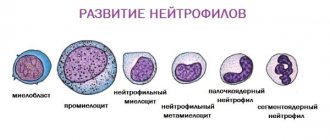
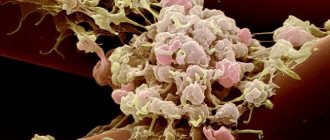
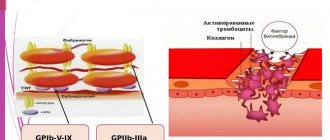
Platelets are small spherical blood plates that do not have nuclei. They perform a vital function in the body, namely they participate in blood clotting. Even minor environmental disturbances activate the red plates. While in a state of activation, they attach to each other and the site of damage, thus forming a blood clot, blocking the damage.
What do low platelets mean?
Platelets are red blood cells that influence the rate at which cuts and wounds heal. When bleeding develops, they create a protective plug that stops it, thereby preventing the development of negative consequences. When the permissible level of PLT decreases in the patient’s body, a blood clotting disorder occurs, which subsequently leads to thrombocytopenia.
Thrombocytopenia acts as a separate disease or is a consequence of another disease. To clarify the overall clinical picture, patients are required to undergo a series of diagnostic tests. There are the main reasons that affect the decrease in platelet levels in the body:
- insufficient production of PLT by the bone marrow;
- increased destruction of platelets in the blood;
- inadequate distribution of platelets in the vessels.

People with chronic diseases of the immune system, patients with leukemia, and citizens who take certain types of medications for a long time are at risk. Low PLT levels are not always accompanied by negative symptoms. In critical cases, when the level of red blood cells in the blood is extremely low, the patient's body may develop internal bleeding, which often leads to death.
One of the most common vascular pathologies is varicose veins, which occurs in men and women, especially after 40-50 years. There are many reasons for the formation of the disease, and by identifying them, you can decide on the optimal treatment method. Read more in the article: “varicose veins on the legs: symptoms and treatment.”
How to normalize platelet levels
To compensate for platelet deficiency, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the imbalance. Here it is necessary to act based on blood tests and the presence of a particular disease.
A decrease in platelet levels is not always critical and requires immediate hospitalization of the patient. Most often, such a deficiency can be replenished at home naturally.
- Normalize your diet. It is necessary to exclude coffee, alcoholic drinks, sugar, and too high-calorie foods. Add fresh vegetables, fruits and herbs to your diet: tomatoes, cucumbers, apples, oranges, parsley.
- Add freshly squeezed juices rich in vitamins and minerals to your diet. You can take vitamin complexes as prescribed by your doctor.

- A mandatory dish in the diet should be fish rich in Omega-3 acids. It could be tuna, salmon.
- It is important to drink plenty of clean water at room temperature.
- It is necessary to follow the correct daily routine. Sleep should last at least 8 hours.
- Whenever possible, do cardio exercises to help strengthen your immune system.
[media=
https://youtu.be/6f7FjnUYSCc
]
It is very often possible to detect a decrease in platelets only after a laboratory test. The disease may not manifest itself in any way for a long period of time. However, once thrombocytopenia is diagnosed, monitoring by medical personnel is required. Treatment should begin after all causes have been clarified. When the platelet level is not critically low, it can be increased at home. But it is important to regularly donate blood for analysis, so that if something happens, you can track negative dynamics and take the necessary measures as quickly as possible.
How does thrombocytopenia manifest?
Most often, patients with low levels of PLT in the body experience the appearance of bruises on the skin, which form from harmless and minor impacts. Thrombocytopenia is accompanied by profuse and continuous bleeding from cuts. Pinpoint hemorrhages are common, which manifest themselves in the form of a hemorrhagic rash. Additional symptoms may include:
- Bleeding gums when brushing teeth, formation of non-healing ulcers. Sometimes hematomas form in the absence of any trauma.
- Regular nosebleeds.
- Periodic nosebleeds.
- The appearance of blood clots in the urine and feces.
- Heavy menstruation. Women may experience severe monthly hemorrhages that exceed the amount of blood loss that they were used to seeing previously.
- The appearance of hematomas on the skin.

