1.What is hemophilia and its causes
Hemophilia
is a blood disorder in which the blood does not clot properly. Typically, this occurs because a person with hemophilia lacks a certain clotting factor. This means it can be difficult to stop bleeding. Moreover, this can apply to both ordinary bleeding from wounds and falls, and bleeding during some operations. It also happens that some people with hemophilia begin to bleed internally for no apparent reason.
There are two main types of hemophilia:
- Hemophilia A
is caused by the absence of active blood clotting factor VIII. According to statistics, approximately 1 in 5,000 male infants are born with type A hemophilia. Blood clotting factor VIII is a plasma protein. The greater the deficiency, the more severe the symptoms of hemophilia. - Hemophilia B
(Christmas disease) is caused by a lack of active blood clotting factor IX in the body. This form of hemophilia is less common and is diagnosed in about 1 in 30,000 male infants.
Hemophilia is usually inherited and almost always affects men. In very rare cases, a person can develop hemophilia without a family history. This is called acquired hemophilia, and it occurs in both men and women.
Causes of hemophilia
Hemophilia, both type A and B, occurs due to a defect in a pair of chromosomes that affects the presence of a certain blood clotting factor in the body and how it works. In the case of acquired hemophilia, the blood clotting factor stops working as it should because it begins to be attacked by antibodies that the body itself produces.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Spontaneously and by inheritance
Article on the topic Diagnosis in inheritance: what is hemophilia and how is it dangerous? Most often, problems with the blood coagulation system are inherited.
A striking example of this is hemophilia, which only affects males and is transmitted through the female line (that is, from a sick grandfather, through his healthy daughter to his grandson). The most famous carrier of hemophilia (dubbed the “royal disease”, because it was most common in royal families, where closely related marriages were allowed to retain the title) was Queen Victoria of England, who passed this incurable disease on to one of her sons, as well as a number of grandchildren and great-grandchildren, including the Russian Tsarevich Alexei Nikolaevich (son of Nicholas II). In the blood of the young heir to the Russian throne, the level of blood clotting factor IX, a protein necessary to completely stop bleeding, was significantly reduced.
However, hereditary hematological diseases affect not only men, but also women.
An example of such a rare disease is von Willebrand disease, whose owners (both sexes) periodically experience spontaneous bleeding (nasal, gastrointestinal, gingival, and in women - uterine).
In the latter, for obvious reasons, the disease is more aggressive and is therefore detected much earlier. What sometimes saves their lives: childbirth for such women is associated with a high risk of bleeding, from which a mother suffering from poor blood clotting can die.
Article on the topic
April 17 is World Hemophilia Day When such a patient is diagnosed for the first time, doctors examine her family: the patient’s immediate relatives may also have chromosomal abnormalities that appear completely unexpectedly and at the most inopportune time - for example, during surgery.
Diseases of the blood coagulation system can also be acquired. The impetus for their occurrence can be the same childbirth (a similar situation occurs in 1 in 1 million mothers), an autoimmune disease, liver disease (hepatitis, cirrhosis), long-term hormonal therapy, taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Sometimes the appearance of antibodies to one of the blood clotting factors is the debut of cancer. And although this happens very rarely, experts prefer not to relax. The sooner such a patient is identified, the greater the chances of prolonging his life and improving its quality.
2. Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of hemophilia may include:
- Bleeding in a joint or muscle area that causes pain and swelling;
- Abnormal bleeding after wounds or surgery;
- Bruising;
- Frequent nosebleeds;
- Blood in the urine;
- Bleeding after dental surgery.
Some people with mild hemophilia may not experience all of these symptoms, especially as the person gets older. However, in infants it is usually possible to diagnose hemophilia based on some signs. So, signs of hemophilia in infancy may be an unusual reaction to the most common vaccination - intramuscular bleeding and serious bruising. Or, for example, bleeding that begins after cutting the umbilical cord and does not stop for a long time (but this happens very rarely).
Visit our Therapy page
Hemophilia: what kind of disease is it, what do you need to know about it?
HEMOPHILIA: what kind of disease is it?
what do you need to know about it?
The unusual frequency with which this disease occurs among different generations of the same family has long led to the suspicion that hemophilia is a hereditary blood disease. It has been established that women, without being sick themselves, transfer hemophilia from one family to another. A typical example of female bloodborne disease in European history is the family tree of Queen Victoria of England, from whom the disease spread to many other royal houses. The son of the last Russian Tsar suffered from this disease.
However, hemophilia does not only affect aristocratic dynasties. It can occur in any child who has a family member who suffered from this blood disease.
