fibrinogen levels are prolonged bleeding and simple bruising on the skin , especially after injury or surgery. [] Many people also experience spontaneous bruising in the muscles (hematomas), and sometimes intestinal bleeding occurs. [, ]
With low levels of fibrinogen in the blood, spontaneous bleeding is also likely, especially on the gums and near the joints. []
Low fibrinogen causes pregnancy complications
Women with low fibrinogen show a greater risk of developing too heavy periods and pregnancy complications , which can lead to miscarriage. [, , , ]
“FLOATING THROMBES”
Low fibrinogen may increase the risk of blood clots
Paradoxically, people with very low levels of fibrinogen may actually have a high risk of free-moving blood clots that can block blood vessels. This is due to the fact that fibrinogen does not interfere with the formation of internal blood clots. [, , , ]
Solution
Deviation from the norm of fibrinogen does not allow us to draw conclusions about a hidden disease. The indicators make it possible to identify increased or decreased results, but not to detect the original source of the disease. To make a correct diagnosis, the patient must undergo additional laboratory diagnostic examination. Correct identification of existing pathologies will solve the problem.
Doctors warn that ignoring the altered level of fibrinogen and refusing to undergo therapeutic procedures provokes external and internal bleeding (with reduced results) or accelerated formation of blood clots (with an increased amount).
The attending physician makes the final diagnosis and selects a treatment regimen. By seeking professional help in a timely manner, the chances of complications and consequences are significantly reduced.
Ways to increase fibrinogen
Replacement therapy
Fibrinogen replacement therapy is recommended for the prevention and treatment of heavy bleeding, especially during pregnancy. [, , ]
Depending on the region of the world, replacement therapy in the form of plasma (blood) - a concentrate of fibrinogen derivatives (frozen plasma containing high concentrations of fibrinogen) may be available. [, ]
Diet
A study of the diets of 1,854 people led to the conclusion that people with high levels of cholesterol and fatty acids in the blood had high levels of fibrinogen. This points to a diet that increases cholesterol levels as a possible way to increase fibrinogen. []
In addition, diets high in iron, sugar, and caffeine also increase fibrinogen levels (study of 206 Japanese immigrants in Hawaii). []
Proteins , in particular, may also be needed to maintain healthy fibrinogen levels . Protein-deficient animals have low levels of fibrinogen compared to their properly fed counterparts. []
A study of 16 adults also found that fibrinogen increased by 20-40% immediately after participants drank a protein shake or nutritional supplement, but no such increase was observed after drinking water. []
Complexes with this research
Examination during pregnancy.
3 trimester 5,730 R Composition Expanded hospital complex Expanded infectious screening for prevention and hospitalization 4,520 R Composition
Women's check-up No. 1 38 studies for annual preventive examination RUB 12,520 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Miscarriage RUB 29,050
- Entry into IVF RUB 15,030
- Preventive check-up 6,870 RUR
- For those at risk of COVID-19 RUR 2,590
- Female infertility RUB 9,790
Causes of elevated fibrinogen levels
Stress
Multiple studies (158 and 636 participants) have found that fibrinogen levels increase immediately after stressful tasks. [, ]
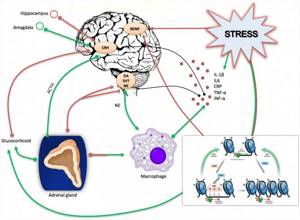
PSYCHOLOGICAL STRESS IMMEDIATELY STIMULATES THE PRODUCTION OF CORTISOL AND INFLAMMATORY PROTEINS (IL-6, IL-1, TNF-a, CRP, INF-a) (https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/113480/fncel-09-00040 -HTML/image_m/fncel-09-00040-g001.jpg)
Additionally, in a study of 302 participants, it was found that people with high blood cortisol levels also had increased fibrinogen . []
This connection may be explained by the activation of genes (fga, fgb, and fgg) responsible for the production of fibrinogen, along with an increase in the inflammatory cytokine IL-6. []
Pregnancy
Pregnant women exhibit increased levels of fibrinogen , likely to prevent excessive bleeding during childbirth. [, ]
As the fetus develops, fibrinogen concentrations increase to 3 times the normal range and then return to their baseline levels within 4 to 6 weeks postpartum. [, ]
Smoking
Multiple studies (9,127 participants; 200 participants; 11,059 participants) have shown that smokers and former smokers have significantly higher levels of fibrinogen in the blood than nonsmokers (11% to 53% more fibrinogen). [, , ]
