Coagulogram
– a procedure aimed at identifying the patient’s blood clotting rate. Since blood clotting is an important protective function of the body and contributes to normal hemostasis (a system in the human body aimed at maintaining blood in a liquid state, stopping blood during bleeding and dissolving “used” platelets), the blood clotting test also has a second name - hemostasiogram or coagulation hemostasis. Although it is worth noting that blood clotting is not the body's only defense mechanism, primary hemostasis is provided by the properties of blood vessels and platelets.
Increased blood clotting rates lead to thrombosis
with bleeding. This phenomenon is called hypercoagulation, and it can lead to a pathological appearance: thrombosis and thromboembolism.
In turn, decreased blood clotting rates or hypocoagulation
observed during bleeding, and can lead not only to fatal consequences, but also be used to treat thrombosis.
When should you take a blood clotting test?
In medicine, there are situations when, in order to make a diagnosis and plan further treatment, it is necessary to conduct a blood clotting test. A coagulogram is prescribed in the following cases:
- When preparing for surgical treatment of a patient
- For various diseases of the liver, heart and blood vessels
- Frequent bleeding in the patient
- The appearance of bruises on the skin at the slightest injury
- To monitor the condition of a pregnant woman
- To study the causes of disruption of the immune defense mechanism
A blood clotting test allows the attending physician to select the correct medications. In some cases, a decrease in blood clotting rates is required to treat vascular thrombosis (stroke, varicose veins, coronary heart disease, and so on).
Research Indicators
A coagulogram is a whole complex of various studies of the blood coagulation system, which give an idea of its work. Based on the number of indicators required for the study, there are 2 types of coagulogram - standard and extended. A standard analysis is prescribed for general health monitoring, but an extended one is necessary during pregnancy, before surgery, to assess the effectiveness of therapy.
Venous blood is placed in a test tube with a specific anticoagulant. It prevents the blood from clotting and allows you to study the specific reactions of the fluid. If any coagulogram indicators are outside the normal range, the specialist tracks the stage at which the violation occurred and begins to study it in detail. Each indicator of blood condition is closely related to the next one. It is this connection that helps to track the norms/pathologies of the coagulation system.
The main parameters of a coagulogram include:
- Prothrombin time and its derivatives. These are laboratory indicators that evaluate the extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. They help determine the effectiveness of warfarin therapy, the degree of liver dysfunction and the saturation of the body with vitamin K.
- Activated partial thromboplastin time. An indicator of the efficiency of the internal and common coagulation pathway. Helps evaluate the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy. Always used in combination with prothrombin time test results.
- Thrombin time. Reflects violations of the final stage of coagulation. Measures the rate of conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin by studying citrated blood plasma.
- Fibrinogen. A colorless protein found dissolved in blood plasma. As soon as bleeding opens in the body, regardless of intensity, the protein is broken down by thrombin and converted into fibrin. Fibrinogen is produced in the liver and eventually turns into a clot, completing blood clotting.
Preparing for a blood clotting test
A seemingly harmless test, but an error in its readings can lead to thrombosis or severe bleeding, which is why it is important to properly prepare for donating blood.
To ensure the reliability of the result, doctors recommend adhering to the following conditions:
Medical certificate
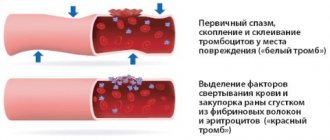
A coagulogram is usually understood as a comprehensive blood test, with the help of which it is possible to assess the functionality of hemostasis - the biological system of the body. It is responsible for maintaining the fluid state of the blood, dissolving/forming blood clots and stopping bleeding. The hemostasis system includes platelets and so-called coagulation factors. When the integrity of the vessel walls is violated, the coagulation system is activated, resulting in the formation of a blood clot that prevents excessive blood loss. After some time, the process of fibrinolysis begins, when the clot dissolves and blood flow resumes.
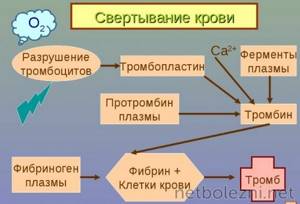
The importance of a blood test for clotting during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a restructuring of a woman's blood circulation occurs, which requires additional blood volume for the pregnant child. To monitor the proper development of pregnancy, women are prescribed a coagulogram every trimester. A blood clotting test helps prevent the following complications during pregnancy:
Sign up for a coagulogram
Make an appointment
Indications for prescribing analysis
A coagulogram is taken to evaluate the blood coagulation system before surgery. This approach helps prevent the development of complications. Other indications for prescribing the study include the following situations:
- Hypermenorrhea (heavy menstruation).
