Published: 02/16/2021 16:45:00 Updated: 02/18/2021
Leukocytes are the most important element of blood and the basis of the body's immunity. Our blood is red in color thanks to erythrocytes - red blood cells. For every thousand red blood cells, there is on average only one white blood cell. However, despite the small percentage, these cells play an important role in human health. They are different in function, shape, appearance. Their main task is to protect the body from viruses, bacteria, fungi and other “pests” that attack it, fight tissue damage and destroy its own aged or mutated cells. They are the foundation of the body's defenses.
Despite the fact that leukocytes are determined mainly in the blood, they are produced by a special organ – the bone marrow. Accordingly, they are formed in response to any tissue damage. This is part of a healthy, natural inflammatory response.
Types of leukocytes
Under a microscope, you can see several dozen different forms of leukocytes - different stages of maturation, or “age”.
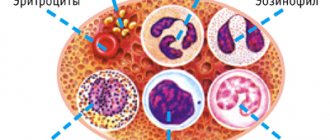
There are 5 main groups of mature cells. Basophils are the smallest group of leukocytes. They regulate blood flow in small vessels, help other white blood cells move through tissues, and influence the growth of new capillaries. Basophils control the occurrence of allergic reactions, suppress allergens, regulate blood clotting, and neutralize toxins and poisons. When an allergen comes into contact with a basophil, this cell releases many bioactive substances responsible for the development of allergic reactions.
Eosinophils - together with basophils, they are markers of a hypersensitive reaction in the body. They also participate in allergic mechanisms, but in a different way. Unlike basophils, which cause an allergic reaction, eosinophils, on the contrary, fight it by binding foreign particles. They have antiparasitic and bactericidal activity, and are responsible for the fight against multicellular parasites - helminths. Their percentage in the blood is normal - about 1-4%. An increase in content, first of all, may indicate severe allergic conditions, helminthiasis, rheumatological diseases, and, less often, oncological pathology.
Neutrophils are a rapid response squad and the most numerous group of leukocytes (up to 80% of the total). As soon as a foreign substance (for example, a splinter, bacteria, or virus) enters the body, neutrophils immediately move to it to destroy it. They release many active enzymes towards the foreign invader and literally break down and digest any substance not related to the body - this process is called phagocytosis. Alas, having won several such battles, the neutrophils themselves die.
Monocytes are a type of large cell. They also carry out phagocytosis - they “eat” bacteria and microbes that enter the body, cleanse the blood of dead leukocytes and produce interferon. They are able to transmit information to lymphocytes about what microbe they have encountered.
Lymphocytes are the main ones in the implementation of cellular and humoral immunity. They secrete protective antibodies and coordinate the work of all other types of white cells.
As we see, leukocytes are a real army of the immune system, guarding our health. Without their correct operation, a person is defenseless against viruses, bacteria and fungi.
Complexes with this research
Healthy child General screening for clinical examination of a child 1,050 RUR Composition
Prevention of childhood colds Examination of children aged 7+ who suffer from colds more than 4 times a year 2,170 RUR Composition
Expanded hospital complex Expanded infectious screening for prevention and hospitalization RUR 7,700 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Certificate for kindergarten, school, camp RUB 1,950
- Your immunity RUB 3,210
- Check-up No. 1 for children and teenagers 10,950 RUR
- Female infertility RUB 16,210
- Examination during pregnancy. 2nd trimester 1,050 RUR
Analysis for leukocytes in the blood
To determine the level of leukocytes, a classic general blood test is used - the most popular test, without which not a single examination can be done.
In addition to identifying five types of white cells, the analysis reveals the number and characteristics of red blood cells, hemoglobin, platelets and other blood components.
It is also necessary in the diagnosis of anemia, diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory processes, as an element of preventive examination, in the diagnosis of a diverse range of diseases and for monitoring treatment.