The more a person smokes, the more fibrinogen readings increase, and fibrinogen levels do not return to normal levels until 15 years after the person quits smoking (studies with 11,059 and 118 participants). [, ]
Women who smoked, had diabetes and/or high cholesterol showed particularly high fibrinogen (two studies involving 200 and 118 women). [, ]
Contraceptives
Oral contraceptives promote an increase in fibrinogen , especially if the woman is found to have high estrogen (randomized crossover study of 28 participants over 16 weeks; and study of 200 women). [, , , ]
Estrogen can increase fibrinogen by increasing FGG gene expression and albumin production, as found in rats. [] As shown in another study of 194 participants, this effect was exacerbated in women who smoked during pregnancy. []
Age
Numerous studies (9,127 participants; 72 participants; 12 participants; 3,967 participants) have found that older people tend to have higher levels of fibrinogen in the blood , with its concentration increasing by 0.1-0.2 g/L every 10 years. [, , ]
Cold temperatures
Cold temperatures increase fibrinogen , causing it to become chronically elevated during the winter months (12 participants; 1-year follow-up of 1,002 people; 1-year follow-up of 24 participants). [, , , ]
Nutrition
Elevated fibrinogen levels in a study of 206 Japanese immigrants in Hawaii were associated with greater dietary iron and sugar intake . This may indicate that a diet high in meat and foods with a high glycemic index (fast carbohydrates) is closely associated with the development of cardiovascular diseases. []
A survey of 1,854 people found that high fibrinogen was associated with low blood concentrations of minerals and vitamins such as iron and vitamin B6 , as well as high cholesterol and fatty acids. This suggests that both undernutrition and overnutrition can increase fibrinogen. []
A study of 16 adults found that fibrinogen increased by 20-40% immediately after participants drank a protein shake or protein shake, but no such increase was found after drinking water. []
Obesity
Multiple studies (87 participants; 200 participants; 64 participants; 1,342 participants) have found that people who are overweight also tend to have elevated levels of fibrinogen. [, , , ]
Although a cause-and-effect relationship has not been proven, the ability of exercise to reduce fibrinogen is known, suggesting the potential of body fat to influence fibrinogen levels (studies with 87 participants; and 3,967 participants). [, ]
Other causes of elevated fibrinogen
- acute inflammation and infections (influenza, tuberculosis)
- stroke (1st day)
- hypothyroidism
- myocardial infarction
- burns
- amyloidosis
- malignant tumors (especially lung cancer)
- collagenoses (rheumatoid arthritis, periarteritis nodosa)
- kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, hemolytic-uremic syndrome)
- nocturnal paroxysmal hemoglobinuria.
Increased protein
A large amount of fibrinogen warns of a hidden inflammatory process and the danger of blood clots. Pathological deviation indicates the presence of:
- rheumatism, nephrotic syndrome;
- heart attack, infections;
- diabetes mellitus, pneumonia;
- hepatitis, DIC syndrome, tuberculosis;
- cancer, trauma, burns.
The increase in fibrinogen volume in pregnant women is explained by the physiological norm. Sometimes an unusual increase in protein is associated with age-related changes and the use of oral contraceptives. If a deviation is detected, the patient must be sent for additional diagnostics to identify the root causes of the abnormal condition.
Negative effects of high fibrinogen
Fibrinogen promotes inflammation
Fibrinogen in the blood and brain activates molecules that increase inflammation (IL-8, MCP-1, MMP-9, Mac-1) while simultaneously inhibiting molecules that can reduce inflammation (PPARα, PPARγ). [, , , ]
Mice with low levels of fibrinogen, or with mutations in fibrinogen that could not bind to white blood cells, showed significantly lower inflammatory responses. [, ]
Certain types of bacteria (streptococci) interact with fibrinogen and contribute to the development of inflammation during infection. []
Therefore, therapy aimed at reducing the bonds of fibrinogen and certain white blood cells (immune cells) may improve symptoms of common inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis , multiple sclerosis , or bacterial infections. [, , , ]
Elevated fibrinogen increases the risk of blood clots
Elevated levels of fibrinogen are associated with a higher incidence of heart disease, blood vessel dysfunction, and stroke. By some estimates, high fibrinogen predicts these diseases and is also a marker for high blood pressure and smoking. [, , , ]