Thrombocytopenia cuts can be life-threatening for the patient. If the level of platelets in the body is critically low, then even with minor trauma to the skin, a person can lose a large volume of blood, which will lead to death. Patients may also experience bleeding not associated with menstruation, which is of unknown origin. Below are a number of reasons that may influence the decrease in PLT levels and the formation of thrombocytopenia.
Vasomotor rhinitis is inflammation and swelling of the nasal mucosa of a chronic nature, accompanied by impaired nasal breathing. There are two types of such a runny nose: allergic (developing in unfavorable conditions) and neurovegetative (arising due to impaired innervation of blood vessels). Read more in the article: “how to get rid of rhinitis forever.”
Bone marrow diseases
Almost all bone marrow pathologies are accompanied by a decrease in platelets in the blood and impaired production of formed elements. The development of bone marrow diseases is influenced by pathogenic external factors. For example, frequent radiation, use of narcotic drugs, long-term therapy with drugs with aggressive composition. Most often, bone marrow diseases develop with long-term use of antibiotics, antidepressants, and antiulcer drugs. Additional reasons include:
- Anemia. The pathology develops against the background of a deficiency of folic acid and cyanocobalamin in a woman’s body. These elements take part in the process of cell reproduction and maturation. If they are deficient, the patient's blood clotting is impaired, which leads to the formation of thrombocytopenia. Also, with low platelets, the likelihood of leukopenia is not uncommon.
- Oncological diseases that affect the bone marrow (leukemia).
- Infectious diseases that affect the hematopoietic organs. For example, HIV, viral hepatitis, mononucleosis.
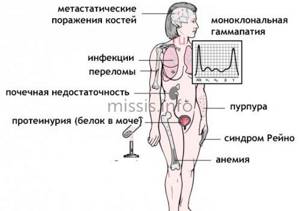
Hereditary bone marrow pathologies can also lead to thrombocytopenia. For example, the May-Hegglin anomaly. This disease is accompanied by a genetic mutation, which results in a deficiency of megakaryocytes and a decrease in the concentration of platelets in the blood.
Diseases accompanied by platelet destruction
Rheumatic pathologies, which are based on autoimmune diseases, often lead to premature destruction of PLT. In this case, the woman’s body produces antibodies that reduce the concentration of red blood cells and lead to thrombocytopenia. PLT destruction is affected by surgery and some medical procedures. For example, hemodialysis, installation of prosthetic heart valves. Additional reasons include:
| Pathology | Manifestation |
| Intoxication of the body | Leads to the death of plasma formed elements and subsequent blood clotting disorders |
| DIC syndrome | Pathology develops against the background of the release of certain substances from tissues, which contribute to the start of the blood clotting process |
| Blood transfusion | In this case, the process of destruction of red blood cells and white blood cells is observed in the human body. This subsequently leads to the formation of thrombocytopenia |
The destruction of PLT can be caused by renal failure and pathologies that lead to poisoning by products of protein metabolism. Accelerated destruction of platelets, which results in thrombocytopenia, is observed with an increase in the size of the spleen. There are frequent cases of blood clotting disorders with uremia.
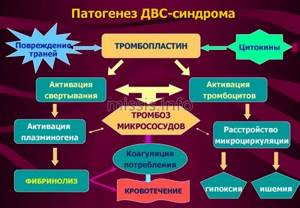
Pathological distribution of blood platelets
Increased venous pressure, which is a common symptom of portal hypertension, leads to platelet redistribution and blood clotting disorders. This pathology develops against the background of liver cirrhosis and blood stagnation. Thrombocytopenia is caused by heart failure, which is accompanied by impaired blood circulation. Low levels of PLT in the blood are observed with an increase in liver size. Auxiliary factors affecting low platelets in the blood of women:
- passion for alcoholic beverages, which inhibit the functions of the hematopoietic organs;
- injuries resulting in heavy blood loss;
- problematic periods;
- During pregnancy and breastfeeding.

