Author: Sozinova A.V., obstetrician-gynecologist, has been in continuous practice since 2001. January, 2021.
Synonyms: platelets, platelet count, PC, plt.
Platelets are blood cells, and their concentration is determined during a general blood test. On the CBC form, platelets are designated as platelet count or PC. Blood for studying its composition, including counting the number of platelets, is taken from a finger (capillary) or from a vein. The unit of measurement for platelets is the number (N) of cells multiplied by 109 per liter.
Platelets, like other formed elements, are formed in the red bone marrow. Their lifespan in the bloodstream is about 7–12 days. Destruction and breakdown of cells occurs in the spleen and liver tissues.
The main function of platelets is to carry out hemostasis, that is, to stop bleeding. Contact with damaged tissues causes transformation of cells, up to 10 processes are formed in them, and when they spread, the wound is closed with a platelet mass (thrombus). Thus, platelets prevent large amounts of blood from leaking out of damaged soft tissues.
Another equally important function of platelets is to protect the injured area from the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms (they secrete lysozyme and B-lysine).
Platelets also participate in the processes of hemostasis (maintaining the internal environment of the body), nutrition of the capillary endothelium (the inner layer of the walls of blood vessels) and regenerative processes of damaged tissues due to the release of growth factors that stimulate cell division.
A 2021 scientific paper provides evidence showing that in addition to the above functions, platelets also play an important role in the human immune system.
Why are platelets needed?
Platelets ensure normal blood clotting. This function is based on the ability to adhesion, that is, to glue cells together. Normally, platelets do not form agglomerations with other blood cells, and also do not attach to the walls of blood vessels. When a capillary is damaged, a thrombus forms - a blood clot. It blocks damaged vessels, which helps stop bleeding. Functions of platelets:
- Nutritious
. This is the saturation of blood vessels with essential nutrients. Achieved due to the normal permeability of the capillary walls. - Construction
. These cells form connective material in the walls of blood vessels. Protective. Platelets help form the immune response. They can attach to foreign proteins that enter the body. This ability does not allow the infectious process to develop. - Exchange
. When platelets are destroyed, a number of substances are released that are involved in metabolic processes. These connections ensure the integrity of many tissues and vessel walls.
A normal platelet level ensures the maintenance of all vital processes. To identify indicators, you need to contact a medical laboratory. The definition is carried out in different ways. This may be a manual count using microscopy.
Colpitis is one of the most common female diseases. The pathology is based on inflammation of the vaginal walls, which occurs against the background of injuries, hormonal disorders and other unfavorable factors. Read more in the article: “atrophic colpitis: symptoms and treatment in women.”
The most reliable results can be obtained by examining a material sample using a modern analyzer. Many medical centers are equipped with such devices. For diagnosis it is necessary to take a general blood test. The sample is taken from a finger or a vein. It is important to take it in the morning before breakfast.
Why does blood remain liquid?
Thrombosis processes are controlled by the coagulation system. Inside the vessels, the blood is liquid thanks to a system with the opposite function, creating the desired balance.
It includes the following components:
- Anticoagulant system responsible for the rate of coagulation. Blood does not clot unnecessarily.
- The system that ensures that the size of the platelet is able to close the vessel is called fibrinolytic. In particular, it dissolves fibrin threads and plugs that are unnecessary in the process and restores blood flow.
Causes of the primary form
The reasons for the increase in platelets in the blood of women are varied. They can be both primary and secondary in nature. Primary thrombocytosis
- a disease caused by a dysfunction of stem cells in the bone marrow.
The most common cause of this disease is problems with the autoimmune system
.
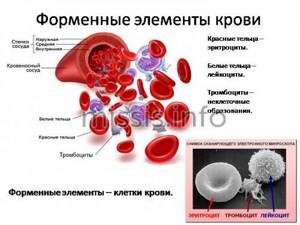
Table of platelet norms in women by age:
| Age | Quantity (thousand/µl) |
| 15-18 years old | From 180 to 340 |
| 18-80 years | From 180 to 320 |
The body begins to perceive its own tissues as pathogenic, which is why such pathogenic responses are formed. The causes of primary thrombocytosis include:
- acute infections
: tuberculosis, tonsillitis, pneumonia, rubella; - blood diseases
: anemia, erythrocytosis, myeloid leukemia, hemolysis, leukemia; - acute poisoning
and large blood loss; - hereditary diseases
: thrombocytopenia, histiocytosis, Chedik-Higashi anomaly, Fanconi syndrome, Bernard-Soulier syndrome and others; - bone marrow lesions
: formation of metastases, bone tuberculosis, radiation after chemotherapy;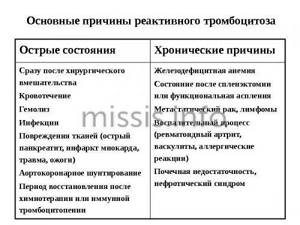
- viral infections
: rickettsiosis, malaria, HIV infection; - frequent bleeding
: both internal and external; - diseases
in which platelet consumption increases: disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, thrombocytopenic purpura, hemodialysis.
Only a specialist can tell you why your platelet levels are high.
Primary thrombocytosis
- myeloproliferative syndrome, which is characterized by the independent proliferation of hematopoietic sprouts in any organ.
Because of this, an excessive number of platelets enter the peripheral blood. In most cases, this disease affects older women; it is rarely diagnosed in young women. Treatment is determined only after a bone marrow myelogram. [media=
https://youtu.be/6f7FjnUYSCc
]
Diagnostics
Thrombocytosis is detected in a clinical blood test. Although very high platelet counts are more common in hematologic diseases, platelet levels alone cannot determine the cause of thrombocytosis. Therefore, if it is detected, you should visit a therapist. The doctor carefully asks about the patient’s complaints, how long ago the symptoms occurred, and conducts a general examination of the patient. Then, based on the data obtained, an additional examination is prescribed, including:
- Blood tests
. In a general blood test, the content of other formed elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes) is determined, and the leukocyte formula is calculated. The concentration of inflammatory markers (ESR, CRP) is measured. The indicators of serum iron, TBC, ferritin are assessed. The presence of autoantibodies (RF, ACCP, antibodies to the cytoplasm of neutrophils) is checked. In case of endocarditis and sepsis, an analysis for procalcitonin and presepsin is performed. - Pathogen identification
. To identify the pathogen, microscopy, bacterial culture of urine and sputum are performed. If tuberculosis is suspected, an intradermal test with tuberculin is prescribed. Using an enzyme immunoassay, antibodies to viruses, parasites, and fungi are detected, and using the polymerase chain reaction method, their DNA and RNA are detected. To diagnose meningitis, a cerebrospinal fluid analysis is informative. - Genetic research
. In patients with myeloproliferative pathologies, mutations of Janus kinase (JAK2V617F), thrombopoietin receptors (MPL), and erythropoietin are determined using fluorescent hybridization (FISH) and PCR. Sometimes chromosomal abnormalities are detected - trisomies, deletions. In chronic myeloid leukemia, cytogenetic analysis reveals the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph). - X-ray
. On an X-ray of the lungs, in case of pneumonia, foci of darkening and infiltrates are noted, in case of tuberculosis - enlargement of the mediastinal lymph nodes, expansion of the roots of the lungs, rounded shadows (cavities) of the upper lobes of the lungs. In patients with arthritis, x-rays of the joints show a narrowing of the joint space, areas of erosion, and marginal osteoporosis. - Ultrasound
. Ultrasound of the abdominal organs in case of pyelonephritis determines compaction and expansion of the pyelocaliceal system, and in case of blood diseases - splenomegaly. In bacterial endocarditis, cardiac echocardiography reveals vegetations of the valves and sometimes effusion into the pericardial cavity. - Endoscopy
. In patients with inflammatory bowel pathologies, fibrocolonoscopy is performed, which reveals hyperemia of the mucous membrane, lack of vascular pattern, erosion, and ulcerative defects. Crohn's disease is characterized by the "cobblestone pavement" symptom - alternating deep ulcers with unchanged mucous membrane. - Histological studies
. In bone marrow aspirate for malignant hematological pathologies, hyperplasia of the megakaryocyte lineage of hematopoiesis is noted (in polycythemia vera - all three lineages), a large number of blast cells (in myeloid leukemia), proliferation of reticulin and collagen fibers (fibrosis). In case of vasculitis, a biopsy of a vessel reveals pronounced perivascular infiltration with lymphocytes and plasma cells.