Hemophilia is a congenital hereditary disease. Of course, it is the most famous among genetically determined blood diseases.
Hemophilia is expressed in increased bleeding, be it as a result of external, even the smallest injuries, or internal bleeding in tissues, joint capsules, etc. An injury that causes almost unstoppable bleeding can be extremely minor.
This blood disease has serious consequences for internal organs and joints, causing concomitant diseases and abnormalities.
Causes of hemophilia
Scientists attribute hereditary factors to the main reasons provoking the development of hemophilia disease. Genetically defective blood clotting is inherited from generation to generation, and the carrier of the defective gene is exclusively the female body, and the patient with hemophilia, as a rule, is a man. In fairness, it is worth noting that there are scientifically described cases of hemophilia in women, but these cases are extremely rare and occur when both parents of a sick girl are carriers of the damaged gene. By passing the disease on to her children, the woman “conductor” herself remains healthy, her sons are doomed to hemophilia, and her daughters also become carriers of the hidden gene until they pass it on to their children. Therefore, the only way to interrupt the pathological chain is to take advantage of the rather cruel advice of geneticists and carefully plan the birth of future offspring. In accordance with the recommendations of modern geneticists, carrier women should not have children at all, and only sons should be born in families of hemophiliac men and healthy women; women who are pregnant with girls are offered to undergo an artificial abortion procedure. Currently, scientists have not yet found a way to eliminate the cause of hemophilia; today, unfortunately, this is not yet possible, because it is embedded in the human genetic code. A patient with hemophilia has nothing left to do except learn to live with this disease and get used to the fact that his body every day needs special precautions and especially careful treatment.

Disorders caused by hemophilia
Blood coagulation is a complex biochemical process in which fibrinogen, a protein contained in plasma, changes its structure. This occurs under the influence of various factors, among which the release of tissue thromboplastin is very important. The formation of thromboplastin occurs with the help of numerous substances that are found in small quantities in the blood. One of them, factor VIII, or antihemophilic factor (AHF), is absent or insufficiently present in those affected by hemophilia. The term hemophilia actually refers to two diseases that have the same symptoms but different causes.
There are two types of hemophilia, namely:
Hemophilia A, or classical hemophilia
Hemophilia B, or Christmas disease
Hemophilia C is an extremely rare type that mainly affects Jews
The second type is less common. Type A lacks factor VIII; in hemophilia B, it is factor IX, or plasma, thromboplastin, called Christmas factor. It is also important for blood clotting, and it becomes almost impossible in its absence.
The third type occurs due to a deficiency of factor XI. Due to the non-standard clinical picture, not so long ago this type was isolated separately and is not included in the types of hemophilia.
What is acquired hemophilia?
Hemophilia is inherited. However, cases have been recorded when manifestations of this disease were observed in adults who had not been sick before and did not have patients in their family. Acquired hemophilia is always type A. In half of the cases, doctors were never able to understand the cause of the disease. In other cases, the cause was cancer, taking certain medications, and other reasons that cannot be systematized.
Signs, symptoms, diagnosis and clinical picture of hemophilia
The clinical picture is characterized by an increased tendency of patients to lose blood. Within a few days after birth, bleeding may appear that does not stop, which puts the life of the newborn at risk. But in some cases, hemophilia only appears when the child starts running.
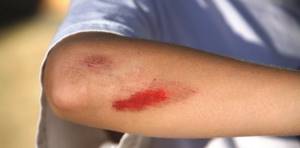
Then parents may observe an increased tendency to bruises, hematomas and bleeding in the skin and mucous membranes after banal microtraumas, such as light shocks, contusions, etc., which indicates this blood disease.
Signs, symptoms of hemophilia
At this age, nosebleeds or bleeding of the oral mucosa (tooth eruption) are also common. In older children, heavy bleeding follows tooth extraction or tonsillectomy. These are the first signs of hemophilia. Bleeding can also occur in internal organs - the liver, spleen, intestines, kidneys and brain, or, as is often the case, in the joints.
In this case, they talk about hemophilic arthropathy or hemarthrosis. As a result of such intra-articular bleeding, especially in the knee, there is a danger of destruction of bones and cartilage and significant limitation of movements of the affected joint, up to their complete absence.
Hemophilia is a disease in which symptoms can occur with varying intensity. The severity of symptoms is proportional to the severity of the genetic defect. If this blood clotting factor is completely absent, the patient is at extreme risk. In severe cases, death occurs in early childhood due to cerebral hemorrhage, too much blood loss after injury, or even because blood accumulates in the neck, leading to suffocation.