Complete blood count of the child: eosinophils
Similar to neutrophils, eosinophil cells contain certain enzymes or granules within themselves. Eosinophils are neutralized not by bacteria, but by immune complexes. When taking a general blood test from a healthy child, their number is most often relatively small (about 1-4%, no more). But their numbers increase significantly, which is called eosinophilia , with various allergies, intestinal diseases, even skin diseases, etc.
Very often, eosinophelia occurs after severe, especially bacterial infections.
Norm of leukocytes in the blood
Speaking about the norm of almost any laboratory analysis, you need to know that laboratories can work on different installations, use different analysis methods and different reagents.
Therefore, depending on the laboratory, reference values - the limits of normal - may vary slightly. Normally, leukocytes in the blood of adult men and women are contained in an amount of 4-9 × 10 U/l.
The content of leukocytes in the blood of a child is normally higher than that of an adult. For example, in newborns this figure reaches 9.2-13.8x10 U/l. As the child gets older, the level of white cells normally decreases. At the age of three years, the normal range is 6-17x10 U/l, and by ten years it is already 6.1-11.4 x10 U/l.
Pregnant women also often have higher white blood cell levels than normal adults. By the end of the third semester, an increased level of white cells is considered normal. This is due to the increased load on the body.
In older people, the production of leukocytes can decrease by 2-3%, and their activity and protective functions are reduced by almost half. This is one of the reasons why older people have weakened immune systems.
A deviation in the level of leukocytes in one direction or another from the norm indicates health problems. In this case, it is important to know not only the indicator of white cells in the patient’s blood in general (total quantity), but also each type of these cells separately.
The leukocyte formula in a healthy adult is as follows:
- neutrophils: band - 1-5%, segmented - 40-70%;
- lymphocytes – 20-45%;
- monocytes – 3-8%;
- eosinophils – 1-5%;
- basophils – 0-1%.
Complete blood test of the child: neutrophils
Each neutrophil inside itself contains certain grains, which can also be called granules. They contain a wide variety of enzymes, the purpose of which is to destroy viruses and any pathogenic bacteria. At the same time, neutrophils exhibit particular activity in relation to bacteria. If an increase in the percentage of neutrophils is observed in the leukocyte formula, then this is a sign of the presence of an inflammatory process caused by bacteria.
All neutrophils differ from each other in their degree of maturity. If a particular neutrophil is a complete, mature cell, it is called a segmented neutrophil. To obtain this title, a cell must go through a series of transformations:
- First, a neutrophil appears (forms in the bone marrow), called a myelocyte . In this state he is completely safe and even helpless;
- during its growth, the myelocyte turns into a metamyelocyte ;
- the next stage is the transformation of a metamyelocyte into a band neutrophil ;
- in this state, in this form, the neutrophil is already a full-fledged defender against bacteria, although it is not yet as fast, not as dangerous as a fully mature cell - a segmented neutrophil .
If the child’s body is in a normal, healthy state, then the responsibility for protecting his immunity falls “on the shoulders of adults,” fully formed segmented neutrophils and a very small number of band neutrophils.
If some kind of disease, some kind of inflammatory process begins, then the level of band neutrophils increases sharply, they come to the aid of segmented neutrophils. Consequently, an increase in bacteria and their activity in a child’s body increases the load on his immunity, which leads to the growth of neutrophils formed up to the third stage - to stab ones. In the event that they cannot provide the necessary assistance, metamyelocytes, i.e., join in the “war” with bacteria. their indicator in the general blood test increases. But the body resorts to their help only in the most exceptional cases, with very serious illnesses.
Most often, which is normal, there are metamyelocytes in the blood, and even more so, myelocytes are completely absent.
Also, as a final note, for reference, I would like to say that a decrease in the level of neutrophils in the blood is called neutropenia , and an increase in their level is called neutrophilosis .
Elevated leukocytes in the blood
Leukocytosis occurs as a consequence of pathological processes.
When aggressors invade the body, it releases a large number of white cells into the blood to fight the threat. Leukocytosis can be observed in the following pathological processes:
- infectious diseases of any nature (including infection with viruses and purulent infections);
- against the background of chronic inflammatory processes;
- for some cancers;
- for allergic reactions;
- in the presence of parasites in the body;
- in situations where the protective barrier of the skin is damaged (with large-scale burns and frostbite).
