Traditionally, in the 7th week of pregnancy, a woman experiences toxicosis, hormonal changes, a feeling of fatigue and weakness. These are natural changes and there is no need to worry about their origin.
Due to intense blood circulation in a woman’s body and increased levels of the hormone progesterone, urination may become more frequent and some difficulties with bowel movements may occur. Positive aspects include improved hair and skin condition. Which is again due to changes in hormonal levels.
Interesting Facts
| Options | Indications |
| Time from conception | 5 weeks |
| Period by month | 7 weeks |
| What month | 2 |
| Dimensions and weight of the fetus | 5-13 mm, 1.7-2 g |
| Uterus dimensions | Comparable to a duck egg or a woman's fist |
| Pregnant weight | Depends on toxicosis |
Your baby is the size of
Blueberry
5-13mm Size
1.7-2 g Weight
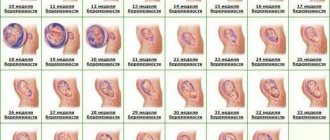
If this is your first pregnancy, and there is a lot of conflicting information around, then you may have a logical question: how long is the seventh obstetric week? This is approximately 1.5 months of pregnancy, the beginning of which is considered to be the first day of the last menstruation. This is the first trimester, the delay in menstruation is 2-3 weeks. If you are interested in the 7th week of pregnancy from conception, you can find information about it on the “Ninth Week of Pregnancy” page of our calendar.
Now you are completely confident in your new position and most likely have already felt all its “charms”: nausea, weakness, dizziness, loss or increase in appetite. What else happens to the baby and mother at this stage? And what can you expect when you visit a gynecologist?
5,6,7,8 weeks of pregnancy: what happens, development of pregnancy and fetus
- home
- Services and prices
- Services and prices
- About Us
- Doctors
- Schedule and appointments
- Reviews
- Doctor training
- Clinic addresses
- Blog
- CIropedia
Week by week 5-8 weeks of pregnancy Elena Gevorkova Obstetrician-gynecologist, Moscow
5th week
BABY
At the 5th week*, an important event occurs - the separation of the body of the embryo from the auxiliary (extra-embryonic) structures - the amniotic bladder, yolk sac and chorion. The process of formation of tissues and organs actively continues: the rudiments of all the main systems of the human body appear.
The size of the embryo is about 1.2-1.5 mm. It is already possible to determine the anterior pole (future head) and posterior pole (future legs). The body of the embryo begins to form according to the “law of symmetry”: a chord is laid along it, which is the axis of symmetry. It is around it that the laying of future organs, which are of a paired nature, occurs. Some of them grow “double” (these are kidneys, lungs, etc.). Other organs are formed from the fusion of symmetrical rudiments (for example, the heart and liver).
During this period, the embryo is curved and similar in shape to the letter “C”. In the very center of the embryo, the heart is formed, which begins to pulsate by the end of the 5th week of pregnancy. From the cells of the mesoderm (middle germ layer) the liver, pancreas, thyroid gland, lungs, as well as the larynx and trachea begin to form.
The central nervous system also begins its formation at the 5th week. The neural tube closes: flat cells begin to twist into a hollow tube. This is a very important process, since the viability of the embryo depends on the complete closure of the tube. Folic acid plays an important role during this period, promoting high-quality closure of the neural tube. Taking folic acid supplements is recommended when planning pregnancy and throughout the first trimester, but it is especially important to take it during the formation of the neural tube, i.e. at 5-7 weeks of pregnancy. The development of the neural tube is closely related to the formation of parts of the brain, which are represented by brain vesicles - bulges located along the tube.
Future muscles look like processes (somites) located along the neural tube.
At week 5, another important event occurs in the life of the embryo - the formation of germ cell precursors. At such an early stage of embryonic development, future people already have the rudiments of sperm and eggs.
Future mom
External changes at this stage are minimal: menstruation is delayed by 1 week. If a woman knows about her pregnancy, this can change her emotional state: peace and thoughtfulness appear, or, on the contrary, excessive activity.
From the 5th week, nausea and odor intolerance may occur. Early toxicosis - nausea and vomiting (usually morning) - affects most women. Its manifestations vary - from mild malaise to severe forms with uncontrollable vomiting, requiring hospitalization.
Sensitivity and a feeling of heaviness in the chest are also early signs of pregnancy.
6th week
BABY
By the beginning of the 6th week, the embryo is about 3 mm long, and by the end it reaches 6-7 mm. During this period, it has a cylindrical shape and resembles a fish embryo. Outgrowths appear along the body of the unborn baby - the rudiments of arms and legs. Moreover, the upper limbs grow faster than the lower ones, and by the end of the 6th week the hands are already formed, while the legs remain at the “kidney” stage. At this stage, complete closure of the neural tube and convexity occurs: the brain vesicles form the rudiments of the hemispheres and parts of the brain.
The heart actively pulsates and continues to develop, meanwhile, processes of division into chambers - atria and ventricles - take place inside it. The contraction of a tiny heart can already be detected using sensitive ultrasound equipment. The heart rate averages from 100 to 160 beats per minute.
The formation of the digestive tube is marked by the formation of various sections - the stomach, small and large intestines.
