Interesting Facts
| Options | Indications |
| Time from conception | 3 week |
| Period by month | 5 weeks |
| What month | 2 |
| Dimensions and weight of the fetus | 1-2 mm, 1 g |
| Uterus dimensions | A little more than normal |
| Pregnant weight | May increase by 1-1.5 kg |
Your baby is the size of
Rice grain
1-2mm Size
1 g Weight
The fifth week of pregnancy has begun. What happens to the woman and the unborn child during this period? Is it time to register and when do you need to urgently contact a gynecologist? We talk about possible complications and methods of preventing them.
What external changes occur to the mother?
As a rule, in the fifth week of pregnancy, the body is still reluctant to give up its “secret”; the woman’s outwardly interesting position is not very noticeable, even in the photo. But you should still be prepared for some changes that may accompany a woman from the first weeks.
Belly in the fifth week of pregnancy.
The size of the fetus is still too small for the uterus and abdomen to expand. Therefore, at this stage, the figure of the expectant mother retains the same proportions as before pregnancy. But progesterone, which is responsible for the onset and maintenance of pregnancy, can cause a slight protrusion of the abdomen. This is due to the fact that this hormone slows down intestinal motility, as a result of which gases can accumulate in it. But a small nutritional correction and exclusion from the menu of foods that cause flatulence can quickly return intestinal function to normal.
Breasts in the fifth week of pregnancy.
By this time, in some women, the mammary glands may increase by 1–2 sizes. And this is the only external change that is observed in the fifth week. But women whose breasts have retained their previous size also note some changes indicating that the body is already preparing to feed the baby. This is an increase in the sensitivity of the mammary glands, enlargement and darkening of the areolas, engorgement of the nipples.
Edema.
This “symptom” is considered by many to be an almost integral part of a healthy pregnancy. But in fact, edema indicates that the urinary system cannot cope with increased loads and is a little worse at removing excess fluid from the body. Therefore, the expectant mother should change her approach to her drinking regime and nutrition and minimize the consumption of salt and foods that provoke thirst (fatty, spicy, sweet).
Feelings of the expectant mother
The main sign by which you can confidently judge your new position is the absence of menstrual bleeding. Also, 5 weeks of pregnancy is the time when toxicosis appears. Nausea most often occurs in the morning, and vomiting may occur. If there are more than 4-5 such episodes during the day, and any food comes back out, be sure to consult your doctor. This condition is dangerous for the expectant mother and fetus and requires drug treatment.
Hormonal changes in the body can cause other symptoms:
- painful and sensitive breasts;
- constant fatigue and drowsiness;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- flatulence and constipation;
- headache and short-term loss of consciousness;
- increase in body temperature to 37-37.2 ° C, not caused by a cold;
- mood swings.
Note that these signs do not appear in everyone and not all together. For many, pregnancy at 5 weeks is completely asymptomatic.
Why is an early ultrasound necessary?
Ultrasound diagnostics is a safe method with no contraindications. But doing it before 4-5 weeks is pointless, the fertilized egg cannot be seen so early. In this case, a transvaginal sensor is used for ultrasound. In public clinics, the first ultrasound diagnosis is carried out as part of the first screening at 12 weeks, and before that it is prescribed only if the woman herself or her doctor is worried about something:
- a woman complains of pain in the lower abdominal region and bloody “spot”;
- the expectant mother has serious chronic diseases;
- pregnancy occurred, although the couple was protected using an IUD;
- the patient took dangerous and heavy medications, suffered an infection, and was irradiated. Although up to 4 weeks the “all or nothing” principle usually applies, doctors recommend being examined;
- the expectant mother and her relatives have a history of multiple pregnancies;
- the embryo was transferred using IVF;
- the doctor suspects a hydatidiform mole, ectopic or frozen pregnancy;
- The patient was diagnosed with various formations in the uterus and ovaries;
- if there is a risk of developing genetic abnormalities (for example, there have already been interrupted pregnancies due to developmental defects, chromosomal disorders).
In all other cases, a woman can voluntarily undergo an ultrasound for a fee. In Kaluga you can get examined at the Elite clinic. Our doctors work with modern high-precision equipment and have extensive experience in instrumental diagnostics.
Fetal development
At the 5th week of pregnancy, the embryo is comparable in size to a grain of rice: it contains no more than 1 gram and 1-2 mm. It looks like a tiny tadpole. But already now the upper respiratory tract, gonads, liver and spleen, circulatory system, eyes, skin, hair and nails are beginning to form in it. The placenta is formed, through which the fetus receives oxygen and nutrients.
The neural tube gradually closes, and in its place appears the spinal cord, brain, spinal column and the entire nervous system. The fetus develops the rudiments of legs and arms, similar to fins.
Due to the active formation of internal organs and systems, the unborn child at the 5th week of pregnancy is very vulnerable to the negative influences of the environment. Mom's stress, exposure to chemicals, infections and taking certain medications can provoke irreversible changes, including developmental defects.
Three-dimensional ultrasound reconstruction in the first trimester of pregnancy
Ultrasound scanner RS80
A benchmark for new standards!
Unparalleled clarity, resolution, ultra-fast data processing, and a comprehensive suite of advanced ultrasound technologies to solve the most challenging diagnostic problems.