Food poisoning, allergic reactions, and long-term use of certain medications also lead to the development of problems with blood clotting. In a child, thrombocytopenia is observed during the rehabilitation period after treatment of viral infections. Sometimes the disease appears in childhood after vaccinations.
The danger of low platelets
The danger of a low platelet count in the blood is that this condition can provoke diseases of the spleen, liver, and cause the formation of blood clots. Increased stress can cause leukemia, a blood disease when blood clotting is impaired. As a result, even a minor wound can lead to heavy blood loss and even death.
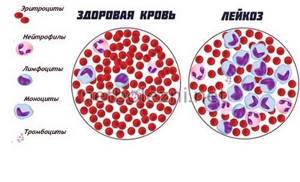
During menstruation, the number of platelets in the blood decreases, which eliminates the risk of strokes and heart attacks and helps in the future to bear offspring. However, excessive bleeding is a reason to consult a specialist to find out the cause of this condition.
Low PLT levels in pregnant women
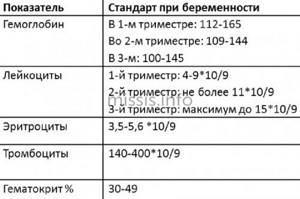
During pregnancy, a slight decrease in PLT is not a pathology. It can occur against the background of an unbalanced diet or the individual characteristics of a particular organism. Normally, the indicators should remain at the level of 100*109/l. If platelet levels drop below this level, this can lead to unpleasant consequences:
- bleeding during childbirth;
- miscarriage in the early stages of pregnancy;
- late toxicosis;
- early birth;
- internal hemorrhage.
At critically low levels, death is likely. If thrombocytopenia is suspected, a pregnant woman must undergo a clinical examination and also have a coagulogram. This is a procedure that determines the level of plasma coagulation in the body. You may also need to be tested for thrombophilia. This is a disease in which the concentration of PLT in the blood also decreases and problems with blood clotting occur.
If the doctor determines that low platelets are an independent symptom that arose against the background of hormonal changes in the body during pregnancy, after childbirth the indicators will normalize. If a blood clotting disorder occurs against the background of an internal disease, then complex treatment will be required. Such measures are necessary in order to eliminate the likelihood of problematic childbirth.
How to avoid bleeding
Cancer and cancer treatments can cause low platelet counts. When your platelet count is low, you are at risk of bleeding. If your doctor has told you that you have a low platelet count, it is important to try to avoid injury.
We will list some general tips that can help you prevent bleeding. It is also very important to discuss your lifestyle with your healthcare professional. They may suggest other ways to prevent bleeding if your platelet count is low.
Personal care
- Do not use sharp objects such as straight razors, scissors or nail clippers. You can use an electric razor.
- Do not: manicure or pedicure;
- waxing;
- electrolysis;
- tattoos
- rectal suppositories (medicines that are inserted into the anus);
Dental care
- Use a brush with soft bristles.
- Consult your doctor before starting dental treatment.
Daily Activities
- Wear gloves when doing gardening, cooking, or making repairs at home.
- Avoid activities that could cause injury. These include: contact sports;
- climbing a stepladder;
- intense physical exercise;
- Biking;
- lifting weights.
- use lubricants if necessary;
Medicines
- Do not take: aspirin or medications containing aspirin;
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen (Advil®, Motrin®) and naproxen (Aleve®);
- vitamin E
to come back to the beginning
Consequences of thrombocytopenia
Small deviations from the norm are not dangerous to human health. With timely diagnosis and treatment, patients can avoid the development of pathological consequences. However, if thrombocytopenia is ignored and there is no comprehensive treatment, sick people risk encountering the following pathologies:
- development of subcutaneous bruises with minor injuries;
- internal bleeding that poses a threat to human life;
- hemorrhage in the retina of the eye, which can result in blindness for a person;
- hemorrhagic stroke.
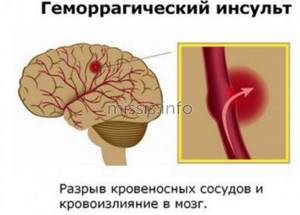
The patient may also experience bleeding in the brain. This is a rare, but quite dangerous phenomenon. It develops most often with serious head injuries, but can also occur spontaneously, without any bruises. Bleeding in the brain also occurs against the background of frequent nosebleeds. The prognosis in this case is unfavorable - a quarter of such cases end in the death of the sick person. The prognosis for recovery with a low platelet level depends on the characteristics of the patient’s body, his age, the duration of the disease, and the presence of auxiliary pathologies in the body.
Types of thrombocytopenia
Pathology is divided into several types. They are classified according to severity and prognosis for the life of the bleating person. Whether the patient needs hospitalization and, in principle, treatment depends on the type of disease diagnosed. Types of thrombocytopenia:
- Mild degree
. The PLT level remains at 50-150 thousand in 1 microliter of plasma. These indicators are considered acceptable for normal blood clotting, so bleeding and hemorrhage do not occur in this case. There is no need to treat the pathology. It is only recommended to normalize your lifestyle and undergo examination every six months. - Medium severity
. The indicators remain at around 20-50 thousand in 1 microliter of blood. The patient experiences bruising, and women may experience heavy periods. Treatment will be required if bleeding becomes regular. People who lead an active lifestyle are also treated. For example, professional athletes.