- Diseases accompanied by the formation of blood clots.
- Hemoptysis.
- Monitoring therapy using anticoagulants.
- Acute inflammatory processes in the body.
- Risk of ischemic stroke.
- Prescribing contraceptive drugs, anabolic steroids or glucocorticosteroids.
- Various pathologies of the kidneys and liver.
It is also recommended that all women undergo a coagulogram when preparing for an upcoming pregnancy. Increased blood clotting entails the threat of premature birth and miscarriages. After conception, expectant mothers take this test several more times.
There are no specific contraindications for this procedure.
However, it is recommended to refuse the analysis for patients who cannot adhere to the preparatory measures. Even the slightest deviation from them (for example, non-compliance with a diet) can distort the final results. As a result, the patient will not receive proper treatment, and the disease will progress.
Medications for lymphostasis of the upper and lower extremities are taken orally, applied externally, and administered intramuscularly. If the dosage is observed, you can count on a positive therapeutic effect and eliminate the risk of complications. Read more in the article: “tablets for the treatment of lymphostasis of the arms and legs.”

Where can I get tested for blood clotting speed in Moscow?
At a multidisciplinary medical center, you can always undergo a blood clotting rate test (Coagulogram)
. Our medical center is located between the Konkovo and Belyaevo metro stations (South-Western Administrative District of Moscow in the area of the Belyaevo, Konkovo, Teply Stan, Chertanovo, Yasenevo, Sevastopolskaya, New Cheryomushki metro stations " and "Trade Union"). Here you will find highly qualified personnel and the most modern diagnostic equipment. Our clients will be pleasantly surprised by our quite affordable prices.
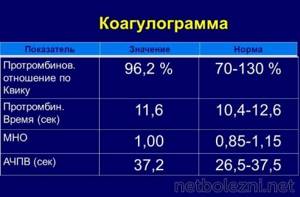
Standard values
You can donate blood for a coagulogram in both public and private clinics. Results are usually ready within 1-2 days. A doctor should decipher them. The table below shows the standard values.
| Hemostasis index | Norm |
| Clotting time | 5-10 min. |
| APTT | 30-42 sec. |
| Thrombin time | 15-18 sec. |
| Prothrombin time | 9.3-13.3 sec. |
| Prothrombin index | 70-120% |
| Fibrinogen | 2-4 g/l |
These standard values are valid for adult men and women. For children and pregnant women, these indicators will differ slightly. They also vary among older people.
Additional examinations in case of deviation from the norm
If the results of the coagulogram are unsatisfactory, the patient is recommended to undergo further examination. Its main goal is to determine the cause of violations and where they originated from. Usually a set of the following diagnostic measures is prescribed:
- General blood and urine tests
. Based on their results, it can be assumed that there are disturbances in the functioning of the liver, kidneys or hematopoietic system.
- Blood biochemistry
. Particular attention is paid to the indicators of creatinine, uric acid, ALT, AST, bilirubin. The study shows pathologies in the liver and kidneys that directly affect coagulogram parameters.
- Blood for tumor markers
. Beta-2-microglobulin, for example, indicates malignant diseases of the hematopoietic system.
- Blood for trace elements
. A deficiency of chlorine, sodium, potassium and a number of other substances can affect the result of a coagulogram.

In some cases, genetic examinations are carried out, with the help of which it is possible to identify hereditary diseases. Hemophilia, Fillebrand's disease or Christmas disease entail changes in hemostasis. You should consult a doctor with the results of the diagnostics.
Table of coagulogram norms in adults and children
The table below shows the normal parameters of an extended hemostasiogram in adults and children. It should be noted that these numbers vary slightly depending on age. Significant differences in the functioning of the hemostatic and fibrinolytic blood systems are characteristic only of premature babies and healthy infants in the first two months of life.
