The rhythm of modern life has a direct impact on people's sense of self. Aspects such as physical inactivity, urbanization, deterioration of the environment, diet and nutritional quality increase the number of vertebro-neurological lesions. Population aging in developed countries is no less important. In elderly people, the frequency of detection of degenerative-dystrophic processes has increased to 60-70%.
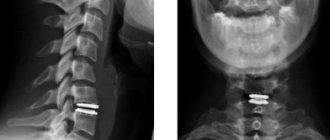
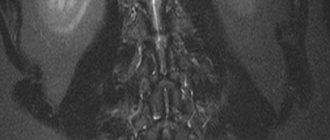
The structure of the thoracic spinal column is unique. He is less mobile than the others. At the same time, the load on it is higher, since the ribs are located in this segment. They are attached to 12 vertebrae, the bodies of which are wider and thicker than the others. Pathologies of this anatomical region are associated with injuries, the development of neoplasms and inflammatory diseases. Damage to solid structures is visualized using radiography in two or three projections or CT. It is highly sensitive to detecting any changes in bone and cartilage structures. It has proven itself well for injuries, fractures, dislocations, hematomas and hemorrhages. If a person has neurological symptoms, an MRI of the thoracic spine is necessary.
What is MRI screening?
Magnetic resonance imaging is a high-tech, clarifying method for studying all body systems. It is required if the first choice methods are not sensitive enough. The study has been used in clinical practice for more than twenty years. A colossal amount of research with a high level of evidence has been accumulated on its safety for the body.
The diagnostic principle is based on the use of the nuclear magnetic response of hydrogen atoms in the human body. Under the influence of a constant high-intensity magnetic field generated by the coils, the atomic nuclei begin to induce energy. The detector picks it up. Based on the data obtained, the tomograph displays layer-by-layer thin-section images of the studied area on the monitor. With their help, a three-dimensional model of the object is built.
Due to technical features, MRI better visualizes the soft tissue structures of the body: nerves, spinal cord, spinal membranes, adipose tissue, muscles and fascia, cartilage formations.
What will an MRI of the spine show?
Deciphering the tomography of the spine will allow:
- Assess the condition and anatomy of vertebral structures.
- Identify congenital anomalies and pathologies.
- Diagnose degenerative diseases of the spine.
- Assess the level of compression of nerves and spinal cord.
- Determine the presence of neoplasms and infections.
- Detect inflammatory processes, damage to blood vessels and spinal membranes.
- Identify areas of injury, as well as changes that occurred after surgery or medical intervention.
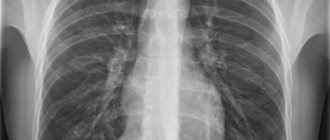
What does the spine look like on MRI images?
Advantages of this technology
She happens to be:
- Non-radiological, that is, it does not exert radiation ionizing load on the body. Therefore, unlike CT, it does not require a recovery period and can be performed as often as necessary.
- Non-invasive - does not require damage to the skin and mucous membranes. This technique does not cause discomfort and eliminates iatrogenic injuries.
- Painless.
- Highly informative;
- Available for use in pregnant women and young children.
Contraindications
Usually your primary care physician or neurologist will be able to tell you whether an MRI of your spine is necessary. This procedure is absolutely safe and painless. But you need to understand that, like any other diagnostic method, it has its contraindications. This type of examination cannot be carried out:
- In the presence of metal-containing implants - prostheses, pins, clips, shunts.
- If there are electronic devices and pacemakers in the body, for example: cochlear implants, insulin pumps, cardiac pacemakers.
- If the patient’s body contains large metal elements - fragments, bullets.
If you do not know the composition of metal structures in the body, you should undergo radiography before diagnosis. It will show whether there is a metal component in the inclusions. Contrast-enhanced spinal tomography should not be performed on pregnant women. Before undergoing a contrast study, you should consult with your doctor if you have asthma, kidney failure, or allergic reactions to any medications. Sometimes these conditions may be a contraindication to MRI of the spine with contrast. If you have any doubts about the possibility of conducting an MRI examination when making an appointment for diagnostics, you can always clarify all questions with your doctor. We will help you find the best diagnostic solution for your individual case.