The gonads continue to develop and ureters are formed. An important event of the 6th week is the laying of the future placenta - the formation of chorionic villi. During this period, active growth of blood vessels and trial “training” of the placenta occurs. As an organ, the placenta has not yet been formed and does not perform its main functions, but the “first steps” are already taking place - this is the exchange of blood between the vessels of the mother and the embryo, a precursor to real blood circulation.
Future mom
At the 6th week of pregnancy, when menstruation is delayed by 2 weeks, the manifestations of early toxicosis may intensify. Nausea is sometimes accompanied by vomiting; if this happens more than 2-3 times a day, you should consult a doctor. The feeling of fullness of the mammary glands may be accompanied by a periodic feeling of tingling: this is how tissues react to fluid retention associated with the fact that due to hormonal changes, a change in vascular permeability occurs. Weakness, fatigue, drowsiness, emotional irritation - all this often accompanies a woman at this stage of pregnancy. It’s all due to hormones trying to provide the best conditions for the baby’s development. Limiting physical activity and stressful conditions, ensuring a good mood are very important at this stage: it has been noted that the severity of toxicosis depends on the initial emotional background.
During this period, the formation of new taste preferences is possible. While trying to ensure a comfortable existence, you should nevertheless adhere to the main principle - common sense. You should not consume harmful foods, no matter how strong the desire (smoking and alcohol, fast food, preservatives, smoked foods, foods containing dyes, etc. are excluded). An important point is to ensure water balance. Insufficient fluid intake can cause relative dehydration of the body, which will only aggravate toxicosis. Water, juices, fruits, and vegetables sometimes become the only possible food for the mother at this stage of pregnancy.
7th week
BABY
The length of the embryo is from 8 to 11 mm, and its weight is less than a gram. The body shape of the embryo at this stage is arched, and its proportions are such that the head is half the size of the entire body. At the lower part of the pelvic end there is a continuation of the coccyx, similar to a small tail.
The 7th week of pregnancy is characterized by intensive development of the arms of the embryo. The hands already have spaces between the fingers, but there is no division into fingers yet. During this period, the formation of the face occurs; a nasal fossa is formed on its surface, from which the nose is subsequently formed. During the same period, the initial development of the auricles from two elevations is observed, and the formation of the upper and lower jaws also begins.
An important event of the 7th week is the formation of the umbilical cord and the circulatory system of the fetus and mother, which, when connected, establish uteroplacental blood flow. From this moment on, nutrition and tissue respiration of the embryo is carried out at the expense of maternal blood. Thus, the baby comes under the protection of the mother’s body, since the chorion (future placenta) serves not only as the delivery of nutrition, but also as a filter - it retains toxins and harmful microorganisms that can have a damaging effect on the embryo.
Future mom
From the 7th week of pregnancy the uterus begins to grow; Your doctor may discover this during a gynecological examination. Many women observe an increase in abdominal volume and happily interpret this situation as a sign of pregnancy. In fact, the size of the uterus and embryo are not so large that it will lead to the growth of the abdomen. Its volume increases due to decreased muscle tone of the anterior abdominal wall and laxity of intestinal loops; The reason for this is the action of progesterone. The resulting bloating leads to bulging of the abdomen, which becomes outwardly similar to a “pregnant” one.
There is an increase in the volume of circulating blood, which is manifested by increased urination. This situation will persist throughout pregnancy, and in later stages it will increase even more. Urination should not be accompanied by pain: you should report it to your doctor. During this period, the situation with bowel function may change: both constipation and diarrhea are possible. Most often this is due to hormonal effects, as well as changes in the usual diet. The activity of the intestines must be strictly “regulated”, since regular bowel movements (preferably daily) ensure the timely removal of waste and toxins from the body, which is extremely important during pregnancy. If you have problems with bowel movements, consult your doctor.
8th week
BABY
By the beginning of the 8th week, the length of the embryo is 15-20 mm, by the end - 40 mm. Its weight is about 5 g. The end of the 8th week of pregnancy is the end of the embryonic period of development and the beginning of the fetal period. From this moment on, the embryo already bears the name of a fetus; that is what he will be called until the moment of birth. The 8th week of embryo development is characterized by intensive growth and change in shape. His body straightens, and more and more clearly there is a division into segments - head, torso, limbs.
This period is marked by rapid development of the nervous system. At the beginning of the 8th week, the division of the brain into sections occurs more and more clearly, the cerebral hemispheres are outlined, and convolutions appear.
The embryo's face becomes more prominent, nostrils, ears, and eyes are formed. By the end of the 8th week, the face is quite clearly formed and the upper lip is completely closed.
A feature of this period is the process of ossification of bones - the upper, lower extremities and skull. The separation of the fingers begins, and the thumb of the hand is already fully expanded and opposed to the palm. The formation of large joints, in particular the elbow and knee, begins.
The active formation of the muscular system and brain structures responsible for muscle tone allows the embryo to perform active movements. By the end of the 8th week, the development of the digestive tract is almost complete, the process of supplying nerve endings to the walls of the stomach and intestines begins (this is necessary for the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract); salivary glands are formed; The formation of the cavities of the heart, kidneys, ureters and bladder is completed.
