Ectopic pregnancy is a dangerous gynecological pathology during which a fertilized egg is implanted outside the uterus. In 95% of cases, engraftment of the fertilized egg occurs in the fallopian tube. Much less often, the egg attaches to the ovary, abdominal organs, and cervix. If the pathology is not diagnosed and eliminated in a timely manner, severe, sometimes life-threatening consequences for the woman develop. Therefore, it is important to know what the early signs of ectopic pregnancy are before a missed period and what symptoms should be a reason to immediately seek medical help. Correcting the pathology in a timely manner will help preserve women’s reproductive health and prevent serious consequences.
What is an ectopic pregnancy
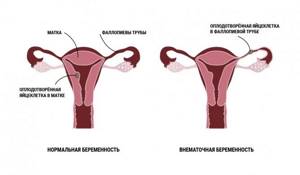
After merging with the sperm, the fertilized egg moves through the fallopian tube and attaches to the inner wall of the uterus. There a child develops from it. But in 2% of cases, the egg is not implanted inside the uterus, but in any other place, for example, in the fallopian tube, in the cervix or in the peritoneum. These places are not suitable for the development of the embryo, therefore all ectopic pregnancies end in the death of the fetus. In addition, ectopic pregnancy often threatens the life of the mother. Without timely medical care, a woman can also die. Emergency treatment will save her life and give her a chance to have a child in the future.
How does the pathological process develop?
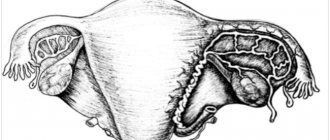
Ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy is a pathology in which the embryo implants outside the uterine cavity. In 98% of cases, the site of embryo implantation is the fallopian tube.
The fusion of sperm and egg occurs in the ampulla of the fallopian tube. After this, during normal functioning of the female body, the zygote (fertilized egg) enters the uterine cavity. The advancement of the zygote is carried out due to the contraction of the muscular layer of the tube and the movement of the cilia of its epithelium.
The journey takes 6-7 days. During this time, during normal pregnancy, the embryo reaches a certain stage of development (blastocyst) and attaches to the endometrium using specific morphological structures.
During an ectopic pregnancy, this process is disrupted: the zygote does not enter the uterine cavity, but gets stuck in the fallopian tube or cervical canal. In addition, it is possible to push the egg out of the tube in the opposite direction and implant it into the ovary or abdominal cavity.
Online consultation with a gynecologist
Online consultation
During the consultation, you will be able to voice your problem, the doctor will clarify the situation, interpret the tests, answer your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
Causes and risk factors
To protect yourself from this formidable complication, you need to know its causes:
- gonorrhea;
- smoking;
- chlamydia;
- any inflammatory processes in the uterus, due to which scars form in it;
- history of tubal surgery;
- another ectopic pregnancy in the past.
There are many circumstances in which a woman is at high risk of experiencing an ectopic pregnancy.
Risk factors:
- abortions;
- pregnancy that occurred despite the use of an intrauterine device;
- surgery on the abdominal organs, especially the uterus, tubes or ovaries;
- endometriosis;
- congenital pathologies of the development of the genital organs;
- age over 35 years.
These circumstances must be taken into account when planning a pregnancy and undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist. In case of any ailments, you should consult a doctor.
Possible complications
The most important and dangerous complication of an ectopic pregnancy is large internal bleeding, which can lead to the death of a woman in just a few hours or even tens of minutes. It is also possible that an ectopic pregnancy may recur in the future or that infertility may develop due to damage to the fallopian tubes. In addition, shock due to internal bleeding can impair the functions of other internal organs, not just the reproductive system.
Due to the fact that an ectopic pregnancy can develop in organs with a rich blood supply, which in particular include the ovaries and the areas where the fallopian tubes enter the uterus, surgery to remove the embryo can result in the removal of one of the fallopian tubes, the removal of one of the ovaries and even the removal of the uterus with both fallopian tubes. But even if all internal organs are preserved, an ectopic pregnancy still reduces a woman’s chances of further conception and normal childbearing. Sometimes, after the operation, an inflammatory process and intestinal obstruction develop, and seals form in the pelvis.