Introduction
Thanks to the development and improvement of technologies, diagnostic and visualization tools, in recent years the interest of reproductive specialists, morphologists and clinicians in the early stages of human embryonic development has increased. Even at the World Congress on Bioethics (1996), the need to comprehensively determine the status of the human embryo, the problem of determining the age at which a human embryo can be considered as a person with rights and protected by law, and the creation of appropriate international rules for institutions working in the field of reproductive technologies were discussed. For a practicing physician, as a rule, the greatest interest is in the possibility of clinical assessment of the course of the early gestational period and the ability to predict pregnancy complications in order to timely correct and monitor the condition of the mother and fetus.
Modern echography makes it possible to monitor the development of the fetus from the earliest stages of intrauterine development. The emergence of ultrasonic devices that make it possible to obtain a three-dimensional image of the object under study, including in “real time” mode, expands the capabilities of ultrasound visualization. Thanks to three-dimensional ultrasound, in the early stages of pregnancy it is possible to more accurately determine the embryonic age, identify gross malformations earlier, and determine the volume of the object under study with a high degree of accuracy. The most important condition for a favorable course of pregnancy and fetal development is the formation of uteroplacental and fetal-placental blood flow. The morphological periods of placental development are quite well studied and described, and the use of three-dimensional technologies in combination with the power Doppler mode makes it possible to assess the degree of development of the organ’s vascular network.
Three periods can be distinguished in the formation of the chorion: the first - previllous (7-8th day of embryonic development) - proliferation of the trophoblast turns it into a “trophoblastic shell” that does not contain villi; the second - the formation of villi (days 9-49 of embryonic development) - cords and septa of the trophoblast forming the primary villi are histologically revealed; by the end of the second week, connective tissue grows into the primary villi - secondary villi are formed; third - the formation of cotyledons (50-90 days) - the transformation of primary villi into tertiary ones is the most important critical period of embryo formation [1, 6, 10]. By the end of the first trimester of pregnancy, placentation is completed, utero-placental and fetal-placental blood flow is established, i.e. by the end of the third month of ontogenesis, the main structural elements of the placenta are formed, it remains immature only in morpho-functional terms; the main starting points for the formation of the primary FPN are laid down [5, 8].
Currently, a few studies have appeared on the use of three-dimensional examination of the vessels of the fetoplacental complex [19, 21]. We did not find any data on the study of blood flow in the chorion in the first trimester of pregnancy in the available literature. The purpose of this work is to demonstrate the possibility of three-dimensional ultrasound examination of the embryo, fetus and chorion during pregnancy from 3 to 12 weeks.
Materials and methods
50 healthy pregnant women without embryo pathology during the normal course of this pregnancy and 110 patients with clinical and ultrasound signs of threatened miscarriage were examined. The gestational age was determined by the date of the last menstruation.
Until the 14th day after fertilization, the world's leading embryologists consider the human embryo as a pro-embryo, believing that before this period it is formed by cellular layers, which are embryonic membranes, material that is not involved in the subsequent construction of the embryo itself [1, 2, 6, 12 , 13]. On days 14-15, the axis of the germinal disc is determined, the primary streak, Hensen's node is formed, and the notochord is formed, i.e. This is the period when the elements of the nervous system of the human embryo begin to form.
Visualization of the embryo is possible for the first time with a three-dimensional examination of the ovum for at least 3-4 weeks
, embryonic stages of implantation cannot be visualized.
It is possible to differentiate the embryo on three-dimensional ultrasound at the stage of the “primary streak”, starting from the 9th somitic stage [3], when the size of the embryo reaches 1.35 - 1.5 mm
(4 weeks of gestation). At this stage, you can see the amniotic cavity, the embryo in the form of a “grain of rice” and the attaching stalk. Echographic differentiation of the head and pelvic ends and intraembryonic structures is not yet possible (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1.
Three-dimensional examination of the ovum.
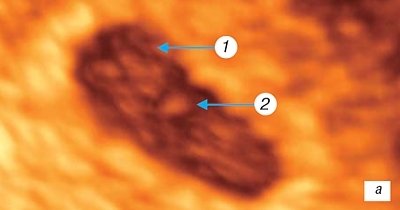
A)
Pregnancy 3 weeks.
b)
Pregnancy 4 weeks.
1 - amniotic cavity; 2 - embryo; 3 - “attaching stalk”.
The embryo is nourished at this stage of development by the allantois, a dense cord of epithelial cells that gradually grows into the tissue of the amniotic leg and connects the embryo with the cavity of the yolk sac [6, 18].
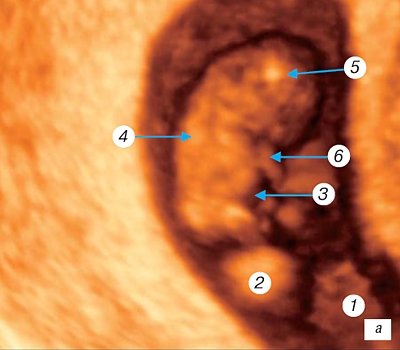
Morphologically at 5 weeks
gestation (Fig. 2 a), the neural tube begins to form.