As the child grows up, he becomes more and more aware that he is sick and learns to control his activity and, if possible, avoid accidents and injuries. If young patients survive early childhood, they can rightfully hope for a long, active life. It is impossible to foresee more precisely how the disease will develop over time. For example, infections can further increase bleeding tendencies. Sometimes you can observe a clinical course, which is characterized by the presence of several phases.
There is a period when injuries cause only slight loss of blood or even no bleeding at all, then again there comes a time when extensive, practically unprovoked bleeding occurs. Those. hemophilia and its symptoms can appear in waves.
Hemophilia is diagnosed by different specialists - first of all, you need to visit a pediatrician, who can write a referral to a hematologist, neonatologist, geneticist, etc. In case of accompanying complications and pathologies, you need to contact the appropriate specialists. The diagnosis is made after a series of laboratory and genetic tests.
Signs of hemophilia
To clarify the diagnosis, tests may be required: determining the amount of fibrinogen; determination of prothrombin index; determination of thrombin time; definitions of mixed
Couples who are expecting a child and are at risk should consult with specialists and conduct appropriate research from the beginning and throughout pregnancy.
Treatment of hemophilia
Hemophilia cannot be cured; a patient who suffers from this blood disease must fight the symptoms and pathologies caused throughout his life. That is, hemophilia is an incurable disease.
It would be irresponsible not to explain to the parents of a child with hemophilia how dangerous this disease is. However, they should not think that their child is lost. Today, even a patient with hemophilia has the opportunity to lead an almost normal life.
To control the bleeding tendency, replacement therapy is necessary. This means that the missing clotting factor must be replaced by introducing it externally. This can be done by infusion of plasma or whole blood, or by using a concentrate of the factor itself (VIII or IX).
It is extremely important that clotting factor is administered as soon as possible when bleeding occurs. In some countries (USA, Scandinavia), many patients with hemophilia give themselves intravenous injections of plasma concentrate as soon as they notice the slightest bleeding, even before going to the nearest specialized medical center. Since it is difficult to obtain a sufficient amount of factor VIII, recently there has been an active search for methods for its genetic production.
Another possibility is agents that directly stimulate the production of factor VIII in the patient's body.
These therapeutic options ensure the safe performance of minor (tooth extraction, etc.) and major surgical operations in people suffering from hemophilia. Orthopedic treatment is also important, since all kinds of damage to bones or parts of joints are very common. They should be warned.
That is, hemophilia is an incurable disease.
It would be irresponsible not to explain to the parents of a child with hemophilia how dangerous this disease is. However, they should not think that their child is lost. Today, even people with hemophilia have the opportunity to lead an almost normal life.
In addition, proper physical and mental education is necessary so that hemophiliacs do not become rejected groups of people in society because they cannot cope with everyday life.
Patients with hemophilia develop chronic arthropathy due to repeated bleeding in the joint cavity. This represents the most important complication of this hereditary disease. More often it affects one of the knees, sometimes both, and thus can significantly limit the patient’s motor ability. In the future, these symptoms can definitely be improved through the systematic use of plasma concentrate, which will significantly reduce the symptoms of bleeding in the joint.
But even today, many patients with hemophilia suffer from the so-called hemophiliac joint. For some unfortunate patients, the only way to cure their ailment is synovectomy (removal of the synovial membrane of the joint, the pathological change of which as a result of bleeding becomes the main cause of hemophilic arthropathy. Some of the hemophiliacs after such an intervention were able to return to an almost normal life after immobility.
During childhood, wise selection of toys and activities can be extremely important in preventing traumatic episodes. At school age, a patient with hemophilia can, without special exceptions, take part in the normal educational process. He should not be excluded from any of the activities of other children. It is very important that he does not feel inferior while suffering from his illness, so that later he can lead an independent lifestyle. Throughout life, a hemophiliac adapts to his illness. He knows what restrictions it imposes, takes them into account and plans his activities accordingly. Most often, patients with hemophilia have above average intelligence.
Forecast and prevention of hemophilia
Long-term replacement therapy leads to isoimmunization, the formation of antibodies that block the procoagulant activity of the administered factors, and the ineffectiveness of hemostatic therapy in usual doses. In such cases, the patient with hemophilia undergoes plasmapheresis and is prescribed immunosuppressants. Since patients with hemophilia undergo frequent transfusions of blood components, the risk of infection with HIV infection, hepatitis B, C and D, herpes, and cytomegaly cannot be excluded.
Mild hemophilia does not affect life expectancy; in severe hemophilia, the prognosis worsens with massive bleeding caused by operations and injuries.
