- How do cancer cells differ from normal cells?
- What are the causes of cancer cells?
- What are the types of cancer genes?
- Basic characteristics and structure of cancer cells
- What do cancer cells look like under a microscope?
- How do cancer cells develop, what stages do they go through in their development?
- Eliminating cancer cells: what helps destroy them?
Cancer cells are often figuratively called rebel cells or cells with antisocial behavior. They “live for themselves,” regardless of the interests of their neighbors and the entire organism: they multiply uncontrollably, do not respond to molecular signals from the outside, do not perform useful functions, and can move around the body at their own discretion. When there are enough of them, they form a malignant tumor, and a person is diagnosed with cancer.
How do cancer cells differ from normal cells?
In order for the human body to work correctly as a single whole, each cell in it must obey general rules and have certain fundamental properties:
- be in its designated place: this is ensured due to cell adhesion, that is, the ability of cells to “stick together” with each other;
- reproduce only when necessary;
- specialize in performing certain functions: for this, each cell consciously limits itself, activates some genes and “turns off” others;
- “repair” your DNA if “breakdowns” or mutations have occurred in it;
- commit “suicide” if irreparable pathological changes have occurred in her, or if she has “gone old”.
In many ways, these functions are provided due to the fact that cells in the body constantly “communicate” with each other and respond to certain signaling molecules. The cancer cell ignores these signals. She begins to live as if she were alone here and should not take into account the interests of her neighbors:
Doesn't stop reproducing. No matter how many copies of itself a tumor cell creates, it will not stop. A malignant tumor constantly grows and spreads in the body.
Does not stick to neighboring cells. On the surface of the “rebels,” the molecules that keep them in the right place among their neighbors disappear. Due to this, the cancer cell can break away from the primary tumor and travel throughout the body. During this journey, it dies or settles in some organ, creates its own clones and forms a new tumor focus - metastasis.
They don't specialize. The cancer cell does not become specialized and does not perform functions useful to the body. The process of cell specialization is called differentiation. The lower the degree of differentiation, the more aggressive the cancer behaves.
They do not “repair” their DNA. As a result, more and more mutations accumulate in tumor cells, they become less differentiated and multiply faster. They are not subject to apoptosis - programmed cell death.
In precancerous conditions, cells also lose their normal properties. But they also differ from cancerous ones, primarily in that they cannot spread in the body. A special type of malignant tumor is the so-called “cancer in situ”. The cells are already cancerous, but have not yet spread beyond their original location. Carcinoma in situ is not technically cancer, but it is generally considered to be the earliest stage of cancer.
Shifts in the formula as health status changes
If the bone marrow contains 1% blasts, this is a standard indicating that everything is fine with the body. A result of 5% to 10% is not normal, but it is not yet an indicator of a specific hematological disease.
Blasts in the bone marrow in such quantities can be either as a result of severe stress or as a consequence of an acute infectious process.
If blast cells in the bone marrow are found in an amount of more than 10%, this is a reason for the doctor to diagnose leukemia.
However, such a diagnosis is made based on a combination of factors:
- low red blood cells, platelets and hemoglobin;
- high white blood cells;
- the presence of blast cells in the bloodstream;
- the presence of blasts in the bone marrow in an amount of more than 10%.
It is important to note that the test to determine the number of immature blood cells is not done independently; As a rule, it is referred to it by a doctor - a therapist or hematologist - if there are compelling reasons. For example, if a patient during an examination presents complaints that could lead to a diagnosis of leukemia, the doctor may refer such a patient for analysis, where they will determine whether his level of blast cells in the blood is exceeded.
What are the causes of cancer cells?
Why cancer cells appeared in the body of a particular person is largely a rhetorical question.
Every living cell functions and reproduces in accordance with the genetic information contained in it. When certain mutations occur, these delicate regulatory mechanisms become disrupted, and malignant degeneration can occur.
It is difficult to say what exactly led to such mutations in each specific case. Modern doctors and scientists know only risk factors that increase the likelihood of malignant degeneration and development of the disease. Here are the main ones:
- Unfavorable environmental situation.
- Smoking.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- Occupational hazards, contact with carcinogenic substances and various radiations at work.
- Obesity, overweight.
- Ultraviolet radiation from the sun and solariums.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Age: Mutations accumulate over time, so older people are more likely to develop cancer cells in the body.
- Unhealthy diet: Predominance of animal fats, red and processed meats in the diet.
None of these factors leads with a hundred percent probability to the development of a malignant tumor.
References
- Jean, G., Lafage-Proust, M., Souberbielle, J. et al. Severe secondary hyperparathyroidism in patients on haemodialysis is associated with a high initial serum parathyroid hormone and beta-CrossLaps level: Results from an incident cohort. PLoS One, 2018. - Vol. 13(6).
- Brunova, J., Kratochvilova, S., Stepankova, J. Osteoporosis Therapy with Denosumab in Organ Transplant Recipients. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2021. - Vol. 9. - P. 162.
- Markus, J. Biochemical Markers of Bone Turnover Part II: Clinical Applications in the Management of Osteoporosis. ClinBiochemRev., 2006. - Vol. 27(3). — P. 123-138.
- Zhao, Y., Song, Y., Zhang, L. Association between bile acid metabolism and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. Clinics (Sao Paulo), 2021. - Vol. 75.
What are the types of cancer genes?
Not all mutations are equally dangerous. Cancer is caused by those that occur in certain genes:
Oncogenes activate cell reproduction. Malignant degeneration occurs when they become too active. An example is the gene that encodes the HER2 protein. This receptor protein is located on the surface of the cell and causes it to multiply.
Tumor suppressor genes inhibit cell proliferation, repair damaged DNA, and cause apoptosis—programmed cell death. Examples of such genes: BRCA1, BRCA2, TP53 (encodes the p53 protein - the “guardian of the genome”, which triggers apoptosis in damaged cells).
Mutations that lead to cancer can be hereditary (occur in germ cells) or somatic (occur in body cells throughout life).

