Published: 02/16/2021 16:45:00 Updated: 02/18/2021
Leukocytes are the most important element of blood and the basis of the body's immunity. Our blood is red in color thanks to erythrocytes - red blood cells. For every thousand red blood cells, there is on average only one white blood cell. However, despite the small percentage, these cells play an important role in human health. They are different in function, shape, appearance. Their main task is to protect the body from viruses, bacteria, fungi and other “pests” that attack it, fight tissue damage and destroy its own aged or mutated cells. They are the foundation of the body's defenses.
Despite the fact that leukocytes are determined mainly in the blood, they are produced by a special organ – the bone marrow. Accordingly, they are formed in response to any tissue damage. This is part of a healthy, natural inflammatory response.
Types of leukocytes
Under a microscope, you can see several dozen different forms of leukocytes - different stages of maturation, or “age”.
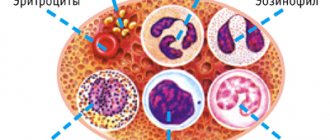
There are 5 main groups of mature cells. Basophils are the smallest group of leukocytes. They regulate blood flow in small vessels, help other white blood cells move through tissues, and influence the growth of new capillaries. Basophils control the occurrence of allergic reactions, suppress allergens, regulate blood clotting, and neutralize toxins and poisons. When an allergen comes into contact with a basophil, this cell releases many bioactive substances responsible for the development of allergic reactions.
Eosinophils - together with basophils, they are markers of a hypersensitive reaction in the body. They also participate in allergic mechanisms, but in a different way. Unlike basophils, which cause an allergic reaction, eosinophils, on the contrary, fight it by binding foreign particles. They have antiparasitic and bactericidal activity, and are responsible for the fight against multicellular parasites - helminths. Their percentage in the blood is normal - about 1-4%. An increase in content, first of all, may indicate severe allergic conditions, helminthiasis, rheumatological diseases, and, less often, oncological pathology.
Neutrophils are a rapid response squad and the most numerous group of leukocytes (up to 80% of the total). As soon as a foreign substance (for example, a splinter, bacteria, or virus) enters the body, neutrophils immediately move to it to destroy it. They release many active enzymes towards the foreign invader and literally break down and digest any substance not related to the body - this process is called phagocytosis. Alas, having won several such battles, the neutrophils themselves die.
Monocytes are a type of large cell. They also carry out phagocytosis - they “eat” bacteria and microbes that enter the body, cleanse the blood of dead leukocytes and produce interferon. They are able to transmit information to lymphocytes about what microbe they have encountered.
Lymphocytes are the main ones in the implementation of cellular and humoral immunity. They secrete protective antibodies and coordinate the work of all other types of white cells.
As we see, leukocytes are a real army of the immune system, guarding our health. Without their correct operation, a person is defenseless against viruses, bacteria and fungi.
What to look for first?
According to therapists, the main parameters are the level of hemoglobin, platelets, leukocytes and ESR, also known as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. And also the leukocyte formula - the percentage of leukocytes of different types.
Hemoglobin, an iron-containing protein in red blood cells that is responsible for gas exchange and metabolism, is the first thing therapists look at. Hemoglobin levels in women are lower than in men due to differences in muscle mass. Elevated levels are much less common than low levels and may hint at pathologies of the heart, kidneys or bone marrow. He is referred to a hematologist, unless the patient is a donor. After a transfusion, their red blood cells are restored sharply, so their number increases greatly and they have to continue donating blood to maintain balance. But the decrease is most often caused by an unbalanced diet, physical overload and liver disease. A greatly reduced reading is a sign of more serious problems.
“If a man has very low hemoglobin, I suspect bleeding,” Shcherbina shares her experience. “Perhaps tiny drops of blood are released in the stomach or intestines, perhaps it’s hemorrhoids, or the ureter is bleeding due to urolithiasis. In women, this, coupled with pallor, indicates serious anemia.”