By this time the length of the embryo reaches 3 mm
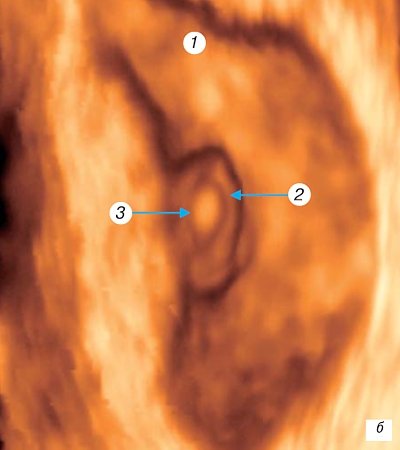
, somites are formed, the rudiments of the heart, lungs, thyroid gland, and umbilical vessels develop. In the open neural tube, the anterior, middle and posterior brain vesicles are already visible. The auditory placode and optic sulcus are formed, the mandibular and hyoid arches are identified; the notochord separates from the underlying endoderm; the anterior, middle and hindgut are distinguishable. The developing heart is determined, closed blood circulation is established through the yolk sac and the embryonic leg [1, 6, 11, 14, 16]. During this period, the amniotic cavity and yolk sac are visualized, the ventral and dorsal surfaces of the embryo, the head and pelvic ends are differentiated, differentiation of internal organs is impossible. Transvaginal echography using color Doppler mapping allows you to determine the pulsation of the heart tube. In the area of the implantation site, typical mesenchymal villi are formed; at the opposite pole of the fertilized egg, the villi stop in their development. At the same time, the invasion of the cytotrophoblast into the wall of the spiral arteries and the opening of the latter into the developing intervillous space were first noted.
Rice. 2.
Three-dimensional examination of the ovum.
A)
Pregnancy 5 weeks.
b)
Pregnancy 6 weeks.
1 - amniotic cavity; 2 — yolk sac (cut); 3 — embryo from the ventral surface; 4 - head end of the embryo; 5, 6 — kidneys of the upper and lower extremities, respectively.
6th week
intrauterine development (Fig. 2 b) completes the somitic period of development of the human embryo.
During this period, the rudiments of the arms and legs are determined, the bud of the forelimb lengthens, the rudiment of the carpal plate appears, the lower limb remains in the form of a kidney. The rudiment of paired cerebral hemispheres appears. Organogenesis of the eyes and ear continues; in a closed neural tube, the parts of the brain are clearly distinguished and the cerebral and cerebellar hemispheres are designated. One-way blood flow through the heart is established, the division of the heart into chambers is almost completed, the heart is functioning. The primary kidney is formed; the rudiments of the ureter, the rudiments of the gonads, as well as the liver, gall bladder, pancreas, and various parts of the intestinal tract are determined [7, 14, 16]. Invasion of the cytotrophoblast towards the spiral arteries continues, which leads to the formation of venous collectors, however, the increasing uteroplacental circulation provides only the needs of the villous tree itself, since it is not yet connected with the circulatory system of the embryo. By the end of the 6th week of gestation, the length of the embryo reaches 6-7 mm
. Morphologically, this period is characterized by the appearance of gill arches, the formation of the optic vesicle, the beginning of differentiation of the pituitary gland, the induction of the lens and the formation of the optic cup. The diencephalon and midbrain are formed, the cavity of the fourth ventricle and hindbrain is determined. The formation of the intestines and anterior abdominal wall begins. Echographically, the amniotic cavity, yolk sac, and embryo 4-5 mm long are determined. The ventral and dorsal surfaces of the embryo, the head and pelvic ends, and the kidneys of the fore and hind limbs are clearly differentiated. When performing horizontal sections, it is possible to visualize the hindbrain, the rudiments of the paired cerebral hemispheres, and the cavity of the fourth ventricle. With a two-dimensional study, especially with the use of color mapping, it is always possible to determine the pulsation of the heart tube. Differentiation of intraembryonic structures, including the heart tube, is impossible at this stage.
Beginning of week 7
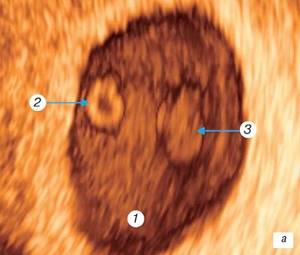
gestation is the post-somitic period of embryogenesis. The length of the embryo by this time reaches 7-8 mm. The upper limb lengthens, a dividing groove appears between the fingers and rotation of the first finger of the hand begins, interdigital spaces are visible, and finger plates appear on the lower limbs. On the surface of the embryo, the eye, mandibular, hyoid and glossopharyngeal arch are identified, the nasal fossa, nasal fold, and auditory eminence appear. Three-dimensional surface reconstruction identifies the fetal head, ventral and dorsal surfaces of the body, the forebrain, the cavity of the fourth ventricle, the upper limb with the digital plate, and the kidneys of the lower limbs. Digital projections on the upper limb cannot be visualized. The umbilical cord is clearly visualized (Fig. 3 a, b). At the same time, the embryo-placental blood circulation finally takes shape and the hemochorial type of nutrition of the embryo tissue is established.
Rice. 3.
Three-dimensional examination of the ovum.
A)
Pregnancy 7 weeks.
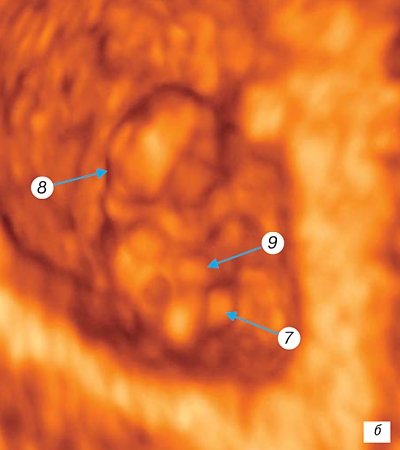
b)
Pregnancy 7 weeks.
1 - amniotic cavity; 2 — yolk sac (cut); 3 - ventral surface of the embryo; 4 - dorsal surface of the embryo; 5 - head of the embryo; 6 - upper limb; 7 - kidneys of the lower extremities; 8 - ventricular cavity; 9 - umbilical cord.
The length of the embryo at the beginning of the 8th week of pregnancy is 15-20 mm.