In order to minimize the negative consequences of ectopic pregnancy as much as possible, after the operation it is necessary to undergo anti-inflammatory and restorative therapy. The hormonal background and protective resources of the woman’s body must be fully restored before the next pregnancy, otherwise the risk of recurrence of the pathology or the development of secondary infertility will be too great. From a medical point of view, you can plan your next pregnancy no earlier than six months to a year after the operation.
Run to the doctor at the first symptoms! An ectopic pregnancy is an extremely dangerous condition for a woman’s health and life, therefore, if any suspicious symptoms and especially acute abdominal pain appear, it is necessary to consult a doctor or call an ambulance as soon as possible. And if the diagnosis is confirmed, you will either be prescribed an termination of this pregnancy, or an operation will be performed to eliminate the consequences of the tubal abortion that has occurred. Today, both surgical and medical methods are used to treat ectopic pregnancy. The specific method is determined by the attending physician based on the patient’s condition and the severity of the disease.
Symptoms
This insidious disease is not easy to recognize immediately due to its nonspecific symptoms. You must carefully monitor your health and immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms in the early stages (no earlier than 2 weeks after the last menstruation):
- pain in the mammary glands;
- delayed menstruation;
- frequent urination;
- nausea;
- weakness and constant fatigue.
Signs at 6–8 weeks:
- pain in the pelvic area or abdomen;
- minor bleeding.
Late symptoms:
- strong and profuse bleeding from the vagina;
- excruciating abdominal pain that intensifies during movement;
- pain suddenly appears on one side and then spreads throughout the lower abdomen;
- fainting;
- dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- slight rapid heartbeat;
- cold sweat;
- pale skin;
- confusion of thinking, disturbances of consciousness.
Every effort must be made to recognize the pathology at the earliest stages. This will allow her to quickly heal and conceive a child again.
What is the danger of ectopic pregnancy: consequences and dangers
An ectopic pregnancy is a serious problem - it can pose a danger not only to a woman’s health, but also to her life. In the case of tubal placement of the embryo, damage to the fallopian tube occurs, as a result, it may rupture. At the same time, damage to larger blood vessels occurs and bleeding into the abdominal cavity develops.
What else can be dangerous about an ectopic pregnancy? An ectopic pregnancy threatens infertility and improper placement of subsequent embryos during conception.
Neglecting the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy and its untimely detection leads to the fact that the embryo constantly grows and takes up more and more space, which can lead to rupture of the ovary or fallopian tube.
Remember, if you have a delay in your period, do not delay your visit to the doctor and ultrasound to find out about pregnancy in time and make sure that everything is developing correctly.
When to see a doctor
If you suspect a pathology in the early stages, you should immediately go to a clinic or antenatal clinic. You need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- cramps in the lower abdomen;
- stabbing or cutting pain;
- bleeding;
- weakness;
- frequent dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- pain in the rectum;
- pain radiating to the neck or shoulder.
The doctor will examine the patient and prescribe treatment; in most cases, surgery is required.
Features of treatment
Most doctors are inclined to believe that when diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy, surgery must be performed. There are special medications, the use of which in the early stages of pregnancy will avoid surgery. The most effective of them include Mifepristone, Mifegin and Methotrexate. But if the period is already long enough or taking medications does not help, doctors resort to surgical removal.
There are several ways to remove an ectopic pregnancy, but the most popular is laparoscopy.
. Until the fallopian tube ruptures, it can still be saved, but doctors very often insist that the tube not be saved. This is due to the fact that a second ectopic pregnancy may soon develop in her. Therefore, during surgery, as a rule, the fallopian tube is removed. This is the most rational solution.
On a note!
Removal of the fallopian tube is usually performed during laparoscopy. This will reduce time and also avoid possible consequences.
When to call an ambulance
You should urgently call an ambulance if severe symptoms occur:
- bleeding;
- unbearable pain lasting more than 2 minutes;
- sharp pain in the rectum and an unbearable urge to defecate;
- dizziness and fainting;
- sharp and sharp pain in the shoulder.
When the fallopian tube ruptures, blood fills the abdominal cavity. It can accumulate near the diaphragm, and then the nerves connected to the shoulder are irritated. This makes your shoulder seem to hurt.
It is impossible to make a correct diagnosis at home, so you need the help of a doctor.
How does a home test indicate a pregnancy complication?
Does the test indicate an ectopic pregnancy? Theoretically yes, but there are some things to consider.