The intensive development of the vascular system of the future placenta continues. Chorionic villi grow deeply into the wall of the uterus. Now there is a full-fledged uteroplacental blood circulation, the vessels of the umbilical cord are functioning, ensuring an adequate supply of the growing fetus with maternal blood enriched with oxygen and nutrients and removing carbon dioxide and metabolic products from it.
Future mom
At the 8th week of pregnancy, no fundamental changes occur in a woman’s body. Already existing symptoms of toxicosis (nausea, vomiting, fatigue, drowsiness) do not change their intensity, but are tolerated more easily, since by this time pregnant women have time to get used to the new state and understand what exactly provides them with comfort - walks, sleep, specific foods and a certain power mode, etc.
*In this article, gestational age is calculated from the first day of the last menstruation.
What happens to the expectant mother
Symptoms and signs of pregnancy that occurred earlier still persist and sometimes even intensify. All changes in the female body are caused by an increase in the concentration of progesterone.
Increased fatigue
You've probably noticed that you get tired much earlier than usual and want to sleep more often. This is because the lion's share of your energy and nutrients goes to the embryo.
Increased appetite
The reason is the same - a growing fetus requires a lot of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. And therefore, if you do not experience toxicosis, that is, you want more.
Changes in the mammary gland
The volume of the breast increases slightly, the tissue becomes denser, and the areola may darken. Mild pain at 7 weeks is not dangerous.
Frequent urination
It occurs because a woman drinks more fluid, blood flow to the pelvic organs increases, and the growing uterus puts pressure on the bladder. If the urge is not accompanied by pain and a burning sensation, then there is no danger.
Skin rashes
Due to a decrease in estrogen levels in 7 weeks of pregnancy, the secretion of the sebaceous glands of the skin increases. As a result, acne, blackheads and pimples appear. Some people also develop age spots on their face and chest.
The norm of indicators determined by ultrasound. Tables by week of pregnancy
Fetal size by week of pregnancy
| Gestation period (weeks) | Weight, g | Length, cm |
| 8 | 1 | 1,6 |
| 9 | 2 | 2,3 |
| 10 | 4 | 3,1 |
| 11 | 7 | 4,1 |
| 12 | 14 | 5,4 |
| 13 | 23 | 7,4 |
| 14 | 43 | 8,7 |
| 15 | 70 | 10,1 |
| 16 | 100 | 11,6 |
| 17 | 140 | 13 |
| 18 | 190 | 14,2 |
| 19 | 240 | 15,3 |
| 20 | 300 | 16,4 |
| 21 | 360 | 26,7 |
| 22 | 430 | 27,8 |
| 23 | 501 | 28,9 |
| 24 | 600 | 30 |
| 25 | 660 | 34,6 |
| 26 | 760 | 35,6 |
| 27 | 875 | 36,6 |
| 28 | 1005 | 37,6 |
| 29 | 1153 | 38,6 |
| 30 | 1319 | 39,9 |
| 31 | 1502 | 41,1 |
| 32 | 1702 | 42,4 |
| 33 | 1918 | 43,7 |
| 34 | 2146 | 45 |
| 35 | 2383 | 46,2 |
| 36 | 2622 | 47,4 |
| 37 | 2859 | 48,6 |
| 38 | 3083 | 49,8 |
| 39 | 3288 | 50,7 |
| 40 | 3462 | 51,2 |
| 41 | 3597 | 51,7 |
| 42 | 3685 | 51,5 |
Deviation of indicators in a smaller direction is a sign of intrauterine growth retardation; changes in a larger direction are a sign of a large fetus, which will complicate natural childbirth. In such cases, doctors prefer caesarean section.
Head sizes by week of pregnancy
| Gestation period, weeks. | Fronto-occipital size (LZR), mm | Biparietal size (BPR), mm | ||
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 11 | 17 | 13-21 | ||
| 12 | 21 | 18-24 | ||
| 13 | 24 | 20-28 | ||
| 14 | 27 | 23-31 | ||
| 15 | 31 | 27-35 | ||
| 16 | 45 | 41-49 | 34 | 31-37 |
| 17 | 50 | 46-54 | 38 | 34-42 |
| 18 | 54 | 49-59 | 42 | 37-47 |
| 19 | 58 | 53-63 | 45 | 41-49 |
| 20 | 62 | 56-68 | 48 | 43-53 |
| 21 | 66 | 60-72 | 51 | 46-56 |
| 22 | 70 | 64-76 | 54 | 48-60 |
| 23 | 74 | 67-81 | 58 | 52-64 |
| 24 | 78 | 71-85 | 61 | 55-67 |
| 25 | 81 | 73-89 | 64 | 58-70 |
| 26 | 85 | 77-93 | 67 | 61-73 |
| 27 | 88 | 80-96 | 70 | 64-76 |
| 28 | 91 | 83-99 | 73 | 67-79 |
| 29 | 94 | 86-102 | 76 | 70-82 |
| 30 | 97 | 89-105 | 78 | 71-85 |
| 31 | 101 | 93-109 | 80 | 73-87 |
| 32 | 104 | 95-113 | 82 | 75-89 |
| 33 | 107 | 98-116 | 84 | 77-91 |
| 34 | 110 | 101-119 | 86 | 79-93 |
| 35 | 112 | 103-121 | 88 | 81-95 |
| 36 | 114 | 104-124 | 90 | 83-97 |
| 37 | 116 | 106-126 | 92 | 85-98 |
| 38 | 118 | 108-128 | 94 | 86-100 |
| 39 | 119 | 109-129 | 95 | 88-102 |
| 40 | 120 | 110-120 | 96 | 89-103 |
An increased size of the fetal head is a sign of hydrocephalus - an increase in the amount of fluid in the brain. To make such a diagnosis, the ventricles must also be enlarged. Sometimes the pathology is accompanied by other developmental disorders, so additional thorough research is necessary.