In a study of 1,363 patients, high fibrinogen was also associated with an increased risk of developing heart disease over the next 18 months. []
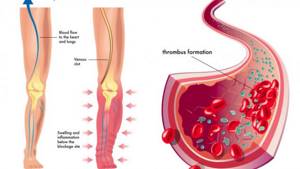
THROMBOPHLEBITIS – DEVELOPMENT OF THROMBOSIS AND INFLAMMATION IN THE VEINS
In addition, another study with 158 participants concluded that people with high fibrinogen release during moments of psychological stress showed poor blood vessel health, and therefore had a greater risk of cardiovascular disease over the next 3 years. []
High fibrinogen may be a marker for the presence of high blood cholesterol , in particular LDL (bad cholesterol), in people without previous cardiovascular disease. [, ]
Fibrinogen and its byproducts have also been found in arterial plaque and in cholesterol, which accumulates on the walls of blood vessels and can lead to atherosclerosis . []
However, laboratory experiments and animal studies have failed to confirm that high fibrinogen causes heart disease. [, , , ]
High fibrinogen may impair brain health
High levels of fibrinogen predict the development of brain disorders , as well as the development of Alzheimer's disease and dementia. [, ]
Fibrinogen can worsen Alzheimer's disease . Studies in laboratories and in rats have shown that by binding to plaque in the blood vessels of the brain, fibrinogen increased damage to brain cells and blood vessels , as well as increased inflammation in the brain. [, , , ]
Elevated fibrinogen was also associated with brain damage in a study of 58 patients with multiple sclerosis , possibly through disruption of the blood-brain barrier. []
Fibrinogen also suppresses the brain's ability to repair itself (in laboratory experiments). This occurred through inhibition of the regeneration of brain cells and the protective myelin sheaths that normally cover them. [, ]
Elevated fibrinogen is associated with diabetes and its complications
People with diabetes have higher levels of fibrinogen in their blood. [, , ]
High levels of fibrinogen are also associated with diabetes and cardiovascular disease, high cholesterol , or diabetes complications such as nerve damage. [, , , ]
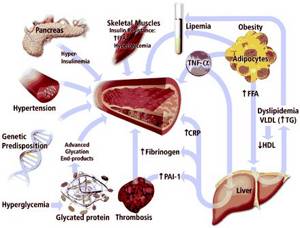
DIFFERENT MECHANISMS AFFECTING THE DEVELOPMENT OF BLOOD VESSEL DISEASE IN TYPE 2 DIABETES
A study of 6 diabetic patients found high levels of fibrinogen and glucagon, the hormone responsible for raising blood sugar, but also normal levels of albumin, a marker of insulin resistance. In other words, increased fibrinogen may precede and possibly promote the development of diabetes mellitus. [, ]
Increased fibrinogen may contribute to cancer development
Elevated fibrinogen is associated with increased cancer growth , and may also predict poor clinical outcomes for patients with uterine cancer, gastric cancer, and kidney cancer. [, , ]
In particular, fibrinogen helps to increase the adhesion (cohesion) of tumor cells and their survival in lung cancer in mice [, ].
It appears that the cancer-helping effect of fibrinogen is due to its inflammatory actions as well as inhibition of natural killer ( NK cell , which can generally stop tumor growth. [, ]
Increased fibrinogen is associated with high blood pressure
People with high blood pressure often also have elevated fibrinogen. [, ]
A study of 143 adults over 3 years of follow-up found that elevated levels of fibrinogen after stressful events predicted later development of hypertension. However, if fibrinogen levels remained stable during stress, these people did not develop high blood pressure. For unknown reasons, this effect was found exclusively in women. []
Ways to reduce fibrinogen
Medicines and diets to reduce cholesterol
A meta-analysis of 22 studies and 2,762 participants found that fibrates , a group of drugs that lower blood cholesterol, also lowered fibrinogen levels compared with another group of drugs, statins. []
Specifically, bezafibrate lowered fibrinogen levels by an average of 40% in 2 double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized studies with 50 and 100 participants. [, ]

FOODS RICH IN DIETARY FIBER (FIBER)
Foods that normalize LDL (bad cholesterol) levels can also lower fibrinogen levels, such as healthy fats and dietary fiber . []
Medicines that slow blood clotting
The drug Ticlopidine for inhibiting platelet aggregation reduces the concentration of fibrinogen by 10-25%. [, , ]
Fish fat
A meta-analysis with a total of 162 participants found that fibrinogen decreased by approximately 10% after taking an average of 2.4 g. per day Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids . [].