The head grows sharply and the body straightens.
The structures of the head are more pronounced, the five primary sections of the brain are formed, the nostrils are formed, and the outer ear is developing. Ossification of the long tubular bones, axial skeleton and skull occurs. The onset of motor behavior in the human embryo
has been established . Three-dimensional reconstruction clearly identifies the fetal head, jaw, and neck. When cutting through the brain structures, the lateral ventricles and the developing choroid plexuses are identified. The rudiments of the fingers of the limbs and the elbow bends are visible. The separation of the fingers begins and a thenar flexion fold appears on the radial side of the hand. The first finger of the hand is completely rotated. The digital arch of the foot and the heel eminence and knee are formed. Despite clearly visualized genitals, sex differentiation is impossible (Fig. 4).
Period until the end of the 8th week
Human embryogenesis (
embryo length reaches 40 mm
, weight 5 g) is characterized by intensive growth and further differentiation of organ systems.
During this period, facial features emerge, which gives the embryo a greater resemblance to the human appearance; the neck is separated, the outer ear and outer parts of the nose are formed, the eyelids and all parts of the limbs and fingers are formed, the tail disappears. The cerebral hemispheres develop intensively; the cortex and basal ganglia are distinguishable in them. The external genitalia are differentiated by sex
. The end of the 8th week of intrauterine development marks the end of the embryonic and the beginning of the fetal period in humans. The main structures and organ systems are differentiated [1, 6, 7, 11, 13]. In the uteroplacental region, active invasion of the cytotoroblast into the myometrium is noted. This corresponds to the growth of the placenta, mainly due to an increase in the length of the villi with lateral branches. The capillaries of the villous tree and the vessels of the chorionic plate develop. The anatomical connection of the placental circulatory network with the allantoic vessels in the umbilical cord determines the presence of constant blood flow in the umbilical cord.
Rice. 4.
Three-dimensional examination of the ovum.
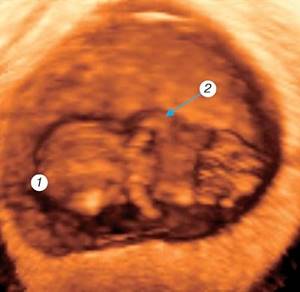
Pregnancy 8 weeks. 1 - fetal head; 2 - upper limb with elbow joint.
Starting from 9th week
In intrauterine development of a person, the fetal period, ending with the birth of the fetus, is characterized by its intensive growth, further differentiation of organs and systems and the formation of their differentiated functions.
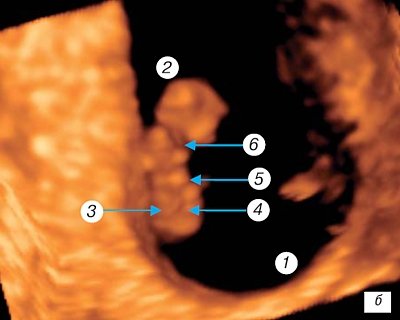
The facial fissures close, fingers and toes
, and a cartilaginous auricle appear (Fig. 5). As the placental villi enlarge, large vessels appear in their center. The same vessels are created in the chorionic plate and connect to the great vessels of the umbilical cord. Further structural differentiation of the placental-umbilical cord region occurs and it merges with the embryonic circulatory system.
Rice. 5.
Three-dimensional examination of the ovum.
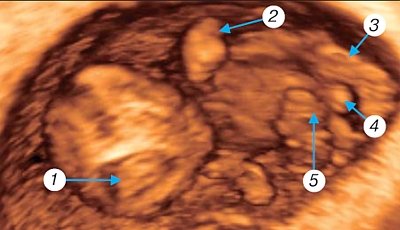
Pregnancy 9 weeks. 1 - fetal head (partially - section through the lateral ventricles); 2 - upper limb with elbow joint and finger plate; 3 - lower limb with heel protrusion; 4 - genitals; 5 - umbilical cord.
At the 10th week, reflex movement of the lips is observed
(the sucking reflex develops) (Fig. 6 a, b). The developing placenta is characterized by a slowdown in cytotrophoblast invasion, and decidualization of the endometrium begins.
Rice. 7.
Three-dimensional examination of the ovum.
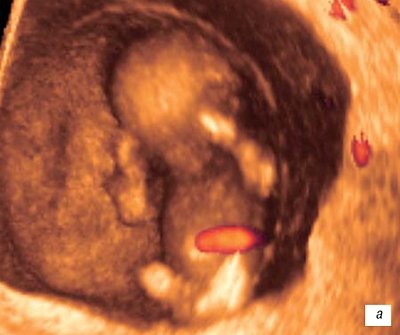
A)
Pregnancy 10 weeks.
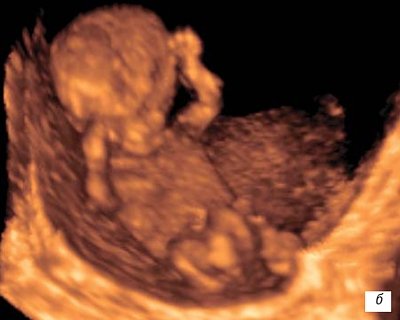
b)
Pregnancy 11 weeks.