Indications for diagnosis
The reason for the research is:

- Pain syndrome radiating to the sternum, under the shoulder blade, shoulder, kidneys, abdominal region, ribs; Radiculopathy;
- Compressive myelopathy; Paraparesis of a spastic nature; Loss of sensitivity;
- Functional disorders of visceral organs: bronchopulmonary system, trachea, duodenum;
- Paresthesia; Thoracalgia; Intestinal motility disorder; Angina pectoris of unknown origin; Intercostal neuralgia;
- Difficulty breathing; Local swelling; Hyperemia; Restriction of natural mobility; Deformations, asymmetry of the musculoskeletal system, violation of statics;
- Muscle spasms in the spinal region; Hump, pathological kyphosis and lordosis.
Scanning is required during the period of preoperative preparation and after radical treatment to assess its quality and the degree of recovery of the body. It is indicated to prevent complications. Allows timely adjustment of therapy.
Interpretation of MRI of the spine
The result of spinal tomography is a series of tomographic images that are interpreted by a radiologist. He compares the anatomical features of the spine under study with the norm and notes all deviations in his conclusion. The decryption procedure takes on average 40-60 minutes. Upon completion, the patient receives the entire package of documents - MRI images recorded on electronic or film media, a written report from a radiologist and recommendations for further steps. The patient should contact his or her physician with the results of the tomography. His tasks include, based on the summary data of the medical history, initial examination and tomography results, making a final diagnosis and suggesting treatment options.
It is difficult for an ordinary person to independently understand and interpret the results that, after an MRI, will be given to him on a digital medium. Therefore, with the conclusion of the radiologist and the photographs, he should go for a consultation with the attending physician, who will make a final diagnosis based on the summary data of the examination, medical history and tomography data. In our clinic , after an MRI, you can have a free consultation with a neurologist or orthopedist . Doctor
- will answer all questions based on the results of the research and the conclusion received
- Helps explain tomography results without using complex radiological terminology
- will conduct an examination and, if necessary, offer treatment.
Which parts of the thoracic spine are visualized?
The technique shows:
- Injuries and damage to bone elements;
- Position of fragments;
- Severity of lordosis;
- The presence of pathological bends;
- The relative position of the vertebral bodies, their height;
- Protrusion of the fibrous ring;
- Diameter of the spinal canal;
- Circulation of cerebrovascular cerebrospinal fluid;
- Compression of surrounding structures;
- Condition of the facet joints;
- Swelling;
- Rupture of muscle fibers, fascia, ligaments;
- Pinched roots;
- Areas of necrosis, ischemia;
- Localization, stage and size of space-occupying formations.
Computed tomography (CT)
This method is based on measuring the attenuation of X-ray radiation passing through the human body in various projections. A CT tomograph allows you to obtain layer-by-layer thin-section images, eliminating their overlap. Its sensitivity to small changes is at least 10 times higher than that of an X-ray machine. Computed tomography is quick and painless, but it is often not recommended, since X-ray radiation can negatively affect the patient’s body.
However, CT is the leading method for diagnosing diseases of the chest organs (lungs and mediastinum), retroperitoneum, and adrenal glands. CT is better than other methods in identifying stones in the urinary system and assessing destructive changes in bone tumors of any location.
Preparing for diagnosis
No special training is required when examining this area. If Gd drugs are to be administered, then tomography is performed on an empty stomach. The last meal should be no later than 3-5 hours before the scan.

Immediately before the procedure, you will need to fill out a health questionnaire. It must indicate chronic diseases, medications taken, the emotional state of the patient, the presence of implanted devices and prostheses.
It is not advisable to consume large amounts of liquid before diagnosis. This may cause discomfort during the scanning process.
Preparation
Preparation is required only for MRI with contrast: the patient must come for examination on an empty stomach or 6-7 hours after eating. In 30 min. Before the procedure, he is tested for sensitivity to a contrast agent, and then (if the test result is negative) this drug is injected into a vein through a subclavian or ulnar intravenous catheter.
In other cases, the procedure does not require any preparation.
Before entering the room with diagnostic equipment, the patient removes and removes from his pockets all metal-containing objects (watch, telephone, jewelry, dentures, coins, etc.). If the clothes of the person being examined have metal buttons, fasteners, snaps, they are replaced with disposable medical clothing.
How does the procedure work?