Abdominal circumference, fetal head
| Gestation period (weeks) | Abdominal circumference, mm | Head circumference, mm | ||
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 11 | 51 | 40-62 | 63 | 53-73 |
| 12 | 61 | 50-72 | 71 | 58-84 |
| 13 | 69 | 58-80 | 84 | 73-96 |
| 14 | 78 | 66-90 | 97 | 84-110 |
| 15 | 90 | 110 | ||
| 16 | 102 | 88-116 | 124 | 112-136 |
| 17 | 112 | 93-131 | 135 | 121-149 |
| 18 | 124 | 104-144 | 146 | 131-161 |
| 19 | 134 | 114-154 | 158 | 142-174 |
| 20 | 144 | 124-164 | 170 | 154-186 |
| 21 | 157 | 137-177 | 183 | 166-200 |
| 22 | 169 | 148-190 | 195 | 178-212 |
| 23 | 181 | 160-202 | 207 | 190-224 |
| 24 | 193 | 172-224 | 219 | 201-237 |
| 25 | 206 | 183-229 | 232 | 214-250 |
| 26 | 217 | 194-217 | 243 | 224-262 |
| 27 | 229 | 205-229 | 254 | 235-273 |
| 28 | 241 | 217-241 | 265 | 245-285 |
| 29 | 253 | 228-278 | 275 | 255-295 |
| 30 | 264 | 238-290 | 285 | 265-305 |
| 31 | 274 | 247-301 | 294 | 273-315 |
| 32 | 286 | 258-314 | 304 | 283-325 |
| 33 | 296 | 267-325 | 311 | 289-333 |
| 34 | 306 | 276-336 | 317 | 295-339 |
| 35 | 315 | 285-345 | 322 | 299-345 |
| 36 | 323 | 292-354 | 326 | 303-349 |
| 37 | 330 | 299-361 | 330 | 307-353 |
| 38 | 336 | 304-368 | 333 | 309-357 |
| 39 | 342 | 310-374 | 335 | 311-359 |
| 40 | 347 | 313-347 | 337 | 312-362 |
Length of shin bones, femur femur
| Gestation period (weeks) | Abdominal circumference, mm | Head circumference, mm | ||
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 11 | 5,6 | 3,4-7,8 | ||
| 12 | 7,3 | 4-10,8 | ||
| 13 | 9,4 | 7-11,8 | ||
| 14 | 12,4 | 9-15,8 | ||
| 15 | 16,2 | |||
| 16 | 18 | 15-21 | 20 | 17-23 |
| 17 | 21 | 17-25 | 24 | 20-28 |
| 18 | 24 | 20-28 | 27 | 23-31 |
| 19 | 27 | 23-31 | 30 | 26-34 |
| 20 | 30 | 26-34 | 33 | 29-37 |
| 21 | 33 | 29-37 | 36 | 32-40 |
| 22 | 35 | 31-39 | 39 | 35-43 |
| 23 | 38 | 34-42 | 41 | 37-45 |
| 24 | 40 | 36-44 | 44 | 40-48 |
| 25 | 42 | 38-46 | 46 | 42-50 |
| 26 | 45 | 41-49 | 49 | 45-53 |
| 27 | 47 | 43-51 | 51 | 47-55 |
| 28 | 49 | 45-53 | 53 | 49-57 |
| 29 | 51 | 48-55 | 55 | 50-60 |
| 30 | 53 | 49-57 | 57 | 52-62 |
| 31 | 55 | 50-60 | 59 | 54-64 |
| 32 | 56 | 51-61 | 61 | 56-66 |
| 33 | 58 | 53-63 | 63 | 58-68 |
| 34 | 60 | 55-65 | 65 | 60-70 |
| 35 | 61 | 56-66 | 67 | 62-72 |
| 36 | 62 | 57-67 | 69 | 64-74 |
| 37 | 64 | 59-69 | 71 | 66-76 |
| 38 | 65 | 60-70 | 73 | 68-78 |
| 39 | 66 | 61-71 | 74 | 69-80 |
| 40 | 67 | 62-72 | 75 | 70-80 |
Length of the humerus, fetal forearm bones
| Gestation period (weeks) | Abdominal circumference, mm | Head circumference, mm | ||
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 16 | 15 | 12-18 | 18 | 15-21 |
| 17 | 18 | 15-21 | 21 | 17-25 |
| 18 | 20 | 17-23 | 24 | 20-28 |
| 19 | 23 | 20-26 | 27 | 23-31 |
| 20 | 26 | 22-29 | 30 | 26-34 |
| 21 | 28 | 24-32 | 33 | 29-37 |
| 22 | 30 | 26-34 | 35 | 31-39 |
| 23 | 33 | 29-37 | 38 | 34-42 |
| 24 | 35 | 31-39 | 40 | 36-44 |
| 25 | 37 | 33-41 | 43 | 39-47 |
| 26 | 39 | 35-43 | 45 | 41-49 |
| 27 | 41 | 37-45 | 47 | 43-51 |
| 28 | 43 | 39-47 | 49 | 45-53 |
| 29 | 44 | 40-48 | 51 | 47-55 |