Platelet count according to Fonio
Causes of the secondary form
Secondary thrombocytosis
- increased platelet levels caused by high levels of these substances in the blood.
Most often, such changes in the body are characterized by a chronic course. Among the most common causes of thrombocytosis in women are injuries, internal inflammation, and hematological abnormalities in functioning. In addition, secondary thrombocytosis can be caused by:
- Infections
- most often the disease occurs due to the influence of any bacteria or virus on the body. The influence of such substances can be recognized by changes in certain indicators: white blood cells and leukocytes increase. This indicates the presence of an inflammatory process. - Hematological disorders
- Low iron levels can cause a high platelet count in the blood. Such changes are characteristic of acute blood loss, anemia, and the consequences of chemotherapy.
- Removal of the spleen
- 30% of all platelets are constantly located in this organ. During the removal of this organ, the blood cells contained in it enter the general channel, which is why the platelet count begins to grow rapidly. - Injury or surgery
- in this case, the body is affected by post-traumatic stress and the consequences of the operation. Also, the number of platelets in women increases due to pancreatitis, enterocolitis, and tissue necrosis. - Inflammatory processes
- due to increased levels of interleukin - an anti-inflammatory protein - the level of the hormone thrombopoepin increases. This substance promotes accelerated maturation, division and release of platelets. - Malignant tumors
- lymphomas, hepatoblastomas, neuroblastomas. - Taking certain medications
.
[media=
https://youtu.be/arLn-Z53ib0
]
Basic blood clotting tests performed in the laboratory
During the analysis, coagulation is examined, the ability to clot is assessed, and a coagulogram is compiled. The main indicators are the values of the coagulation and anticoagulation characteristics in combination. The schedule will show whether the balance between processes has been maintained.
When examining a sample, the following basic values are revealed:
- PTT – prothrombin time.
- PTI - prothrombin index or INR - international normalized ratio.
Symptoms of the primary form
In most cases, thrombocytosis manifests itself only in the case of the primary form. Adult women often do not pay attention to the emerging signs of this disease, which subsequently leads to disastrous consequences. Most often, this disease is diagnosed completely by accident when a woman receives the results of a blood test. Primary thrombocytosis can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- headache is the very first sign of the primary form;
- frequent nosebleeds;