Platelets are responsible for blood clotting. If their level is low, the patient will not be taken for surgery - it will not be easy to stop the bleeding. At elevated levels, there is a high risk of thrombus formation—blood clots that block a vessel and cause a heart attack or stroke. The level of platelets indicates the condition of blood vessels, and in combination with others helps to understand the nature of many diseases.
Leukocytes protect the body from infections, viruses and allergens. Before the healthcare reform in Russia, the norm was considered to be (6−8)*109/l, now (4−11)*109/l. A deficiency of white blood cells may indicate problems with the immune system, a lack of B vitamins, or a malfunction of the bone marrow. An elevated level indicates inflammation in the body, and the degree of its intensity helps to understand the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
“If leukocytes are less than 4*109/l, ESR is more than 30 mm/h, and in the leukocyte formula neutrophils are increased to 70−80%, I am looking for a source of inflammation,” says Victor Shcherbina. — At a temperature below 40 °C it can be pneumonia or acute prostatitis. If the situation is the opposite - an excess of leukocytes and a lack of neutrophils, I suspect lymphocytic leukemia and refer to a hematologist.”
Thus, the leukocyte formula helps to understand the source of problems based on the immune reaction: as a rule, only cells, for example, lymphocytes, react to viruses, and neutrophils react to bacteria. According to Andrey Besedin, for example, inflammation can be caused by both viruses and bacteria, and leukocyte counts are needed to determine treatment tactics and monitor the patient.
Analysis for leukocytes in the blood
To determine the level of leukocytes, a classic general blood test is used - the most popular test, without which not a single examination can be done.
In addition to identifying five types of white cells, the analysis reveals the number and characteristics of red blood cells, hemoglobin, platelets and other blood components.
It is also necessary in the diagnosis of anemia, diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory processes, as an element of preventive examination, in the diagnosis of a diverse range of diseases and for monitoring treatment.
General urine analysis
Urinalysis is the basic method for assessing the condition of the urinary system. It allows you to diagnose signs of infectious processes and suspect vesicourethral reflux, as well as kidney diseases, which are characteristic of childhood:
- lipoid nephrosis;
- poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis;
- polycystic kidney disease and other disorders.
The results of a general urine test are always considered in conjunction with the symptoms of the disease and the results of other laboratory tests. That is why analysis is included in the mandatory examination program for schoolchildren.
Norm of leukocytes in the blood
Speaking about the norm of almost any laboratory analysis, you need to know that laboratories can work on different installations, use different analysis methods and different reagents.
Therefore, depending on the laboratory, reference values - the limits of normal - may vary slightly. Normally, leukocytes in the blood of adult men and women are contained in an amount of 4-9 × 10 U/l.
The content of leukocytes in the blood of a child is normally higher than that of an adult. For example, in newborns this figure reaches 9.2-13.8x10 U/l. As the child gets older, the level of white cells normally decreases. At the age of three years, the normal range is 6-17x10 U/l, and by ten years it is already 6.1-11.4 x10 U/l.
Pregnant women also often have higher white blood cell levels than normal adults. By the end of the third semester, an increased level of white cells is considered normal. This is due to the increased load on the body.
In older people, the production of leukocytes can decrease by 2-3%, and their activity and protective functions are reduced by almost half. This is one of the reasons why older people have weakened immune systems.
A deviation in the level of leukocytes in one direction or another from the norm indicates health problems. In this case, it is important to know not only the indicator of white cells in the patient’s blood in general (total quantity), but also each type of these cells separately.
The leukocyte formula in a healthy adult is as follows:
- neutrophils: band - 1-5%, segmented - 40-70%;
- lymphocytes – 20-45%;
- monocytes – 3-8%;
- eosinophils – 1-5%;
- basophils – 0-1%.