| 30 | 46 | 42-50 | 53 | 49-57 |
| 31 | 48 | 44-52 | 55 | 51-59 |
| 32 | 49 | 45-53 | 55 | 52-59 |
| 33 | 50 | 46-54 | 58 | 54-62 |
| 34 | 52 | 48-56 | 59 | 55-63 |
| 35 | 53 | 49-57 | 61 | 57-65 |
| 36 | 54 | 50-58 | 62 | 58-66 |
| 37 | 55 | 51-59 | 63 | 59-67 |
| 38 | 56 | 52-60 | 64 | 60-68 |
| 39 | 57 | 53-61 | 65 | 60-70 |
| 40 | 58 | 54-62 | 66 | 61-71 |
Nuchal translucency (NVP) values in the first trimester of pregnancy
| Gestation period (weeks) | Thickness of collar space, mm | |
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 10 weeks 0 days – 10 weeks 6 days | 1,5 | 0,8-2,2 |
| 11 weeks 0 days – 11 weeks 6 days | 1,6 | 0,8-2,2 |
| 12 weeks 0 days – 12 weeks 6 days | 1,6 | 0,7-2,5 |
| 13 weeks 0 days – 13 weeks 6 days | 1,7 | 0,7-2,7 |
If the nuchal translucency indicators are too high, the woman should consult a geneticist and undergo additional examinations as prescribed by a specialist:
- blood test for alpha fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotropin;
- amniocentesis - study of amniotic fluid;
- placentocentesis - study of placental cells;
- cordocentesis is the study of blood taken from the fetal umbilical cord.
Coccygeal-parietal size values 1st trimester of pregnancy
| Gestation period (weeks) | Coccyx-parietal size, mm | |
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 10 weeks | 31 | 24-38 |
| 10 weeks 1 days | 33 | 25-41 |
| 10 weeks 2 days | 34 | 26-42 |
| 10 weeks 3 days | 35 | 27-43 |
| 10 weeks 4 days | 37 | 29-45 |
| 10 weeks 5 days | 39 | 31-47 |
| 10 weeks 6 days | 41 | 33-49 |
| 11 weeks | 42 | 34-50 |
| 11 weeks 1 days | 43 | 35-51 |
| 11 weeks 2 days | 44 | 36-52 |
| 11 weeks 3 days | 45 | 37-54 |
| 11 weeks 4 days | 47 | 38-56 |
| 11 weeks 5 days | 48 | 39-57 |
| 11 weeks 6 days | 49 | 40-58 |
| 12 weeks | 51 | 42-59 |
| 12 weeks 1 days | 53 | 44-62 |
| 12 weeks 2 days | 55 | 45-65 |
| 12 weeks 3 days | 57 | 47-67 |
| 12 weeks 4 days | 59 | 49-69 |
| 12 weeks 5 days | 61 | 50-72 |
| 12 weeks 6 days | 62 | 51-73 |
| 13 weeks | 63 | 51-75 |
| 13 weeks 1 days | 65 | 53-77 |
| 13 weeks 2 days | 66 | 54-78 |
| 13 weeks 3 days | 68 | 56-80 |
| 13 weeks 4 days | 70 | 58-82 |
| 13 weeks 5 days | 72 | 59-85 |
| 13 weeks 6 days | 74 | 61-87 |
| 14 weeks | 76 | 63-89 |
Normal heart rate by stage of pregnancy
| Gestation period (weeks) | Heart rate, beats. |
| 10 | 161-179 |
| 11 | 153-177 |
| 12 | 150-174 |
| 13 | 147-171 |
| 14 | 146-168 |
A child's normal heartbeat is rhythmic, occurring at regular intervals, clear and distinct. Irregular heartbeats may indicate a congenital heart defect or fetal hypoxia, and a dull sound may indicate intrauterine oxygen deficiency.
If the heart rate exceeds the norm, a diagnosis of tachycardia is possible; if it decreases to 120 or less, a diagnosis of bradycardia is possible. A heart rate that goes beyond normal limits often occurs as a result of a reaction to a decrease in oxygen in the blood - fetal hypoxia. In this case, the woman is prescribed inpatient treatment aimed at improving uteroplacental blood flow and intracellular metabolism.