For ectopic insemination, the pregnancy test is positive in about 50% to 70% of cases because the home test works by detecting the presence of beta-hCG in the urine.
The pregnancy hormone beta-hCG is released in the body when a fertilized egg is implanted, anywhere. Therefore, if two stripes are detected and the presence of the specific signs of ectopic pregnancy described above, the presence of fertilization pathology should be considered. Testing for beta-hCG levels in the blood is much more reliable. If an ultrasound shows no embryos in the uterus, and the level of beta-hCG in the blood is high, an ectopic pregnancy can be suspected. Note that an ectopic pregnancy on the test can be visualized as two bright stripes or one bright, the other less pronounced.
It is important to emphasize the quality of the tests used to diagnose pregnancy at home. It is important to choose ultra-sensitive tests, with 99.9% accuracy of results. Gynecologists advise resorting to the use of long-proven tests from the German brand “FRAUTEST”. Doctors note their high reliability, so there is no need to resort to using other, more expensive tests to detect pregnancy.
Diagnostics
When a pregnancy test shows two lines, you should urgently contact a gynecologist to undergo a qualified examination. The doctor will do an ultrasound, examine the pelvic organs, and take tests. The most informative laboratory test is a test for the level of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). During an ectopic pregnancy, its content is much lower than during a normal pregnancy. The hCG test is performed at 48-hour intervals. If during this time its level has not doubled, this may be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy.
An ultrasound will tell you whether the egg has implanted inside the uterus. There the doctor will be able to see the condition of the fallopian tubes.
Surgery

Mono and bi-polar device for laparoscopic operations
The choice of surgical treatment for ectopic pregnancy depends on the degree of internal bleeding, gestational age and location of the embryo.
If hemodynamics are positive, laparoscopy is used - a minimally invasive technology that differs:
- atraumatic;
- short rehabilitation period;
- low level of side effects.
To perform laparoscopy, small incisions and special manipulative instruments are sufficient.
In difficult situations, when laparoscopy is ineffective, laparotomy is performed - a classic surgical operation. Indications for laparotomy:
- finding the fertilized egg in the accessory horn of the uterus;
- strong adhesions in the pelvic organs;
- profuse internal bleeding.
During the operation, the issue of preserving or removing the fallopian tube is decided. If the gestation period is short and the pathological changes are insignificant, then organ-preserving surgery is performed.
Ectomy (removal) is performed in case of pronounced anatomical changes, significant adhesions and other complications.
Treatment
To treat an ectopic pregnancy, you will need surgery. There are two types of operations:
- Salpingectomy - when the fallopian tube ruptures, it is removed completely or partially;
- Salpingostomy is an incision in the wall of the fallopian tube (the incision site then heals).
Laparoscopy may be performed if there is no heavy bleeding or serious damage. The fertilized egg is removed from the fallopian tube. In severe cases, a laparotomy is performed and stitches are placed.
If the pathology is detected early and surgery cannot be performed, the woman is prescribed intravenous or intramuscular injections of methotrexate. After administration of the drug, the placenta stops growing and a miscarriage occurs.
Treatment and recovery
The least traumatic method of treating ectopic pregnancy is medication. But it can be resorted to only in the earliest stages of the development of pathology. It is usually used in cases where an ectopic pregnancy is accidentally discovered during a gynecological examination, since women tend to tolerate changes in their condition “to the last.” To get rid of the pathology, a special hormonal drug is introduced into the woman’s body, which stops the development of the embryo and provokes an artificial miscarriage. This method appeared relatively recently. It requires a thorough preliminary examination of the woman before the procedure and highly qualified medical personnel. Under no circumstances should you try to find the name of these drugs on the Internet and resort to the method of medicinal termination of intrauterine pregnancy on your own!
Sometimes doctors combine surgical and medicinal methods, injecting a woman with a drug, after which the incorrectly attached fertilized egg is detached and then removed by squeezing. Further restorative treatment is aimed at eliminating inflammatory processes in the appendages on the opposite side. Usually, a woman’s recovery after surgery occurs quite quickly - especially if it was a laparoscopic intervention (an operation performed through small incisions). The wounds heal completely in 2-3 weeks, but for another 2-3 months the woman should avoid physical activity and try to prevent constipation. Also, after treatment for an ectopic pregnancy, it is customary to take a hCG test several times to make sure that there are no fragments of the ovum membrane left in the woman’s body, which can continue to grow and eventually turn into a tumor.