| Parameter and unit of measurement | Normal for adults | Norm for children |
| Bleeding time (according to Duke), min. | 2-4 | 2-4 |
| Lee-White coagulation time, min. | 5-7 | 4-9 |
| Prothrombin time, sec. | 11-15 | 13-17 |
| Prothrombin according to Quick,% | 78-142 | 78-142 |
| Prothrombin consumption,% | 75-125 | 75-125 |
| PTI, % | 73-122 | 73-122 |
| GRP plasma recalcification time, sec. | 60-120 | 90-120 |
| Thrombin time, sec. | 10,3–16,6 | 10,3–16,6 |
| Platelets, g/l | 150-400 | 150-350 |
| Activated recalcification time of AVR, sec. | 81-127 | 81-127 |
| APTT (APTT, ARTT), sec. | 22,5-35,5 | 22,5-35,5 |
| INR (international normalized ratio) | 0,85-1,25 | 0,85-1,25 |
| RFMK | 3.55-4.0 mg/100 ml | 1.25-4.0 mg/100 ml |
| Fibrinogen | 2.7-4.013 g/l | 5.9-11.7 µmol/l |
| Lupus anticoagulant | absent | absent |
| D-dimers, ng/ml | 243-500 | 243-500 |
| Protein C,% | 70-140 | 70-140 |
| Protein S, units/ml | 67-140 | 67-140 |
| Antithrombin III,% | 75,8-128 | 40-134 |
| Factor II and V activity,% | 60-150 | 60-150 |
| Factor VII activity,% | 65-135 | 65-135 |
| Factor VIII, IX and IX activity, % | 50-200 | 50-200 |
| Factor X,% | 60-130 | 60-130 |
| Factor XI,% | 65-135 | 65-135 |
| Factor XII,% | 65-150 | 65-150 |
Decoding the results
Now let’s look at what the most important indicators from this table mean, and what the deviation of the analysis results from the norm, up or down, indicates.
Bleeding time
To establish this indicator, the doctor performs a simple test - pierces the patient’s earlobe or finger with a special lancet at least 4 mm, and records how many minutes it takes for the bleeding to stop. The sooner this happens, the better (the norm is 1.5-2 minutes), but prolongation of time may indicate hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, hemorrhagic fever, cirrhosis of the liver or an overdose of anticoagulants.
Lee-White clotting time
This is the time during which a blood clot forms at the site of damage to the vessel. If this happens too quickly, then there is a risk of developing thrombosis, and if it happens too slowly, then the patient has a tendency to bleed - he may lose a lot of blood as a result of injury or during surgery.
Venous blood should clot in 5-7 minutes, and capillary blood should clot faster (in 30 seconds - 5 minutes).
An increase in blood clotting time is typical for diseases: hemophilia, late-stage disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, burn disease, malignant tumors, severe inflammatory lesions of internal organs, systemic autoimmune diseases, phosphorus poisoning.
A shortening of the Lee-White clotting time is observed in myxedema, anaphylactic and hemorrhagic shock, and disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome in the initial stages of development.
Activated recalcification time (ATR)
This is the period during which a network of fibrin fibers is formed in plasma saturated with calcium and platelets.
In healthy people, the figure is 81-127 seconds.
There is also an indicator of VRP - plasma recalcification time, it also characterizes the overall activity of the coagulation system, the differences lie only in the method of conducting the test. A greater deviation of both of these parameters from the norm indicates hemophilia, thrombocytopathies, long-term use of anticoagulants, post-traumatic shock, and a lesser deviation indicates the risk of thrombosis.
The time should be at least 1-2 minutes.
Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT, APTT, ARTT)
APTT is activated partial thromboplastin time. This is perhaps the most informative diagnostic parameter of a coagulogram. It reflects the effectiveness of hemostasis and characterizes the period during which a fibrin “patch” is formed at the site of tissue damage.
Reference values: 22.5-35.5 seconds.
Prolongation of aPTT is observed in congenital and acquired deficiency of blood coagulation factors, autoimmune diseases, severe liver pathologies, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, overdose of anticoagulants, hemophilia, von Willebrand's disease, vitamin deficiency, chronic glomerulonephritis, condition after blood transfusion.
A shortened APTT may indicate the onset of DIC, a tendency to thrombosis, acute blood loss, metastasis of a malignant neoplasm, or simply that the blood for analysis was taken incorrectly.
Read more: APTT is elevated - what does it mean?
Activity of all blood coagulation factors (II, V, VII, VIII, IX, X, XI, XII)
These parameters never change without serious reasons: the increase and decrease in the activity of coagulation factors clearly indicates a disease characterized by either excessive thrombus formation or bleeding.
When interpreting the results, data on the activity of coagulation factors should be considered together with other indicators.
Prothrombin time (PT)
This is the period during which a thrombin clot is formed in plasma with calcium and thromboplastin. Measuring prothrombin time allows us to evaluate the work of the so-called internal circle of hemostasis, which is responsible for stopping bleeding in organs and tissues, and not on the surface of the body.
In premature babies, after birth, a longer prothrombin time is recorded than in full-term babies - 14-19 seconds versus 13-17. And in adults this parameter varies between 11-15 seconds.
Prolongation of PT is observed with a deficiency of coagulation factors or fibrinogen, stenosis of the biliary tract, liver pathologies, amyloidosis, hemorrhagic diathesis, vitamin deficiency, and celiac disease.