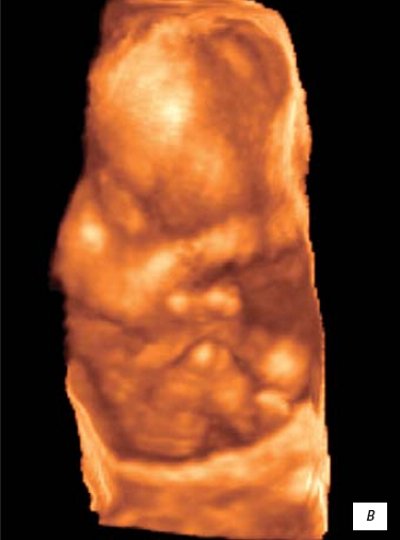
V)
Pregnancy 12 weeks.
At 12 weeks
During intrauterine development,
the fetus reaches 87 mm in length
and weighs about 45 g, acquiring more and more human features in the formed parts of the face and head.
The reflex movement of the fingers of the limbs in response to touch
indicates the development of the corresponding central neural connections.
The neural mechanisms of some spinal reflexes of the fetus also develop. Respiratory movements
are noted (Fig. 6 c). The placenta acquires a lobular structure, numbering about 30 cotyledons. Anatomically, septa and cellular islands are designated in it. Its mass is about 20 g; in terms of functional organization, it is significantly ahead of other organs of the embryo.
The technique we used to study the volume and intraplacental blood flow included the following steps:
- determination of the chorion study area in gray scale and power Doppler mode (the capabilities of the sensor allow you to record the fertilized egg up to 13 weeks of pregnancy in full) (Fig. 7);
- selection of the examination angle (for all examinations, an angle of 15° was selected - allowing for the correct identification of the chorion in all sections of the fetal egg);
- constructing an image area of the chorionic vasculature;
- selection of cut frequency (for all studies, a frequency corresponding to a cut thickness of 1.5-2 mm was selected, which is sufficient to obtain reliable results);
- constructing a histogram of the vascular component in the full volume of the chorion.
Rice. 7.
Fetal face.
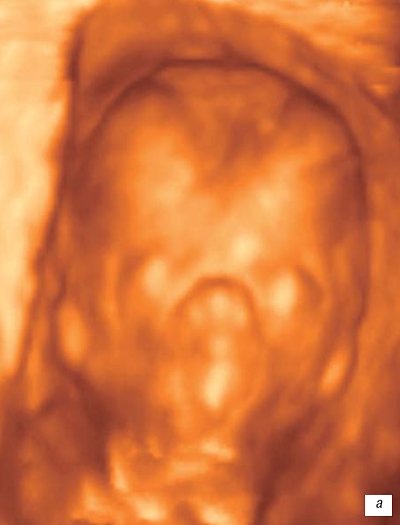
A)
13 weeks pregnant.
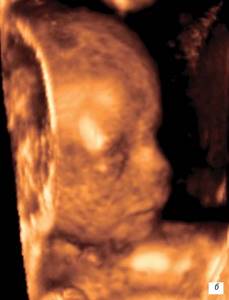
b)
14 weeks pregnant.
In all cases, the total volume of chorionic tissue was determined.
When computer processing of placentograms [21], the following parameters were automatically calculated:
- VI is the vascularization index, which reflects the percentage of vascular elements in the volume of placental tissue of interest;
- FI is the blood flow index, which reflects the number of blood cells transported at the time of the study, i.e. blood flow intensity.
As a result of the studies, patterns of formation of the vascular component of the chorion during physiological pregnancy were revealed. According to the periods of structural formation of the chorion, the data were analyzed separately in the period of villi formation (up to 7 weeks) and in the period of cotyledon formation (up to 12-13 weeks) (Fig. 8, Table 1).
Rice. 8.
Chorionic vessels. Three-dimensional reconstruction.
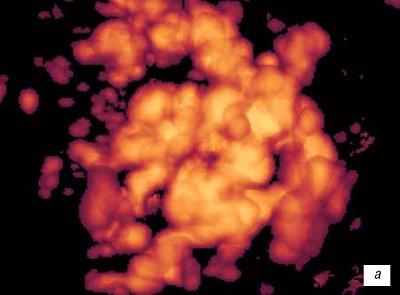
A)
7 weeks gestation.
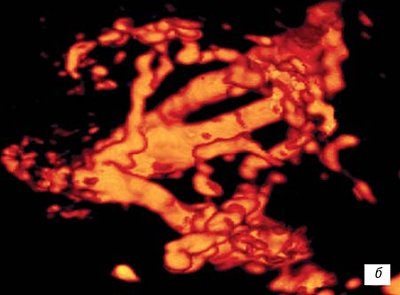
b)
12-13 weeks of gestation.
Table 1
. Volumetric blood flow in the chorion in the first trimester of uncomplicated pregnancy.
| Gestational age | Number of observations | Chorion volume, cm³ | VI (vascularization index) | FI (blood flow index) |
| 5 weeks | 4 | 5,5 | 14,4 | 33,6 |
| 6 weeks | 4 | 9,2 | 18 | 30 |
| 7 weeks | 3 | 15,8 | 15 | 41 |
| Averages | 12,3 | 14,5 | 36,0 | |
| 8 weeks | 2 | 20,2 | 17 | 40 |
| 9 weeks | 2 | 32 | 18,8 | 40,9 |
| 10 weeks | 3 | 71,6 | 22,6 | 41 |
| 11 weeks | 3 | 147 | 16,2 | 49 |
| 12-13 weeks | 4 | 158 | 18 | 49 |
| Averages | 104 | 14,2 | 45,4 | |
From the table 1 shows that in the first trimester of pregnancy there is a gradual increase in the volume of chorion tissue from 5.5 to 158 cm³ by the 13th week of gestation, and during the period of completion of the formation of villi, the increase in the volume of chorion occurs “intermittently”, within 2 weeks (with 10 to 12 cm³), the volume of the chorion almost doubles (Fig. 9).