There are a number of conditions that are not associated with diseases, but in which the level of leukocytes in the blood also increases.
We are talking about severe stress, smoking and strict diets. There are also several physiological conditions that naturally cause elevated readings. As we described above, in pregnant women, leukocytes increase closer to childbirth. The indicator rises immediately after eating and returns to normal after a few hours - so it is important to donate blood at least 5 hours after eating. A bath or sauna and vigorous physical activity before the test can also raise the level of white blood cells.
To get a reliable result, a general blood test must be taken strictly in a calm state on an empty stomach.
Complete blood count of the child: monocytes (infectious mononucleosis)
The formed elements of the blood, called monocytes, may seem like the best, most useful. The fact is that they engage in phagocytosis. In simple, understandable language, this is the process of absorption and subsequent digestion of various bacteria, cells that have already died but remain in the blood, as well as other particles that have no place in our blood (foreign). The life of a monocyte lasts (approximately) 30 hours, during which it has time to form, grow and mature. At the last stage, at the stage of maturation, the monocyte is called a macrophage and in this state it lives for about one and a half to two months. At this time, he takes an active part in the ongoing immune reactions, “eating” (phagocytizing) bacteria, already dead cells, etc.
An increase in the number of these cells ( monocytosis ) is a sign of a prolonged infection that has passed into a sluggish state (tuberculosis, for example). Moreover, monocytosis very often signals a disease - infectious mononucleosis.
Low leukocytes in the blood
A condition characterized by a low level of white cells in the blood is called leukopenia.
Quite often it is temporary, but if the indicator is consistently low, this may indicate serious pathologies. A low level of leukocytes in the blood may be due to the following reasons:
- damage to the bone marrow (for example, radiation), in which it is not able to produce the required number of white cells;
- disturbances in blood circulation;
- too rapid breakdown of leukocytes;
- consequences of chemotherapy;
- autoimmune and rare hereditary diseases;
- taking certain medications;
- strict diets.
To restore the normal value of leukocytes, it is necessary to discover the primary cause of the pathology.
Complete blood test of the child: basophils
This type (species) of cells is small in number and rarely found in the blood. The level of basophils in a general blood test, regardless of a person’s age, is approximately 1%. The clear purpose of their existence, their purpose has not yet been determined, but it is known that they take part in the process of blood clotting and in the body's reaction caused by allergies.
An increase in the number of these cells occurs extremely, extremely rarely, in exceptional diseases. In medicine, it is generally accepted that the absence of basophils in the blood does not mean anything and does not affect the diagnosis of diseases.
Interesting Facts
- Species of white bodies vary in life expectancy. Neutrophils, for example, protect us for only a few days, while tissue macrophages protect us for several years. Cells that live in the blood live shorter than those that live in tissues.
- A complete blood count determines five types of leukocytes. In fact, there are dozens of cell forms that are essentially immature forms of the main five types.
- Leukocytes interact with each other. They transmit information to each other, trigger the activity of different types of white cells, and control their own mortality and fertility. This is an entire intelligent city that provides our protection.
- Although leukocytes are called “white cells,” they are actually transparent.
Author:
Baktyshev Alexey Ilyich, General Practitioner (family doctor), Ultrasound Doctor, Chief Physician
Complete blood count of the child: plasma cells
The purpose of plasma cells in the formation of antibodies. For adults, the norm is their complete absence in the blood, but in a child, only one in 200–400 leukocytes can be found.
An increase in their number symbolizes the presence of a viral infection, but one that has a detrimental effect (destroys) lymphoid tissue: rubella, measles, chicken pox, infectious mononucleosis.
You can read about the reliability of materials related to child health by clicking on the link provided.
You can find more information on your child’s health in the section of our parents’ club of the same name by following the link provided, and/or in its subsection “Handbook for Parents.”