A shortened PT is characteristic of low hematocrit, increased levels of antithrombin III, activation of fibrinolysis, thromboembolism and thrombosis.
Prothrombin according to Quick, prothrombin index (PTI) and INR
This is the ratio of the patient's prothrombin time to the ideal value of this parameter, which is expressed as a number or as a percentage. Currently, these indicators are considered outdated, since in 1983 the World Health Organization introduced a new term - INR - international normalized ratio, which means essentially the same thing.
The obtained relative indicators range from 73-122%, and in pregnant women they can reach 150% or more.
Deviation of PTI and INR from the norm to a greater or lesser extent is explained by the same reasons as prolongation and shortening of prothrombin time, since these parameters are directly related to each other.
Thrombin time (TV)
This indicator characterizes the final stage of hemostasis and is calculated by adding thrombin to the plasma.
The normal range for this test is 10.3-16.6 seconds, and for pregnant women - 11-18.
If the fibrin network takes too long to form, this indicates acute fibrinolysis and fibrinogen deficiency, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, autoimmune disease, severe liver pathology, multiple myeloma, uremia, long-term therapy with streptokinase or urokinase.
If a “patch” of fibrin forms too quickly, this indicates the beginning of the development of DIC syndrome and the use of heparin or fibrin polymerization inhibitors.
Fibrinogen
This is a protein that is produced by the liver. When bleeding begins, fibrinogen is converted into fibrin under the influence of Hageman factor, and from it, in turn, a “patch” is formed. Therefore, fibrinogen is classified as an acute phase protein.
An increase in fibrinogen indicates injury, burn, myocardial infarction, growth of a malignant tumor, inflammation of internal organs, and autoimmune pathology.
A decrease in the level of fibrinogen indicates its congenital deficiency, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, liver diseases, leukemia, homonucleosis, food poisoning, taking heparin, androgenic hormones, anabolic steroids, barbiturates, valproic acid.
Soluble fibrin-monomer complexes (SFMC)
These substances are fibrin breakdown products and are recorded in the blood during fibrinolysis. Accordingly, RFMC is of primary importance for the early diagnosis of DIC syndrome.
Normally, the figure is up to 4.0 mg per 100 ml.
If, when interpreting the results, an increase in the level of RFMC is detected, this may also indicate thrombosis, thromboembolism, renal failure, autoimmune pathology of connective tissues, sepsis, shock, postoperative complications, gestosis, preeclampsia in pregnant women.
Antithrombin III
It is from this protein that three-quarters of the effectiveness of the entire fibrinolytic system, which is necessary to control blood clotting and dissolve unnecessary blood clots, depends.
The norm is 75.8-128%.
| Age | Reference values |
| Less than 3 days | 58 — 90 % |
| 3 days – 1 month | 60 — 89 % |
| 1 month – year | 72 — 134 % |
| 1-6 years | 101 — 131 % |
| 6-11 years | 95 — 134 % |
| 11-16 years old | 96 — 126 % |
| More than 16 years | 83 — 128 % |
The level of type 3 antithrombin increases with hepatitis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis and other inflammatory diseases, as well as after kidney transplantation and long-term use of anabolic steroids.
Lack of antithrombin III is typical for liver failure, liver cirrhosis and the period after liver transplantation, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, and the use of oral contraceptives.
Read more: Antithrombin III – what is it?
Lupus anticoagulant
This is a protein that indicates the presence of antiphospholipid syndrome or antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APAS). It leads to the formation of multiple blood clots and pathologies during pregnancy. In a healthy person, this parameter should not contain any data.
Normal time is less than 1.2 seconds.
D-dimers
These substances are constantly present in the blood, but especially many of them appear as a result of the breakdown of large amounts of fibrin. And this process indicates too active blood clotting and dissolution of unclaimed blood clots.
Normally, the level should be below 243 ng/ml. But the permissible level is up to 500 ng/ml.
Exceeding the norm of D-dimers in the coagulogram indicates the onset of development of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, blood poisoning, acute heart attack, thromboembolism, kidney or liver failure, postoperative complications, growth of a malignant neoplasm, large hematoma, and gestosis.
Read more: D-dimer - what is it? Normal indicators
Protein C
This protein is needed to control the process of hemostasis and prevent the formation of too large clots inside damaged vessels.
The doctor is concerned if the level of protein C in the blood is too low. This may indicate the development of DIC, liver disease, or simply a congenital deficiency of the corresponding protein.
Protein S
And this is an activator of protein C and antithrombin III - without it, the anticoagulant function of the blood would be impossible. Lack of protein S can also be hereditary, or it can develop against the background of long-term use of blood thinning drugs (Heparin, Warfarin, Aspirin).