A person takes off clothes made from fabrics that contain metal threads in advance. These are mainly modern tracksuits and underwear made of spandex and lycra. You cannot leave wardrobe items with metal fittings. This is necessary to avoid injuries and burns, since under the influence of a magnetic field, ferromagnetic products are attracted to the device, and non-ferromagnetic ones are heated to high temperatures. In order not to change clothes, it is worth dressing in advance in comfortable clothes that do not restrict movement. Electronic devices, telephones, and bank cards will need to be placed in a special cabinet to avoid their demagnetization, reset, or draining the battery.
If the tomography is performed with contrast, then a drug based on a rare earth metal is injected into a vein in the patient’s elbow using a special injector. The substance is called gadolinium. Once in the bloodstream, it improves the clarity of images, visualizing areas with impaired vascular bed or abnormal blood supply.
After this, the subject lies down on a movable table-couch, on which he is fastened with elastic belts. The risk of blind spots – artifacts – becomes lower. This helps to remain motionless for a significant time, because the procedure is long. Its duration is from half an hour to 90 minutes, depending on the difficulty of making a diagnosis.
The couch is placed in the tomograph tube or rolled under the emitter of an open device. During operation, magnetic coils produce characteristic unpleasant sounds. To prevent them from disturbing the patient, it is better to use headphones or earplugs.
During scanning, personnel are located in a separate shielded room. Communication with diagnosticians is maintained using a signal bulb. By pressing on it it is easy to stop the examination.
After the check is completed, the person can go about his business. He does not need additional medical supervision. The exception is situations where the examination was carried out using general anesthesia. In this case, the anesthesiologist observes the patient’s condition, his cardiac and respiratory activity for 30-60 minutes.
Features of the procedure
How is an MRI of the thoracic spine performed?
The patient is instructed in advance. He is informed about the nuances of the procedure. The nurse in the diagnostic room reminds that the person being examined must remove all objects containing metal. Often a person will have to remove almost all of their clothing and put on a disposable shirt, specifically designed for undergoing an MRI of the thoracic spine and lungs.
The medical staff warns about the noise made by the device. During operation, various knocks and hums are heard. To reduce discomfort during the examination, the client is offered earplugs or headphones.
We recommend
Anti-wrinkle facial massage: 10 effective techniques Read more
A prerequisite for obtaining reliable results is complete immobility during the procedure. Otherwise, the information content of the study will be significantly reduced, since the resulting images will be of poor quality, which is why a repeat MRI will be prescribed.
After instructions, the subject goes to the office where the device is located.
The tomograph is equipped with a movable couch on which the patient sits comfortably, lying on his back. To immobilize the client, he can be secured with specially designed belts and bolsters.
After all the necessary preparations, the couch is sent into the tomograph tunnel. If an examination is planned using an open device, the couch is moved in such a way that the top of the tomograph is hung above the person’s chest area.
Even if the patient has signs of claustrophobia, he is quite comfortable with this position of the device, due to the large distance between the upper part of the mechanism and the body. The head and limbs are located outside.
There is a communication device inside the tomograph. It is needed to inform the patient about the progress of the procedure and provide him with complete peace of mind. In addition, the subject can ask the nurse to end the session at any time. Sometimes this happens due to sudden panic attacks or other unforeseen situations.
The duration of an MRI session of the thoracic spine is about 20 minutes. If a contrast agent is used, the procedure takes approximately 40 minutes.
During this study, the patient does not experience any discomfort or pain. The temperature regime in the tomograph tunnel remains unchanged.
If there is a need for the presence of a loved one in the office for moral and psychological help, this is permitted.
To ensure a detailed study of all tissue structures, the study is carried out in 3 projections (frontal, sagittal, axial). Using this technique, a three-dimensional model of the diagnosed area is built, which allows you to accurately determine the location of pathological processes.
The device produces sections no larger than 4 mm at intervals of 0.5–1 mm, resulting in an accurate search for possible violations, even the most minor ones.
What does tomography reveal?
It can be used to verify:
- Protrusions and intervertebral hernias;
- Dorsopathies;
- Fracture, including pathological and compression;
- Dislocations and subluxations of the vertebrae;
- Cracks;
- Bias;
- Radiculopathy;
- Radicular syndrome;
- Structural anomalies;
- Osteochondrosis;
- Osteoporosis;
- Osteoarthritis;
- Spinal tuberculosis;
- Myelopathy;
- Osteochondropathies;
- Osteomyelitis;
- Osteoma, osteosarcoma, chondroma and other neoplasias of malignant and benign origin;
- Secondary foci of cancer, that is, metastases;
- Osteosclerosis;
- Syringomyelia;
- Spondyloarthrosis;
- Spondylosis;
- Hematomyelia;
- Meningomyelitis;
- Rheumatism;
- Encephalomyelitis;
- Abscess;
- Neurosyphilis;
- Schmorl's hernia;
- Degenerative, inflammatory, necrotizing processes;
- Spinal canal stenosis and splitting;
- Pathologies of adjacent vessels and nerves.