To summarize, we can say that in the case of an ectopic pregnancy, it is better for a woman to play it safe than to delay her visit to a specialist in the presence of frightening symptoms. It is advisable to see a gynecologist immediately when a delay occurs, so that he can determine its true cause and, if necessary, quickly prescribe treatment. If an ectopic pregnancy was treated in a timely manner, a woman can become pregnant again in the future, paying attention to the prevention of this pathology.
Womenfirst
- Ectopic pregnancy: early diagnosis and treatment Babajanova Gulzhakhon Sattarovna, Khojaeva Dilufar Nuriddinovna, Razikova Komola Khasanovna 2021 / Biology and Integrative Medicine
- Analysis of the reproductive health of patients after ectopic pregnancy Erkenova S.E., Ergalikyzy A., Kaldybekova A.K., Kurbanova M.O., Shadenova E.E., et al. 2021 / Bulletin of the Kazakh National Medical University Murtazin A.I. Obstetrics and gynecology. Standards of medical care. Quality assessment criteria. Formulary. 2021
- Prediction and prevention of recurrent ectopic pregnancy: abstract of thesis. Magomedova Patimat Aripovna; - Moscow, Scar pregnancy - a new type of ectopic pregnancy Maltseva L.I., Fattakhova F.A., Zamaleeva R.S., Kurtasanova E.S., Khruleva G.Kh. 2021 / Practical medicine
RUS2124800-2 from 03/20/2020
Consequences
One of the most common consequences of an ectopic pregnancy is further infertility. The ability to conceive and bear a child is reduced by 40%, so a woman still has a chance to give birth to a child. But the risk of recurrence of an ectopic pregnancy remains high.
During the first month, the woman’s health is restored. During this period, she needs the support of family and friends, as well as the help of a psychotherapist, in order to overcome psychological trauma. Talking to other women who have experienced an ectopic pregnancy will help.
What could be the consequences?
The most common consequences are repeated ectopic pregnancy and infertility. The risk of infertility is high in patients with a removed fallopian tube. In addition, the likelihood of infectious diseases of the genital organs and the formation of adhesions increases.
Rehabilitation lasts 2–3 months and may consist of antibacterial therapy, diet therapy, and physiotherapeutic methods. Physiotherapy (electrophoresis, galvanization, ultrasound therapy) improves the patency of the fallopian tubes, avoiding the development of infections and the formation of adhesions.
Consequences for the body and prevention
After the first ectopic pregnancy, there remains a risk of repeated cases of this pathology. True, the probability that a subsequent pregnancy will also be ectopic is only 20% of all cases, while the probability that the pregnancy will proceed normally remains within 50%.
Timely treatment of inflammatory processes occurring in the pelvic organs is very important for preventing the possible development of ectopic pregnancy. Even when planning the desired pregnancy, both partners must undergo smears for urogenital infections. Do not forget about contraception, because abortion is one of the main reasons for the development of ectopic pregnancy.
How to recover quickly
After treatment for an ectopic pregnancy is completed, the woman needs time to fully recover. We are talking not only about physical, but also about psychological health, because a woman needs to come to terms with the fact that she has lost her child. Fortunately, there are proven ways to speed up the rehabilitation process. Below are step-by-step instructions that will help with this. Study remedies for seborrhea of the scalp at the link.
Table. Methods of recovery after ectopic pregnancy.