- decreased body strength;
- pain in the fingertips - occurs due to a rush of blood to the extremities;
- constant itching of the skin;
- weakness, lethargy;
- decreased visual acuity.
If you notice at least a few of these changes, consult your doctor immediately.
To suspect thrombocytosis, a woman does not have to notice all the symptoms at once. To do this, it is enough to diagnose yourself with at least 2-3 certain signs
.
The vaginal secretion of a completely healthy girl is characterized by a characteristic, barely perceptible odor that does not cause disgust. The appearance of a nauseating fishy odor indicates a violation of the vaginal microflora and a deterioration of the bacterial or fungal composition. Read more in the article: “discharge with a fishy odor in women: causes, treatment.”
The manifestations of this disease should not be ignored, as there is a high risk of serious complications. Pregnant women need to be more attentive to the condition of their body. Primary thrombocytosis is especially dangerous with a high risk of plaque formation in the veins.
doctor
With size under consideration, platelets are examined for average volume. A popular question that is asked to the doctor: what does excess volume mean?
Answer: about the quality of platelets, not about the number. Mature cells occupy less volume in a given amount of blood. The reason for this is size.
Platelets with a formed structure differ from immature ones, which take up more space. An increase in volume above normal indicates the presence of immature (defective) platelets.
Symptoms of the secondary form
Secondary form of thrombocytosis
- a latent course of the disease that does not manifest itself with external signs.
The disease can only be recognized based on the results of functional diagnostics. Doctors make this diagnosis when:
- hemorrhagic syndrome;
- neurological disorders: cerebral ischemia, microcirculation pathologies;
- disruption of pregnancy or miscarriage;
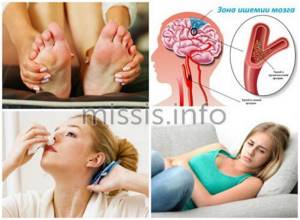
- thrombosis or thromboembolism;
- erythromelalgia - low vasomotor reflexes.
It is quite difficult to recognize the secondary form of thrombocytosis in women.
. External signs may be absent at all or may differ depending on the characteristics of the organism. The disease can be suspected by a constant feeling of fullness in the abdomen, pain in the joints, subcutaneous bleeding, chronic fatigue, shortness of breath, and migraines. It is advisable to consult a doctor if you have at least several signs. If necessary, he will give you medication to reduce the number of these cells.
Indications
Prescription of an OAC with a study of platelet concentration is indicated for all patients who visit the clinic, undergo a routine medical examination, or receive a referral for inpatient treatment. Also, platelet determination is prescribed to all patients requiring surgery (emergency or planned). The main indications for platelet testing include:
- suspicion of disturbances in the hemostatic system (bleeding, formation of subcutaneous hematomas);
- suspicion of a malignant process;
- immunity disorders;
- bronchopulmonary pathology;
- diseases of the digestive tract and urinary system (stomach ulcer, glomerulonephritis);
- cardiovascular pathology;
- endocrine disorders (obesity, diabetes).
Symptoms that should alert you
- red, purple bruises on the skin
- frequent nosebleeds, bleeding gums
- prolonged bleeding of even small wounds or cuts
- heavy menstrual bleeding in women
How to treat pathology
Scientists do not know why the bone marrow begins to produce more megakaryocytes, which increase the production of blood platelets, and what to do to normalize their number. This means that therapy comes down not to eliminating the cause of the pathology, but to treating the consequences. Excess blood cells are treated with medication. Appointed:
- drugs that reduce blood clotting (anticoagulants);
- medications that prevent platelets from sticking together (antiplatelet agents);