Rice. 7.
Dynamics of changes in chorion volume.
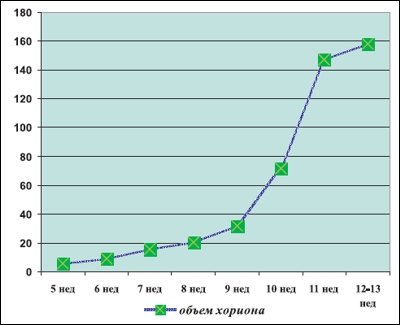
Rice. 9.
First trimester of physiological pregnancy.
Vascularization index, i.e. the ratio of the vascular component and parenchyma in a given volume of tissue increases gradually, reaching maximum values by 10 weeks of gestation, then decreases slightly (Fig. 10).
Rice. 7.
Dynamics of changes in the chorion vascularization index.
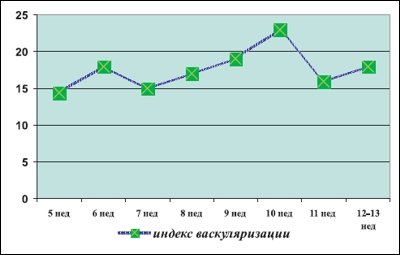
Rice. 10.
First trimester of physiological pregnancy.
The blood flow index gradually increases during the first trimester of pregnancy; no significant differences in the values of this indicator were detected during the formation of villi and during the formation of cotyledons.
When studying various sections of the chorion - regional and central - it was found that in pregnancy up to 11 weeks, heteromorphism of blood flow in the chorion is not expressed, no significant differences in the blood supply of the regional and central sections were identified. After 12 weeks of pregnancy, vascular heteromorphism appears - the vascularization index in the central zone of the chorion is higher than in the peripheral areas (Table 2).
table 2
. Comparative indicators of volumetric blood flow in the chorion in the first trimester of uncomplicated pregnancy.
| Gestation period, weeks | Vascularization and blood flow index | Central zone | Paracentral zone | Peripheral zone | The entire chorion |
| Until 11 | VI | 15,1* | 14,9* | 12,8* | 15,8* |
| FI | 35,6* | 35,0* | 30,0* | 34,6* | |
| 12-13 | VI | 20,8 | 15,3 | 7,7 | 14,8 |
| FI | 55,6 | 44,1 | 33,6 | 45,4 |
Note. *—differences are statistically insignificant.
In addition, 110 pregnant women with clinical and ultrasound signs of threatened miscarriage in the first trimester were examined. The chorion volume was measured and their volumetric blood flow indicators were calculated. Changes in size and disruption of blood flow in the developing chorion were detected in all observations (Table 3).
Table 3
. Average values of volume and vascularization of the chorion in the first trimester with the threat of miscarriage.
| Index | Chorion volume, cm³ | Vascularization index VI | Blood flow index FI |
| Up to 8 weeks | |||
| Averages | 8,9 | 3,9 | 33 |
| 8-13 weeks | |||
| Averages | 63 | 4,23 | 35,1 |
The disruption of the formation of the chorion vascular network was expressed in the absence of a clear structure of the vascular tree and the visual absence of heteromorphism (Fig. 11).
Rice. eleven.
Chorionic vasculature:
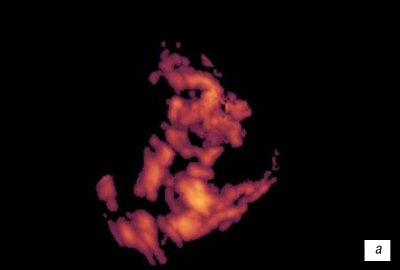
A)
With a non-developing pregnancy, 8 weeks.
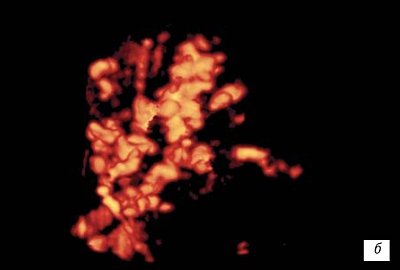
b)
If there is a threat of termination of pregnancy 12 weeks.
Depending on the degree of reduction in volume and vascularization, all pregnant women were retrospectively divided into 3 groups. Group I consisted of 76 women in whom the chorion volume was reduced by 25-35% relative to the norm for a given gestational age, and the vascularization index (VI) was reduced by 45-55%. In group II, which combined 21 observations, the volume of the chorion was reduced by 36-58%, and group VI - by 56-65%. Group III included 13 patients with the most severe disorders: the volume of the chorion was reduced by 56-78%, VI - by 70% or more. All those examined received standard therapy for the threat of miscarriage and subsequent pathological conditions that developed during gestation. Perinatal outcomes, depending on the degree of features of the formation of placental blood flow identified in the first trimester, are presented in Fig. 12 and 13.
Rice. 12.