What other research may be needed?
In addition to imaging tests, laboratory tests and lumbar puncture are often required. It involves taking cerebrospinal fluid from the subarachnoid space for its subsequent study. It allows you to identify neuroinfections and cancer.
Myelography shows the condition of the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord and its roots. Discography helps to study the integrity of intervertebral discs. Requires administration of contrast. For a comprehensive study of the neuromuscular system of the back, electroneuromyography and EMG are prescribed.
What parts of the spine are examined on MRI?
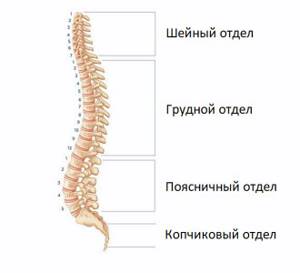
The spine consists of the cervical, thoracic, lumbosacral and coccygeal regions. Each of its segments has its own special properties. For the cervical spine this is flexibility. The ribs are attached to the thoracic vertebrae, forming the rib cage. The lumbosacral segment is capable of supporting a huge weight of several hundred kilograms.
The spine has special properties due to its unique structure. The vertebrae are connected to each other by intervertebral discs and joints, giving a person flexibility. Strength is due to powerful ligaments and tendons strengthened by muscles. The canal formed by the openings in the vertebrae serves as a container for the spinal cord. The spinal cord, in turn, has roots that form nerves that activate muscles and transmit signals to the brain from sensory endings in all organs and tissues.
Previously, due to such a complex structure of the spine, doctors had to have several diagnostic methods. Radiography has been used to diagnose bone pathologies. There were separate methods for studying the spinal cord, which were sometimes painful and dangerous. MRI can diagnose all possible back diseases at once.
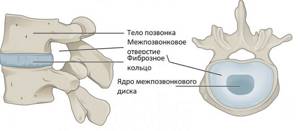
MRI is prescribed to examine all parts of the spine, starting from the neck and ending with the tailbone. This is a universal method that can detect any disease with maximum accuracy.
Decoding the results
After the procedure, the diagnostician studies the information received and, based on it, writes an examination report. This takes from 20 minutes to a day, depending on the workload of the medical worker.

The transcript indicates the size and anatomical features of the spinal column and the presence of anomalies. The MRI technician does not prescribe treatment. Diagnosis and selection of therapy is carried out by the attending physician based on the conclusion, taking into account the clinical picture, anamnesis, concomitant diseases and the compatibility of pharmacological drugs.
Interpretation and evaluation of MRI results
All information received is studied by a radiologist. He is the one who deciphers the pictures. In the process of interpreting the results, the specialist determines the indicators of the condition of the spine in the thoracic region. The diagnostician must assess the size and shape of the spinal cord and spinal column. Normally, the spinal cord has clear shapes and is located exactly in the middle. In addition, the doctor determines its width. If this indicator is increased, an intramedullary tumor will most likely be diagnosed. Next, the subarachnoid space is analyzed for the presence of syndromes such as “crescent” or “linear stripe”. They may indicate a hemorrhage in the spinal cord.
To more accurately determine the location of pathological processes in the obtained images, the diagnostician examines the second and fifth cervical vertebrae, since other areas of the thoracic region cannot act as landmarks for identifying the location of the tumor, the site of the localization of the inflammatory process, etc.
In addition to the above disorders, MRI images show places of deposition of calcifications (calcium salts) and petrification in the soft tissues.
What contraindications exist for scanning?
Insurmountable obstacles are:
- The presence of complex medical devices in the body: pacemakers, ferromagnetic implants, insulin pumps, and so on. The influence of a magnetic field can damage the device beyond repair or cause a deterioration in the patient’s condition, even leading to death.