Bleeding disorders
Some people are terribly afraid of the sight of a cut finger, especially their own, but this fear is irrational. A healthy person simply cannot bleed through even fairly large cuts, since nature has provided us with an excellent blood clotting mechanism. But how can you tell if clotting has worsened?
Who clots the blood
The hemostasis system (stopping bleeding) consists of two parts - vascular-platelet and coagulation, also known as plasma.
The vascular-platelet unit acts as follows: at the moment of injury, damaged cells of the vessel wall release a number of special substances that activate platelets. As a result, platelets become entangled with each other, forming a loose mass, and acquire the ability for adhesion (sticking to the damaged area of the vessel) and aggregation (sticking together into piles). This is how a primary loose thrombus is formed. For capillary bleeding (cut finger) it is enough, but in large vessels where blood moves at high speed, such a design will simply be “knocked out” by the pressure.
Therefore, a coagulation link is necessary - this is the actual coagulation. Coagulation factors (FCs) are constantly present in the blood plasma, and in such quantities that it would be enough for almost all the blood at once (this suggests a plot for a horror film). But, like platelets, PS are in an inactive state until the wounded vascular wall emits its biochemical “cry for help.” Once activated, coagulation factors form a three-dimensional network of fibrin, the task of which is to wrap the primary thrombus, strengthening it and firmly fixing it on the damaged area.
Irregularities in the work of the first link
Since the first link has two components, problems can arise with any of them. Decreased coagulation of platelet origin can have two reasons: a decrease in the number of platelets or their genetic inferiority. Increased fragility of the vascular wall (also, as a rule, genetically determined) also leads to bleeding.
Any of these options will make itself felt by easily occurring bruises that appear “from nowhere,” that is, with such light blows that a person does not even remember; Frequent nasal, gingival, and, in women, uterine bleeding are also typical.
Elevated leukocytes in the blood
Leukocytosis occurs as a consequence of pathological processes.
When aggressors invade the body, it releases a large number of white cells into the blood to fight the threat. Leukocytosis can be observed in the following pathological processes:
- infectious diseases of any nature (including infection with viruses and purulent infections);
- against the background of chronic inflammatory processes;
- for some cancers;
- for allergic reactions;
- in the presence of parasites in the body;
- in situations where the protective barrier of the skin is damaged (with large-scale burns and frostbite).
There are a number of conditions that are not associated with diseases, but in which the level of leukocytes in the blood also increases.
We are talking about severe stress, smoking and strict diets. There are also several physiological conditions that naturally cause elevated readings. As we described above, in pregnant women, leukocytes increase closer to childbirth. The indicator rises immediately after eating and returns to normal after a few hours - so it is important to donate blood at least 5 hours after eating. A bath or sauna and vigorous physical activity before the test can also raise the level of white blood cells.
To get a reliable result, a general blood test must be taken strictly in a calm state on an empty stomach.
When is one analysis enough?
In some cases, the doctor, having received the test result from a fingerprint, already understands what the problem is and how to solve it.
“Blood very often helps to determine various signs of a disease by the balance of blood cells and the ratio of cells,” says Andrey Besedin, candidate of medical sciences, family doctor at GMS Clinic. — For example, a deficiency of red blood cells coupled with low hemoglobin is a typical picture of anemia and it is imperative to look for and eliminate its cause. Sometimes this is enough to immediately prescribe iron supplements at the appointment.”
A blood test makes it possible to understand, for example, that the patient has a serious infectious disease and not a common cold. The level of leukocytes will scream about this.
“With a banal acute respiratory infection or acute respiratory viral infection, you can do without analysis,” says Viktor Shcherbina, a therapist at polyclinic No. 2 in the city of Sergiev Posad. “But often there are additional signs: prolonged fever, severe cough, etc. For example, a patient comes with a cold, but the temperature lasts for more than a week at 37.2-37.5°C. It turned out that the cause was an inflammatory process from pyelonephritis - the patient caught a cold in the pelvic area.”