Complications of pregnancy and childbirth:
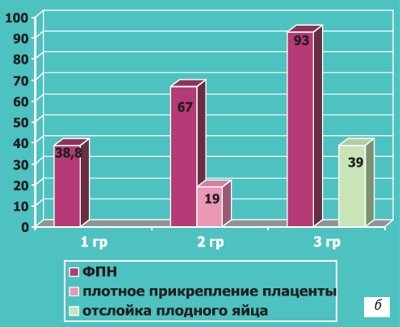
a, b)
In case of impaired vascularization of the chorion in the first trimester of pregnancy.
conclusions
Three-dimensional echography is a new step in the diagnosis of intrauterine development of the fetus, it allows you to visualize the embryo in sufficient detail from the early stages of pregnancy, determine the timing of gestation as accurately as possible, starting from 8 weeks it makes it possible to identify gross malformations of the embryo and fetus, some markers of chromosomal pathology. Obtaining a three-dimensional image of the fetus and reconstructing its appearance opens up new opportunities for parents who can see their unborn child with photographic accuracy.
Three-dimensional Doppler testing with calculation of volumetric blood flow indicators demonstrates the patterns of formation of the vascular component of the chorion in the first trimester of uncomplicated pregnancy and can serve as a criterion for selecting patients at risk for the formation of a pathological course of pregnancy already in the first trimester of gestation.
Literature
- Zavarzin A.A. A short guide to human and vertebrate embryology. - Leningrad, Narkomzdrav, 1939. - 204 p.
- Kurilo L.F. Morphofunctional characteristics of oogenesis in humans and mammals // Diss. ... Doctor of Biol. Sci. - M., 1985. - 470 p.
- Kurilo L.F. Fertilization and intrauterine development of humans.
- Medvedev M.V., Kuryak A., Yudina E.V. Dopplerography in obstetrics. - M.: Real Time, 1999.
- Medvedev M.V., Yudina E.V. Intrauterine growth retardation. - M.: RAVUZDPG, 1998.
- Milovanov A.P., Savelyev S.V. Intrauterine human development//Guide for doctors. - M.: MDV, 2006. - 384 p.
- Savelyev S.V. Stages of embryonic development of the human brain. - M.: “VEDI”, 2002.
- Stygar A.M., Medvedev M.V. Ultrasound examination of the placenta, umbilical cord and amniotic fluid // Clinical guide to ultrasonic diagnostics. Under. Edited by Mitkova M.V., Medvedev M.V. - M.: Vidar, 1997.- T.2. — P. 68.69.
- Falin L.I. Human embryology. Atlas. - M.: Medicine, 1976. - 544 p.
- Fedorova M.V. Kalashnikova E.P. Placenta and its role during pregnancy. - M.: Medicine, 1986. - 265 p.
- Bodemer Ch.W. Modern embryology // NY, 1968; 475p.
- Corliss CE Patten`s human embryology. Elements of clinical development // McGroww.Hill Book Company, A Blackiston Publication, NY, ao, 1976; 470 p.
- Edwards RG Sciense et ethique de la segmentation des embrions humains in vitro // Contracpt. Fertil Sex 1986;14:4:313.318.
- England MA Farbatlas der Embriologie // FKShattaner Verlag. - Stuttgart.NY1985;25.
- McLaren A. IVF: regulation of prohibition? Nature 1989;342: 6249:469.470.
- McLaren A. Research on embryos in vitro. The various types of research. Report - Council of Europe's Third Symposium on Bioethics, 1996; Strasbourg.
- Moore KL The Developing Human: Clinically oriented Embryology Philadelphia, L, Saunders, 1973;374.
- Patten BM Foundations of embryology // NY 1958.
- Pretorius DH, Nelson TR, Baergen RN, Pai E., Cantrell C. Imaging of placental vasculature using three.dimensional ultrasound and color power Doppler: a preliminary study // Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol, 1998 Jul; 12(1): 45.9.
- Welsh AW, Humphries K., Congrove DO, Taylor MJ, Fisk NM Developments of three-dimensional power Doppler ultrasound imaging of fetoplacental vasculature // Ultrasound Med Biol, 2001 Sep; 27 (9): 1161.70.
- Kurjak A., Kupesic S., Zoclan T. Three-dimensional and power Doppler in the study of angiogenesis // Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol, 2001 Okt; 18 (4).
Ultrasound scanner RS80
A benchmark for new standards!
Unparalleled clarity, resolution, ultra-fast data processing, and a comprehensive suite of advanced ultrasound technologies to solve the most challenging diagnostic problems.
Analyzes and research
Suspecting pregnancy and having done a home test, a woman turns to a gynecologist. It’s still too early to register, but the doctor can already prescribe a number of preliminary tests:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- test for HIV, hepatitis and AIDS;
- determination of blood group and Rh factor.
If we are talking about the 5th week from conception - the embryonic period, which is 2 weeks longer than the obstetric period - you will find an extensive list of tests and consultations with specialists.
What can be seen on an ultrasound
Ultrasound allows you to accurately confirm or refute the fact of pregnancy. At week 5, the embryo is already clearly visible; the specialist assesses the size and number of embryos, the condition of the uterus and the correspondence of these indicators to the expected gestational age. In other words, they will tell you exactly how many weeks and days the unborn child is now.
In some cases, by the fifth week you can already listen to the fetal heartbeat.
Fifth week of embryonic development
The embryonic (true) gestational age is counted from the first day of the last menstrual period plus another two weeks. It is in the middle of the cycle that ovulation occurs, i.e. approximately on the 14th day after the critical days. In other words, the 5th week of embryonic development corresponds to the 7th obstetric week.
14 days after IVF, a hCG test is performed, which determines whether pregnancy has occurred. In case of successful conception, women undergo the first ultrasound as early as the 5th week of gestation. The examination allows you to determine:
- Dimensions of the uterus;
- Embryo location;
- Number of surviving blastocysts;
- The presence or absence of pathologies in fetal development.