- Metal pins, vascular clips, implants, fragments, foreign objects, Ilizarov apparatus. They are able to heat up or move under the influence of the tomograph
Relative contraindications include:
- Body weight exceeding the load-bearing capacity of the couch. Typically, the permissible weight is 150-200 kilograms, depending on the model of the device. For people with unusual height or weight, it is better to choose open appliances;
- Pregnancy in the first 12 weeks. Today there is no reliable information about the effect of MRI on the fetus during the period of active embryogenesis;
- State of alcohol or drug intoxication.
Tattoos made with ink containing metal particles can make visualization difficult and contribute to the creation of blind spots-artifacts.
Indications for the introduction of sedation or anesthesia are when a person is unable to remain motionless for a long time. This:
- Psychoneurological diseases in a state of exacerbation;
- Hyperkinetic syndrome;
- Severe acute pain;
- Panic disorders;
- Cardioneurosis;
- VSD;
- Claustrophobia;
- Newborn and younger children.
When studying with contrast, you need to take a biochemical blood test 1-2 weeks in advance. Indicators such as glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and creatinine level (CREA) should be checked. This will help prevent a rare complication - contrast-induced systemic fibrosis. In addition, the paramagnetic is not administered when:
- Hepatic and cardiac dysfunction;
- Decompensated form of diabetes mellitus;
- Bronchial asthma in the acute stage;
- Allergies to components of paramagnetic substances;
- Pregnancy at any stage. The drug is able to penetrate the placental barrier. Recent studies have shown its ability to accumulate in the pituitary gland. However, there is no reliable information about how this will affect the child’s health in the future.
When breastfeeding, lactation will have to be interrupted for two days until Gd is completely eliminated from the body.
Tomography procedure
Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine does not require preparation. The patient simply needs to sign up for the examination in advance and arrive at the medical center 15 minutes before the start of the examination to complete all the documents. You can undergo diagnostics in your own clothes. For a visit to the MRI center, it is best to choose clothes that are comfortable for lying down for a long time and do not restrict movement. There should not be any metal elements on it, for example: zippers, rivets, buttons, rhinestones. Before the scan begins, the patient will be asked to remove all metal from the body and remove all electronic devices from their pockets.
In the diagnostic room, the patient will be helped to take a horizontal position on the tomography table. A special MRI coil will be installed in the examination area. The table is then slid into the scanner. The operator will leave the room and launch the scanning program in the control room.
The patient will understand that the tomograph has started working by the noise of the operating machine. This will be the sounds of periodic tapping. If this noise annoys a person, they will be offered special noise-canceling headphones. During the procedure, two-way communication is maintained with the subject. He can report his discomfort at any time via the microphone inside the tomograph. The operator will immediately stop the scan and try to remove the cause of the discomfort.
The duration of examination of one part of the spine is on average 10-20 minutes. All this time, the person being diagnosed must remain motionless. Any movement can cause the final tomograms to have artifacts. This will reduce the information value of the images.
Questions about diagnostics
Dress code
You can enter the MRI room in any clothing that does not contain metal. When going to the clinic, it is best to wear loose, non-restrictive clothing without metal elements (zippers, rivets, hooks), in which you can lie comfortably. For women, we recommend bringing a T-shirt or not wearing a bra with metal wires or hooks.
Preparation
This tomography does not require any preparatory steps from the patient.
Is MRI harmful to health?
MRI is a completely harmless diagnostic method for the human body. This method of examination can be carried out at any age and for any disease an unlimited number of times, unless you have contraindications.
Contraindications
Some pacemakers and foreign objects in the body may pose serious limitations to tomography. In particular, cochlear implants, vascular clips, stents, heart valves and insulin pumps, pacemakers, neurostimulators, steel screws, staples, pins, plates, joint endoprostheses may be a contraindication to diagnosis. The patient must notify the radiologist about all implanted objects in the body. The diagnostician will be able, based on information about the composition and model of the implant, to assess the possibility of conducting diagnostics.
If you are having an MRI with contrast, be sure to report any allergies to medications or kidney problems. It is also necessary to inform the radiologist about a possible pregnancy.
Is it possible to do an MRI with braces and dental implants?
Dental implants and crowns are not a contraindication to magnetic resonance imaging. The magnetic field does not have any negative effect on them. Fixed brace systems can produce artifacts on tomograms during MRI of the head. If the light effect is too strong, the doctor will stop the study and offer the patient alternative diagnostic methods.
Is the device noisy?
Any MRI machine in working condition makes noises reminiscent of tapping. The open tomograph is one of the quietest installations. The noise from its operation is significantly lower compared to closed tomographs. If the sounds of the operating unit cause you anxiety, you will definitely be offered special noise-canceling headphones.