A general analysis is also a primary oncological screening for diseases of the hematopoietic organs. If suspected, the therapist will immediately refer you to a hematologist or oncologist.
“In case of serious pathology, several parameters may differ from the norm at once,” says Besedin. - There are exceptions - a woman’s temperature “jumped” from 35.5° to 38.5°C for no reason during the day, and there was severe weakness. All the analysis parameters were in order, but the relative and absolute level of lymphocytes turned out to be many times overestimated. This made it possible to detect blood cancer at an early stage.”
Low leukocytes in the blood
A condition characterized by a low level of white cells in the blood is called leukopenia.
Quite often it is temporary, but if the indicator is consistently low, this may indicate serious pathologies. A low level of leukocytes in the blood may be due to the following reasons:
- damage to the bone marrow (for example, radiation), in which it is not able to produce the required number of white cells;
- disturbances in blood circulation;
- too rapid breakdown of leukocytes;
- consequences of chemotherapy;
- autoimmune and rare hereditary diseases;
- taking certain medications;
- strict diets.
To restore the normal value of leukocytes, it is necessary to discover the primary cause of the pathology.
CLINIC FOR IMPAIRED COAGULATION
Bleeding disorders in medical practice are combined into the groups of thrombocytopenia and thrombophilia. They are usually associated either with coagulation factors (vessels, the production and process of platelet destruction, deficiency of substances that are involved in the production of blood platelets).
Coagulation disorders clearly appear (their symptoms may indicate diseases):
- long-term healing of wounds after injury;
- bleeding from the gums during routine brushing of teeth;
- frequently appearing hematomas, bruises, bruises at the slightest mechanical reaction;
- prolonged menstrual bleeding cycles indicate clotting problems;
- formation of petechiae (spots caused by subcutaneous effusions of blood, they can be pink/purple/violet).
People with bleeding disorders experience muscle pain after the slightest exertion. Laboratory examinations reveal an enlarged spleen and an increased volume of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow.
Interesting Facts
- Species of white bodies vary in life expectancy. Neutrophils, for example, protect us for only a few days, while tissue macrophages protect us for several years. Cells that live in the blood live shorter than those that live in tissues.
- A complete blood count determines five types of leukocytes. In fact, there are dozens of cell forms that are essentially immature forms of the main five types.
- Leukocytes interact with each other. They transmit information to each other, trigger the activity of different types of white cells, and control their own mortality and fertility. This is an entire intelligent city that provides our protection.
- Although leukocytes are called “white cells,” they are actually transparent.
Author:
Baktyshev Alexey Ilyich, General Practitioner (family doctor), Ultrasound Doctor, Chief Physician
Fecal analysis for helminth eggs
Testing for helminth eggs allows one to identify parasites that live in the lower gastrointestinal tract. Helminthiases (helminthic infestations) are diseases caused by parasitic worms (worms, helminths) that live in the human body. Of the identified cases of helminthiasis, more than 90% are detected in children. First of all, these are children whose hygienic skills are not sufficiently developed due to age - they more often put unwashed objects in their mouths, and also more often consume insufficiently processed vegetables and fruits. In addition, it is children who often come into contact with domestic animals - cats, dogs, birds, which are sources of parasites.
Signs of helminthic infestation depend on what type of parasite the child was infected with. If the infection occurs immediately with a large number of worm eggs, the health condition may deteriorate significantly within 2-3 days. In other cases, signs of worms in children may be absent for a very long time or may be nonspecific.
The first symptoms of helminthiasis include:
- periodic increase in body temperature;
- deterioration of sleep, lethargy and tearfulness;
- poor appetite;
- bowel disorders - both diarrhea and constipation;
- rumbling and discomfort in the abdomen, periodic pain in the navel, nausea;
- allergic manifestations - itching, small rashes.
When infected with some types of helminths, children may experience anal itching at night; when infected with others, they may experience a cough, signs of bronchitis, and swollen lymph nodes.