It should be understood that embryologists determine the gestational age of the fetus differently than obstetricians. After IVF, specialists can accurately determine the day of conception, which is counted from the moment of implantation of the blastocyst into the uterus.
In the mid-embryonic period, the fetus is located near the wall of the yolk sac, which is visualized using ultrasound as a small spherical cyst with a fertilized egg inside. The embryo is located eccentrically inside the sac, which is why a typical ultrasound picture of a “double bubble” appears on the monitor.
At this stage of embryonic development, many organs and vital systems are already beginning to develop, but it is very difficult to visualize them using transabdominal ultrasound. That is why, to determine the characteristics of the course of pregnancy, specialists resort to transvaginal examination, with the help of which it is possible to obtain a more detailed picture.
Possible complications
Pregnancy in the early stages often ends in spontaneous abortion. Among the main negative factors:
- lack of progesterone and thyroid hormones, excess androgens and other hormonal disorders;
- genetic abnormalities of embryo development;
- excessive physical activity;
- Rhesus conflict;
- sexually transmitted diseases;
- viral hepatitis, rubella, complicated influenza and tonsillitis;
- chemical poisoning as a result of uncontrolled medication use.
Timely drug therapy, including in a hospital setting, in many cases allows you to maintain pregnancy. In particular, with hormonal disorders. It is only important to seek help in time. Therefore, if at week 5 you notice a sharp deterioration in your general health, bloody discharge from the genital tract, you should not hesitate. Other alarming symptoms are severe pain in the lower abdomen and lower back.
Note that a slight brown “smudge” is acceptable in the early stages, as a symptom of successful embryo implantation.
Do's and Don'ts
A pregnant woman is surrounded by various prohibitions almost from the first weeks. Do not lift anything heavy, do not dye or cut your hair, do not go to the movies or concerts where it is loud and crowded. Let us note that most of these prohibitions are prejudices and myths. It is important for the expectant mother to take care of herself and not overwork herself. You really shouldn't lift more than 3-5 kg. But there is no need to prohibit yourself from having fun or going to the hairdresser.
Same dietary recommendations. You should not suddenly switch to sprouted grains, a raw food diet and buy only products labeled BIO. Eliminate fast food, sausages and other processed foods, alcohol and caffeine. However, if you really want something, treat yourself in moderation. Food is not only “fuel” for the body, but also a source of positive emotions, and there should be as many of them as possible during pregnancy.
Nausea
It usually appears in the morning, and may intensify during the day. In some women, nausea becomes so severe that it progresses to the stage of uncontrollable vomiting. To date, there are no 100% effective remedies for this unpleasant condition. And to ensure that toxicosis ruins your life as little as possible, try following a few recommendations:
- Eat more often, but in small portions;
- Avoid foods with unpleasant odors;
- Eat foods high in protein;
- To avoid dehydration, drink enough fluids;
- Rest often;
- Avoid stressful situations.
Checklist for the fifth week of pregnancy
- Stick to your daily routine, get enough sleep.
- Try different ways to combat toxicosis: split meals, ginger tea, crackers and drying. Find your own method, but if you vomit frequently, be sure to consult a gynecologist.
- If you suddenly feel a sharp tug in your stomach or lower back, seek medical help immediately.
- Discharge at the 5th week of pregnancy should normally be light, transparent, and perhaps slightly yellowish. All other cases should be discussed with your doctor.
- Start looking for courses for pregnant women: useful information about pregnancy and childbirth, as well as communication with a team of like-minded people is very valuable.
- Check with your gynecologist at what time you need to register for pregnancy. Usually this is 6-8 weeks.
Pregnancy is an exciting and incomparable time. Get rid of the fears of complications and pathologies during pregnancy by contacting the specialists of the Women's Medical Center. We draw up individual observation programs and have many years of successful practical experience in managing patients with a complicated medical history.
Diagnosis of anembryonia
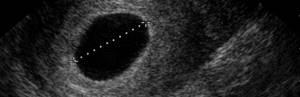
The main way to detect this pathology is ultrasound examination. It is with its help that the presence of an embryo in the fertilized egg and its normal development can be established. In a normal pregnancy, the embryo is not visible on average until 6-7 weeks after conception, so at this stage, indirect signs of pathology can be a drop in the level of hCG in the blood or a deficiency of progesterone.
To make a diagnosis of anembryonia, the following conditions must be met:
- absence of a yolk sac in a fertilized egg with a diameter of 8-25 mm;
- absence of an embryo in a fertilized egg larger than 25 mm.
There are also additional signs of anembryonia, in particular deformation of the ovum, an abnormally low increase in its size, mild decidualization of the endometrium at the point of implantation, and unregistered heartbeat at 6-7 weeks of pregnancy. Such a diagnosis may also be supported by signs of fetal rejection - changes in uterine tone, the appearance of areas of chorionic detachment with the formation of subchorionic hematomas.
Depending on the clinical picture of the pathology revealed during ultrasound examination, 3 types of pathology are distinguished:
- Anembryonia type I - the embryo is not detected on imaging, the size of the fertilized egg is usually no more than 2.5 mm, and the uterus is enlarged only until 5-7 weeks of pregnancy;
- Anembryonia type II - there is no embryo, but the size of the fertilized egg and uterus corresponds to the gestational age.
Separately, it is worth highlighting the resorption of embryos during multiple pregnancies. Most often, this condition occurs after in vitro fertilization, when several embryos are implanted into the patient at once to increase the chances of successful conception. Usually only one of them takes root, but in rare cases 2 or more embryos are successfully implanted. In this case, some of them freeze in their development, after which they resolve or are removed from the body naturally.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!