| Steps, photo | Description of actions |
| Do an online search for different treatments for ectopic pregnancy. In addition to laparoscopy, salpingostomy can also be used. Find out more information about these procedures and the possible consequences for your body. Also find out about the features of recovery after a particular treatment method. | |
| The attending physician is the person to whom you should turn for advice and help first. Only he can prescribe certain medications or procedures that will speed up the recovery process, depending on the type of treatment for the ectopic pregnancy. As practice shows, recovery after laparotomy can last 5-6 months, and after surgical laparoscopy – no more than 4 weeks. | |
| Emotional recovery is also considered an important part of recovery after the procedure, so you need to talk to someone about what happened. It's best if it's a boyfriend or spouse, although women often prefer a heart-to-heart conversation with their close friends. Regular, frank conversations will help you cope with your surgery. | |
| Regular participation in active sports will help you take your mind off the problem and restore your energy supply. Doctors also recommend doing yoga or meditation for mental relaxation. This will help clear your mind of negative thoughts and plunge headlong into the world of sincerity, happiness and love. But before engaging in any sport, you should consult a doctor. He will tell you when you can start training. | |
| If, after suffering an ectopic pregnancy, you want to become pregnant again, you should definitely talk to your doctor before doing so. After a complete examination, he will be able to tell when your body is ready for this. He will also advise on risk factors that could cause this deviation to recur. First of all, this concerns bad habits, pelvic inflammation and endometriosis. |
Visualization technique
Ultrasound is the imaging modality of choice for women with symptoms of VD. Ideally, pelvic ultrasound for these patients includes both transabdominal and transvaginal assessment. Transabdominal assessment (Fig. 1A, B) is performed using a low mid-frequency transducer (1-5 MHz) after adequate bladder filling. It includes a wider field of view of the pelvis and provides better visualization of the uterine fundus and superiorly positioned adnexa. It can also be used to visualize free fluid or hemorrhage in the abdomen.
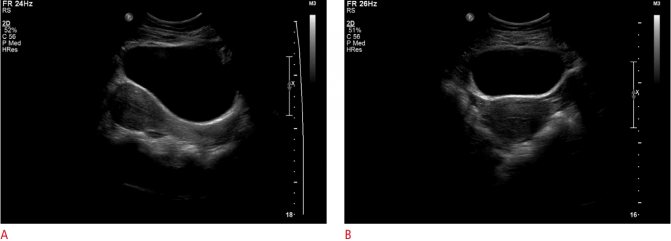
Figure 1: A, B. Transabdominal sagittal and transverse views of the pelvis showing a normal uterus and bladder.
Transvaginal examination (Fig. 2A, B) is performed using a high-frequency intravaginal probe (> 7 MHz) after urination. It provides excellent near-field resolution, allowing detailed assessment of the endometrial cavity. Transvaginal ultrasound also provides a more detailed assessment of the ovaries and other adnexal structures.
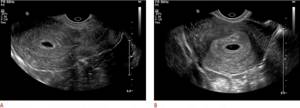
Figure 2: A, B. Transvaginal sagittal and transverse views allow better visualization of the endometrium. The intrauterine gestational sac is visible with the yolk sac.
Ultrasound results after treatment
Methotrexate has been shown to be a safe and effective treatment for ectopic pregnancy. After treatment with methotrexate, ultrasound is indicated only if tubal rupture is suspected based on persistent clinical symptoms or hemodynamic instability. Sonographic findings after medical treatment can be misleading, as there is often a paradoxical increase in ectopic pregnancy due to bleeding and swelling after treatment (Fig. 10A, B). An ectopic mass/hematoma may be visible more than 2 months after treatment. In the context of clinical improvement and a corresponding decrease in β-hCG levels after medical treatment, these sonographic findings usually represent the expected resolution of the ectopic pregnancy.
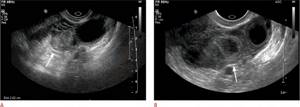
Figure 9: Sonographic findings after treatment with methotrexate. This is a 31-year-old woman with a positive but declining beta human chorionic gonadotropin level. A. There is a heterogeneous echogenic mass in the left adnexa (arrow) adjacent to the left ovary (open arrow). The patient was diagnosed with a left tube ectopic pregnancy and was started on methotrexate. B. On a follow-up pelvic ultrasound 10 days after starting methotrexate treatment, there is an increase in the left tube ectopic pregnancy interval (arrow) due to surrounding bleeding and swelling.
Etiology of occurrence
In the vast majority of cases, ectopic pregnancy develops due to narrowing of the lumen of the tubes and disruption of their patency. The following factors can lead to this:
- untreated chronic inflammatory processes occurring in the pelvic organs;
- infectious diseases of the pelvic organs;
- history of abortion;
- malformations of the fallopian tubes;
- progressive endometriosis;
- benign and oncological neoplasms in the tubes;
- complications of previous births in the form of an inflammatory process, which could lead to the formation of adhesions;
- intrauterine contraception for a long time;
- surgical and gynecological interventions.