- interferon, which stimulates the immune system;
- Anagrelide is a drug that inhibits the formation of platelets from megakaryocytes.
In some cases, when there is a tendency to further increase, doctors resort to the procedure of plateletpheresis. The blood is separated to reduce the excess level of blood cells. It must be remembered that blood viscosity increases:
- hormonal drugs;
- contraceptives;
- diuretics;

- smoking;
- alcohol.
Information about these factors should be reported to your doctor.
Blood clot formation
Blood clotting occurs with any damage to blood vessels. Platelets come to this place, as a result of which further leakage stops.
With a minor injury, a primary white thrombus occurs. If a large vessel is damaged, an enzyme is activated, leading to a series of reactions, activation of coagulation factors.
Fibrin molecules line up in the form of threads, forming a strong blood clot. Calcium ions crosslink them in the form of bridges. If fibrin does not have enough strength, the wound takes a long time to heal. When such a complex of reactions is triggered, a red blood clot is obtained (the result of secondary hemostasis).
Tibetan healing methods
Diagnostics in Tibetan medicine, in addition to traditional methods, includes:
- Inspection
. The specialist examines the general appearance of the patient: body features, posture, how he walks, how he speaks. Carefully examines the condition of the eyes, tongue, skin, and lymph nodes. - Survey
. The doctor collects a detailed medical history: finds out what events preceded the onset of the disease, what lifestyle the patient leads, how he reacts to stressful situations, and what food preferences he has. - Pulse diagnostics
. Based on the nature of the pulse, a doctor of Tibetan medicine determines the condition of each individual organ and the body as a whole, and identifies the disease in its very infancy.

Depending on the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed individual treatment. In oriental medicine centers, it consists of a set of therapeutic measures and procedures that make it possible to eradicate the real cause of the disease, and not just eliminate visible clinical symptoms. Much attention is paid to correcting the patient’s lifestyle, including a transition to proper nutrition, the introduction of reasonable physical activity and achieving a balanced state of the nervous system.

A set of external procedures, including energy acupressure, acupuncture, stone therapy, moxotherapy, vacuum therapy, restores energy balance, normalizes regulatory and metabolic processes, activates organ functions, and improves blood circulation. Herbal medicine is an effective method of treating thrombocytosis. Tibetan herbal remedies and Baikal herbs cleanse the blood and tone the walls of blood vessels.
Thrombocytopoiesis
Thrombocytopoiesis is a type of hematopoiesis process. The result is the production of platelets - parts of the cytoplasm of megakaryocyte cells.
Thrombocytopoiesis consists of the following stages:
- The process of maturation of megakaryocytes, megakaryoblasts, promegakaryocytes.
- They are preceded by c-mpl cells with the receptors to which it binds.
- As a result of the signal, c-mpl grow and mature.
- The membrane stabilizes and divides the cytoplasm into fragments.
- These areas are separated from the original cell. Platelets have formed.
Foods that affect platelets
The following foods raise blood platelet levels when levels are low in adults:
- Liver
. It donates a large amount of iron, which is necessary for the normal function of the hematopoietic system.
- Buckwheat
. Contains a high level of protein, which is required for synthetic processes occurring in the body. - Fruits (apples, bananas, oranges)
. Fruits contain a large amount of various vitamins required for all synthetic processes during hematopoiesis. - Fish (sea species)
. Contains a large amount of protein and elements required for the formation of blood cells. - Dairy
. These products contain a high content of calcium and protein, without which biochemical processes in the human body do not occur.

When dieting to reduce platelet counts, the following rules must be followed:
- Eat meals at the same time every day.
- Eliminate from your diet foods that contain large amounts of fats and carbohydrates.
- Include foods containing iodine and organic acids in your diet.

The following foods are prohibited on this diet:
{banner_banstat8}
- drinks containing alcohol;
- cereals;
- smoked meats;

- sweet carbonated drinks;
- various confectionery products.
Foods that should be included in the diet to achieve normal platelet values have been presented previously.
Preventive measures
In the early stages of the disease, patients can prevent its progression in the future. To do this, it is necessary to normalize the level of physical activity, that is, to abandon active training. It is permissible to perform only light warm-up and morning exercises. Patients with low platelet counts are advised to choose an office-type job. The basis for good health in thrombocytopenia is adequate sleep and proper nutrition. Adults need to sleep at least 9 hours a day.
As for the diet, women and men should avoid eating pickles, pickled foods, spicy and smoked foods. The use of alcohol and tobacco products, sugar, and hot seasonings is unacceptable. The emphasis in the diet should be on food of plant origin. Doctors do not recommend taking antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs such as Aspirin or Analgin during an exacerbation of the disease. To maintain the functioning of the body, you need to take vitamin and mineral complexes.