With severe thrombocytopenia, women and men develop spontaneous bleeding from the nose, oral mucosa, and vagina. Patients may observe the appearance of plasma clots in the stool and urine. In this case, urgent hospitalization is required to prevent the possibility of hemorrhage in the brain or retina.
Treatment
If your platelet count is 10,000 microliters or less, you may need a platelet transfusion to increase your platelet count.
You may also need a transfusion if your platelet count is more than 10,000 microliters, but you are bleeding heavily, are having an invasive (involving going inside the body through an incision, cut or puncture) procedure, or have signs of other problems.
If you experience heavy menstrual bleeding, consult your doctor.
You may need to start hormonal therapy with birth control pills to prevent your next menstrual bleeding. to come back to the beginning
Hospitalization for thrombocytopenia
Adult patients who have a mild form of pathology do not require hospitalization or complex treatment. They need to normalize their lifestyle, monitor their diet, and give up bad habits. Also, such patients will need to undergo regular examinations and tests in order to monitor the level of PLT in the blood and timely notice pathogenic changes in the body.
For a moderately severe disease that is not accompanied by severe symptoms, home therapy is recommended. In such cases, doctors prescribe the necessary medications and instruct patients about the dangers of thrombocytopenia. Patients will need to give up active physical training and complex homework. They will also need to normalize their diet and remove alcohol and cigarettes from their lives.
If platelet counts are critically low, sick people will require mandatory hospitalization. This condition is life-threatening, so all patients in this case should be under close medical supervision. Those citizens who regularly experience bleeding from the nose, mouth, or vagina are also subject to hospitalization.

What does it mean to have a reduced average platelet volume in the blood of an adult?
Platelets are an important component of blood, since they are responsible for coagulation processes and nutrition of blood vessels. If the integrity of the blood vessels has been compromised, platelets fuse with each other to restore its integrity and prevent blood loss. If the average platelet volume is low, this may cause excessive bleeding. This is why it is so important to understand what the MPV index means in a blood test and how treatment is carried out.

Normal blood test
Like other blood indicators, average platelets also have standards that are necessary for the proper functioning of the body: for children and adults the indicators are 200-400*109/l, for MPV (average platelet volume) is 7.5-11 Fl.
Blood cells are sensitive to external conditions (temperature, humidity, pressure level), the state of the body, so a decrease or increase in the blood is not always a pathological condition.
Preventive measures
In the early stages of the disease, patients can prevent its progression in the future. To do this, it is necessary to normalize the level of physical activity, that is, to abandon active training. It is permissible to perform only light warm-up and morning exercises. Patients with low platelet counts are advised to choose an office-type job. The basis for good health in thrombocytopenia is adequate sleep and proper nutrition. Adults need to sleep at least 9 hours a day.
As for the diet, women and men should avoid eating pickles, pickled foods, spicy and smoked foods. The use of alcohol and tobacco products, sugar, and hot seasonings is unacceptable. The emphasis in the diet should be on food of plant origin. Doctors do not recommend taking antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs such as Aspirin or Analgin during an exacerbation of the disease. To maintain the functioning of the body, you need to take vitamin and mineral complexes.