Prevention involves medical and genetic counseling of married couples with a family history of hemophilia. Children with hemophilia should always have a special passport with them, which indicates the type of disease, blood type and Rh affiliation. They are prescribed a protective regime and injury prevention; clinical observation of a pediatrician, hematologist, pediatric dentist, pediatric orthopedist and other specialists; observation in a specialized hemophilia center.
Every year, World Hemophilia Day is celebrated under a new slogan, which focuses on a particular problem associated with this disease. And although today, thanks to the efforts of doctors and scientists, as well as international organizations to combat hemophilia, this disease is no longer a “death sentence” for the patient, it is still impossible to stop there - this is what World Hemophilia Day reminds humanity.
Head of the clinical and diagnostic laboratory A.M. Radulskaya
3.Diagnostics and treatment
Diagnosis of hemophilia
If your doctor thinks you or your child may have a blood clotting problem, a blood test will be done. The tests will help check your body's clotting factor, the type of hemophilia, and the severity of the disease. The severity of the problem depends on how much clotting factor the body produces and how often and under what conditions bleeding occurs.
Depending on this, there are several types of hemophilia:
- Mild hemophilia
. The blood clotting factor level is at least 5% of normal. This type of disease is not always noticed, especially if the person has not had heavy bleeding after a major injury or surgery. - Moderate hemophilia
- the level of blood clotting factor is from 1% to 5% of normal. Bleeding usually begins after a fall, sprain, or severe muscle strain. - Severe hemophilia
is diagnosed when blood clotting factor levels are below 1% of normal. People with severe hemophilia often bleed up to several times a week, without any obvious reason.
If you have a family history of hemophilia and you are planning a pregnancy, ask your doctor about special tests that can show whether you are a carrier of the disease (only women can be carriers).
Treatment of hemophilia
Hemophilia can be treated by replacing missing clotting factors
. During this therapy, clotting factor concentrate is injected into a vein. This replacement therapy can prevent or treat bleeding.
You may need to take special medications to treat hemophilia. Sometimes such drugs are prescribed before a certain procedure, which may be accompanied by blood loss - surgery or, for example, dental treatment at the dentist. In some cases, it is also necessary to take pain medications to help manage pain due to joint damage.
By following all your doctor's recommendations for treating hemophilia, you will be able to lead a normal life with this disease. As a rule, modern clinics have the necessary resources to help patients with hemophilia.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Under control
Article on the topic
Useful tips from Tatyana Ressina: Do not stop bleeding with hydrogen peroxide! Fortunately, recently our hematologists have had such an opportunity. Since 2005, the state has taken care of the treatment of a number of such patients.
Previously, the presence of a severe disease of the blood coagulation system was a death sentence for its owner, and the life expectancy of patients with hemophilia, for example, was only 30–34 years. This disease was treated with plasma transfusions, after which those suffering from hemophilia, in addition to one serious illness, often received another - hepatitis C. Others became disabled due to hemorrhages that deformed and destroyed joints. But thanks to the state federal program “7 nosologies”, which included the treatment of a number of the most expensive diseases (including blood), there are much fewer such neglected patients in our country. And their hospitalization decreased by 4 times.
By the way
Blood clotting is a protective reaction of the body that prevents blood loss during injuries and other life-threatening conditions. This process is a sequential biochemical reaction that occurs with the participation of blood clotting factors (a number of plasma proteins and calcium ions). To date, 13 blood clotting factors are known, each of which is designated by Roman numerals. And how many children were saved! After all, if you start taking the necessary medications on time, a child with hemophilia can grow up absolutely healthy: go to school, play sports. And when in 2007 a group of teenagers with severe hemophilia climbed Elbrus, for thousands of patients and their parents it was not just a victory. For them, this meant a change from an era of despair to an era of hope.
Of course, such patients have to give themselves intravenous injections of the missing blood clotting factor for life, avoid injuries, blood-thinning drugs containing aspirin, NSAIDs, and carefully undergo vaccinations and other invasive medical procedures and procedures. But otherwise, the lives of people with hereditary and acquired diseases of the blood coagulation system today are practically no different from the lives of their healthy peers. The main thing is to identify the disease in time and keep it under control.
4.What can be done at home for hemophilia?
To prevent bleeding and improve your well-being, patients with hemophilia can recommend the following:
- Ask your doctor about how to manage bleeding if you have hemophilia;
- Maintain a healthy weight. Additional stress on joints due to excess weight can cause bleeding in hemophilia;
- Choose forms of physical activity with caution. It is better to give preference to swimming and other sports that do not put unnecessary stress on the joints;
- Consult your doctor before taking any medications. And do not take aspirin, ibuprofen or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs because they affect blood clotting.
- Organize your living space to avoid injuries and accidents as much as possible.