Normal values for placental thickness per week
| Gestation period (weeks) | Average, mm | Allowable fluctuations, mm |
| 20 | 21,96 | 16,7-28,6 |
| 21 | 22,81 | 17,4-29,7 |
| 22 | 23,66 | 18,1-30,7 |
| 23 | 24,55 | 18,8-31,8 |
| 24 | 25,37 | 19,6-32,9 |
| 25 | 26,22 | 20,3-34 |
| 26 | 27,07 | 21-35,1 |
| 27 | 27,92 | 21,7-36,2 |
| 28 | 28,78 | 22,4-37,3 |
| 29 | 29,63 | 23,2-38,4 |
| 30 | 30,48 | 23,9-39,5 |
| 31 | 31,33 | 24,6-40,6 |
| 32 | 32,18 | 25,3-41,6 |
| 33 | 33,04 | 24,6-40,6 |
| 34 | 33,89 | 25,3-41,6 |
| 35 | 34,74 | 26-42,7 |
| 36 | 35,59 | 28,2-46 |
| 37 | 34,35 | 27,8-45,8 |
| 38 | 34,07 | 27,5-45,5 |
| 39 | 33,78 | 27,1-45,3 |
| 40 | 33,5 | 26,7-45 |
If the thickness of the placenta exceeds the permissible normal values, this may indicate inflammation of the placenta (placentitis).
Normally, the placenta should be attached to the posterior wall of the uterus (rarely to the anterior or fundus). It should be 6 cm or more from the internal os of the cervix. Low attachment, marginal or central presentation with overlap of the internal os is a dangerous pathology that threatens the life and health of both mother and child. It often occurs in women who have given birth repeatedly, terminated pregnancies, or have inflammation or uterine fibroids. In this case, the woman needs careful hospital monitoring or at home with complete rest. With complete placenta previa, the birth of a child is possible only by caesarean section. If it is low, natural birth is possible, but there is a high risk of bleeding.
Degree of maturity of the placenta
| Gestation period (weeks) | Maturity level |
| up to 30 | 0 |
| 30-34 | 1 |
| 35-39 | 2 |
| after 39 | 3 |
The reason for late maturation of the placenta may be smoking by a pregnant woman or the presence of chronic diseases, and premature maturation may be due to gestosis, intrauterine infections, endocrine pathologies, termination of a previous pregnancy, and also smoking.
If such a deviation is detected in a woman, she needs to undergo a Doppler ultrasound and be tested for infections. After which a course of therapy is prescribed aimed at treating fetal hypoxia, vitamin supplementation, reducing uterine tone and getting rid of infection (if necessary).
Amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid) index
| Gestation period (weeks) | Average, mm | Allowable fluctuations, mm |
| 16 | 121 | 73-201 |
| 17 | 127 | 77-211 |
| 18 | 133 | 80-220 |
| 19 | 137 | 83-225 |
| 20 | 141 | 86-230 |
| 21 | 143 | 88-233 |
| 22 | 145 | 89-235 |
| 23 | 146 | 90-237 |
| 24 | 147 | 90-238 |
| 25 | 147 | 89-240 |
| 26 | 147 | 89-242 |
| 27 | 146 | 85-245 |
| 28 | 146 | 86-249 |
| 29 | 145 | 84-254 |
| 30 | 145 | 82-258 |
| 31 | 144 | 79-263 |
| 32 | 144 | 77-269 |
| 33 | 143 | 74-274 |
| 34 | 142 | 72-278 |
| 35 | 140 | 70-279 |
| 36 | 138 | 68-279 |
| 37 | 135 | 66-275 |
| 38 | 132 | 65-269 |
| 39 | 127 | 64-255 |
| 40 | 123 | 63-240 |
Deviation of indicators towards a smaller or larger direction indicates oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios, respectively. In case of polyhydramnios, a woman is prescribed mandatory treatment with antibiotics and drugs to improve uteroplacental blood flow. Oligohydramnios indicates a severe fetal malformation - the complete absence of kidneys. In this case, appropriate therapy is carried out to support the child.
An important indicator is the quality of the amniotic fluid. Normally, it should be transparent, without turbidity, mucus, or flakes. Otherwise, this may be a sign of the development of an infectious process.
How does an embryo develop at 7 weeks?
You are 7 weeks pregnant, fetal development and sensations are changing rapidly. The baby continues to grow, its size is now 5-13 mm, like a medium-sized blueberry. But every hour thousands of cells are formed in it, organs and tissues grow rapidly:
- the heart is already four-chambered, large arteries and vessels appear;
- Primary neural connections are formed, the brain is divided into hemispheres;
- skeletal bones and tooth rudiments are formed;
- the lungs and bronchi continue to form;
- The placenta becomes denser every day, the development of the umbilical cord is completed, and very soon it will begin to transfer nutrients from mother to fetus.
The embryo cannot yet perceive surrounding sounds or the emotional state of the mother, since the nervous system has not yet developed. However, at this time, the development of the unborn child can be disrupted by such negative factors as infections and injuries to the mother, uncontrolled use of medications.
25-28 weeks
At this time, the period of most active growth ends. From the twentieth to the thirtieth week, the baby’s weight doubles; by the end of the period, the weight is already in the range of 1-1.5 kg. The baby's eyelids are not tightly closed until the twenty-eighth week, which promotes the development of the retina.
During these weeks, the child begins to distinguish tastes and hear sounds. You can note his numerous movements in response to various sounds and touches. The nervous system and brain are in a stage of rapid growth and development.
You can read more about the features of weeks 25-28 here.
Tests and ultrasound
The expectant mother needs to visit specialized specialists: an ophthalmologist, an otolaryngologist, a dentist and a therapist. If you have chronic diseases, you should additionally consult with specialized doctors.