What should I do if I have claustrophobia?
An open tomograph is the optimal solution for patients suffering from panic attacks in a closed space. It is open on the sides on three sides and does not create a claustrophobic feeling.
Can I take sedatives before an MRI?
If you are a little nervous, before the tomography you can take mild sedatives, for example, valerian, motherwort infusion or afobazole. Taking sedatives does not have a negative impact on the quality of MRI.
Why is it important not to move during the test?
Any movement during the examination reduces the quality of the resulting images. Multiple motion artifacts may appear on the images, and the MRI results will be uninformative.
Can I do the research with an accompanying person?
Absolutely yes. You can invite any accompanying person from among your family and friends to the MRI room. It is important that your companion does not have metal implants or artificial pacemakers in his body.
How much does the examination cost?
The price varies from 2200 to 11000 rubles. It depends on the policy of the medical center, the tomograph model, and the need for additional manipulations.
The easiest way to see how much an examination at a selected institution will cost is in the price list on the main page. There are two amounts indicated there: the first is native, that is, standard tomography, the second is a study with paramagnetic preparations.
Here you can find information about benefits and current promotions. And by booking a ticket through the service, our visitors will receive a discount of up to 1000 rubles.
Which tomograph is best for MRI of the spine?
| OPEN TYPE MRI | SEMI-OPEN MRI | CLOSED MRI |
The quality of magnetic resonance imaging of the spine depends on three factors:
- tomograph power;
- personnel qualifications;
- application of contrast.
In medical centers in St. Petersburg, you can undergo examination using open and closed type devices.
Open-type devices are low-field tomographs with an induction force of 0.2-0.5 Tesla. Diagnostics on them takes place in comfortable conditions for the patient, however, the scanning power of these machines is lower than that of closed-type devices. These devices will cope well with the diagnosis of degenerative changes in the spine - hernias, protrusions, spondylosis, osteochondrosis. If there is a suspicion of tumor lesions or demyelinating diseases, magnetic resonance imaging of the spine should be performed using closed tomographs. The closed-circuit device is a cylindrical tube into which the patient is placed for the duration of the study. It allows you to create a strong magnetic field, and the quality of the resulting images will be maximum. This level of detail will make it possible to identify space-occupying formations and foci of demyelination up to 1 mm in size. The final decision on the model and type of tomograph should be made by the attending physician. Based on the initial diagnosis, he will be able to indicate the minimum thermal power of the installation in his direction for MRI. If the patient independently decides to undergo diagnostics for preventive purposes, you can begin your diagnostic journey with an inexpensive open-type MRI or a high-field 1.5 Tesla unit. It is reasonable to resort to an expensive examination with 3 Tesla tomographs if you have serious medical conditions or are undergoing complex spinal surgery. Author: Belik Ekaterina Mikhailovna
Radiologist with 19 years of experience
How to book a ticket for MRI diagnostics
Using the portal, it is easy to choose a medical center that meets your requirements. The service is designed to help patients, so its services are free. The site contains:
- Contact information, location, telephone numbers, clinic opening hours;
- Directions to the institution of interest;
- Number of coupons available for registration;
- Infrastructure: ramps, elevators, cooler, waiting area and other important advantages;
- Availability of nearby parking for car owners;
- Information for people with limited mobility about the provided comfortable accessible environment;
- Possible payment methods;
- Technical characteristics of the devices: tunnel type, load capacity, magnetic field indication power;
- Qualification, work experience, experience of diagnosticians and doctors;
- Current, constantly updated rating;
- Reviews from those who have already undergone scanning at this institution.

Operators accept calls from 8:00 to 24:00. They will tell you in detail how to prepare for the procedure. Our portal works only with verified licensed clinics. All medical centers have the necessary documents and adhere to legal, medical and ethical standards.
You must have with you a passport or other identification document, the results of previous hardware tests, and a referral from a doctor, if available.
results
At the end of the study, the radiologist who monitored the MRI proceeds to write a report-conclusion. As a rule, the conclusion is given to the patient within an hour, but in rare difficult cases it is ready only the next day.
The patient gives this conclusion, together with the images obtained during MRI and copied to a disk or other electronic device, to the doctor who referred him for examination (neurologist, neurosurgeon, oncologist, vertebrologist or traumatologist).