A double-blind crossover study with 20 participants demonstrated that 6 grams of fish oil per day reduced fibrinogen by 20% after 6 weeks of supplementation. []
Another study of 25 participants found that 3 g. per day of fish oil for 4 weeks reduces the fibrinogen content in the blood by 3% on average. []
Weight loss and exercise
Several studies have found a relationship between regular exercise and decreased fibrinogen levels (studies with 1,284, 2,398, and 3,967 participants). [, , ]
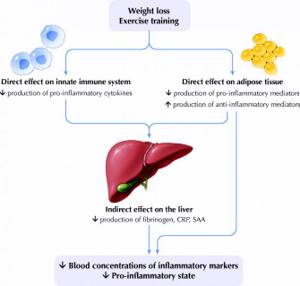
WEIGHT LOSS AND EXERCISE HELP REDUCE INFLAMMATION (AND FIBRINOGEN) (https://www.cmaj.ca/content/172/9/1199.figures-only)
It appears that strenuous physical activity reduces fibrinogen levels. Two studies showed (involving 156 and 8 adults) that fibrinogen levels decreased by 10-20% after intense exercise. [, ]
Turmeric
Curcumin from turmeric, a known treatment for inflammation and heart disease, reduced fibrinogen levels in a study of 30 patients. Fibrinogen can also bind to curcumin in such a way that the curcumin will be metabolized more slowly in the blood. [, ]
Traditional Chinese Medicine
In traditional Chinese medicine, Quyu Jiedu and Xuebijing contributed to the reduction of fibrinogen levels in the findings of 2 meta-analyses (15 studies with 1,364 patients; 11 studies with 686 patients) that evaluated the use of traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of high blood pressure and chest pain in heart diseases. [, ]
Moderate alcohol consumption
Multiple studies (117 participants over 1 month; 20 participants over 6 weeks; 11 participants over 12 weeks) have shown that daily moderate consumption of alcohol ( wine or beer ) decreased fibrinogen levels in the blood. [, , ]
A glass of red wine a day for 40 days has been shown to reduce fibrinogen in the blood by 8-15% (clinical study with 69 healthy adults). []
Olive oil
In a double-blind crossover study, 6 grams of olive oil per day reduced blood fibrinogen levels by an average of 18% (observation of 20 healthy volunteers) after 6 weeks of oil intake. []
Fermented soybean
A study of 12 healthy adults found that one dose (2,000 units of the enzyme Nattokinase) , derived from fermented soybeans, significantly reduced blood fibrinogen after 4 hours. []
Anabolic steroid
A two-week course of anabolic steroids lowered fibrinogen levels by 22% in an experiment involving 12 healthy adults. []
Hormone replacement therapy
Multiple studies (152 women for 1 year; 29 women for 6 months; study of 4,837 women; study of 300 women) have found that hormone replacement therapy can help reduce fibrinogen levels in postmenopausal women, although the effect is minimal . [, , , R]
B vitamins
B vitamins, especially B6 , B9 and B12 , increase the breakdown of fibrinogen, reducing the amount of the amino acid homocysteine. [, ]
A study of 24 adults found that 5 mg/day of vitamin B9 for 4 weeks reduced fibrinogen levels by an average of 9%. []
Another 4-week study showed that receiving vitamins B6, B9, B12 led to a decrease in fibrinogen levels in the blood of 21 patients with sepsis. []
Why get tested?
A cardiologist, internist, surgeon, hematologist or gynecologist - any of the specialists can order a fibrinogen test to determine protein levels, evaluate the body's ability to form blood clots and identify disorders associated with it. In what cases is this research necessary?
- for vascular diseases;
- with low blood clotting;
- before surgery;
- during pregnancy;
- in the presence of liver pathology;
- during infectious diseases;
- in case of severe injuries and burns;
- for cancer of internal organs.
Laboratories usually perform tests such as APTT, coagulogram No. 1, antithrombin III
.
In the list of enzymes and elements, fibrinogen comes first and is called Factor I. Its amount is measured in grams per liter. [media=
https://youtu.be/86buh8A9B78
?t=9s]
Blood for studying plasma is taken from a vein. Before taking the tests, it is recommended:
- do not eat for 12 hours;
- exclude drugs that increase blood clotting;
- reduce physical activity;
- reschedule the test if there are signs of colds;
- do not smoke for at least half an hour.
A deviation from the norm is a reason to conduct additional examination and begin serious therapy.
Combination with medications
People with low fibrinogen levels are advised to avoid taking aspirin or other blood thinners , which will reduce their ability to form floating blood clots, unless prescribed by a doctor. [R]
On the other hand, anticoagulants, such as heparin , aspirin , or Lepirudin are recommended in combination with fibrinogen replacement therapy , to reduce the likelihood of internal blood clots. []
The information on this site has not been evaluated by any medical organization. We do not seek to diagnose or treat any disease. The information on the site is provided for educational purposes only. You should consult your physician before acting on information from this site, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, taking medications, or have any medical condition.
Rate this article
Average 4.8 Total votes (13)