The list of appointments also includes the following procedures:
- ECG – for diagnosing cardiovascular pathology;
- Ultrasound – to exclude ectopic pregnancy and confirm gestation;
- gynecological examination in a chair - to assess the condition of the cervix, the uterus itself and the cervical canal.
Unscheduled ultrasounds are prescribed as necessary and at the request of the patient
In some cases, a pregnant woman is prescribed an unscheduled ultrasound. It may be needed to assess the woman’s condition and prevent possible complications if pathologies or alarming symptoms occur:
- abnormal fetal development;
- discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the gestational age;
- abdominal pain;
- bloody issues;
- pathologies of placental maturation;
- absence of movements and other signs of the fetus;
- intrauterine developmental delay of the child.
Additional studies can be prescribed by a specialist at any period of gestation until birth.
What to discuss with your doctor
Check the schedule of your visits to the gynecologist. Usually in the 1st trimester it is once every 2-3 weeks. Discuss acceptable weight gain during pregnancy. In the seventh week, your increase is insignificant and is more likely associated with an increasing blood volume and tissue swelling.
Find out if you have any restrictions and contraindications: whether sex, playing sports, taking usual medications is possible.
Before each visit to the gynecologist, write down your questions in a notebook. This will help you not to miss important and especially exciting things. Please note that while monitoring your pregnancy at the Women’s Medical Center, you have the opportunity to contact your doctor at any convenient time.
What will an ultrasound show at 6 weeks of pregnancy?
What an ultrasound scan shows at the 6th week of pregnancy is very important, since it determines how the pregnancy will proceed in the future and whether its continuation is possible in principle.
Ultrasound at 6 weeks
shows:
- Is there a pregnancy?
- Location of the fertilized egg. The norm is the uterine location.
- Number of embryos. At the 6th week it will be possible to determine a multiple pregnancy.
- Dimensions of the fertilized egg. This indicator is necessary for doctors to clarify the gestational age.
- Fetal heartbeat. Only modern equipment can allow you to listen to the heart of an unborn baby at the 6th week. If the ultrasound machine does not have this capability, you will have to wait another 1-2 weeks to accurately assess the beating frequency of the small heart.
At the 6th week, it is too early to talk about identifying any developmental defects, since not a single system or organ in the fetus has yet formed.
If the embryo in the cavity of the ovum is not visualized, this may signal the fading of pregnancy (that is, the death of the fetus). After the ultrasound, you can take a photo in which the outlines of the future baby will be visible.
Complications of the seventh week of pregnancy
How do you understand that everything is fine with the child, because there are no movements yet? Listen to your body and be sure to consult a doctor if you experience sharp pain in your stomach and lower back, bloody or brown discharge, loss of consciousness, and if nausea suddenly disappears. These are possible signs of a frozen pregnancy and the threat of miscarriage.
Among other alarming conditions at the 7th week of pregnancy, we note the following.
Spasms
Mild nagging pain in the lower abdomen is normal in the early stages. This occurs against the background of a growing uterus and stretching tissue. Severe, unremitting pain accompanied by bleeding should alert you.
Diarrhea and constipation
Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract are associated with progesterone, which relaxes smooth muscles, including the intestines, whose peristalsis is noticeably affected by this. To help it, include apples, oatmeal and other foods rich in pectin in your diet.
Unusual vaginal discharge
You should be alert to bloody, brown or pink discharge, which may indicate a threat of interruption. Yellow, cheesy-white, with an unpleasant odor are also pathological - this is a symptom of infections.
How is an ultrasound performed at 6 weeks of pregnancy?
There are two options for how doctors do an ultrasound in the 6th week of pregnancy:
- The transvaginal method
is the insertion of a vaginal ultrasound sensor protected by a special condom into the vaginal cavity of a pregnant woman. - Transabdominal method
- through the skin of the abdomen. Before the scan, women apply a special gel to their abdomen.
The first method may cause some discomfort to the woman, but its results will be more accurate and complete. Contraindications to transvaginal ultrasound for a pregnant woman may include bleeding or abdominal pain.
Do's and Don'ts
At 7 weeks, the embryo is very sensitive to negative environmental factors. Therefore, exclude any negative influences harmful to the baby:
- alcohol and smoking, including passive smoking;
- heavy lifting, which can cause miscarriage;
- uncontrolled use of any medications;
- stress and long-term experiences;
- overheating in a bath, sauna or steam bath, because it dilates blood vessels and provokes uterine bleeding.
Try to be in the fresh air more often, do breathing exercises for pregnant women, and do physical exercise.
What will an ultrasound scan show?
An ultrasound in the eighth week of pregnancy, if it is progressing correctly, visualizes a fertilized egg with a living embryo inside. Also, based on the results of the study, it will be possible to judge the place of attachment of the chorion, the position of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity.
An ultrasound at the 8th week should show the fetal heartbeat, and its frequency can be assessed.
At a period of 8 weeks, it is already possible to identify some pathologies in the development of the fetus, in particular in the functioning of its heart. At the same time, experts have not yet made clear conclusions about the presence of a heart defect.
The ultrasound will also show how the neural tube of the fetus develops and how the limbs are formed.
Embryo research
Most of all ultrasounds at the eighth week
studies the embryo. Its size, location, structure are important. It is also necessary to evaluate the motor activity of the embryo, which should be present even at such a short period. At the eighth week, the embryo should be clearly visualized. If it is not there, most likely its development has stopped or there is a fact of anembryony, that is, the initial absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg (or its death immediately after conception).