Basic characteristics and structure of cancer cells
Cancer cells have three fundamental characteristics that make cancer so dangerous:
- The ability to reproduce uncontrollably.
- The ability to invade - to grow into surrounding tissues.
- The ability to metastasize - spread throughout the body and form new foci in various organs.
Not every tumor cell is cancerous. Cancer or carcinoma are malignant tumors of epithelial tissue that lines the skin, mucous membranes of internal organs, and forms glands. Sarcomas develop from connective tissue (bone, fat, muscle, cartilage, blood vessels). Malignant diseases of the hematopoietic organs are called leukemia. Tumors from cells of the immune system - lymphomas and myelomas.
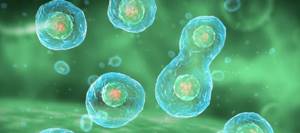
What do cancer cells look like under a microscope?
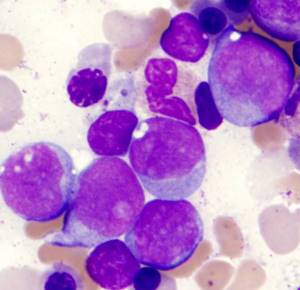
In short, they are very different from the normal ones that a pathologist expects to see when he examines a piece of tissue under a microscope. Cancer cells are larger or smaller, irregular in shape, and have an abnormal nucleus. If normal cells in one tissue are all approximately the same size, then cancer cells are often different. The nucleus contains a lot of DNA, so it is larger (its size is also variable), and when stained with special substances it looks darker.
Normal cells form certain structures, such as glands. Cancer cells are located more chaotically. For example, they form distorted, irregularly shaped glands or strange masses that do not look like glands at all.
Blast cells: their number and condition in a healthy body
When a person has not been diagnosed with any disease, there is no stress, no infectious diseases or other factors, the following occurs:
- blast cells are completely absent in the bloodstream;
- in the bone marrow they are recorded in no more than 5% of the total number of cells.
Let us repeat: normally, blast cells should be completely absent in a blood test; “0%” should be written on the result form. Even a small number of blasts in the bloodstream is a very serious reason to consult a doctor and conduct additional research.
How do cancer cells develop, what stages do they go through in their development?
Cancerous tumors grow due to the division of cells that are part of them. During division, a malignant cell forms two copies of itself, thus growing exponentially. For example, it takes about 30 doublings to form a 1 cm tumor. After 40 doublings, the neoplasm reaches a weight of 1 kg, and this size is considered critical and fatal for the patient.
According to modern concepts, so-called tumor stem cells are responsible for the growth of a malignant tumor. They actively divide, while other tumor cells simply exist. Modern scientists are busy searching for treatments that target these stem cells.
The doubling time of tumor cells varies. For example, with leukemia this happens in 4 days, and with colon cancer - in 2 years. It takes a long time for the tumor to become large enough to cause any symptoms. For example, if a cancer patient began to have some complaints, and after that he lived for a year, probably the tumor in his body had already existed for about three years at the time the complaints appeared, he just did not know about it.
While the cancerous tumor is small, it has enough oxygen. But as she grows, she increasingly experiences oxygen starvation - hypoxia. To meet their needs, tumor cells produce substances that stimulate the formation of blood vessels - angiogenesis.
As the tumor grows, invasion occurs—the spread of cancer cells into surrounding tissue. They produce enzymes that destroy normal cells.
Some of them break off from the mother tumor, penetrate the blood and lymphatic vessels, and form secondary foci in them - metastases. This is the main danger of malignant tumors. It is metastatic foci that cause the death of many cancer patients.

Preparation for analysis for the presence of blasts in the blood
To ensure that the analysis result is not distorted and does not have to be retaken, it is recommended to follow a few simple rules:
- the last meal should be 8 hours before the test;
- the day before the study you should not drink any alcoholic beverages;
- 2 hours before the test, eliminate the effects of nicotine on the body;
- It is recommended to stop taking medications 72 hours before the test.

If it is not possible to complete any of the points, you must definitely tell the laboratory assistant who will take your blood.
Tell him about all medications you are taking 3 days before the medication test. If for health reasons you cannot go without food for a long time, be sure to tell the laboratory assistant exactly what you ate. This information will help you correctly adjust the analysis results. They will still most likely be distorted, but the doctor in the conclusion will be able to correctly reflect the information, taking into account the information you provided.