Yolk sac examination
When performing an ultrasound at 8-9 obstetric weeks of pregnancy, it is necessary to evaluate not only the condition of the embryo itself, but also organs outside its structure. These organs include the yolk sac.
Its presence in the fertilized egg is temporary. The pouch appears approximately 15-16 days after fertilization and disappears by the end of the first trimester.
The yolk sac plays a large role in the development of the embryo - it produces germ cells, forms embryonic red blood cells for the first time, produces proteins necessary for development, helps form immunity, and so on.
At the eighth week, an ultrasound should show a yolk sac. Its size should be approximately 4-5 mm. An increase in the size of the yolk sac may be the first sign of pathological development of the fetus.
Checklist for 7 weeks of pregnancy
- You and your baby need a lot of energy - eat a varied, nutritious diet, including as many vegetables and fruits as possible in your diet.
- Healthy sleep is more important now than ever: don’t stay up late, allow yourself to take an hour’s nap during the day, at least on weekends.
- Review your wardrobe: choose soft, comfortable clothes that do not put pressure on the pelvic organs. It's time to buy a maternity bra, because breast sizes have increased.
- The seventh week of pregnancy is the best time to visit the dentist and have tooth decay treated.
Entrust your pregnancy management to the specialists of the Medical Women's Center. All analyzes and studies are in one place, without queues, at a time convenient for you. Our gynecologists have many years of practical experience in managing patients with complicated histories, including endocrine disorders, pregnancy as a result of IVF and after miscarriage.
How does a woman feel at 7 weeks?
When the 7th week of pregnancy begins, the expectant mother may have very different feelings. The 7th week of pregnancy is characterized by the onset of toxicosis, poor health and malaise. It is worth noting that not every representative of the fairer sex encounters such manifestations, and this is absolutely normal. However, most women believe that toxicosis is a sign that everything is in order, but this is not entirely true. At seven weeks of pregnancy, the expectant mother may experience mild morning sickness.
This feeling is especially intensified in the absence of breakfast and while brushing your teeth. This reaction may go away on its own within a few hours of waking up or remain throughout the day. Women also often react to odors. The aroma that I used to really like now disgusts me. During toxicosis, the expectant mother wants to eat something special. Some women say they have a craving for sweets. Others note a desire to eat salty and spicy foods.
There is also a group of women who want to do something unusual, for example, eat chalk. In addition to nausea and changes in taste preferences, intestinal dysfunction may occur. This is a consequence of hormonal changes and dietary disturbances. Some expectant mothers talk about the occurrence of constipation at this time.
Others note increased frequency and thinning of stool. Almost all women at this stage experience increased gas production. The consequence of this may be pain at 7 weeks of pregnancy. At this stage, growth of the tummy has not yet been observed. However, multiparous women may notice that their jeans have become too tight for them. Women also experience increased breast growth. They become more elastic and fuller. The nipples become sensitive and may darken. All this is normal and does not require additional medical intervention.
Pregnancy and beauty
There are many prejudices around pregnancy, including a ban on cutting hair for the entire period of pregnancy. One version of the origin of the myth: in ancient times it was believed that a child in a woman’s womb receives energy through the mother’s hair. There is no scientific basis for this fear, so if before this interesting situation you preferred haircuts, feel free to go to the hairdresser. In addition, a good hairstyle perfectly lifts your mood. You can also dye your hair, but give preference to products that are natural and without ammonia.
As your breasts and belly grow, your skin stretches. While the period is short, the changes are not so noticeable. But now many women are afraid of the appearance of stretch marks. This is possible with sudden weight gain or decreased skin elasticity. Special cosmetics for pregnant women will help prevent the formation of stretch marks in the chest, thighs, buttocks, abdomen and arms. However, given the individual characteristics of each woman’s body, there is no guarantee of effectiveness. After the baby is born, you can try massage of problem areas and wraps. The most effective way to get rid of scars and stretch marks is laser resurfacing; but laser correction has contraindications.
Useful tips and tricks

At the 7th obstetric week of pregnancy, you must adhere to the following set of rules:
- Even if you feel very hungry, there is no need to overeat - this will have a bad effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Visit a gynecologist and register with the antenatal clinic.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, avoid stress and physical activity.
- Swap your heels for comfortable shoes, and your clothes for loose items made from natural fabrics.
- Take vitamin supplements and do gymnastics.
- Avoid crowded places to reduce the risk of viral or infectious diseases.
It is necessary to systematically visit the gynecologist who is leading the pregnancy, strictly adhere to the recipe recommended by him, take tests in a timely manner, and be present at every scheduled examination. Only in this case the baby will be healthy and the pregnancy will pass without complications.

Ultrasound at seven weeks of pregnancy is a procedure prescribed for indications of ectopic pregnancy, as well as for a number of other pathological factors and complaints of a woman about deterioration of well-being. An ultrasound examination will help to accurately determine the gestational age and the date of the upcoming birth. The diagnostician will report the results of the ultrasound and issue a special paper that must be presented to the gynecologist. Based on this paper, the gynecologist determines the further course of pregnancy management.